Schemes for installing a floor on the ground in a house, basement, garage or bathhouse
In houses without basements, the floor of the first floor can be made according to two schemes:
- supported on the ground - with a screed on the ground or on joists;
- supported on walls - like a ceiling over a ventilated underground.
Which of the two options will be better and easier?
In houses without a basement, floors on the ground are a popular solution for all rooms on the first floor. Floors on the ground are cheap, simple and easy to implement; they are also beneficial to install in the basement, garage, bathhouse and other utility rooms. Simple design, application modern materials, placement of a heating circuit in the floor (warm floor), such floors are made comfortable and attractively priced.
In winter, the backfill under the floor always has a positive temperature. For this reason, the soil at the base of the foundation freezes less - the risk of frost heaving of the soil is reduced. In addition, the thickness of the thermal insulation of a floor on the ground may be less than that of a floor above a ventilated underground.
It is better to abandon the floor on the ground if backfilling with soil is required to a height that is too high, more than 0.6-1 m. The costs of backfilling and soil compaction in this case may be too high.
A ground floor is not suitable for buildings on a pile or columnar foundation with a grillage located above the ground.
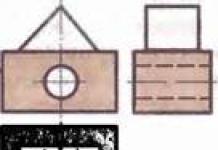
Three basic diagrams for installing floors on the ground
In the first version concrete monolithic reinforced floor slab rests on load-bearing walls, Fig.1.
After the concrete hardens, the entire load is transferred to the walls. In this option, a monolithic reinforced concrete floor slab plays the role of a floor slab and must be designed for the standard load of the floors, have the appropriate strength and reinforcement.
The soil is actually used here only as temporary formwork when installing iron concrete slab ceilings This type of floor is often called a “suspended floor on the ground”.
A suspended floor on the ground has to be made if there is a high risk of shrinkage of the soil under the floor. For example, when building a house on peat bogs or when the height of bulk soil is more than 600 mm. The thicker the backfill layer, the higher the risk of significant subsidence of the fill soil over time.
Second option - this is a floor on a foundation - a slab, when reinforced concrete monolithic slab, poured onto the ground over the entire area of the building, serves as a support for the walls and a base for the floor, Fig.2.
Third option provides for the installation of a monolithic concrete slab or laying wooden logs in between load-bearing walls supported on bulk soil.
Here the slab or floor joists are not connected to the walls. The load of the floor is completely transferred to the bulk soil, Fig.3.
It is the latter option that is correctly called a floor on the ground, which is what our story will be about.
Ground floors must provide:
- thermal insulation of premises in order to save energy;
- comfortable hygienic conditions for people;
- protection against penetration of ground moisture and gases - radioactive radon - into premises;
- prevent the accumulation of water vapor condensation inside the floor structure;
- reduce the transmission of impact noise to adjacent rooms along the building structures.
Backfilling the soil cushion for the floor on the ground
The surface of the future floor is raised to the required height by installing a cushion of non-heaving soil.
Before starting work on backfilling, be sure to remove the top soil layer with vegetation. If this is not done, the floor will begin to settle over time.
Any soil that can be easily compacted can be used as a material for constructing a cushion: sand, fine crushed stone, sand and gravel mixture, and at a low level groundwater– sandy loams and loams. It is beneficial to use the soil remaining on the site from the well and (except for peat and black soil).
The cushion soil is carefully compacted layer by layer (no thicker than 15 cm.) by compacting and pouring water onto the soil. The degree of soil compaction will be higher if mechanical compaction is used.
Do not place large crushed stones, broken bricks, or pieces of concrete into the cushion. There will still be voids between large fragments.
The thickness of the bulk soil cushion is recommended to be in the range of 300-600 mm. It is still not possible to compact the fill soil to the state of natural soil. Therefore, the soil will settle over time. A thick layer of fill soil can cause the floor to settle too much and unevenly.
To protect against ground gases - radioactive radon, it is recommended to make a layer of compacted crushed stone or expanded clay in the cushion. This underlying captage layer is made 20 cm thick. The content of particles smaller than 4 mm this layer should contain no more than 10% by weight. The filtration layer must be ventilated.
The top layer of expanded clay, in addition to protecting against gases, will serve as additional thermal insulation for the floor. For example, a layer of expanded clay 18 cm. corresponds to 50 in terms of heat-saving ability mm. polystyrene foam To protect insulation boards and waterproofing films, which in some floor designs are laid directly on the backfill, from crushing, a leveling layer of sand is poured on top of the compacted layer of crushed stone or expanded clay, twice the thickness of the backfill fraction.
Before filling the soil cushion, it is necessary to lay water supply and sewerage pipes at the entrance to the house, as well as pipes for the ground ventilation heat exchanger. Or lay cases for installing pipes in them in the future.
Construction of floors on the ground
In private housing construction, the floor on the ground is arranged according to one of three options:
- ground floor with concrete screed;
- ground floor with dry screed;
- ground floor on wooden joists.
A concrete floor on the ground is noticeably more expensive to construct, but is more reliable and durable than other structures.
Concrete floor on the ground
Floors on the ground are a multi-layer structure, Fig.4. Let's go through these layers from bottom to top:
- Placed on a ground cushion material that prevents filtration into the groundmoisture contained in freshly laid concrete (e.g. plastic film thickness not less than 0.15 mm.). The film is applied to the walls.
- Along the perimeter of the walls of the room, on overall height all layers of the floor are fixed separating edge layer from strips 20 – 30 thick mm, cut from insulation boards.
- Then they arrange a monolithic concrete floor preparation thickness 50-80 mm. from lean concrete class B7.5-B10 to crushed stone fraction 5-20 mm. This technological layer, intended for sticking waterproofing. The radius of concrete joining the walls is 50-80 mm. Concrete preparation can be reinforced with steel or fiberglass mesh. The mesh is placed in the lower part of the slab with protective layer concrete at least 30 mm. For reinforcing concrete foundations it can alsouse steel fiber 50-80 long mm and diameter 0.3-1mm. During hardening, the concrete is covered with film or watered. Read:
- For hardened concrete floor preparation weld-on waterproofing is glued. Either two layers of rolled waterproofing or roofing material on a bitumen base with each layer placed on the wall. The rolls are rolled out and joined with an overlap of 10 cm. Waterproofing is a barrier to moisture and also serves as protection against the penetration of ground gases into the house. The floor waterproofing layer must be combined with a similar wall waterproofing layer. Butt joints of film or roll materials must be sealed.
- On a layer of hydro-gas insulation lay thermal insulation slabs. Extruded polystyrene foam will probably be the best option for insulating floors on the ground. Foam plastic with a minimum density of PSB35 (residential premises) and PSB50 for heavy loads (garage) is also used. Polystyrene foam breaks down over time upon contact with bitumen and alkali (that's all cement-sand mortars). Therefore, before laying foam plastic on a polymer-bitumen coating, one layer of polyethylene film should be laid with an overlap of sheets of 100-150 mm. The thickness of the insulation layer is determined by thermal engineering calculations.
- On the thermal insulation layer lay the underlying layer(for example, polyethylene film with a thickness of at least 0.15 mm.), which creates a barrier to moisture contained in freshly laid concrete floor screed.
- Then lay a monolithic reinforced screed with a “warm floor” system (or without a system). When heating floors, it is necessary to provide expansion joints in the screed. The monolithic screed must be at least 60 thick mm. executed from concrete class not lower than B12.5 or from mortarbased on cement or gypsum binder with a compressive strength of at least 15 MPa(M150 kgf/cm 2). The screed is reinforced with welded steel mesh. The mesh is placed at the bottom of the layer. Read: . To more thoroughly level the surface of a concrete screed, especially if the finished floor is made of laminate or linoleum, a self-leveling solution of factory-made dry mixes with a thickness of at least 3 is applied on top of the concrete layer. cm.
- On the screed installing finished floor.
This is a classic ground floor. Based on it, various design options are possible - both in design and in the materials used, both with and without insulation.
Option - concrete floor on the ground without concrete preparation
Using modern building materials, concrete floors on the ground are often made without a layer concrete preparation . A layer of concrete preparation is needed as a basis for gluing roll waterproofing on a paper or fabric base impregnated with a polymer-bitumen composition.

