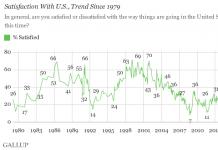
Due to geological features, the house is exposed to external factors not only from the atmosphere, but also from the soil. Installing a blind area around the house is one of the stages of comprehensive protection that allows you to protect the building from the manifestations of nature (rain, melt, groundwater). Roof and drainage system protects the walls and the house itself from water, but precipitation flows to the ground near the building and destroys the foundation. What is a blind area? Why do you need a foundation blind area, what is its purpose and how to do it yourself?
What is a blind area at home
A blind area is a covering around the perimeter of a house, designed to protect the foundation, basement and basement from water. It is made of waterproof material at a slope from the foundation.
Why do you need a blind area around the house (functions):
- hydrobarrier - protecting the foundation of a building from moisture. First of all, rain and melt water are diverted away from the foundation using a blind area. In addition, the presence of a blind area imparts thermal insulation properties to the foundation;
- comfort - the blind area can be used as a path around the house. A wide blind area can become the basis for arranging a recreation area or terrace near the house. With the correct calculation of the load, it is possible to organize the movement of a car or its parking along the blind area;
- aesthetics - design of the site and local area, giving the structure completeness.
- the blind area stabilizes the air-gas regime in the soil surrounding the foundation. The soil invariably contains oxygen, which is necessary for plant growth and the vital activity of soil microorganisms. Large pests also create passages for air to enter the soil;
- eliminates the possibility of damage to the foundation due to frost heaving of soils. It occurs due to the fact that water, solidifying in the soil during the cold season, increases its volume. Soil heaving in itself does not pose any threat, but it creates a significant lateral load on the foundation of the house, which can result in a distortion of the foundation of the house, which will ultimately lead to the destruction of the building standing on it. Thus, the blind area allows you to distribute the load more evenly.
Types of blind areas around the house
Taking into account the fact that the period of operation of the blind area should be equal to the period of operation of the structure itself, special attention should be paid to the choice of material for its construction.
In practice, several approaches to making a blind area are used, but in general it is classified as either hard or soft.
Rigid blind area
1. Concrete blind area
The blind area is made of concrete in the vast majority of cases. Concrete is a reliable material, time-tested and proven by more than one generation of users. Almost every man has an idea of how to make a concrete blind area. And knowing the nuances of pouring it, he can do the work with his own hands.


It is mostly used to protect the foundations of multi-story buildings. This is caused by two factors. Firstly, it is difficult to compact the material (considerable effort is required). Secondly, to keep the asphalt in a condition suitable for pouring, its temperature should be about 120 degrees. Agree, it is difficult to make a blind area from asphalt without special equipment. Thirdly, when heated, asphalt emits harmful impurities, and therefore few users are ready to replace clean air country house, for a typically urban scent.


3. Blind area made of ceramic tiles
It is classified as hard because the tiles are laid on a concrete mortar. Used as facing material clinker tiles, as more resistant to external influences. This blind area copes well with its functions, but the cost of clinker tiles is high. Therefore, its analogue, concrete paving slabs, has become more widespread.


Soft blind area
4. Blind area made of paving slabs (paving stones)
A relatively new direction in protecting foundations from water. Despite the novelty of the material (or rather, the old one, since it is a prototype of paving stones - a cheaper analogue), laying paving slabs with your own hands does not cause any particular difficulties.


5. Blind area made of gravel (crushed stone) or natural stone
The gravel blind area (made of cobblestones, rubble stones) has not become popular for several reasons: the difficulty of compaction, the inconvenience of movement, the need to constantly correct the coating (it can be washed away by unorganized drainage), and the possibility of weeds sprouting. Stone blind area - good option, but more complex installation and high cost compared to tiles.


6. Hidden blind area around the house
IN in this case The facing material is soil on which you can plant lawn grass, flowers, and arrange flower beds. A blind area of a hidden type is made according to the general principle: the top layer of soil is removed, a layer of waterproofing, a layer of sand and crushed stone are covered. The difference is that the top of the pie is covered with geotextile or PVP membrane, on top of which soil is poured. It is not advisable to walk on a hidden blind area; there is a risk of damaging the profiled membrane and trampling the grass. But, if done correctly, it will serve faithfully for a long time.


