The wooden floor, especially in a private house, has been and remains the most traditional. This is explained simply - naturally warm material with a beautiful textured pattern and various shades can fit into the interior, decorated in any style. But in order for such a floor to serve for a long time, it will not be enough just to nail the boards to the logs, especially if it is arranged above the ground, and not on a prepared basis.
- this is one of the main stages of its arrangement, since raw wood well absorbs moisture and swells, and then, drying, deforms. In addition, moisture for most types of wood is the beginning of debate or decay, followed by decomposition. Therefore wooden details must be well processed themselves and securely covered from the possible penetration of high humidity from the ground.There are several types of waterproofing works depend on the device wooden floor. Having become acquainted with possible technologies, you can choose the one that maximum degree suitable for each specific case.
One of the oldest and most effective means protection of wood from moisture - its impregnation with certain compounds.
To date, a lot of impregnations made on various chemical bases are on sale. They are applied to wooden parts before floors are made from them. All impregnations are designed to protect wood for a long time not only from exposure to moisture, but also from biological damage (microorganisms, insects, rodents, etc.) And, such processing is necessary not only for wooden floor elements, but also for walls or ceilings.
There are complex impregnations, as well as aimed at specific area protection:
Antiseptics, which are designed to protect against the penetration of insects and microorganisms into the wood;
Flame retardants - these impregnations will save wood coatings from fires;
Solutions aimed at preserving wood from moisture;
Compositions that combine several protective functions at the same time.
Impregnation that protects against moisture penetrates deep into the wood structure and becomes a kind of waterproofing for each individual wooden element. It is easy to apply, absorbs well and does not wash out for a long time. The drying of the composition takes place within two to three hours, then, if desired? you can apply another layer. A very important advantage of such waterproofing can be considered that the material does not lose its ability to "breathe". Such compositions impregnate not only the boards of the wooden floor, but also the logs on which they are laid.
Such solutions are especially necessary for rooms with high humidity, such as a bathroom, steam room or other bath rooms.
Floor waterproofing on the ground
No matter how dry the soil under the floor being installed, waterproofing should in any case be carried out. It can be made using different materials. But before waterproofing, it is necessary to prepare a base consisting of several layers.
- The first and very important layer is well-compacted soil, which can be compacted manually or using special compaction equipment.
- The next step is to add sand, which in itself is good. waterproofing. On dense soils, 10 cm of sandy layer is sufficient, but if the soil has heaving structures prone to freezing, and therefore to absorbing moisture, then the height of the bedding increases to 20 cm.
- Next, a ten-centimeter layer of crushed stone of a large or medium fraction is poured and also compacted. These layers are designed to prevent the penetration of moisture to higher layers, if it is planned to make a screed, and block access to floor beams and logs. In addition, they strengthen the base and make floors more reliable.
If the groundwater is deep enough, no higher than two meters from the surface, then the gravel can be replaced with expanded clay, which, in addition to waterproofing, will also serve as a heat insulator.
These three layers are essential when choosing any type of waterproofing and wood floor installation. Subsequent work is carried out depending on what result is planned to be obtained in the end - the wooden floor will be laid immediately, or the concrete coating will be laid first.
Wooden floor on poles
- Inside the basement, over the entire area over which the wooden floor will be arranged, at a distance one and a half meters, pits are dug into which a sand and gravel cushion is arranged and waterproofing is laid from polyethylene film to the entire depth with its exit to the surface of the soil by 20-30 cm.
- Further, columns are laid out of bricks, which, after the mortar has dried, are treated with waterproofing mastic.
- Sheets of roofing material are laid on the entire surface of the underground, which are hermetically fastened together with bituminous mastic. The roofing material is raised to the walls of the basement by 15-20 cm and also glued with bitumen. Corners are closed neat is better do not cut the material, but fold it into folds. The roofing material should form a kind of sealed container at the bottom of the underground.
- The columns are coated with bitumen on top and pieces of roofing material are laid out on them, preferably in several layers.