 In floors without concrete preparation As waterproofing, a more durable polymer membrane specially designed for this purpose, a profiled film, is used, which is laid directly on the ground cushion.
In floors without concrete preparation As waterproofing, a more durable polymer membrane specially designed for this purpose, a profiled film, is used, which is laid directly on the ground cushion.
The profiled membrane is a sheet of polyethylene high density(PVP) with protrusions molded on the surface (usually spherical or in the shape of a truncated cone) with a height of 7 to 20 mm. The material is produced with a density from 400 to 1000 g/m 2 and is supplied in rolls with widths ranging from 0.5 to 3.0 m, length 20 m.
Due to the textured surface, the profiled membrane is securely fixed into the sand base without deforming or moving during installation.
Fixed into a sand base, the profiled membrane provides a solid surface suitable for laying insulation and concrete.
The surface of the membranes withstands the movement of workers and transportation machines without ruptures concrete mixtures and solutions (excluding tracked vehicles).
The service life of the profiled membrane is more than 60 years.
The profiled membrane is laid on a well-compacted sand bed with the spikes facing down. The membrane spikes will be fixed in the pillow.
The seams between the overlapping rolls are carefully sealed with mastic.
The studded surface of the membrane gives it the necessary rigidity, which allows you to lay insulation boards directly on it and concrete the floor screed.
 If slabs made of extruded polystyrene foam with profiled joints are used to construct a thermal insulation layer, then such slabs can be laid directly on the ground backfill.
If slabs made of extruded polystyrene foam with profiled joints are used to construct a thermal insulation layer, then such slabs can be laid directly on the ground backfill.
Backfill of crushed stone or gravel with a thickness of at least 10 cm neutralizes the capillary rise of moisture from the soil.
In this embodiment, the polymer waterproofing film is laid on top of the insulation layer.

If top layer If the ground cushion is filled with expanded clay, then you can dispense with the insulation layer under the screed.
The thermal insulation properties of expanded clay depend on its bulk density. Made of expanded clay with a bulk density of 250–300 kg/m 3 it is enough to make a thermal insulation layer with a thickness of 25 cm. Expanded clay with bulk density 400–500 kg/m 3 to achieve the same thermal insulation ability, you will have to lay it in a layer 45 thick cm. Expanded clay is poured in layers 15 thick cm and compacted using a manual or mechanical tamper. The easiest to compact is multi-fraction expanded clay, which contains granules of different sizes.
Expanded clay is quite easily saturated with moisture from the underlying soil. Wet expanded clay has reduced thermal insulation properties. For this reason, it is recommended to install a moisture barrier between the base soil and the expanded clay layer. A thick waterproofing film can serve as such a barrier.
 Large-porous expanded clay concrete without sand, encapsulated. Each expanded clay granule is enclosed in a cement waterproof capsule.
Large-porous expanded clay concrete without sand, encapsulated. Each expanded clay granule is enclosed in a cement waterproof capsule. The base for the floor, made of large-porous sand-free expanded clay concrete, will be durable, warm and with low water absorption.
Floor on the ground with dry prefabricated screed
 In floors on the ground, as the top load-bearing layer, instead of a concrete screed, in some cases it is advantageous to make a dry prefabricated screed from gypsum fiber sheets, from sheets of waterproof plywood, as well as from prefabricated floor elements from different manufacturers.
In floors on the ground, as the top load-bearing layer, instead of a concrete screed, in some cases it is advantageous to make a dry prefabricated screed from gypsum fiber sheets, from sheets of waterproof plywood, as well as from prefabricated floor elements from different manufacturers.
For residential premises on the first floor of the house more than simple and cheap option There will be a floor on the ground with a dry prefabricated floor screed, Fig. 5.
A floor with a prefabricated screed is afraid of flooding. Therefore, it should not be done in the basement, nor in wet areas- bathroom, boiler room.
The ground floor with a prefabricated screed consists of the following elements (positions in Fig. 5):
1 — Flooring- parquet, laminate or linoleum.
2 - Adhesive for joints of parquet and laminate.
3 - Standard underlay for flooring.
4 - Prefabricated screed made of ready-made elements or gypsum fiber sheets, plywood, particle boards, OSB.
5 - Glue for assembling the screed.
6 - Leveling backfill - quartz or expanded clay sand.
7 - Communications pipe (water supply, heating, electrical wiring, etc.).
8 - Insulation of the pipe with porous fiber mats or polyethylene foam sleeves.
9 - Protective metal casing.
10 — Expanding dowel.
11 - Waterproofing - polyethylene film.
12 - Reinforced concrete base made of class B15 concrete.
13 - Foundation soil.
The connection between the floor and the outer wall is shown in Fig. 6.
The positions in Fig. 6 are as follows:
1-2. Varnished parquet, parquet, or laminate or linoleum.
3-4. Parquet adhesive and primer, or standard underlay.
5. Prefabricated screed from ready-made elements or gypsum fiber sheets, plywood, particle boards, OSB.
6. Water-dispersed adhesive for screed assembly.
7. Moisture insulation - polyethylene film.
8. Quartz sand.
9. Concrete base - reinforced screed made of concrete class B15.
10. Separating gasket made of waterproofing roll material.
11. Thermal insulation made of polystyrene foam PSB 35 or extruded polystyrene foam, thickness as calculated.
12. Foundation soil.
13. Plinth.
14. Self-tapping screw.
15. External wall.
As mentioned above, the soil cushion at the base of the floor always has a positive temperature and in itself has certain heat-insulating properties. In many cases, it is enough to additionally lay insulation in a strip along the external walls (pos. 11 in Fig. 6.) in order to obtain the required thermal insulation parameters for a floor without underfloor heating (without heated floors).
Thickness of floor insulation on the ground
 Fig.7. Be sure to lay insulation tape in the floor, along the perimeter of the external walls, with a width of at least 0.8 m. From the outside, the foundation (basement) is insulated to a depth of 1 m.
Fig.7. Be sure to lay insulation tape in the floor, along the perimeter of the external walls, with a width of at least 0.8 m. From the outside, the foundation (basement) is insulated to a depth of 1 m.
The temperature of the soil under the floor, in the area adjacent to the plinth along the perimeter of the external walls, depends quite strongly on the temperature of the outside air. A cold bridge forms in this zone. Heat leaves the house through the floor, soil and basement.
The ground temperature closer to the center of the house is always positive and depends little on the temperature outside. The soil is heated by the heat of the Earth.
Building regulations require that the area through which heat escapes be insulated. For this, It is recommended to install thermal protection at two levels (Fig. 7):
- Insulate the basement and foundation of the house from the outside to a depth of at least 1.0 m.
- Lay a layer of horizontal thermal insulation into the floor structure around the perimeter of the external walls. The width of the insulation tape along the external walls is not less than 0.8 m.(pos. 11 in Fig. 6).
The thickness of the thermal insulation is calculated from the condition that the overall resistance to heat transfer in the floor-soil-basement area must be no less than the same parameter for the outer wall.
Simply put, the total thickness of the insulation of the base plus the floor should be no less than the thickness of the insulation of the outer wall. For the climatic zone in the Moscow region, the total thickness of foam insulation is at least 150 mm. For example, vertical thermal insulation on a plinth 100 mm., plus 50 mm. horizontal tape in the floor along the perimeter of the external walls.
When choosing the size of the thermal insulation layer, it is also taken into account that insulating the foundation helps reduce the depth of freezing of the soil under its base.
These are the minimum requirements for ground floor insulation. It is clear that what larger sizes thermal insulation layer, the higher the energy saving effect.
Install thermal insulation under the entire floor surface for the purpose of energy saving, it is necessary only in the case of installing heated floors in the premises or building an energy-passive house.
In addition, a continuous layer of thermal insulation in the floor of the room can be useful and necessary to improve the parameter heat absorption of the floor covering surface. Heat absorption of the floor surface is the property of the floor surface to absorb heat in contact with any objects (for example, the feet). This is especially important if the finished floor is made of ceramic or stone tiles, or other material with high thermal conductivity. Such a floor with insulation will feel warmer.
The heat absorption rate of the floor surface for residential buildings should not be higher than 12 W/(m 2 °C). A calculator for calculating this indicator can be found
Wooden floor on the ground on joists on a concrete screed