Which blind area is better - made of paving slabs or concrete?
Each of the above types of blind area has its own advantages, disadvantages and construction features. According to statistics and reviews, today the most popular (most often used) blind areas are poured from concrete and laid out from tiles. Therefore, it would be correct within the article to consider what is better, concrete or paving slabs for the blind area?
This question is asked by many craftsmen and users. Practical operating experience indicates the effectiveness of the tiles. The advantages are as follows:
- the ability to create a continuous, strong and stable blind area. At the same time, ensuring the integrity of a concrete blind area is much more difficult than a tiled one;
- maintainability. The tiles can be dismantled completely or partially. Thus, the process of repairing a blind area or laying communications is significantly simplified. In the case of concrete, it is necessary to destroy part of the blind area, dispose of the concrete fractions, and restore it again after laying. Eliminating tile subsidence or replacing a defective element in a tile blind area is not difficult and will not take much time. And most importantly, the tiles can be reused;
- reliability. The tiled blind area drains water well thanks to a large number seams. This allows us to assert that it does not deform as a result of soil heaving or water freezing. Water that has frozen on the surface of a concrete blind area can lead to local cracking of the material. At first, these cracks will not pose a threat, but each subsequent flooding will cause the crack to expand and the blind area to collapse.
Another nuance is the location where the blind area adjoins the house. As you know, the blind area should not form a single structure from the foundations (should not be connected to it). Soil movement and freeze/thaw cycles will inevitably cause this bond to break. When laying tiles it is easier to ensure the required technological gap. In addition, the destruction of concrete most often occurs precisely at the place where it adjoins the foundation or plinth (the blind area comes off);
- foundation insulation. The technology for laying paving slabs involves the arrangement of several layers, incl. the use of clay and the possibility of laying insulation. An insulated foundation blind area is an additional protection for the basement and ground floor, which reduces heat loss and ultimately leads to savings on heating the house;
- reduction in plinth height. With a rigid blind area (made of concrete), the minimum height of the plinth should be at least 500 mm. When soft (tiles, paving stones, gravel, natural stone) a height of 300 mm will be sufficient. This reduces the cost of installing a plinth;
- ease of work, no need for a reinforcing frame, minimum waste, minor dustiness of the work;
- additional waterproofing of the foundation blind area. While a concrete blind area protects the foundation only from the influence of surface water (rain or melt), a clay hydraulic lock, which is made by forming a cushion for laying paving slabs, allows you to protect the base of the building from groundwater;
- more aesthetically pleasing appearance compared to a concrete blind area. A variety of installation options, designs, sizes and colors allows you to create a unique blind area.
The main advantage that led to the use of concrete as a material for the blind area is its low cost. Buying paving slabs and materials for laying them will cost more, even if you do the installation yourself.
Cost of blind area of a private house
In order not to be unfounded, we will give a brief comparative description, i.e. We will indicate in the table the prices for blind areas made of concrete and paving slabs. All prices for 2015, approximate, are presented for information purposes as a guideline for drawing up estimates.
The cost of a concrete blind area (width 1 m, thickness 10 cm)
| Material | Material consumption per 1 sq.m. | Price | The cost of a concrete blind area per 1 sq.m. rub. | |
| Concrete M22, class B-15 | 1 | RUB 3,500 | 350 | |
| For self-cooking concrete | ||||
| per 1 cubic meter | For 1 sq.m. | |||
| Cement M 500 | 320 kg | 32 kg | 200 rub/50 kg | 128 |
| Screenings or crushed stone (fraction 5-10 mm) | 0.8 cubic meters | 0.08 cubic meters | 160 | |
| Sand | 0.5 cubic meters | 0.05 cubic meters | 400-600 rub/m3 (the price is also affected by the loading location: quarry or delivery) | 30 |
| Water | 190 l | 19 l | At local rate | |
| Concrete additives* | ||||
| For pillow | ||||
| Geotextile, PVC film) | 1 sq.m. | 110-2500 rub/roll (50 sq.m.) | 100 | |
| Sand | 0.05-0.1 cubic meters Depending on the thickness of the layer and the composition of the finishing base for the tile | 400-600 rub./m3. | 25-50 | |
| 0.1 cubic meters | 1800-2000 cubic meters (the price is also affected by the loading location: quarry or delivery) | 190 | ||
| Reinforcement | ||||
| Fittings, diameter 6 mm. | 12 m.p. | 10 r/m.p. | 120 | |
| Reinforcing mesh 50x50, diameter 3 mm. | 1 sq.m. | 60 rub./piece (1000x2000) | 60 | |
| Reinforcing mesh 150x150, diameter 3 mm. | 1 sq.m. | 33 RUR/piece (500x2000) | 66 | |
| Formwork installation | ||||
| Boards for formwork** | ||||
| Beam 30x30 for spacers** | ||||
| Total: | ~ 800 rub/sq.m. | |||
* We are talking about additives (plasticizers) that give concrete additional properties (strength, frost resistance). Adding plasticizers to the composition concrete mortar is at the discretion of the master. In the given “classic” recipe their cost is not taken into account.
** to form the formwork when pouring a blind area, in practice, old boards or used plywood are used. Therefore, their cost is also taken into account.
The cost of a blind area made of paving slabs 1 meter wide
| Material | Material consumption per 1 sq.m. | Price | The cost of a blind area made of paving slabs per 1 sq.m. rub. |
| For pillow | |||
| Clay | Depends on the soil and the desired thickness of the hydraulic lock 0.05-0.1 cubic meters. | 250-400 rub/m3. (depending on the location of the quarry and the fat content of the clay) | 15-30 |
| Geotextiles, PVC film | 1 sq.m. | 110-2500 rub/roll (50 sq.m.) | 100 |
| Sand | 0.15-0.2 cubic meters Depending on the thickness of the layer and the composition of the finishing base for the tile | 400-600 rub/m3 | 75-100 |
| Screenings or crushed stone (fraction 3-10 mm) | 0.1 cubic meters | 1800-2000 cubic meters (the price is also affected by the loading location: quarry or delivery) | 190 |
| For the finishing layer | |||
| Cement M 500 | 10 kg. Depends on the purpose of the formwork | 500 rub/50 kg | 100 |
| Sifted sand | 2.5 - 10 kg. Depends on the purpose of the formwork | 100 rub/50 kg | 10 |
| For the front layer | |||
| Tile | Depends on the size of the tile. 50 pcs. for the “brick” shape | 300-1,500 RUR/piece. on average 400 rubles. for the “brick” shape | 2000 |
| Border | 2 pcs. | 75-300 rub/piece. depending on thickness | 360 |
| Water for irrigation sands and blind areas | Before puddles form | At local rate | |
| Total: | ~ 3000 rub/sq.m | ||
How long does it take to install a blind area?
An important point, based on the experience of constructing blind areas of various types, we can give the approximate time for the construction of each of them. The calculation was made based on the total time spent by one person on making a blind area of 50 square meters.
- Completion of all work on preparing the base, forming the formwork and pouring the concrete blind area takes approximately 40-50 minutes. per 1 sq.m. (20-25 minutes when using ready-made concrete).
- Filling the pillow and laying tiles 1 sq.m. takes 60-70 minutes. Moreover, a significant amount of time is spent on the process of compacting the base.
It should be noted that with increasing square meters (area), the speed of work increases.
How to make a blind area around the house with your own hands - video
Construction of a blind area for a house - SNiP and GOST
The second aspect that needs to be taken into account before you start building a blind area with your own hands is the provisions and recommendations of regulatory documents. These include:
GOST 9128-97. Mixtures of asphalt concrete road, airfield and asphalt concrete. Contains recommendations on determining the angle of inclination of the blind area.
GOST 7473-94. Concrete mixtures. They contain requirements for the quality of concrete used for arranging the blind area. Required when arranging a blind area that serves as a driveway for a car.
SNiP 2.04.02-84. Water supply. External networks and structures. SNiP regulates the construction of a blind area around a well, contains recommendations for choosing the angle of inclination, as well as for arranging a castle made of clay or rich loam.
SNiP 2.02.01-83 Foundations of buildings and structures. Regulates the main parameters of the blind area device (dimensions):
1. Width of the blind area around the house (foundation)
Determined from the position of soil type. As you know, soil with different compositions subsides differently. For example, clay soil is divided into two types:
- Type 1 soil does not sag under its own weight or its subsidence is no more than 50 mm and can be caused by external factors.
- Type 2 soil can sag under its own weight.
Thus, based on soil data, the composition and thickness of the base layers for laying paving slabs is selected. Based on the provisions of SNiP, craftsmen determine how wide the blind area around the house should be.
It has been verified by practice that for the 1st type of soil minimum width the blind area should be at least 700 mm, for the 2nd - at least 1,000 mm.
 If there is normal soil on the site, the optimal width of the blind area can be 800-1,000 mm. In this case, the width can be considered sufficient if it is greater than the overhang roofing material over load-bearing walls by 200 mm (for normal soil) and 600 mm for type 2 clay soil.
If there is normal soil on the site, the optimal width of the blind area can be 800-1,000 mm. In this case, the width can be considered sufficient if it is greater than the overhang roofing material over load-bearing walls by 200 mm (for normal soil) and 600 mm for type 2 clay soil.
The final decision on how wide the foundation blind area should be depends on the users and the purpose of the blind area. Which may consist of the following: only foundation protection, protection + occasional human movement, protection + heavy pedestrian traffic (for example, a terrace or gazebo) or protection + car traffic.
Such parameters as the length and height (thickness) of the blind area are not regulated by SNiP. Users advise taking them as:
2. Length of the blind area around the house
3. Thickness (height) of the blind area around the house
Minimum thickness of the blind area: no less than 70 mm, optimally 100-150 mm.
Note. The height of the blind area is not determined to zero. It should rise above the soil by at least 50 mm.
For the blind area that serves as a pedestrian zone, the requirements are becoming more stringent. They mainly concern the design of the pillow. For the automobile zone, it is advisable to make the most durable base possible and, when choosing paving slabs, give preference not to vibratory-cast slabs, but to vibro-pressed ones.
SNiP III-10-75 Landscaping. The standard regulates the location of the blind area. It should fit tightly to the base at an angle. At the same time, the slope of the blind area should be within 1-10% in the direction opposite to the load-bearing wall.
4. Slope of the blind area of the house
The angle of inclination of the blind area is measured in percentages and degrees. For 1 m of blind area width, the slope should be 10-100 mm, i.e. 1-10%. In practice, the slope does not exceed 15-20 mm per 1 linear meter. This slope is invisible visually, but does an excellent job of draining water from the foundation and base of the house.
Note. A large slope can lead to the fact that the flow of water will increase speed when moving along the blind area and, gaining strength, quickly destroy its outer edge.
Another document worth considering is the “Schemes for operational quality control of construction, repair and construction and installation work" Based on it, you can study the permissible deviations from the given standards.

5. Expansion joint in the blind area (deformation, temperature)
To compensate for the movement of the blind area and reduce the pressure on the foundation, an expansion joint is provided - a gap between the wall (basement) and the blind area. A thermal seam is formed by installing a sheet of insulation or several layers of roofing felt to a vertical surface. Sometimes a wooden board is installed at the junction, which is then removed, and the place where it is installed is sealed (covered) with sand. This is a labor-intensive method, because removing a board from hardened concrete is quite difficult.
Conclusion
The information provided from the theoretical part will become a useful basis for constructing a blind area around the house with your own hands. Knowing how to properly make a blind area, you can be sure that the created structure will last a long time and effectively.
The blind area around the house is simple, but greatly prolonging the life of its structure structural element . From two completely identical individual houses built at the same time in an area with flat favorable climate one, whose owners decided to save on the blind area, less than 20 years later demanded overhaul with a partial replacement of the foundation, and the second has already outlived its fellow by more than twice and stands as if nothing had happened without signs of any violations in the structure.
At the same time, the blind area can be made completely with your own hands, incl. and around already existing building, without possessing any construction skills and thereby maintaining family budget, at current prices, at least 150,000 rubles. This is for a house 10x12 m in plan and a blind area of the simplest type. If the house is 12x15 m and the blind area is permanent, the savings from installing it yourself will be more than 250,000 rubles.
If now you immediately want to study the step-by-step instructions for laying a blind area, then please, here is a detailed video:
However, this is quite true, but only one concrete example. Meanwhile, only in officially approved construction sites regulatory documents you can count at least 20 blind area schemes for different climatic conditions, the nature of the soil, the type of building, the availability of local resources for building materials, etc. And the notes to each diagram indicate when, under what conditions and how this design can be changed in order to simplify and reduce the cost.
Therefore we Next, we’ll deal with what you can’t tell in the video. Namely: we will try to explain about various subtleties blind area so that you, the reader, understand the meaning of each element, each production operation and could provide long life your home without unnecessary work and costs.
Why do you need a blind area?
A blind area in the general sense is a cornice attached to a wall, covering the horizontal angle between it and the ground or floor. An ordinary floor plinth is also a blind area, only internal. The operating principle of the blind area is simple: do not completely block the path of unfavorable factors (moisture, dust, etc.), but take them to the side where they will not cause harm. The plug will eventually leak, but if nothing is leaking here, then nothing will leak. The obvious is easy to overlook, but the simple is difficult to invent: the blind area in construction appears only in Ancient Greece.