- Thick floor beams treated with a penetrating waterproofing agent are installed on the posts. They are fixed on supports with metal fasteners.
- Logs are mounted on the beams with a certain step. From below, a cranial bar is attached to each lag, which will become the basis for the subfloor.
- The rough floor is laid out from low-quality boards, but if gaps form between them, it is better to seal them with clay diluted to medium density. This material is also good waterproofing. If it is planned to lay in the cells of the subfloor thermal insulation material, for example, mineral wool, then it will be completely safe from moisture.
- Next, the draft floor is covered with plastic wrap or roofing material. The strips are necessarily overlapped, with an overlap of at least 100 - 150 mm. Joints are required sealed surfacing or special adhesive tape.
- Insulation is laid (if provided for by the construction plan.). Spread on top of the insulation vapor barrier film and fix it to the lags.
- Further, a wooden floor is laid on the logs, the boards for which must be pre-treated with complex compositions.
- Thus, the floor taught the triple line of protection against soil moisture - waterproofing the very surface of the earth, the subfloor and the hydro-vapor barrier membrane directly under the plank floor.
Waterproofing a wooden floor on a concrete base
If the wooden floor is arranged on a concrete screed, then first of all waterproofed there should be a base for it. In conditions when moisture begins to destroy the concrete from below, it will soon reach its surface and the wooden floor elements.
Installation of a concrete floor begins with the same two layers - sand and gravel, laid and compacted on the ground.
1. waterproofed tie in one layer
- Sheets of roofing material are laid on the compacted surface with an overlap on the walls of the basement by 100 - 150 mm. Sometimes, with very wet soil, it makes sense to lay roofing material in two layers, along and across the covered area.
- Sheets of waterproofing material are fastened together with bituminous mastic, heating it gas burner- this ensures perfect tightness. Corners are sealed with particular care.
- A heater is poured onto the surface of the waterproofing - expanded clay, or extruded high-density polystyrene foam is laid out.
- Over the thermal insulation layer again spreads waterproofing material- in its capacity in this case, a dense polyethylene film can be used. This will not only be an additional line of protection from moisture from below, but will also prevent the concrete solution from being absorbed into the insulation and spreading through the cracks.
- The film also rises to the walls, and sticks on it damper tape or a thin foam is laid, which will serve as a good compensator when expanding the concrete screed.
- Next comes the reinforcement metal grid with cells 50 × 50 mm in size. Install the reinforcement belt carefully, so as not to violate the integrity waterproofing film. Reinforcement will evenly distribute the mechanical load on the insulation layer and give the required rigidity to the floor.
- On this entire structure, beacons are installed at the zero level, which are fixed with concrete mortar.
- When the beacon system is ready, a finishing screed is laid and leveled. It is left until fully ripened, while, starting from the second day, it is moistened with water every day, which gives the concrete additional strength.
2. waterproofed screed poured in two stages
- A polyethylene film with a thickness of at least 200 microns is spread on the compacted layers of sand and gravel, which is placed on the walls of the basement to the height of the future screed. Between themselves, the sheets are glued together with waterproof tape, the corners are also hermetically sealed. It is very important that the waterproofing is a single space without damage.
- A rough rough screed is laid on the waterproofing, consisting of cement and gravel mix. Its thickness should be from 40 to 70 mm. This layer does not have to be leveled to the ideal, since it will be leveled from above with a finishing screed. Thus, a beacon system is not required for it - only a few reference marks are needed for approximate alignment.
- After the concrete has hardened, it is necessary to lay another layer of roofing felt waterproofing. The overlaps between its sheets are also hermetically sealed.
- This is followed by a heater - expanded clay layer, the thickness of which can be from 100 to 150 mm.
- On a leveled and maximally compacted expanded clay is laid reinforcing mesh with cells of the order of 100 × 100 mm.
- The zero level of the future finishing screed is determined. Above the reinforcing belt are exposed beacons - guides which are fixed with concrete.