Base slab made of concrete class B 12.5, thickness 80 mm. over a layer of crushed stone compacted into the ground to a depth of at least 40 mm.
Wooden blocks - logs with a minimum cross-section, width 80 mm. and height 40 mm., It is recommended to lay on a layer of waterproofing in increments of 400-500 mm. For vertical alignment, they are placed on plastic pads in the form of two triangular wedges. By moving or spreading the pads, the height of the lags is adjusted. The span between adjacent support points of the log is no more than 900 mm. A gap of 20-30 mm wide should be left between the joists and the walls. mm.
The logs lie freely without attachment to the base. During the installation of the subfloor, they can be fastened together with temporary connections.
For the construction of the subfloor, wood boards are usually used - OSB, chipboard, DSP. The thickness of the slabs is at least 24 mm. All slab joints must be supported by joists. Wooden lintels are installed under the joints of the slabs between adjacent logs.
The subfloor can be made from tongue-and-groove floorboards. Such a floor made from high-quality boards can be used without floor covering. Permissible humidity wood flooring materials 12-18%.
If necessary, insulation can be laid in the space between the joists. Mineral wool slabs must be covered with a vapor-permeable film on top, which prevents microparticles of insulation from penetrating into the room.
Rolled waterproofing made of bitumen or bitumen-polymer materials glued in two layers onto the concrete underlying layer using the melting method (for fused rolled materials) or by sticking on bitumen-polymer mastics. When installing adhesive waterproofing it is necessary to ensure a longitudinal and transverse overlap of the panels of at least 85 mm.
To ventilate the underground space of floors on the ground along the joists, the rooms must have slots in the baseboards. Holes with an area of 20-30 are left in at least two opposite corners of the room. cm 2 .
Wooden floor on the ground on joists on posts
There is another structural floor scheme - this wooden floor on the ground on joists, laid on posts, Fig.5.
Positions in Fig.5:
1-4 - Elements of the finished floor.
5 —
6-7 - Glue and screws for assembling the screed.
8 - Wooden joist.
9 — Wooden leveling gasket.
10 - Waterproofing.
11 - Brick or concrete column.
12 - Foundation soil.
Arranging the floor on joists along columns allows you to reduce the height of the ground cushion or completely abandon its construction.
Floors, soils and foundations
Ground floors are not connected to the foundation and rest directly on the ground under the house. If it is heaving, then the floor can “go on a spree” under the influence of forces in winter and spring.
To prevent this from happening, the heaving soil under the house must be made not to heave. The easiest way to do this is underground part
Design of pile foundations on bored (including TISE) and screw piles involves the installation of a cold base. Insulating the soil under a house with such foundations is a rather problematic and expensive task. Floors on the ground in the house pile foundation can be recommended only for non-heaving or slightly heaving soils on the site.
When building a house on heaving soils, it is necessary to have an underground part of the foundation to a depth of 0.5 - 1 m.
 |
| In a house with external multilayer walls with insulation on the outside, a cold bridge is formed through the base and load-bearing part of the wall, bypassing the insulation of the wall and floor. |
The process of constructing a private wooden house consists of several stages, one of which is related to the construction of the floor structure. Its type is chosen at the design stage of the structure and many factors are taken into account. What kind of floors there are in a wooden house, and the features of their designs will be discussed in this article.
The floor on the first floor in a wooden house, when there is an unheated basement, has its own characteristics. In this regard, several types of structures can be distinguished:
1. Cold floor construction, installed on an earthen base (without underground). The installation of this type of cold floor is possible only if there is dry soil under the building and a high location of the floors of the lower floor, under which a layer of compacted sand is laid. Another layer of clean, calcined, dry sand is poured on top of it. Logs made from softwood timber with a thickness of more than 150 mm are buried in the formed soil foundation and rest against special recesses in the walls of the house. On top there is a single plank flooring, the thickness of which is from 30 to 40 mm.

2. Warm floors with a cold underground are recommended in areas where there is high level groundwater. This design is arranged as follows:
- cleaned sand in a layer of 10 - 15 cm is laid on the ground in the underground and compacted;
- install supports with a height of at least 50 cm. To do this, you can fill concrete mortar into vertically buried pipes with a metal frame of the required height;
- a double layer of waterproofing material and wooden dies 3 cm thick are laid on top of the supports;
- load-bearing beams are laid.
To install thermal insulation, it is necessary to install a subfloor laid on slats nailed to the ends of the joists. For flooring, cut unedged boards are used. Then a layer of vapor barrier and insulation are laid. After this, a plank covering is laid over the beams.

3. The installation of a cold floor with a warm subfloor is recommended where the soil has a low level of soil water. In the same way as in the previously described method, the structure is installed, but the stage of installing a subfloor with insulation is skipped and a clean floor is installed.
What should a wooden house be like?
The floor in a wooden house should be strong, durable, warm and smooth, with an aesthetic appearance.
When performing work on installing a floor in a wooden house independently, take into account the above requirements, and also determine the procedure for performing the upcoming work, take into account the characteristics of the building’s structures and individual characteristics operation of the house. First we need to consider different options floors that can be installed in a wooden house, study their pros and cons and, taking into account operating conditions, choose the appropriate option.

An important criterion that the floor must meet is its evenness. Regardless of the flooring material, it must meet sanitary, hygienic, structural, operational and aesthetic requirements.
Types of floors
Floors in wooden houses are made of wood or concrete - the most common building materials. The technology of installing a “warm floor system” can also be implemented.
Now there are several types of “warm floors” on the construction market. They differ in the type of coolant and operating efficiency. We'll tell you in our article.
Concrete floor
A popular way to obtain a level base in a relatively short time is to pour a concrete screed. While it may take a month for the screed to dry completely, installing a new wooden one will take longer.

Advantages concrete floors are as follows:
- In a significant reduction in the cost of the device finishing coating.
- After the screed has dried, a flat base is obtained, but which can be laid with any finishing material.
- With an initially high-quality screed, additional leveling before the final stage of work may not be necessary, which will save time, physical strength and material costs.
- The screed can be installed independently, without the involvement of specialists.
You will learn how to install a concrete floor in a private house yourself in two main options - on the ground and on the floors.
Among the disadvantages, one can note the large weight of the monolithic floor structure and, as a result, an increase in the load on the foundation. That's why necessary calculations foundations are carried out at the design stage of the house. Another nuance is that when the walls vibrate, the screed may crack, which will lead to heat loss. Therefore, when installing a heated floor, it is necessary to perform high-quality thermal insulation of the base.