Foundation blind area - a low but wide cornice of the basement lying on the ground with a slope(see figure on the right), made of material that does not allow moisture to pass through and does not allow gases to pass through easily. The foundation is the basis of the building, and the blind area ensures its reliability and durability. Its significance for the foundation consists of 3 functions:
- Protective - from atmospheric precipitation;
- Safety – as a gas regime stabilizer in the soil around the foundation;
- Insulation – neutralizing the effect of heaving of freezing soil on the foundation of the house.
First. Due to thermal deformations and unequal shrinkage of the soil and foundation material, a gap inevitably arises between them. Through this gap, rain and melt water flow down the foundation, albeit in a very weak stream. The drop wears away the stone, and this flow washes away the foundation. And if the blind area takes it to the side, then water will naturally seep through the capillary passages of the soil. The water in the capillary can no longer wash away anything, because... its gravitational pressure is compensated by the force of surface tension.
Second. All soil inhabitants need oxygen. There are many among them who support “soft power”: plants – root aggressors and relatively large burrowing animals; both create passages in the soil through which water can again flow under the foundation and wash it away. At the same time, the soil around the house should not be allowed to suffocate; then chemically aggressive substances will form in it, which are not only smelly and harmful to health, but also destroy the foundation.
The blind area allows enough air to pass through so that there is enough useful soil fines, approximately the size of a nutritious grass root and an earthworm. And large “agents of influence”, finding that their oxygen is blocked from above, move away: there is enough land around, they can grow and dig somewhere else. Here the unreasonable creatures turn out to be smarter than other famous politicians.
Third. Frost heaving of the soil is dangerous primarily due to uneven lateral pressure on the foundation; it can lead to skewing of the building. The same house from sand-lime brick 10x12 m in plan and 6.5 m high from the base to the roof ridge, tilted as a whole by only 1 degree, 20 years after construction it begins to collapse due to horizontal stresses in the structure. The blind area creates a layer of unfrozen, and therefore plastic, soil around the foundation, which evenly distributes lateral pressure.
Note: in the simplest case, the blind area acts as a snow coat on winter seedlings; here it does not release heat upward like the same cornice, only in the opposite direction. If construction geology is in this place unfavorable, then it may be necessary to insulate the blind area, see below.
Based on this, we can immediately draw important conclusions:
- The blind area should frame the house with a continuous strip: any gap will attract harmful factors, which will entail increased weakening of the foundation, which is especially dangerous because it is concentrated in one place.
- Cracks in the blind area are unacceptable for the same reason.
- The blind area cushion (see below) should not be buried more than 1/2 of the calculated freezing depth in a given area, otherwise it will turn into a rigid appendage of the foundation and lose all its functions; the blind area should “play” together with the ground without losing connection with the foundation. However, throughout the entire territory of the Russian Federation this condition is met without any additional measures.
How is the blind area arranged?
The construction of the blind area is also simple: it is a trench 20-50 cm deep, dug along the perimeter of the building close to the foundation. A thermal gap (expansion joint) is immediately made between the blind area and the foundation; To do this, it is covered with a rubber-bitumen compound and then with 2 layers of roofing material, the lower ends of which are bent into the trench by 50-70 cm.
Note: if the blind area is insulated, then the thermal break is superimposed on the insulation of the base/foundation.
Then the trench is lined with waterproofing made of polypropylene film; it gives just the right gas permeability. A cushion of sand and crushed stone is poured into this trench; in most cases - in a cage made of geotextile (road mesh), which prevents the migration of the cushion material into the ground, but does not prevent the outflow of moisture from it to the sides. Modern technologies for building blind areas involve laying multi-layer cushions. Alternating layers of sand and crushed stone make the blind area much simpler and cheaper, while at the same time increasing its efficiency.

The cushion for a monolithic covering is poured into the formwork, for a slab covering it is limited from the outside by a curb stone, and for a soft covering it is placed either in the curb, or just like that. By previous ideas it is the covering that is the actual blind area, and the pillow only supports it. But multilayer cushions in geotextile with propylene insulation can take on all the functions of a blind area, so the coverings of modern blind areas can only be decorative and ergonomic. In general, blind areas are divided into 3 types:
- Rigid - monolithic made of concrete, asphalt and cement-filled crushed stone with iron-plated surfaces;
- Semi-rigid - with a multi-layer cushion and flooring made of paving slabs, cobblestones, porcelain stoneware, reinforced concrete slabs an extra pillow;
- Soft - bulk made of crushed stone on a multi-layer cushion.
When is what kind of blind area needed?
All types of blind areas cope with their responsibilities perfectly, but different terms. The durability of monolithic ones is almost equal to the service life of the building, but they are labor-intensive and expensive. This also applies to asphalt: its binder – tar – is modern conditions remains profitable only on a large scale road construction. Cement self-leveling coating is inexpensive and relatively labor-intensive, but is applicable only on stable soils; on heaving soils (wet loams, etc.) it is strictly not recommended. In addition, all hard coatings are not decorative.
Note: a case when you need to unconditionally choose a hard covering - an insulated blind area. It is useless to insulate semi-rigid and soft blind areas. And when you need to make a blind area with insulation, let's look further.
Soft covering is very cheap and easy to make. But it lasts no more than 5-7 years, but on any soil in any climate and replacing it is elementary, as far as this concept is generally applicable to construction work. It is optimal as a temporary one if there is a shortage of funds or you are simply tired of construction. We'll sort out the finances, we'll raise our hands again, we'll finish it thoroughly, but for now it will serve just fine.
In general, Taking into account modern construction achievements, preference should be given to semi-rigid blind areas. Their service life is up to 20-25 years in most parts of the Russian Federation, except for the permafrost zone, and in terms of labor intensity, maintainability and possibility complete replacement they are almost equivalent to soft ones. The cost depends on the coating material; work as expected on any soil.
The decorative qualities of semi-rigid blind areas are also determined by the coating material, for example. From the point of view of a landscape designer, a blind area (we will consider it in more detail) is no different from a garden path. Nothing is an exaggeration. The partial water permeability of the slab blind areas at the seams between the slabs makes it possible to dispense with internal slopes in the multilayer cushion, and leave the flooring horizontal, i.e. It will be possible to walk on it even in icy conditions.
Next we will look at how to properly make a blind area from the already mentioned paving slabs; The technology for constructing cobblestones differs from it only in the coating material. Along the way, we’ll deal with soft crushed stone and self-leveling cement, because The pillows needed for them are the same as for slab ones. Let us dwell in more detail on the concrete blind area as the most durable and the only one suitable for insulation. And we will touch on specific issues: the width of the blind area, its slope, insulation, drainage and the subject of discussion among builders - the connection between the blind area and the base.
Tile blind area
Overall true the diagram of a slab blind area with internal slopes has been circulating on the RuNet for a long time, but along with it there are also inaccuracies. Since the original information is advertising and commercial, perhaps the authors protected their know-how in this way. Let's try to supplement source material until ready for use. The correct blind area from paving slabs is made according to the diagram in the figure:

First, pay attention to the outer bend of the waterproofing up to the crushed stone. Its purpose is to prevent the first layer of sand from spreading. And drainage of a thin (3-5 cm) layer of sand will be ensured through the crushed stone layer overlying it.

Secondly, the recommended total cushion thickness of 30 cm is only valid if the blind area lies entirely in humus. If the humus layer is thinner, then the drained layers should not be buried in dense soil; The layer of crumpled clay is in any case 15-20 cm. What if there is less than 20 cm of humus or no humus at all? Install drains, see fig. right. Prefabricated gutters are placed on the ground 1-2 m from the lowest corners along the overall slope. In general, drains are desirable for slab blind areas on any soil, but it is better to place the collections in a storm drain or drainage well, if there is one.
Third, the thickness of the crushed stone layer is 3 times the thickness of the first sand layer, and the upper sand layer is 2 of the same. For the blind area to function properly, the proportions must be maintained, but the thickness of the lower sand layer must be at least 3 cm. The thickness of the overlying layers is calculated along the wall and increases outward in accordance with the slope.
Finally, the slopes. They should decrease slightly from bottom to top. In this case, the slope of the clay preparation outward is 0.08-0.12 (8-12 cm/m), the lower crushed stone is 0.05-0.07, the upper crushed stone is 0.03-0.04. The top of the tile cushion is horizontal.
Soft and cement
The design of a soft crushed stone blind area is even simpler, see fig. The conditions for penetration into humus, slopes and the “trough” of waterproofing are the same, and the thickness of the crushed stone layer is equal to the total thickness of the crushed stone and top sand with tiles in the previous case.

The cement-filled blind area is done in the same way, but in formwork, and 2-3 cm less crushed stone is placed, see fig. below. Then the top is poured cement-sand mortar no worse than M200; for its proportions and method of preparation, see the section on concrete blind area.