- Then the screed itself is poured - this layer must be perfectly aligned. solidification will take place during three – four weeks, depending on the thickness of the layer and features component composition concrete mortar. For the strength of the coating, the hardening screed at first is sprayed daily with water.
For greater clarity - the structure of a common "pie" with thermal and waterproofing of the floor
With any approach to the screed device - in one or two layers, when it is fully prepared, the surface must be additionally treated with impregnating, strengthening and waterproofing compounds, which are applied to the floor and walls to a height of up to 20 cm. For this, penetrating, coating, plastering or paint compositions that will create a sufficiently strong and reliable film on the surface that does not allow moisture to penetrate into the premises. More information about possible methods of waterproofing is described in our website.
- To do this, the floors are marked out, and logs are installed according to the markings, securely fixing them to the concrete base.
- Then, between the lags and along the perimeter along the walls, a heater is laid (polystyrene foam or mineral wool). However, if the screed has received reliable insulation, then the space between the concrete and the wooden coating may not need additional thermal insulation - it all depends on the region and the design features of the house .
- From above, the entire resulting lattice is closed vapor barrier material(plastic wrap) which is a stapler. fixed on the lags.
- And, finally, a coating of floorboards pre-treated with water-repellent impregnation is mounted. The resulting floor can be additionally protected from water by coating it with varnish or wax.
One more note. Sometimes by wooden floor plan to pour a self-levelling compound, for example, for further installation ceramic tiles. It is clear that without reliable waterproofing here too:
Video: self-leveling floor on a wooden base
A brief introduction to floor waterproofing can lead to the misconception that it is not hard to do. However, the installation of an insulated screed or waterproofing on pure wooden floors is a rather laborious process that requires a lot of time and effort. Be that as it may, one cannot do without this element in the design of the floor. Ignoring reliable waterproofing can lead to the fact that the flooring work will be done absolutely in vain, and in a few years it will be necessary to replace not only the wooden coating, but also the concrete screed that has been soaked with moisture. Even if the concrete base retains its strength and integrity, if moisture gets between it and the walls, mold will begin to appear in the rooms, wet spots on the interior decoration, and an unpleasant smell of dampness is inevitable.
The conclusion is clear - waterproofing is always necessary step when arranging any type of floor, but for wooden floors, its value is generally difficult to overestimate.
But it is not without a number of shortcomings. If you forget to make vents in the strip foundation (or incorrectly calculate their cross section), then over time this can lead to problems. Due to insufficient ventilation of the underground wooden logs covered with fungus, mold and rot. Excess moisture in the base also leads to destruction concrete floors floor of the first floor.
To avoid this, you can replace traditional vents with a closed ventilated underground. This is detailed in the article. “Do I need air in the basement” . But there is another option - to abandon the underground and build a floor on the ground on the basis of a strip foundation, as FORUMHOUSE experts advise.

Floors on the ground: what is itsuch
This design is a monolithic concrete base (screed). Here is the device of the floor on the ground: the screed is poured inside the perimeter of the strip foundation onto well-compacted soil, with which the sinuses of the foundation and the insulation layer are covered. Underfloor heating can be installed together with a concrete base. This design accumulates heat, so it is well suited as an element of an energy-efficient home.
 The composition of the floor on the ground for a residential building.
The composition of the floor on the ground for a residential building.
There are the following options for floors on the ground:
- On the prepared base (well-compacted soil), a floor slab is poured, rigidly connected with strip foundation;
- A floor slab is poured onto the prepared base, which is not connected to the strip foundation, the so-called "floating" screed.
Let's take a closer look at the pros and cons of these options.
Michael1974:
- If you fill in a “floating” screed, then the construction of the tape and the floor is “untied”. If shrinkage occurs, then the floor screed structure on the ground will “play” regardless of the foundation, cracks will not appear in the structure, because. no stress. This is a plus. But there is also a minus - the design "lives its own life", separate from all other structures.