Wooden floor
Another common material for flooring in a wooden house is natural wood. Its advantages include the following:
- Environmentally friendly material with a rich natural pattern.
- Wood is safe because it does not contain harmful additives, it is completely natural and does not release harmful toxins into the environment.
- Aesthetic appearance And organic combination wood with the rest of the building surfaces, while the concrete floor will not look natural.
- When installing a wooden floor, you can refuse other finishing materials. With the help of varnishes, oils, stains and other impregnations, a finished wooden base can become stronger, more durable and acquire an original, noble appearance.
- Wood is very durable and, depending on the species, you can choose a material with certain operational properties and texture.

The undeniable quality of natural wood gives an atmosphere of warmth and comfort, creates an optimal microclimate and comfort in the house.
Important! The wooden floor is repairable. To carry out current repairs its fragment will not require dismantling the entire flooring; you can replace a separate fragment. This will require a minimum set of tools and construction skills.

Among the disadvantages of a wooden floor, the high cost of the material and the labor involved in its installation are noted. In addition, it can be quite difficult to obtain a perfectly even base.
Which is better - concrete or wood?
At the design stage of a private house, you must immediately decide what the floor will be - wooden or concrete. To choose the most suitable option, you need to know what the difference is between these floors.
Price
To fill a screed 5 cm thick, you will need 0.5 bags of cement (300 rubles/bag) and 1.5 (50 rubles/bag) bags of sand. Thus, 1 m 2 screeds will cost an average of 225 rubles. If the work will be performed by a hired person, then the cost of the work must be added to this amount - 250 rubles / m 2.

If we take as a basis dry timber 10 x 10 cm, in increments of 40 cm (400 rubles / m 2) and OSB boards (600 rubles / m 2) with a thickness of 18 mm. With the work of a carpenter, the cost will be 1250 rubles/m2.

Communications
IN modern houses The heating, water supply and sewerage system is laid inside the floor structure. In the event of a pipe break, wooden pipes can be quickly sawed and access to communications can be gained. WITH concrete floors more difficult - to remove the screed you will have to use professional tool, and the process itself will take a lot of time and effort.
Deadlines
The screed gains full strength within 28 days from the date of pouring. Moreover, it gains 70% of its strength in the first week. All this time, the solution gives off moisture and nothing can be laid on it.
Wooden floors can be used immediately after installation.

Durability
If the installation of a wooden floor is not carried out by a professional craftsman, then after a couple of weeks you can hear a characteristic creaking sound when walking on the floor. Concrete screed does not have this drawback. Moreover, when work is performed by hired workers, the result and quality of their work can be assessed immediately.

Weight
The weight of 1 m 2 OSB sheet with a thickness of 18 mm is 12 kg, logs per 1 m 2 weigh about 25 kg, depending on the type of wood. Thus, 1 m2 of wooden floor will weigh about 40 kg. And 1 m 2 ties with a thickness of 5 cm weighs 100 kg.
The process of constructing floors on pillars
When constructing such a floor, it is necessary to perform next order actions:
- Prepare the base. To do this, marking and excavation of soil is carried out plant layer. The resulting depression is filled with crushed stone and sand on top, which is then compacted.
- Then the bricks are installed support pillars taking into account the basic design requirements regarding the height of the finished floor and the structure below it.
- It is mandatory to take into account the ratio of the height of the support column and the section of the brick. So, with a support height of 25 cm and above, the recommended width of the support column is equal to two bricks.
- It is necessary to start installing supports first along the perimeter of the future room, and then within the specified boundaries.
- I lay two layers of roofing material on the upper plane of each column to ensure waterproofing of the structure.
- Then the wooden linings are fixed. Logs made of logs or timber are installed on them. The width of the step of their location relative to each other is chosen depending on the width of the floor boards to be laid.
- Slag backfill, the height of which does not reach the log by 5 cm, is used to prevent the mobility of the floor structure in the cold season when the soil freezes. The remaining free space provides ventilation to the structure.

Laying the floor on top of the installed joists is done using boards, which begin to be laid at a distance of 1.5 cm from the wall. The resulting gap fulfills ventilation function, which is very important for the correct and long-term operation of a natural wood floor.
The boards are attached to the joists using long nails driven at an angle of 45 degrees. While the wood is not completely dry, install temporary skirting boards.

Single layer floor
The single floor structure can be placed on poles, as described above. Only on top of the supports are beams placed, on top of which the flooring is made of tongue-and-groove boards.
The second option is to install the floor along beams embedded in the body of the load-bearing enclosing structures of the building. Beams serve as the basis for the floor, and brick supports are no longer required.

Due to the large free distance between the beams, the fastening of the flooring from the boards is carried out along the sheathing:
- The sheathing is made of timber with a square section of 5-6 cm.
- The pitch of the timber in the sheathing depends on the thickness of the floor board. The thinner the board, the smaller the distance between the lags.
- During the installation of the sheathing, it is important to control its horizontal position so that the end result is an even plank covering.
- Fastening the boards begins after all the logs are installed in their places and securely fixed with nails.
- If it is not planned to lay additional flooring on top decorative covering– laminate, tile, linoleum, then it is finished.
- After the single decking is installed, it is covered with two layers of protective varnish.

Advice. If the flooring is rough, then you can use an unedged board for its construction.
When making a single floor, no serious professional skills, serious temporary and financial costs. But its disadvantage is its low thermal insulation properties.
TO optimal solution When arranging a floor in a wooden house, a two-layer structure is used, consisting of a rough and finishing layer. Installation of such a structure occurs in the following way:
- The subfloor is installed from unedged boards up to 4.5 cm thick, treated with an antiseptic compound. In this case, preference should be given to coniferous wood - it is durable, resistant to moisture, dampness and decay.
- The boards are laid close to each other, and a layer of thermal insulation made of mineral wool, polystyrene foam, expanded clay or sawdust is laid on top.
- In addition to insulation, it is necessary to steam and waterproof the structure to extend its service life.
- The finished floor boards are laid as for other types of structures, leaving a gap of 1.5 cm between them with the subfloor.
A clean floor can serve a function finishing coating or serve as a basis for laying decorative flooring, which will not only decorate the room, but also increase the thermal insulation properties of the floor.

Start of work - installation of the subfloor
Subfloor upon installation plank covering necessary for several reasons:
- To increase the operational life of the structure due to the presence of high-quality floor ventilation.
- It serves as a solid base for laying insulation and the finished floor.
- Makes the frame of the building more rigid.
Before starting work on the installation of the rough structure, check the following:
- The wood chosen as a material for constructing a subfloor must have an optimal level of humidity - this will exclude possible deformation structure during its subsequent operation.
- The boards should not have obvious defects.
- If an inexpensive board can be used for the subfloor, then for the finished floor it is purchased with a reserve, so that later you do not have to look for material of the same shade.

Preparation
Installation of the subfloor can be carried out both on the ground and on the floors. In any case, it is necessary to carry out a set of preparatory measures:
- The walls of the building must be equipped with ventilation windows, closed from the outside with special grilles.
- All wooden parts treated with antiseptic compounds to increase the service life of the structure.
- Taking into account the size of the room in which the floor will be installed, calculate the required amount of material.
- Throughout all work, it is important to monitor the horizontal position of the floor structure to prevent the formation of a slope.
- Timber and logs are subject to processing, in which they are cut to eliminate slopes and bevels.