When the solution has set, but is still wet (watch out, don’t miss the moment!) to increase its resistance to abrasion, the surface of the pouring is ironed: sprinkle with an even layer of dry cement from M400 in a thin layer, just enough to cover the fill, and rub it thoroughly with a polisher.
Then the blind area is covered with a dark film (the iron surface ripens better without light) and periodically once a day or two, lifting the film, sprayed with water. An ordinary broom will work as a sprinkler. The period of aging until suitability for use is from 20 days. Outside temperature for the period of work - not lower than +12 degrees.
Note: in the blind areas already described and in all other blind areas that require clay preparation, the clay should be thicker. It works here more as a heat insulator, and fatty clay has less moisture absorption.
Once and for all!
What advantages and disadvantages does a monolithic concrete blind area have, are stated above. In addition, it requires careful implementation. It must be said that a blind area made of ready-made reinforced concrete slabs does not fully possess the qualities of a monolithic one; it is the same slab blind area, only more expensive and heavier. It is used more in industrial construction when there is a stock of reinforced concrete products or a source of their supply.
A summary diagram of a monolithic concrete blind area is shown in Fig. below. It only requires some explanation. Firstly, it is installed under the fill after laying the waterproofing. Its outer bend upwards, as in a multi-layer pillow, is not needed here. However, it is highly advisable to place geotextiles on the insulation before installing compensators (see below) and laying reinforcement around the perimeter of the formwork so that the sand does not spread later. You don’t have to bring the textile tape all the way to the wall, but place it on the formwork up to its edge, and at least press it there with push pins so that the mesh doesn’t slide down during further work.

Second, after filling the cushion, but before laying the reinforcement, the formwork must be divided into sections using thermal deformation compensators; Without them, a solid concrete strip will soon crack. The maximum section length is 3 m, but expansion joints must, in addition, be installed between all pairs of adjacent and external corners of the building, see fig. That is, each section of the blind area should be a convex geometric figure in plan, without corners protruding into its contour.

Compensators are made of wooden planks 15-30 mm thick. Since they will not remain in the blind area forever, the workpieces must be thoroughly soaked, twice, with hot bitumen. It’s better not to soak it, but to scald it: boil it in bitumen, brought almost to a boil, for 10-20 minutes, turning it all the time. Compensators are installed immediately with the required slope - along them, like beacons, using a long rule or, if there is some construction experience, with a half-polish, the filling surface will be formed.
Note: If you have the opportunity to get hold of to treat wood with creosote, don’t! Creosote is a strong poison and carcinogen; its use is steadily declining in industry, where special installations can be used to protect personnel.
Third is the pouring solution. The final grade of reinforced concrete must be at least M200, i.e. cement is needed from M400. But this is not enough, you still need to accurately follow the composition recipe. You can’t get by with volumetric parts “by the bucket”, or even by eye, the tape through some time will pass crack, and repairing a monolithic blind area is more difficult than laying a new one. Components should only be measured by weight! The pouring of a monolithic concrete blind area is carried out with a solution of the following composition, calculated per cubic meter of finished material:
- Cement M400-M600 – 280 kg.
- Crushed stone – 1400 kg.
- Construction sand, fraction 0.2-0.35 mm – 840 kg.
- Technically pure water – 190 l.
The solution, as we see, turns out to be very dry, even drier than for floor screed. This is necessary because fresh pouring should maintain the specified slope until it hardens. Filling is done section by section, in fairly large portions of the solution, so you shouldn’t rely on a handy tub and a hammer drill with a mixer; you need a concrete mixer. Mixing is done in the following order:
- Weigh out the portions of components required for the next section.
- Dry cement is thoroughly mixed with at least 20-25 revolutions of the mixer hopper; this is necessary to break up its clots and lumps.
- Sand is introduced in 3-5 doses, mixing each dose with 5-6 revolutions of the hopper.
- Crushed stone is introduced in the same way.
- Add water in a gentle stream over 3-5 turns of the hopper.
- Add another 10-15 revolutions of the hopper.
The poured section is compacted with a vibrating plank, trying not to touch the reinforcement with the working part, in order to avoid the formation of cavities with cement laitance, which greatly reduce the strength and durability of the blind area. Then the slope is derived using compensators, like beacons. After the solution has set, it is advisable to iron it, as for a cement-filled blind area, and just like it, the monolithic one is covered with a dark film and periodically sprinkled with water. It is forbidden to cover with a damp cloth, such as, for example, a foundation! The solution on top will get wet, weaken and the entire blind area will crumble!
Do or pay?
Now you know enough to decide what kind of blind area you need. Further material will help you understand the details, and to decide whether to take on the work yourself or order it from builders, we inform you: the price of work alone on constructing a blind area in Central Russia ranges from 2000-2500 rubles/sq.m. m for soft crushed stone up to 3300-4200 rub./sq. m for concrete monolithic. We emphasize: this is only work, the purchase of materials with delivery is the owner’s, so there is no need to count on wholesale discounts.
This is due to the fact that a normal customer, a normal designer and normal builders make the blind area at the same time as the entire structure. A finished house without a blind area is unfinished, but how much do builders like to finish unfinished projects and whether such work is profitable for them, you can ask any of them. Perhaps expand your knowledge of Russian, in parts not reflected in general-purpose dictionaries.
How can you save money?
But how to reduce the cost of a homemade blind area? To determine the scope of work, you need to know its width; the length will be given by the perimeter of the building, and the depth will be given by the selected scheme. According to SNiP, the blind area must extend at least 20 cm beyond the roof overhang, including gutters, but not narrower than 70 cm.
That is, we climb onto the roof with a plumb line and beat its outline along the ground. Then we measure along the entire length; if somewhere up to 0.7 m is missing, add as much as needed. Then we measure the resulting perimeter of the blind area; We now have a complete set of data to calculate the volume of materials and labor purchased.
Note: To avoid acidification of the soil, a blind area width of more than 1.5 m at a length of more than 2 m is undesirable. If this happens somewhere, we make the actual blind area 20 cm from the edge of the roof, and the rest will need to be paved with paving slabs on a simple sand cushion, like a path. You can make a playground in this place for children or for relaxation, with a barbecue, or somehow solve the issue based on landscape design methods.
Insulation and drainage
The next circumstance that can significantly increase the cost and complicate the blind area and still turn to professionals is its insulation. However, it will only be of any use if the blind area is monolithic, expensive and complex. Taking into account the fact that insulation most often has to be combined with drainage, the cost of work here can be a small fraction of that of materials. But is insulation necessary at all? And when, if so? Insulation of the blind area is necessary in the following cases:
- The house has a heated basement or ground floor.
- The house was built on heaving soil: clay or loam with high moisture absorption.
- The winter is unstable, with prolonged thaws, and the house stands on dusty soil with high moisture permeability; these are sandy, loess and alluvial soils.
- The freezing depth can reach that calculated according to SNiP (see below) more often than once every 3 years or once for any period of time for more than 2 months.
What and how to insulate?
From heat-insulating materials Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) and polyurethane foam are suitable for insulating the blind area. The latter, at first glance, is tempting with its cheapness, but it only seems so. Below we will deal with foam, but for now we will deal with EPS.
If the need for insulation is caused only by point 1, and the winter in a given area is consistently not very severe and the soil under the building is stable, the blind area should be insulated according to the diagram on the left in Fig. The principle is clear from there: the insulated blind area pushes the zero isotherm away from the house, which ensures its durability, as described above, but already in difficult conditions operation.

Designations on the diagrams:
- reinforced concrete monolith;
- Eps boards;
- waterproofing;
- sand cushion;
- stone border;
- geotextile drainage pipe clip filled with crushed stone;
- drainage pipe.
The simplified (left) diagram differs from the traditional ones, which we will talk about in more detail. First, how much EPS should I put under the blind area? This material is not very cheap, and every extra centimeter of its thickness means in this case an overspending of about 10,000 rubles. and higher.
Here it is appropriate to use the experience of traveling construction teams, that is, coven workers. They, by the way, are not at all such grabbers and scammers as they signed with the Soviet “Crocodile”. If the wolf is fed by his legs, then the coven, like a banker, is his reputation. Which consists not only of the speed and quality of work, but also of the savings on materials that are visible to the owner, because coven workers do not carry them with them.
So, the shabashniks have long ago developed an empirical formula to calculate the minimum permissible thickness of EPS under a blind area, namely: take the estimated freezing depth under the house in centimeters, subtract from it the width of the blind area, also in centimeters, and multiply the resulting value by 0.75, this and there will be the minimum required thickness of EPS in millimeters. Let’s say freezing is 1.8 m or 180 cm; The width of the blind area is 1 m, then you need a layer of EPS from 60 mm. More won’t hurt, as long as the customer forks up.