 Floor device on the ground.
Floor device on the ground.
With a rigid structure, the foundation / screed unit works as a single unit. The screed will not shrink, because lies on the foundation. But if the soil is not compacted well enough, after a while it may sink, and the screed will “hang” in the air. With a heavy load, if there are walls, partitions on the screed, supporting elements, this can lead to deformation of the base, cracks and loss of bearing capacity the entire structure of the floor on the ground.

How to make a floor on the ground
Both screed options have both pros and cons. The quality of the concrete floors on the bulk soil depends largely on the quality of the compaction of the bulk soil and on how correct the design will turn out.
Michael1974:
– When pouring a “floating” screed, the “foundation wall/screed” assembly must really be untied, otherwise the structure may be pinched in the tape frame. Those. the floor inside the tape frame must move relatively freely, otherwise the whole point of the floating screed is lost.
To do this, a damper is made of an elastic material between the screed and the foundation (wall), which restores its original shape after the load is removed - in this case, it is appropriate to place an isolon 8-10 mm thick. This will allow the concrete screed to “float” freely and compensate for its thermal expansion.
A common mistake is to tie all nodes as tightly as possible. As a result, increased loads occur in the structures. In the case of a floating screed, the "floor" and "foundation" elements work independently of each other.
Ground floor: device.Basic principles
An important rule: a well-prepared foundation is a guarantee long term service of the entire structure. The filling base (the best backfilling of the floor on the ground is sand) must be spilled with water and carefully compacted in layers of 10-15 cm.

Due to the backfilling of crushed stone, when the rammer passes through it, a local impact occurs, as a result, there is a deep additional compaction of the soil layers lying at the lower levels. On the correct methodology tamping sand is worth building up attention.

- In all the instructions for vibrating plates it is written that the plate rams sand to a depth of 20-30 cm, but how well this layer is compacted, I doubt that it is enough. Therefore, I believe that for reinsurance it is better to compact the sand in layers of about 10 cm. It looks like this:
- We spread the sand in a layer of 10-15 cm;
- We pass through the sand with a vibrating plate "dry";
- Spill sand with water from a hose. It is necessary to do this not with a jet of water, so as not to break the layer, but through a spray nozzle;
It is necessary to spill water so that the sand is wet, but not oversaturated with moisture. If the amount of water is too large, then the sand base is practically not rammed.
- We pass through the moistened sand with a vibrating plate 2 times with a change in the orientation of movement;
- Spill the sand with water again;
- We pass along the moistened sand with a vibrating plate 2-3 more times with a change in the direction of movement.

What kind of waterproofing to put on the floor on the ground
After thorough preparation of the base, we proceed to laying the hydro-vapor barrier, which will protect the floor structure from moisture. It is often asked whether it is necessary to make a footing before laying this layer. After all, welded or glued waterproofing, in order to avoid damage, must be placed on a flat, rigid base.
An earthen floor is one of the simplest and most obvious flooring options for a home. In the old days, the recess was filled with several layers of tightly packed clay. Today, the earth floor in the original sense is very rare in houses, baths or other outbuildings. However, the very principle of covering the ground has developed and improved, is now known as a dirt floor or floor on the ground, and is widely used in cottage construction.
An earthen floor is one of the simplest and most obvious flooring options for a house.Due to the fact that the building is located on the ground, contact between the foundation and the frame with moisture is inevitable even in areas with a dry climate. The impact of moisture is carried out in three ways: capillary contact of groundwater with elements of the floor base, accumulation of water vapor and contact with precipitation.
- In the first case, water during periodic freezing and heating mechanically destroys the structure of concrete or wood flooring. In addition, mineral impurities contained in water have corrosive characteristics.
- In the second case, water vapor causes rotting materials and the occurrence of fungi, bacteria and mold that are dangerous to health. In the third case, precipitation falls on the basement of the house, penetrates into the ground. All this reduces the service life of the building several times and gives the residents of the house a lot of practical inconvenience, not to mention excessive cash expenses. It is expedient to prevent premature destruction of the building even at the construction stage by making a competent hydroprotection.