Laying the subfloor
To ensure that the floor does not creak, does not vibrate, is smooth and warm, it is necessary to pay attention special attention laying the subfloor and, first of all, the joists.

The logs should be suspended on the beam supports in increments of 60 cm - insulation will be laid in the gap formed. It is not worth saving on beams in order to avoid sagging and vibration of the floor during operation.

Where heavy equipment, such as a stove or fireplace, will subsequently be installed, the floor is reinforced by placing beams in 30 cm increments.

Fastenings in such places are also further reinforced.

At the bottom, beams are nailed across the beams. Between floors, beams are nailed along the beams - this will save the height of the room and, if necessary, use the upper beams as decorative element in the interior after their additional finishing.

In the gap, an OSB sheet is laid on the beams.

After this, mineral wool slabs are laid in a checkerboard pattern, and on top there is a continuous layer of vapor barrier, which covers the logs and is fixed with construction stapler. The vapor barrier seam is taped.

The second layer of vapor barrier is laid overlapping, and a ventilation gap. To do this, use a 40 x 100 mm block, screwed to the floor joists. The finishing floor will be installed on top of these bars.

Important! All wooden elements must be treated with antiseptic compounds.
Video - Insulating a wooden floor
Finished floor installation
To obtain an aesthetically attractive and durable finished floor, it is recommended to use a milled board with a tongue-and-groove fastening.

Table 1. Instructions for laying finished floorboards
| Illustration | Description |
|---|---|
 | The first board is laid with a groove against the wall, leaving an expansion gap. |
 | It must be secured with self-tapping screws so that you can later cover the attachment point with a plinth. There are 2 options for further fastening the boards. |
 | The first option uses self-tapping screws that are twice as long as the floorboard. |
 | Self-tapping screws are screwed into each joist in the center of the board. Subsequently, the caps can be masked using wood putty. |
 | Then they take next board and combine the tenon with the groove. |
 | If necessary, the boards are adjusted by hitting them with a mallet through a block. |
 | Or they press it with a chisel. |
 | The second fastening option involves screwing self-tapping screws at an angle of 45 degrees into the tenon. To prevent the board from bursting, you must first drill a hole for the screw. |
 | With this option, the boards fit closer to each other, and the fastening elements are invisible. |
After all the boards are laid, their surface is sanded and coated with wear-resistant varnish in several layers.
Concrete floor in a wooden house
The most common way to install a concrete floor in a wooden house is to pour it over the ground, but with prerequisite that the soil must be dry.

Stage 1 – preparation
Preparatory work includes the following steps:
- Using a level, determine the main indicators and calculate the excavation work.
- To prevent soil subsidence and cracking of the concrete floor in the future, the soil is carefully compacted using special devices.
- A well-compacted sand cushion is placed over the ground. The backfill will be denser if you pour material that exceeds the required volume by 25%, moisten it and compact it thoroughly using a roller or vibrator.
- An expanded clay or gravel layer is laid on the sand.

Stage 2 - waterproofing
The next step is to perform , so that it does not absorb moisture from the concrete screed, and it will also protect the floor from ground moisture. For this they use roll materials based on bitumen. You can use thick plastic film.
The waterproofing material is laid overlapping, extending it onto the wall by 20 cm, and then the joints are taped. It is important that the material is homogeneous and without damage.
An alternative method is the coating method, when mastic waterproofing is applied at the stage of pouring the subfloor.

Stage 3 - pouring the subfloor
The subfloor or technological floor serves as the basis for the hydro- and vapor barrier layer. For its production, concrete of class B7.5 - B10 and crushed stone of size 50-20 are used. There are no strict rules for pouring the rough layer, the main thing is that its thickness is about 50 mm, and the difference does not exceed 4 mm.
Stage 4 – vapor barrier and insulation
A vapor barrier material in the form of inexpensive membranes made of fiberglass or polyester is laid on top of the subfloor. Durable material resistant to rotting are PVC membranes. Insulation is laid over the vapor barrier - this can increase the energy efficiency of a living space by 20%. The following materials can be used as insulation:
- Mineral wool, the density of which does not exceed 120 kg/m 3. To prevent it from accumulating cotton wool, it is insulated with polyethylene.
- Where the floor is subject to heavy loads, it is recommended to use extruded polystyrene foam, which deforms when compressed and then returns to its original state.
- When using polystyrene foam, it is covered with polyethylene on all sides to give strength.

Stage 5 – final screed
At the final stage, the final screed is performed, which will become the basis for the decorative floor covering. It can be monolithic or dry. In the first case, pouring a solution with a coarse filler in the form of crushed stone, stones, small pebbles or a cement-sand composition (quartz sand) is carried out along the beacons. Begin pouring the screed from the far corner of the room, leveling the solution using the rule. Complete drying of the screed occurs after 30 days.

An alternative is dry screed based on fiberboard, plywood and asbestos cement sheets, GKLV. The technology is simple and fast:
- Line with plastic film.
- A technological gap of 1 cm is left along the walls, into which soundproofing material is placed.
- Execute sand backfill 5 cm thick.
- The sheet material is laid in two layers and securely fixed together using self-tapping screws or construction adhesive.
- Perform puttying and sanding of joints.

Finishing materials
The material for finishing the floor in a wooden house is selected depending on the interior design. If the appearance of the house inside retains the color of natural wood, which on the walls and ceiling is not hidden behind other finishing, then flooring should be organically combined with it.
Table 2. Types of flooring
| Illustration | Description |
|---|---|
| In a wooden house, the best solution would be to install a floor made of natural wood. It will organically fit into the interior with wooden wall paneling. Wood has low thermal conductivity, it is environmentally friendly and safe. Natural wood flooring is distinguished by a variety of textures and rich natural patterns. |
| A beautiful and natural floor covering for a wooden house can be obtained by laying parquet made of natural wood, which has high aesthetics, a variety of shades and good performance. |
| In rooms with high humidity - bathroom, shower bath, kitchen, as well as in the hallway, laying tiles will be a practical solution. |
| An alternative material to expensive natural wood is laminate, which is highly durable, wear-resistant and decorative. This material imitates many, even rare and very expensive types of wood. |
Prices for popular types of block parquet
piece parquet
A wooden house has a special atmosphere home comfort and warmth, so natural materials look natural in its walls.
To build private house, you have to work hard, and all the processes performed require significant costs.
In an effort to save money, some do some of the work themselves, so the question arises: how to make a floor in a private house without calling in construction crews for help?
Anyone who has all the necessary materials can do this kind of work. suitable tools and certain knowledge.
Types of floors
 Diagram of a single and double plank floor
Diagram of a single and double plank floor Before starting work, you should decide what design the main coating will have.
Among the most popular types it is necessary to highlight following types floors:
- single;
- double;
- concrete.
The choice of each of them is determined design features buildings in which future installation is planned, and the conditions of further operation.
Features of flooring
 Single floors are recommended only for summer cottages
Single floors are recommended only for summer cottages
Single flooring is usually quite simple design, for which there is no need to spend a lot of materials and time. The floorboard is fixed directly to the joists using nails.
The disadvantage of this plank floor is its limited use. This coating is most often used only in the country, or in small houses and fully performs only the functions of holding the weight of all objects and people located indoors, combined with moderate cheapness.
In premises where year-round living is planned, such structures are used less and less.
 Double floors consist of a finishing and rough screed and are thermally insulated
Double floors consist of a finishing and rough screed and are thermally insulated A double floor is a structure suitable for installation in a room where people will stay all year round. What should the floor be made of so that it is warm even when it’s cold outside?
This design consists of two layers: rough and finishing screed. Between them are laid waterproofing and thermal insulation materials. They perfectly protect not only the floor from destruction, but also the entire house from blowing and dampness.
 Floor arrangement diagram
Floor arrangement diagram The rough coating is made from unedged boards, and the finishing coating is made from tongue-and-groove boards. All the processes required to build a floor in a private house can be done with your own hands.
The concrete floor is a regular poured screed. To accomplish this, first implement preparatory work to dismantle the old coating and place the guides, then a waterproofing layer is laid and a solution is made with which the prepared area is filled.
In order for the floor to be of high quality and ready for further finishing work, it should be given the necessary time to set.
Concrete consumption table for poured floor.