The freezing depth can be accurately calculated according to SNiP 2.02.01-83 “Foundations of buildings and structures”, with annexes and design manuals, and according to SNiP 23-01-99 “Building climatology”. In recent years, houses are often built on heaving soils, because... plots for development on them are cheap and there are a lot of them left from Soviet times, when they tried not to build “on the pukka”. In this case, the map in Fig. will help you decide on insulation, and for certain specific points of the Russian Federation - table. lower, because Calculation according to SNiP, although simple, is painstaking and requires taking into account many factors.
| City | M | √M | Soil freezing depth according to SNiP, m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| loams and clays | fine sand, sandy loam | coarse sand, gravelly |
|||
| Arkhangelsk | 46,1 | 6,79 | 1,56 | 1,90 | 2,04 |
| Vologda | 38,5 | 6,20 | 1,43 | 1,74 | 1,86 |
| Ekaterinburg | 46,3 | 6,80 | 1,57 | 1,91 | 2,04 |
| Kazan | 38,9 | 6,24 | 1,43 | 1,75 | 1,87 |
| Kursk | 21,3 | 4,62 | 1,06 | 1,29 | 1,38 |
| Moscow | 22,9 | 4,79 | 1,10 | 1,34 | 1,44 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 39,6 | 6,29 | 1,45 | 1,76 | 1,89 |
| Novosibirsk | 63,3 | 7,96 | 1,83 | 2,23 | 2,39 |
| Eagle | 23,0 | 4,80 | 1,10 | 1,34 | 1,44 |
| Permian | 47,6 | 6,90 | 1,59 | 1,93 | 2,07 |
| Pskov | 17,9 | 4,23 | 0,97 | 1,18 | 1,27 |
| Rostov-on-Don | 8,2 | 2,86 | 0,66 | 0,80 | 0,86 |
| Ryazan | 34,9 | 5,91 | 1,36 | 1,65 | 1,77 |
| Samara | 44,9 | 6,70 | 1,54 | 1,88 | 2,01 |
| Saint Petersburg | 18,3 | 4,28 | 0,98 | 1,20 | 1,28 |
| Saratov | 26,6 | 5,16 | 1,19 | 1,44 | 1,55 |
| Surgut | 93,3 | 9,66 | 2,22 | 2,70 | 2,90 |
| Tyumen | 56,5 | 7,52 | 1,73 | 2,10 | 2,25 |
| Chelyabinsk | 56,6 | 7,52 | 1,73 | 2,11 | 2,26 |
| Yaroslavl | 38,5 | 6,20 | 1,43 | 1,74 | 1,86 |
Note: within the same region, the depth of freezing can vary significantly depending not only on the soil, but also on the presence of communications in it, etc. If desired, achieve maximum savings must be calculated exactly according to SNiP and geological data directly under the house.
On the left diagram of Fig. at the beginning of the section, another crazy trick is visible: the vertical EPPS base slab (its thickness is calculated in the usual way based on the heat loss of the building) is not brought down to the freezing depth, but breaks off at the lower edge of the insulation of the blind area. The fact is that an insulated blind area reduces heat loss through the bare root of the foundation, and you won’t have to groan over bills for fuel or electricity for heating. The existing methods for calculating heat loss do not take this circumstance into account. But a weak additional heat flow from the side, combined with an upward geothermal flow (our planet has a positive heat balance, otherwise life on it would be impossible) pushes the zero isotherm even further. This is a case where harm turns to good.
When is drainage needed?
If, under the operating conditions of the building, at least one of paragraphs is present. 2-4, the blind area already needs to be drained from above. How - shown in right diagram rice. with diagrams. Drainage pipe diameter 110-200 mm; slope - within 0.03-0.1; You can drain the drain into a storm drain.
Note: If you come across a description somewhere of how to replace a special drainage pipe with a homemade one made from a sewer pipe, try to find the author and let him show where one will last at least a year without falling into complete disrepair.
How to lay EPS?

The actual insulation of the EPS blind area is not difficult: the slabs are simply placed on a sand cushion before laying the reinforcement, see fig. There is only one nuance here that can increase the efficiency of insulation: it is made of two layers of half-thickness slabs, and approximately half of the lower slabs are cut in half lengthwise and the halves are laid along the edges of the trench. This will result in a displacement of the seams along and across, which will negate thermal bridges.
What about foam?
Now let's see why it is undesirable to insulate yourself with cheap and technologically advanced foam. But because it is generally impenetrable, neither to moisture nor to gas. Therefore, when insulating with foam, in any case, a drainage depth of approximately 1 m is required, see fig. below.
Firstly, you can’t get by with open gutters here; without a filter grid on them, the drainage will quickly become clogged. Special gutters (on the right in the figure) are roads. Secondly, you can’t bring a deep drain into a storm drain; you need to build a prefabricated well with pumping. As a result, a seemingly cheap blind area becomes much more expensive.

When things fall apart
The worst case is when the house is located in a drainless lowland, in a place with high groundwater levels or prone to flooding. What is needed here is full-fledged lower drainage of the entire building, and this is such a topic that the blind area, as they say, rests. Just look at the figure, and this is only a summary diagram of the drainage of a house, without a collector network, a well and pumping. As for the blind area, in this case it is not recommended to insulate it at all: general drainage will not allow the soil to swell.

When to finish the base?

Usually it is recommended to do the blind area as a last resort, after finishing the base. But these tips go back to the times of Khrushchev-Brezhnev mass construction, when plinths were, at best, plastered. And now, for example, how to make a waterproof thermal joint between the blind area and the base, trimmed with relief stone or base siding?
Taking into account the use of modern finishing materials, the base of the building should be finished after installing the blind area. It won't get worse, it will only get better. Look at fig. In the place marked with a red dotted circle, above the thermal seam, the finishing of the base forms a small cornice - a teardrop. Now only a tropical hurricane can drive moisture into the seam.
What slope is needed?
It remains to deal with the slope of the blind area. For some reason in RuNet they recommend it at 10-15 degrees and even refer to SNiPs. Anyone except builders can know where these SNiPs exist. And it is clear that the authors of these tips themselves did not walk on such blind areas in slush or ice. And in those SNiPs according to which they actually build, it is recommended to maintain the slope of the blind area within 0.03-0.1. What will happen (remember about sines-arcsines?) 1.72-5.74 degrees.
About the curb
A proper blind area does not need a border. But it can be useful if there are cultivated plants near the house - root aggressors: raspberries, blackberries, poplars, plane trees, etc. of the same kind. Then the cushion under the lock of the curb stone is made approximately a spade bayonet deeper than the standard one and is made of sand in half with broken glass. Continuing the analogy with “soft power”, agents of influence now immediately stumble upon a well-trained and organized counterparty, tough, firm and prickly.
Why do you need a blind area around the house? Can you make it yourself? The blind area, first of all, serves as a kind of protection along with a decorative function. It is installed after finishing laying the walls, when the time comes exterior finishing. It protects the foundation from precipitation or its consequences. The blind area looks like a wide strip, hermetically adjacent to the outer part of the foundation, encircling the house on all sides. It is this adjacent area that is exposed to the greatest amount of precipitation that flows from the roof or walls of the building, so it must be reliable, waterproof, and strong.
In addition to its direct purpose, the blind area “works” as insulation basements buildings.
As for the width of this protective strip, the rule “the more, the better” applies here. According to SNiP, the minimum width of the blind area should be at least 80 cm, while the maximum can be any - at the discretion of the owner of the house.

There are certain requirements when arranging this architectural element:
- The width of the strip should not be equal to the level of the roof overhang, and it cannot be narrower than its edge.
- The blind area around the house must be continuous.
- Protection of the building foundation depends on the width of the strip.
- Installation is carried out with a slope from the house of at least 1.5°.
It should be wide enough so that you can easily walk on it without touching the walls. The most optimal width is 1 meter.

Construction of a blind area around the house
A blind area of any type consists of two layers - underlying and waterproof. The bottom layer is usually gravel, crushed stone or sand, and the top layer can be made of concrete, natural stone, paving slabs, or asphalt.
The optimal slope angle from the house is 3-5°; if the building stands on normal soil, then the width of the blind area should be approximately 20-30 cm larger than the cornice. If your home is built on subsiding or marshy soil, then the width should be at least 90-110 cm.
It is worth mentioning that some types of foundations (for example, screw and pile) do not need a blind area at all. They require the installation of a protective coating only in areas where water drains from the roof.
If the house is located on heaving soil, then it is better to make a blind area with insulation - this is necessary so that the protection does not allow moisture to pass through. In winter, water freezes and expands the soil, so polystyrene foam placed in the blind area can prevent this factor. Extruded polystyrene foam not only does not allow water to pass through, but is also characterized by high thermal insulation qualities.
Expanded polystyrene is placed between the layers of the blind area (crushed stone or gravel bed), it is best to pour concrete on top or lay tiles or cobblestones. This method of insulation is very effective and shows good results.

Let's consider the types of blind areas around the house:
- The simplest, but almost never used material for constructing a protective strip is clay. It is an excellent hydraulic lock for the foundation of a house. Nowadays, the use of clay is no longer relevant, since new modern materials confidently occupy a leading position in the construction market.
- A concrete protective strip is the most common option for arranging foundation protection. It is quickly installed, has a low cost for the price of the building materials used, has a long service life, and is resistant to natural factors.
- The tile blind area around the house is placed on a layer of sand. Tiles are convenient because they can be matched to the appearance of the building or decorative features summer cottage. This type of protective strip around the house is durable and easy to install.
- Natural stone laid around the house looks very beautiful and has a long service life, but requires patience and care when installing.
- The asphalt coating of the protective strip is used infrequently, due to the lack of decorativeness and a specific odor when heated sun rays and high cost.
- A waterproof protective strip is made only if there is a well-installed drainage system. In this case, much attention is paid to the installation of drains from the roof so that moisture is removed at a considerable distance from the foundation of the building. Such protection around the house is more decorative than practical.
- One of the most expensive types of blind area is made of granite. Respectable appearance, quality, durability are the main criteria for this method of protection.
It will be ideal if outside The entire perimeter of the protective strip around the house will be equipped with a drainage system (it does not have to be very deep). This technique will maximally protect the foundation from contact with moisture.
How to make a blind area with your own hands around the house?
As mentioned above, the blind area consists of two structural layers– underlying and covering. The underlying layer provides a smooth, dense base for laying subsequent materials. The role of “bedding” is sand, clay, and fine crushed stone. The thickness of the bedding layer depends on what material the protective strip will be covered with.
The coating fulfills its main purpose - protection from water, and it does not matter what material it is made of.
As an example, consider phased construction concrete blind areas:
- Initially, the future protective strip is marked; for its arrangement, we will take a width of 1 meter as a basis.
- Along the entire perimeter of the house (in accordance with the markings), we remove a layer of soil (20-30 cm) and compact the base.