 An earthen floor is often used in cottage construction.
An earthen floor is often used in cottage construction. Necessary conditions for high-quality waterproofing
- Reliable waterproofing of the floor on the ground cannot be considered as a separate independent operation.
- The construction of any building begins with the development of a project, taking into account the type of soil, climate and groundwater levels.
- This is followed by work on the foundation, in which there is also horizontal and vertical moisture insulation.
- If necessary, drainage outlets are created against the inflow of water from below at the base and blind areas against surface precipitation.
- Without these measures, even the most expensive and thorough waterproofing of floors on the ground will turn into a waste of resources and time.
- The durability of the building directly depends on the observance of construction technologies and the use of high-quality materials.
 The durability of a building directly depends on compliance with technology
The durability of a building directly depends on compliance with technology Soil waterproofing technology
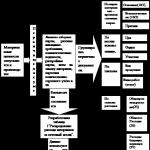
After the foundation is created and the walls with the ceiling are erected, you can proceed to the floor device. In general, the entire floor structure is a multi-layered cushion of reinforcing, insulating and warming materials, or the so-called "pie". Below is the procedure for laying the tiers of the floor device.
The lower base is the compacted native soil, top part which is removed at the stage of laying the foundation. good decision the laying of a densely packed layer of homogeneously mixed clay is considered. Clay to a small extent passes moisture, acting as a reliable barrier to groundwater. However, this step requires additional shrinkage time and is rarely used.
The soil inside the contour of the foundation walls is covered with sand to a height of 10 centimeters or more. The sand is compacted using special equipment and additionally sags with the help of irrigation. This type of work requires river sand any size with high ability pass water. Other types of sand may contain clay impurities and are not suitable for these purposes.
 A good solution is to lay a tightly packed layer of homogeneously mixed clay.
A good solution is to lay a tightly packed layer of homogeneously mixed clay. Next, crushed stone of a large fraction is poured to approximately the same height, and it is also carefully compacted. Has the highest strength and frost resistance crushed granite, so it is preferred over gravel. It should be clarified that sand and gravel together create a cushion that prevents the rise of water from below. A large stone is used for the reason that the voids between the individual grains do not allow water to build up pressure and rise up. At this stage, the building is protected against capillary wetting. At the same time, both layers, when compacted by their own weight, press on the soil below, which also contributes to waterproofing and the overall strength of the structure, as well as the stability of the foundation.
 Large rubble will not allow water to rise up
Large rubble will not allow water to rise up At the next stage, the work will differ depending on which floor is provided in the building: concrete or wood. A non-decaying geotextile is laid on top of the gravel to prevent the concrete from leaking into the gravel layer. A cement screed of low strength is poured from above. The thickness of the layer is calculated by the designers based on the expected load of the building on the base. This screed is a preparation before waterproofing and is called a subfloor. For a wooden floor, a frame with lags is built above the primary screed, a draft floor of boards or plywood is stuffed on them.
Further, the waterproofing of the floor on the ground is carried out directly, at present it practically coincides with the vapor barrier. There are several types of floor waterproofing: coating, plastering, gluing, cast and impregnating. Each of the methods has its own characteristics, which should be carefully studied, compared and choose the most optimal in terms of price and quality.
 Film floor waterproofing
Film floor waterproofing In the coating method, liquid sealants, micro-solutions, rubber compounds and polymer varnishes are used. The method is relatively easy to use, does not require special skills and sophisticated equipment. Plaster insulation refers to coating and differs in materials. It uses plaster mortars higher density with fillers, cement, polymers or gypsum.