Installation of a single floor made of wood
 The instructions presented below will help you understand the question of how to properly install a floor in a private house, while observing the order of all actions.
The instructions presented below will help you understand the question of how to properly install a floor in a private house, while observing the order of all actions.
- The installation of a single floor will be carried out on poles, which, as a rule, are mounted during the construction of the main structure. At the same time, the interval between the pillars should be maintained at 80 cm. Subsequently, beams 10 cm thick are laid on each of the supports.
- On top of this structure we lay a grid of logs, which should have a cross-section of 5x5 cm. If the board prepared for the ceiling has a cross-section of 3 cm, then the distance between the logs should be maintained at 50 cm. Level the system using special wedges and firmly fix it with nails.
- A rough floor made of unedged boards is laid on this structure with your own hands, and a floor covering, usually linoleum or laminate, is laid on top of this layer.
For such floors, thermal insulation does not play a big role, since they are constructed for temporary or ancillary buildings.
However, when placed in residential buildings, before laying the subfloor, the space between the joists should be filled with sheets of polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene. Positive properties are low cost and quick construction.
Double wood floor
 The structure of this design is somewhat more complicated. It includes, along with the rough screed, layers of steam, heat and water protection with a tier of finishing coating located on top. The last layer is usually made of tongue and groove boards.
The structure of this design is somewhat more complicated. It includes, along with the rough screed, layers of steam, heat and water protection with a tier of finishing coating located on top. The last layer is usually made of tongue and groove boards.
How to build a floor that keeps it cool in summer and provides a pleasant microclimate in winter? Read more about correct device watch the floor in this video:
You can do all the processes yourself if you follow the step-by-step instructions:

When placing the boards, it should be taken into account that there should be an air pocket of at least 2-3 cm between the vapor barrier and the layer of finishing boards.
For good ventilation in the air pocket, special through holes that need to be covered with decorative sheathing.
Concrete floor
Initially, markings are made to make such a coating. To do this you should use laser level, which will accurately help set the marks along which the threads will subsequently be pulled.
Calculation and tools
 Concrete floor installation
Concrete floor installation To carry out all processes, you must have:
- vibrating rammer;
- roofing felt;
- fine expanded clay;
- durable polyethylene film;
- foam boards;
- reinforced mesh;
- spirit or laser level;
- slats.
Only by making a durable, perfectly level concrete floor can you hope for a high-quality floor covering.
Concrete floor installation
 Before making floors in a private house, you need to read the instructions, which will help you carry out all the processes in strict accordance with the rules and regulations:
Before making floors in a private house, you need to read the instructions, which will help you carry out all the processes in strict accordance with the rules and regulations:
- Initially, the base of the surface on which the concrete floor will be made is prepared. For this, a rough foundation is prepared, which can be made from layers of broken brick or crushed stone using M100 concrete.
- The next stage involves installing a waterproofing layer. It is very practical in this case to use roofing material.
- After this, you need to take care of thermal insulation. You can use expanded clay or foam boards for this purpose. IN middle lane It is advisable to place both of these layers at the same time, starting with the foam.
- On top of the laid layers, it is best to place a small wooden sheathing followed by laying the chain-link mesh.
- On top of the erected frame, starting from the corner farthest from the entrance, a smooth pouring of concrete begins with simultaneous leveling according to the rule along the marked beacon lines. Filling is carried out in one go.
- The final stage is leveling the top layer with liquid cement mortar or a special self-leveling compound. To learn how to properly fill a subfloor, watch this video:
To successfully complete your floor pouring tasks, you should follow the included instructions and purchase quality consumables and devices.
When you start building a house, the question of flooring arises first of all, since both the strength of the coating and the preservation of heat in the rooms, and therefore the health of the residents, will depend on them. Flooring in a private home can be installed in several ways, but you need to consider each of them in order to evaluate the pros and cons of each option.
- Wooden flooring has always been considered the most popular and comfortable floor for a home, since wood, unlike concrete, is itself a warm material.
- Concrete coatings are more durable than wood, but require good insulation, so they are often combined with wooden floors.
- Loose or floating floors weren't as popular with homeowners in the past, but lately many are increasingly turning to this option, as it is simple to set up and can be done literally in one day.
Whichever gender is chosen, it has specific features of your device, depending on the design of the house, the area on which it should be placed, the difficulties and nuances of installation, and even the financial capabilities of the homeowners.
In order for the floor in a private house to be warm and pleasant to walk on, each of its types requires insulation, so it is necessarily included in the general improvement plan.
Wood floors can be made in different ways, but they are always secured to logs, which are made from beams laid on a concrete base, support pillars, or embedded in the walls of the house. The latter option is only possible in a room with a small area, for example, narrow corridor or a small hallway.
Besides this, wooden floors are divided into single-layer and two-layer, i.e. with subfloor.
Pole-supported floors
Floors on supporting pillars are made in cases where it is not possible to connect the logs to the walls of the house or this is not enough for the strength of the overall covering. A log system installed only on support pillars is called “floating”.
"Floating" floor on supporting pillars
Floors using this system are arranged as follows:
- The first thing to do is to dig holes in the underground space of the house for installation brick pillars. Such mini-pits are marked at a distance of 70-100 centimeters from each other. The depth of the pits should be at least fifty centimeters. The size of the section will depend on the height of the supports being erected; the higher the pillar should be, the greater its width and thickness.
- Crushed stone, gravel or sand, at least twenty centimeters thick, is poured into the bottom of the dug holes, then filled with water and thoroughly compacted. The better the bottom is compacted, the more reliable the support for the joist system will be, so this process must be carried out conscientiously.
- Red brick pillars are laid on the compacted cushion, or formwork is arranged, reinforcement is installed, and a cement-gravel mixture is poured. If the pillars are made of concrete, then their cross-sectional size should be at least 40×40, and preferably 50×50 cm. The erected pillars are checked for level, and, if necessary, their height is adjusted.
- On top of the pillars, to a depth of 10-15 centimeters, threaded rods are embedded or anchors are installed, onto which the floor beams will subsequently be attached.
- It should be noted that if a building or room has small area, then support pillars can only be installed along the perimeter of the future room, but in this case it is necessary to lay massive beams on them.
- After the pillars are ready, waterproofing material is laid on their upper part. It is better if it is three or four layers of roofing material.
- Holes are drilled in the beams through which the mounting pins will pass.
- Beams made of timber or logs are laid on the waterproofing, they are put on studs and leveled, leveled using wooden boards. When the base of the floor is laid, it is better to fix the pads to the bars using nails, and the beams themselves also need to be secured by screwing them to the posts with nuts through a wide washer. If the studs have excess height, it is cut off with a grinder.
- It is best to pour expanded clay onto the surface of the underground in a layer of 15-20 centimeters - it will well retain moisture that can come from the ground and additionally insulate the floors.
- In order for the floor installed in this way to be warm, it is better to make it two-layer, especially since in this embodiment all the conditions have been created for this. If you plan to immediately lay a floorboard on the beams, then the underground must be completely filled with expanded clay, leaving between it and wood covering distance no more than ten centimeters.
floor boards
Subfloor
The subfloor can be constructed in several ways. The choice of a specific method will depend on the insulation material.
- If slag or expanded clay is used as insulation, then the subfloor is made solid, from boards that are nailed to the bottom cut of the beams. The cracks between the boards are coated with clay diluted to a not very thick state. After the clay has dried, insulation can be poured into the cells, on top of which a vapor barrier film is laid.
- If the floors are insulated with mineral wool, then the boards are nailed to the underside of the beams at a distance of 50 centimeters from each other.
- A vapor barrier is attached to the beams and bottom boards and thin plywood is laid. Insulation is laid on it, which is also covered with a vapor barrier on top, attached to the beams using a stapler and staples.
- Then logs measuring 10 × 3 centimeters are nailed onto the beams, on which floorboards or thick plywood will be laid.
Video: a visual example of installing a subfloor
Wooden floor on the ground
A wooden floor is also installed on the ground. There is a scheme for this, focusing on which you can draw up a work plan.
- The soil in the underground must be compacted well, and a cushion of sand, gravel or medium-fraction crushed stone, 20 to 40 centimeters thick, placed on top of it, and then compacted again.
- Rigid waterproofing, for example, roofing felt, is laid on the compacted cushion. If desired, you can lay reinforcement mesh under it for greater strength. Waterproofing should extend to the walls at least 10 centimeters.
- For waterproofing, bricks or concrete blocks are placed on the mortar, which will subsequently become a support for the beams. The supports are placed in such a way that the beams are at a distance of 60 centimeters from each other ( standard width insulation).
- The first layer of insulation is laid around the bricks - this can be 50÷100 mm polystyrene foam or mineral wool.
- Install on bricks, or better yet, on concrete blocks wooden beams, level them and secure them with a corner.
- Between the laid beams, for greater insulation, you can additionally lay mineral wool slabs.
- Insulation on top, cash yeah attach a vapor barrier film.
- Then lay the floorboard, which is secured with nails carefully driven into its side.
- The board is laid at a distance one - one and a half centimeters from the wall to ensure ventilation.
Wooden floor on concrete screed
When installing the floor on concrete screed or slab, logs can be laid directly on concrete or, if you need to raise the floors to a small height of 10-20 centimeters, on threaded studs.
When laying floors on concrete, you cannot skimp on joists - they must be quite massive, then the floors will be reliable and non-creaky.
It should be immediately noted that with such a floor arrangement it is imperative to make it two-layer, i.e. with the subfloor described above, otherwise it will be very cold.
- First on concrete covering Preliminary marking of the location of the logs is made. They should be installed at a distance of 60 centimeters, taking into account future insulation. Marking is done by marking a line with color.
- Next, marks are made on the broken lines at a distance of 30-40 centimeters.
- At these points, holes are drilled into which studs are installed with clamps located at approximately the same height from the floor - they will hold the beams.
- Holes are drilled in the beams themselves at a measured distance corresponding to the location of the studs mounted into the surface of the concrete, after which the beam is placed on the studs.
- Then, using a level, tighten the clamps in one direction or the other, bringing all the beams to an ideal horizontal level, controlling it with a level.
- The nuts are tightened on top of the studs, driving them into the prepared recess, and the excess part of the studs is cut off with a grinder.
- The next steps are the installation of the subfloor, insulation and laying of the finished floor.
Fastening the joists directly to the screed
Place joists on the concrete floor not difficult at all, and you can do it yourself if you have the right tools.
- Strips are struck on the concrete surface, also at a distance of 60 centimeters from each other, but from the wall they should be at a distance of the thickness of the insulation (150-200 mm).
- Then, using anchors, the logs are securely installed on the concrete floor. In this case, the beams can be of any height - this will depend on the desire of the owner of the house and on the ability to raise the floors to the desired height.
- Then, it would be a good idea to lay thin insulation, for example, polyethylene foam, which can be secured to the joists using staples.
- All over the wall, all over strips cut from mineral wool mats are installed around the perimeter of the room.
- Next, they are laid on the covered polyethylene. insulation boards material or expanded clay of fine or medium fraction is poured.
- The top of the insulation must be covered with a vapor barrier film.
- Next, a floorboard or thick plywood is laid, and a decorative coating can be laid on top.
Concrete floor
Concrete floors are also installed in different ways, but in general they are similar in technology, with minor deviations or additions.
Concrete coating is mainly done in houses with concrete or brick walls, and begin its construction after the walls are removed and the roof is covered.
- If necessary, the top layer of soil is removed to place a sand cushion in its place, which should be 10-15 centimeters deep. It needs to be compacted well by pouring water.
- The next layer is crushed stone of the middle fraction, which also needs to be compacted. The thickness of its backfill should be at least 10 centimeters.
- Next they arrange rough screed. It can be made insulated by adding expanded clay or foam chips to the solution. In addition, in this case the solution can be mixed not on sand, but on gravel. The screed is leveled and left to harden.
- On the finished hardened rough screed you need to spread waterproofing, which should extend 15-20 centimeters onto the walls. For it, you can take roofing felt or ordinary thick polyethylene film - the main thing is that the material is laid hermetically, with overlaps glued.
- Insulation - expanded clay - is poured onto the waterproofing, or high-density extruded polystyrene foam is laid, the thickness of which is chosen at the request of the house owner and depending on the climatic conditions region where the house was built.
- A metal sheet is installed on top of the insulation reinforcement mesh, and then the finishing screed is poured, to which you can also add insulation material. To ensure that the screed is level and there are no differences in floor height in the room, it should be done according to those exhibited according to the construction beacon level.
- If desired, additional insulation can be added to such a coating. You can lay wooden floors on the finished screed, lay laminate linoleum or ceramic tiles. Nothing prevents you from organizing a “warm floor” system.
Dry screed floors
There is nothing complicated about installing floors using a dry screed - it is done much faster than a concrete or wooden floor. That is why in recent years it is being used more and more often.
The main thing in its installation is a high-quality uniform bulk material. For such a floor, perlite, quartz or silica sand, slag or fine-grained expanded clay are used. These materials are not only convenient to use, but also perfectly perform the task of sound insulation and thermal insulation. If the bulk material is well distributed over the area of the room, it almost does not shrink, so if the work is done conscientiously, the bulk floors will last a long time.
Leveling the bulk mixture
- To ensure that the floors keep their shape and the dry screed does not crumble, special bulkheads made of boards are installed.
- Plates made of moisture-resistant GVP, plywood or other sheet materials are laid on top of the dry screed. The most important thing is to set the first slab perfectly level - this is done using a level. The next slabs to be laid will be aligned with the first one. The laid material does not need to be pressed into the dry mixture, but should be moved very carefully along the surface. The evenness of laying sheets during all work is controlled using a level. in areas that are subject to the greatest load, for example, in aisles.
- On gypsum fiber the sheets have folds with which they are connected to each other when laying them on a dry screed.
- The sheets are stacked with an offset of half a sheet, similar to brickwork- this will increase the stability of the coating.
- Having laid the first layer of slabs on a dry screed, they usually move on to laying another one - it will make the floor more durable and stable. If used for flooring gypsum fiber sheets, then a fold is cut off from them on the first layer so that they fit tightly together and bulk material cannot get between the first and second layers.
- The second layer of sheets is always laid perpendicular to the bottom sheets.
- The laid top layer of sheets is fixed with the bottom with using glue and additionally fastened with self-tapping screws. They must be twisted under load - to do this, simply stand on the top sheet, and the weight of the master will serve as the necessary load.
- Exactly along the line doorways It is not recommended to join the sheets - it is necessary that the sheet be distributed in this place to both rooms. sealed with waterproofing material, for example, sealant.
- If such floors are installed in a room where humidity is high, the entire surface of the floor is treated with coating waterproofing before laying the decorative coating.
Thus, it is obvious that the floor in a private house on a dry screed can be installed quite easily if you take the work seriously, do it carefully and take your time. Rush absolutely inappropriate– in terms of time for completing work, such a technology under any circumstances is many times superior to any other.
A wooden house is associated with comfort and warmth. Natural wood materials create special atmosphere, they are safe for health. At the same time, wood requires special care and compliance with operating requirements. Construction of a floor in a wooden house also requires a special approach. Let's look at how you can do this correctly.
Floor requirements