- If there are plants under the layer of removed soil, their roots can be treated with herbicides so that they do not subsequently begin to make their way through the coating.
- We make removable formwork from the boards.
- We lay a thin layer of clay on the compacted soil, and on top of it a sandy layer (about 10 cm). Clay and sand should be thoroughly compacted after installation. In the immediate vicinity of the foundation, sand is compacted especially carefully.
- We spill the sand layer with water, but not very much, since there is clay below.
- We lay the crushed stone in a thin layer, approximately 6-8 cm.

- In order for the future protective strip around the house to be strong and withstand compression and tension loads, it must be reinforced. A reinforcement mesh with a pitch of 10 cm is suitable for this purpose.

- In the place where the blind area is adjacent to the base, you need to make an expansion joint, sometimes called a temperature or deformation joint. This seam provides a kind of protection during soil subsidence. It has a width of 1-2 cm. Thus, this gap between the base and the blind area is filled with a sand-gravel mixture or roofing felt; it can also be filled with resin or polyethylene foam (rope), sealant. Installation required expansion joints in all corners of the house.
- How to fill a blind area at home? The construction of expansion joints is simply necessary when arranging the correct protective strip around the house. When pouring concrete, thin wooden boards placed edgewise must be installed every 2 or 3 meters. For these purposes, ordinary wooden slats are optimally suited; they must be laid so that the upper surface coincides with the level of the surface of the concrete mass and always taking into account the slope! Wooden elements can be pre-treated protective equipment from rotting.

- What kind of concrete is needed for the blind area around the house? The concrete used to create it should not be inferior to its road counterpart in terms of frost-resistant characteristics. Brand M250 or M300 is perfect; it is mixed with sand, fine gravel, and water until a homogeneous mass is obtained. This mass is laid on top of the reinforcing mesh and wooden ribs, compacted (by vibration or bayonet) and leveled using a rule.

- The concrete blind area around the house, made with your own hands, will become as strong as possible if you use the ironing method immediately after pouring. This construction technique has two methods - dry and wet. With the dry method, cement is sprinkled onto a fresh, leveled layer of concrete. It is sifted on a fine sieve. By tapping on this sieve, it is evenly distributed in a thin layer (2-3 mm) over the entire surface of the protective layer. After these manipulations, this layer is carefully compacted using a plaster spatula. Dry cement draws moisture from wet concrete and, when hardened, forms additional reinforcing armor. With the wet ironing method, sifted cement is mixed with water to a dough-like consistency and applied to the dried concrete layer using a plaster spatula. The thickness of such protection is 2-3 mm. Sometimes ceresite or liquid glass is added to such a solution, but in any case, the strength of the protective layer depends on the quality of compaction and smoothing.
- At the final stage, the concrete is covered with a wet cloth and periodically moistened. This protects the concrete layer from drying out until it finally hardens. After 7-10 days, your concrete blind area will be ready.
You can take an easier route - save time. This method is now very popular, as it has good protective qualities and gives house strip attractive look.
To do this, after removing the soil layer, sand is poured into the bottom of the trench and liquid glass mixed with a hardener is poured on top. After hardening, an attractive monolithic surface is obtained, which has high moisture-resistant characteristics.
How to repair a crack in the blind area of a house?
Cracks or damage to concrete surface may also appear due to certain circumstances. Shallow cracks can be filled with a liquid cement solution; larger cracks are pre-cut out along the entire length of the damage and cleaned of debris and dust. After cleaning, the crack is filled with a mixture of bitumen, asbestos and sand.
Large damage can also be filled with fresh concrete after priming it. Next, the “patch” is cared for in the same way as a regular screed - the surface is moistened until the concrete hardens completely.
If the damage is serious, then additional reinforcement of the cracks is carried out, followed by filling them with a sand-cement mixture with the addition of crushed stone. After complete hardening, the patches are treated with a primer.
Soft blind area around the house

The soft blind area does not have a hard top covering; instead, crushed stone of various colors is filled in, or soil with grass is generally used. The soft blind area is not afraid of soil deformation due to freezing and subsequent thawing. When laying such a protective strip, it is not necessary to observe the slope angle. If based soft covering If a layer of expanded polystyrene is provided, it will additionally help reduce the depth of soil freezing in the foundation area.
The blind area around the house made of crushed stone is done like this:
- A layer of soil is removed, compacted, then a layer of clay (10 cm) is laid over the entire area of the resulting trench. To avoid subsequent swelling, the clay must be absolutely clean, that is, free of sand.
- The clay is also compacted and placed on top of it (with a reserve). waterproofing film. If circumstances are such that the blind area moves away from the foundation, then the supply of film will be able to compensate for the resulting shortage of material. The film is fixed by overlapping directly onto the foundation.
- Sand is poured over the waterproofing.
- The next stage is the laying of geotextiles over the entire area of the future blind area.
- Crushed stone is poured onto geotextiles. The embankment layer can be from 10 to 15 cm.
- Geotextiles are re-laid, onto which decorative crushed stone is poured.
Thus, any blind area around the house, made with your own hands, will help to significantly increase the service life of your home and add additional aesthetics and attractiveness.
A blind area is a covering that surrounds a building. Its purpose is to protect the foundation, basement or ground floor from moisture seepage.
The blind area can be made from asphalt, concrete mortar, paving stones, ceramic or paving slabs. This strip should have a slight slope away from the house. In most cases, the blind area is a convenient walking path.
If it is not built, then after a while the water will begin to flood the basement. Or in winter, frozen moisture will destroy the foundation of the building.
Features of moisture-proof coating
The easiest option would be a concrete blind area 0.6-1 m wide. In order for it to fully fulfill its purpose, you should adhere to the following rules:
- The covering should not have a width equal to or less than the roof overhang. Minimum size stripes are the width of the cornice plus 20 centimeters.
- The coating must be laid continuously around the entire perimeter of the building. Only in this case will the foundation, basement, and basement of the house be reliably protected from water seepage.
- The wider the coating, the better it will protect the perimeter of the house from moisture.
- The blind area should be made with a slope. It is needed for better water drainage. The minimum slope from the building towards the ground should be 1.5º. It can be made steeper, which depends on the lining of the blind area. The tilt is done at the stage of laying the underlying cushion or installing the finishing.
The duration of operation of the foundation of the house, its base or basement depends on the correctness of the construction of the blind area. If it is done correctly, then you will not have to repair these building elements for a long time.
The blind area consists of two main layers:
- Underlay pillow. Its purpose is to form a smooth and dense base for cladding. For the pillow you can use gravel, crushed stone, clay, sand. Its thickness should be about 15-20 cm. (Read how to choose the right crushed stone)
- Facing coating. It must be waterproof. The covering is actually a blind area that protects the building from water. It can be made from asphalt, concrete, paving and ceramic tiles, paving stones.
Required tools and materials
Before work you need to prepare the following:
- quartz sand;
- crushed stone or gravel;
- Portland cement grade M-400;
- polyurethane sealant for expansion joints;
- boards for formwork (their width should be equal to the total thickness of the protective strip);
- trowel and wide spatula;
- rule for leveling concrete;
- trough for preparing the solution;
- bubble level;
- shovel and bayonet shovel for earthen and concrete work.
How to independently arrange a blind area around the house: step-by-step instructions
So, how to make a concrete blind area. Initially, it is necessary to mark it. For this purpose, it is necessary to postpone external walls at home 1 meter, drive in stakes and pull a cord along them.

Next, follow the markings and remove the soil. Here you need to take into account what the cover of the protective strip will be. For a blind area made of concrete mortar, a trench 0.2-0.25 meters deep is required. When you dig it, compact the bottom of the ditch using a tamper.
Construction of formwork
The formwork prevents the concrete mixture from spreading and forms its configuration. It’s quite simple to assemble, you don’t need any special skills:
- WITH outside twine, with a step of 1.5-2 m between them, drive wooden pegs into the ground exactly vertically.
- Place boards on edge along the entire trench. Fix them to the stakes with self-tapping screws. (Read this article on how to choose the right screws)
- Reinforce the intersection points of the boards at the corners with stakes.
- Secure solid boards to each other. Do this from the outside using screws and pieces of planks. The length of the pieces should be about 40 centimeters, with an overlap of 20 centimeters on both sides.
- Align the upper edges of the box according to the building level to the thickness of the future blind area.
- Fix the corner sections of the formwork securely steel corners, screwing them from the outside with screws.
Typically, the length of inch boards (their thickness is 25 millimeters) is 6 meters. Based on this, calculate them required quantity it won't be difficult for you. Measure the length of the perimeter of the protective strip according to the markings made. Divide the resulting number by 6. This will be the number of boards needed for the formwork. Add another board to the number. From it you will cut pieces to connect the planks to each other.
Laying the cushion and reinforcing the blind area
Lay quartz sand in a layer of 10 centimeters on the compacted bottom of the trench. This part of the underlying layer will need to be thoroughly compacted. Before doing this, moisten the sand with water. There is no need to pour it too much, otherwise you will wash away the soil under the sand. Compact the cushion especially carefully near the foundation.
To increase the strength of the blind area, tie a reinforcing mesh at the bottom of the trench. The size of its cells should be 10-15 centimeters. Concrete has good resistance to compressive loads. Metal frame will give it the ability to withstand tensile stress.
What to make an expansion joint in the blind area from
Where the blind area meets the foundation, you will need to make an expansion joint.
It is also called temperature compensation. This element of the protective strip will protect the foundation and blind area from deformation and possible destruction during shrinkage or lifting of concrete and soil during temperature changes. In this case, the coating will sag or rise along the prepared joint without harming the structures.

The thickness of the deformation gap should be 10-15 millimeters. It can be:
- hammer with sand mixed with fine crushed stone;
- pour molten bitumen or mastic;
- fill with rolled roofing felt;
Sometimes a polyethylene foam cord is used to fill the expansion gap. Its cross-section should be 20% larger than the thickness of the gap. This way the cord will sit tightly in the seam. The upper part of the harness should be located at a depth equal to half the height of the gap. It is convenient to lay the cord in the expansion gap with a piece of plywood.
In addition to the wall expansion joint, similar gaps will need to be made along the entire length of the blind area (across it). They will protect concrete from tearing in winter.
To create expansion joints, you can use wooden slats. They should be placed on edge every 2 meters. The planks must be laid so that their top edge is flush with the plane concrete covering.
To protect the wood from rotting, it must be coated with a water-repellent compound. This could be industrial oil, bitumen, or an antiseptic composition.
Concrete laying
Now you can lay the concrete. It is mixed from one part of cement, two parts of sand and two parts of crushed stone. Water is added to the dry composition in such an amount that the resulting solution is viscous and not too liquid.

After laying it, the concrete will need to be compacted using bayonet. Then it is leveled by the rule. The expansion joint strips will serve as guiding beacons.
To strengthen the concrete coating, it can be immediately ironed while it is wet. To do this, the solution is sprinkled with dry cement, which is then leveled using a rule. Thin cement layer will give concrete special strength and water resistance.
After filling the blind area, cover it with film and periodically spray it with water. This way the concrete will dry and gain strength gradually. In rainy autumn weather this may not be necessary. The concrete will finally harden and gain strength 28 days after it is poured.
- When pouring concrete, do not forget that the blind area should have a slope from the building towards the ground. For a concrete surface, a slope of 3º is sufficient. To create it, you should set the expansion joint slats at the appropriate angle.
- To increase the reliability of the blind area, it can be waterproofed. To do this, you can spread thick plastic film or roofing felt on the underlying pillow. Their panels must be laid on top of each other with an overlap.
- In hot weather, hardening concrete may crack due to the rapid evaporation of moisture. Therefore, it must be covered with burlap or plastic wrap. It should lie on the coating until the coating dries.
Insulated blind area
If the site is located in an area with soil prone to frost heaving, then the blind area will need to be thermally insulated. In this case, the corresponding material must be moisture-resistant, dense and durable. EPS (extruded polystyrene foam) fits these definitions. For the blind area, you need to use material 5-10 centimeters thick, based on the climate of your region.
Extruded polystyrene foam boards are not resistant to point loads. Based on this, the material should be laid not under the underlying cushion, but under the concrete solution.
You can make a blind area around the perimeter of the house yourself. There is nothing particularly difficult about this. The main thing here is to follow the rules, do everything carefully and without mistakes. In this case, the foundation, basement or basement of your house will be reliably protected from moisture.
Check out the video that concludes the article. In it you will find additional information on how to make a blind area around the house:
To prevent erosion of the soil around the house by rain and melt water, as well as to remove precipitation from the foundation, a blind area is made around the house. These works must be carried out before the final finishing of the base. More specifically, decide for yourself. But it is undesirable to delay: leaving a house or bathhouse over the winter without a blind area, you may end up with several cracks in the foundation in the spring.
The blind area around the house is a simple structure. However, it greatly extends the life of buildings. During autumn bad weather, water seeps into the foundation. In cold weather, it freezes, increasing in volume, which creates excess pressure. As a result of this load, cracks appear in the foundation, into which water also penetrates. Freezing makes them even wider. Without a blind area for some time, the foundation requires serious and expensive repairs. Sometimes the damage is so severe that it cannot be repaired.
But these are not all the functions that protective coating around the house can perform. In some cases it is used as a path. Sometimes, by laying insulation and a layer of waterproofing under the blind area, you can improve performance characteristics buildings and correct some shortcomings made during construction in heat and. In addition, from a decorative point of view, it serves as a logical conclusion to the design of the house.
What is the blind area made of?
Most cheap option- from concrete mortar. But it takes more time to create such a design. Especially on heaving soils: a special cushion and reinforcement are required. The entire time until the solution gains strength, you cannot walk on it, and this is at least four to five days.

Other types of protective belt covering around the house are paving slabs, paving stones, bricks, natural stone, porcelain tiles, etc. There are a lot of options today. The main thing is that they have the following properties:
- did not let water through;
- did not crack when freezing/thawing;
- had high abrasion resistance;
- had aesthetic appeal;
- had a long service life.
There is another material for the blind area, but it is rarely used in private housing construction - asphalt is laid around the house. As for attractiveness (as in the case of concrete), the issue is debatable, but the other characteristics are simply excellent.
But a protective coating is not everything. Other materials will be needed. Which ones specifically depend on the option you choose to implement. We can say for sure that sand and crushed stone will be required. You may need waterproofing and slab insulation.
Dimensions
Because main task remove the thawed blind areas and rainwater, its width should be at least 20 cm greater than the roof overhang. But experts do not recommend doing it less than 60 cm - moisture can seep into the foundation.
The width of the protective belt also depends on the type of soil. If these are normal soils that drain water well, then 60 cm is enough. If the house is on loam, other heaving or unstable soils, the width should be up to 1 meter.
 Basic parameters of the blind area for normal drainage of water from the foundation
Basic parameters of the blind area for normal drainage of water from the foundation But the blind area must also go deeper. Its depth depends on the type of soil, the functions it will perform and the thickness of the top finishing layer.
If the house stands on normal, non-heaving soils (not clay or clay-containing soils), and people will not walk on the surface, it is enough to make a backfill of sand 10 cm thick. You can lay tiles, stones, etc. on top. This means that the depth of the trench will be about 10-20 cm - it depends on the thickness finishing material. Only for a coating that is made up of fragments, a border is required. So you dig in edge stones around the perimeter, reinforce them, and only then pour sand into the bottom of the trench.
If the formwork will be used as footpath, a more serious, weight-distributing substrate is needed. At the bottom of the ditch, crushed stone of a medium-sized fraction of about 15-20 cm is first laid, and then sand is placed on it, and only then the finishing coating.

What else is mandatory is compliance with the slopes: the decline comes from the house. So the moisture will flow into drainage system or the soil located around. The amount of slope depends on the type of protective coating used. For concrete and asphalt, the slope is 3-5% (height difference per 1 meter is 3-5 cm). When laying stone, tiles, porcelain stoneware, the slope is 5-10%.
Work order
After the dimensions have been selected, the actual installation of the blind area begins. In general, this occurs in several successive stages.
Marking and removing soil
The selected width is laid around the perimeter of the building. Here it must be said that in those places where people will walk, it can be made wider.
They are usually marked by driving in pegs. By stretching a string or cord between the pegs, they outline the front of the work. Over this entire area it will be necessary to remove the turf and some of the soil. At the same time, the roots of the plants are removed. Frequently processed chemicals, which prevent plant germination. If this is not done, as they germinate, they will destroy the coating.
Construction of expansion joint

It is very important to remember when doing this that the blind area and the foundation should not be connected. To do this, it is necessary to leave an expansion joint around the perimeter of the foundation, about 2 cm wide. In practice, this is either strips of foam plastic 2 cm thick, or two layers of folded roofing material attached to the foundation.
An expansion joint is necessary so that when the soil moves under the blind area, it does not put pressure on the foundation. If this is not done, instead of preventing destruction, it will create pressure, which will sooner or later lead to cracks in the walls.
Bedding and finishing coat
If you follow the “folk” technology, a layer of clay is poured onto the bottom of the trench. It will prevent moisture seepage. It is compacted, already at this stage creating a slope from the foundation. This backfill is suitable for any type of soil. It may take a long time to compact it, but it will not conduct water. If you use sand for the blind area of a house standing on clay soils, most of the water will end up just under the foundation.