A properly laid floor in a wooden house must satisfy such parameters as practicality and durability. It needs to be made warm and even. Its aesthetic appearance plays an important role. If we lay a floor with additional insulation, we must not forget that in this case it will be necessary to raise it.
To lay the floor with your own hands in accordance with these requirements, you need to determine the order of work and take into account all the individual features of the operation and design of the building.
The whole process can be divided into several stages:
- Considering Properties various designs gender;
- Study of the installation process depending on the selected type;
- Construction and installation of the selected type of structure.
The most common types of flooring in a wooden house are concrete, plywood or laid on joists. Using joists or concrete screed, you can raise the floor level. In the photo you can see how the floor looks using different materials.
Please note: Regardless of the type chosen, you can equip it with a heated floor system. This will be very useful when year-round accommodation in the house. Such designs also allow you to raise the floor level.
Features of concrete floor

- Minimum time spent on work, compared to a full floor made of wood materials;
- Cost reduction;
- To build a concrete floor with your own hands, no special construction skills are required. It is enough to fill the screed in accordance with the level. The result is a leveled surface on which any floor covering can be laid.
The disadvantages include:
- There is a noticeable load on the foundation, so preliminary calculations should be made to avoid problems in this area;
- Small vibrations can cause cracks to appear in the concrete surface, which can lead to heat loss.
Features of wood construction

Wooden base, like any other, has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include:
- safety for health, the tree does not emit any hazardous substances;
- you can design any design structure;
- if necessary, all work can be carried out with available tools and materials.
We must not forget that in order for the floor in a wooden house to last for many years, it must be laid in compliance with all requirements and recommendations. This will prevent the floor from sagging, because then you will either have to replace the floor or be puzzled by the question of how to raise it.
The disadvantages include:
- complexity of installation;
- high cost;
- duration of work;
- difficulty in leveling the structure.
What is the construction of a wooden floor?

To correctly lay the floor with your own hands, you should take into account that its structure consists of a subfloor, a layer of thermal and waterproofing, a finished floor and a floor covering.
The design can be double-layered or single-layered. If we install the second method, then there may be no lag. Their presence or absence is determined by the thickness of the boards and the distance between the beams.
Sometimes it happens that a wooden structure shifts under the influence of various factors, which leads to deformation of the subfloor. When constructing a multilayer structure, the upper layers are kept stationary.
If there are support pillars, as well as in cases where beams are inserted into house walls, it is necessary to lay the logs in the correct order.
How to make flooring using logs?

You can lay a subfloor in a wooden house with your own hands using one of two options:
- on the logs;
- using floor beams.
Logs allow you to raise the floor level, so it is not always rational to use them in rooms with a low ceiling. They are attached either on top of the foundation or to the walls of the log house. Before placing the material, the logs should be brought into the room in order to acclimatize them, where they should remain for several days.
Stelem as follows:
- We place two of them along opposite walls and connect them using nylon threads; they should be placed at a distance of one and a half meters from each other. These threads will be used as guides to which the remaining joists will be attached. The space between the joists is filled with a layer of insulation;
- When thick boards of 30 or 40 cm are used, you can make the distance between the lags up to 0.8 m. When the boards are less than 30 cm thick, the distance between the lags needs to be reduced to 0.5-0.6 m. When the boards are thicker than 40 cm, the distance can reach 1 m;
- Using wedges made of chipboard or fiberboard, you can level the floor surface by adjusting the height of the logs. Such wedges are secured with self-tapping screws or long nails;
- When it is supposed to fasten the lag on top concrete base, then the fastening can be done with dowels or anchors. In no case should we forget about treating lags with an antiseptic composition;
- The next step is to lay and strengthen the boards. The first row is fastened with a 1.5-centimeter distance from the walls. Pre-drilling of holes for self-tapping screws is required;
- Lay the boards on each of the joists and then secure them. The gaps that remain between the walls and the floor made of boards are closed with baseboards. You can also use staples; they are connected to the boards and secured with nails. In the video you can see how this process is carried out.
If fiberboard or chipboard is selected as the base for the floor
Using this method, you can also raise the floor with your own hands in a wooden house. In order to lay the subfloor, you can choose plywood, chipboard or fiberboard. This material is characterized by reliability, strength, and does not lend itself to deformation. In addition, if necessary, materials such as fiberboard or chipboard can be easily dismantled and replaced.
The layout of the sheets must be previously thought out and marked. Then, in accordance with the markings, lay the lags. In the photo you can see an example of such a scheme.

To lay the floor flat, you can use beacons. To do this, you need to install them on the entire floor surface. For these purposes, the entire area of the room is divided into squares of 30-40 cm, into the corners of which self-tapping screws are screwed. To install beacons you will need a level. After this, you can lay the logs, which will later be covered with chipboard or fiberboard.
The thickness of the chipboard or fiberboard sheets determines the distance between the logs. In general, it is no more than 40 cm. When boards are installed across the beams, they should be fastened at a distance of half a meter from each other.
To prevent sagging logs, you can also make substrates from pieces of chipboard or fiberboard, which must first be lubricated with parquet glue. Impregnating the entire floor surface with glue will prevent cracking. Between the logs and sheets of chipboard, fiberboard or plywood we make a layer of moisture-proof material.
It is advisable that all edges of the sheets used fall on the joists, and that they themselves chipboard sheets(Fibreboard) were laid at a distance of a couple of millimeters from each other, this is necessary in case of deformation of the material. The joints must be sanded to level the surface. In the video you can see how to lay sheets of plywood (chipboard, fiberboard or other material).
Making a finished floor

It is best to lay the finished floor with your own hands using tongue and groove boards (pictured below). They imply a convenient connection with each other. When one board is attached to the previous one using a special lock.
You can adjust the boards to each other using a mallet by tapping them. You can fasten the board to the joists with long nails, which should be driven in at a slight angle, recessing the nail head into the board.
The finished floor, made of tongue and groove boards, must be sanded and coated with varnish or paint.
The arrangement of the finished floor with tongue and groove boards is suitable for both double and single construction. The double will certainly be much warmer. She should be given preference when living year-round in a wooden house. A diagram of this design can be seen in the photo.
How to lower the floor?
Owners of old houses often have to deal with the problem low ceilings. To increase the space with your own hands, it is best to raise the ceiling. If this is not possible, the floor surface can be lowered.