Things will go faster if you use a tamping machine. If there is no such thing, take a log of medium diameter and saw off 80-90 cm. The height should be such that you do not have to bend over - you should be able to reach the top edge with your hands. On one side they fill the crossbar - the handle. This deck is used to compact it, raising and lowering it.
Then add a layer of sand. It is spilled with water and also thoroughly compacted. In normal soils and if people will not walk on the blind area, you can lay paving slabs or paving stones. When using concrete as a protective covering, it will be necessary to pour and compact a layer of crushed stone, arrange formwork and expansion joints, lay out the reinforcing belt and only then pour the solution. So making concrete path takes a lot of time.
Insulation of the blind area
If a blind area is made around a house with a basement or ground floor, it must be thermally and waterproofed at the same time. Insulation is necessary for everyone slab foundation- it will prevent the soil under the slab from freezing.
Some experts argue that in middle lane Russia and the north, insulation is necessary in any houses with seasonal accommodation. The fact is that in a heated house, the heating itself prevents the foundation from freezing. And if they insulate the blind area, it is only for the purpose of saving fuel. In a house with seasonal residence, it is necessary to take additional measures to extend the life of the building. And here's why. Any material can withstand a certain number of freezing and thawing cycles. After which it begins to collapse. In the absence of insulation, in one season the foundation will freeze and freeze as many times as the weather changes - in autumn and spring the weather is often alternately warm and cold. It is clear what this state of affairs will lead to: after some short time, destruction will begin.
For thermal insulation to the entire depth of the ditch (and better than foundation) a thermal insulation layer is attached to the base. It is also laid on the bedding under the protective coating. To insulate the blind area around the house, the following materials are used:
- expanded polystyrene;
- foamed polyurethane;
- polystyrene foam
Insulation with extruded polystyrene foam
This material is one of the best for insulating foundations. At the same time, it retains heat and does not allow moisture to pass through: its hygroscopicity is close to zero. Its downside is that it melts easily. But for insulating the foundation and formwork, this drawback is not significant.
It is advisable to spread plastic film on horizontally laid out slabs - it will protect the joints of the slabs from water leakage.

Formwork with polystyrene is done in this way:
- Compacted coarse sand in a layer of 15 cm.
- Ruberoid. In this case, it must be placed on the walls by 15 cm.
- Polystyrene boards, joints are sealed with sealant. The thickness of the layer is 10 cm. It can be either one slab, or two 5 cm each. If there are two slabs, they need to be glued with overlapping seams - this will provide more reliable protection against moisture penetration.
- Polyethylene film 200 microns.
- Layer of sand. It is carefully compacted, trying not to push through the slabs.
- Protective material.
Any film is used as a protective material. But under the concrete, an additional reinforcing mesh is placed (metal with a cell of 10*10 cm) and only then the solution is poured downhill.
Foamed polyurethane
It is sprayed from special devices. It does not rot, practically does not absorb water, the operating temperature range is from -60 o C to +150 o C. It is applied quickly - all work can take three to four hours, but the use of a special apparatus entails payment for services. They are not cheap - one of the components is toxic. So, for all its attractiveness, this method is used infrequently.

Foam insulation
This is the cheapest of the insulation materials. It has good heat-insulating properties, does not allow water to pass through, and also has good sound-proofing properties. Its only drawback is small mechanical strength. When using it, an additional reinforcing belt is required. The sequence of actions is the same as when insulating with polystyrene, only two differences:
- pour sand on top of the insulation in a thicker layer, compact it only by patting it with a shovel, and you cannot walk on the foam;
- under tiles or paving stones, a reinforcing belt is also needed, which is covered with a second layer of sand on top.
Despite the low price, polystyrene foam is not best choice: He is too afraid of stress. If people will walk on the path, it should not be used. To reduce the cost of insulation, you can use it for gluing to the foundation, and purchase polystyrene foam for the formwork itself. This will be the best option.
Waterproofing
Waterproofing is necessary for heaving soils and lack of insulation of the foundation and blind area. In this case, the less water there is under the building, the less likely it is that heaving forces will damage your building.
The sequence of layers for waterproofing is as follows:
- Waterproofing layer - regular dense polyethylene film 200-300 microns thick - clay is laid. There is no need to tighten it - there should be some freedom of movement so that it does not tear during seasonal movements of the soil. The height of the approach to the foundation is 15-20 cm. It is nailed to the foundation with a pressure strip (if it is wooden, then it must be treated with hot drying oil so that it does not rot). But this is done later, after laying a layer of sand and geotextile. So for now, fix the film on the wall, for example, with a few nails.
- 10-15 cm of sand is poured onto the film. It's being compacted. Geotextiles are laid on top. It is a godsend for blind areas - it allows moisture to pass through, redistributes the load, does not tear, does not allow different layers to mix, is not damaged by insects and rodents, and does not allow plants to germinate. And all this is some kind of woven or non-woven membrane (they come in different types). Lay the geotextile so that it overlaps the film laid below, and attach both layers with a strip to the foundation. On the other hand, it must cover the entire remaining height of the dug trench.
- Then there are two options:
- To save money, you can fill the remaining pie with crushed stone, and lay a reinforcing layer on it - metal mesh made of steel rod in increments of 10*10 cm. Concrete can be poured on top.
- If you use paving stones or tiles, the cake will be more difficult. It will be necessary to lay another layer of geotextile on the compacted crushed stone. Lay another layer of sand on it, and then lay protective and finishing tiles on top of the sand.
 Two options for constructing a blind area - from concrete and tiles, rubble stone, etc.
Two options for constructing a blind area - from concrete and tiles, rubble stone, etc. This design drains water perfectly.
Soft hidden blind area
Modern waterproofing materials allows you to avoid making a protective coating around the house. They effectively retain and drain water, while the cost of such a pie is much lower. In this case, they talk about a hidden blind area. And all because right from the foundation you can sow grass or arrange a flower garden, and all the layers that drain water are located in the thickness of the rock.
Profiled membranes are used to install a soft blind area. They have a nonlinear structure - small protrusions and depressions.

A soft blind area around the house is easy to implement with your own hands. The only thing that can cause some difficulties is the rather large volume earthworks. The width of the ditch is desirable from 1.2 m to 1.5 m. But the depth can be small - about 25-30 cm.
The procedure for installing a hidden soft blind area is as follows:
- First, the soil is removed and a slope of 3-5% from the house is immediately formed.
- They are treated with chemicals from plants.
- Roll out the profiled membrane over the entire width of the blind area, place one edge slightly onto the wall and secure it, the other is simply left free.
- A layer of geotextile is rolled out on top. It is laid in the same way - one edge is fixed to the wall. Both layers of waterproofing materials can be secured together with one clamping strip.
- Pebbles or a large fraction of screenings are poured onto the geotextile and crushed.
- The next layer is medium and fine screening, and sand on top. Each layer is compacted separately.
- poured on top fertile soil and plants are planted.
Despite the apparent unreliability, this design removes water even better than those made by traditional technologies. But, as you can see, the work is not complicated or expensive. If necessary, you can lay tiles or paving stones on a layer of sand. Then the look will be more traditional.

There is one caveat: if the soil on the site is clay (namely clay) or your house is on a slope, you will need to supplement the structure with a drainage pipe. It is laid at a distance of 1.2-1.5 m from the wall of the house, at the level where the geotextile bevel ends (you can lower it a little lower). But at the same time, the membrane and geotextile must cover it from below and from the outer side, so that the collected moisture flows through the perforation into the pipe, and then through it to the sewer or drainage system.
Features of concreting
When installing a concrete blind area around the house with your own hands, you need to take into account some of the subtleties of the technology.
Firstly, the composition of the solution must be frost-resistant. It’s clear why. You can buy ready-made mixtures, but they are not cheap. You can use additives that increase the frost resistance of concrete. In the simplest case, add more cement. Make the solution at the rate of: one part cement, three parts sand and crushed stone.

Secondly, to avoid cracks, expansion joints must be made. For this, boards with a thickness of 25 mm are usually used. They are treated against rotting with hot drying oil or. Then they place it on the edge, setting the required slope, approximately every 2-3 meters. Secure with metal pins or wooden pegs. When pouring the solution, they can be used as beacons. In the future, the planks will ensure the mobility of the formwork during seasonal soil movements.
And thirdly, to give the surface greater strength and a more aesthetic appearance, it is sprinkled with dry cement, which is rubbed down with a trowel. This is done after the filling is completed. This process is called ironing of concrete. The surface then becomes strong, smooth, with a slight shine.
Results
Setting up a blind area around the house with your own hands is not the easiest, but it’s also far from the most difficult task. There are many solutions that will improve the performance of a building and extend its service life.