 In the coating method, various mixtures are used
In the coating method, various mixtures are used In gluing insulation, specially designed roll, tile or sheet materials, for example, polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC film, diffusion membranes, roofing material, only. Often there are economical recommendations with the use of a film as an insulator. The film is laid with a rise on the walls and with an overlap along the edges of 10 - 15 cm, the seams between the strips are glued with adhesive tape. It should be noted that at the slightest damage and rupture of the film, the insulating role loses its power. In comparison with bitumen-based roll materials, the film with more than one layer is significantly inferior in strength and durability. It is much more efficient to fuse a roll on a screed bituminous material with obligatory access to walls with a height of several centimeters up to the upper level of the foundation.
 The film is applied to the floor and rises slightly to the walls
The film is applied to the floor and rises slightly to the walls  Roll materials are perfect for waterproofing
Roll materials are perfect for waterproofing Cast waterproofing is the filling of the surface with a continuous layer of special hot mastic. This process is more time consuming than the others, as it requires special training and equipment. The surface to be coated must be dust-free, leveled, absolutely dry and pre-primed with bituminous mortar. For greater efficiency, the process is repeated two or more times.
 For greater efficiency, the process should be repeated several times.
For greater efficiency, the process should be repeated several times. Impregnation waterproofing of the floor - application to the base of a substance that can be absorbed by concrete and stone surfaces. The materials are mixtures containing bitumen, polymers, liquid glass, synthetic resins. Distinctive feature this method It can be called that it is used not only at the construction stage, but also when it is necessary to repair the house.
 This method can be used not only at the construction stage, but also when repairing a house.
This method can be used not only at the construction stage, but also when repairing a house. With regard to a wooden floor, it should be noted that the underground must be ventilated by natural or forced ventilation. This must be taken care of at the stage of laying the foundation. All wooden elements structures are covered with liquid several times protective compounds. The draft floor can be covered with a film, cast or impregnating method.
At the end of the waterproofing work, the surface is laid with a heater. The most common extruded polystyrene is a durable option with a low water saturation coefficient. The connection of the foundation, walls and floor is vulnerable to low temperatures. It is advisable to additionally equip the lower sides of the walls with vertical pieces of polystyrene. Instead, fibrous layers of mineral, slag wool, foam glass, expanded clay can be used.
 Film waterproofing is perfect for a balcony
Film waterproofing is perfect for a balcony If a vapor barrier was not provided during the waterproofing, it is produced on top of the insulation layer. Suitable as a protective layer different kinds specialized films or liquid rubber.
 Waterproofing floors on the ground is effective in combination with other construction activities
Waterproofing floors on the ground is effective in combination with other construction activities The last, floating screed reinforced with mesh is poured onto the extreme insulating layer of the concrete floor.
The final stage is the laying of any finish coat floor, the choice of which is dictated by the design of the room, profit or other considerations of the customer.
Summing up, we repeat that the waterproofing of floors on the ground is effective in combination with other construction measures. The direct impact on the quality of workmanship is influenced by the observance of technologies and the responsible choice of materials. When choosing them, it is necessary to evaluate technical indicators, quality, predicted service life, suitability in data climatic conditions, consumption, compatibility with each other, and other details. It is extremely difficult for a beginner to take into account possible risk factors. All stages of construction, including the arrangement of a concrete or wooden floor, are recommended to be carried out by experienced specialists.
Video: Floors on the ground. How to do it right?
Video: Floor waterproofing - repair technology
The floor covering needs mandatory protection from the harmful effects of moisture. This task is of particular importance in the case of foundation on the ground, which are often equipped in a warm climate. Here, both the waterproofing of the earth floor and the concrete floor are equally important, since in the first version it cuts off the capillary penetration of moisture from the soil, and in the second it prevents its absorption by the concrete screed.
Why is it necessary to waterproof the floor on the ground: what is the danger of penetrating moisture
At some depth of the soil there is a water-saturated layer. Since any soil is water-permeable to some extent, it is natural that, as it becomes more porous, it absorbs moisture. The capillary rise is the greater, the more dense the soil is, and the pores in it are thinner.
Moisture, even in the case of dense and oily clay, very slowly, but rises above the aquifer by at least 12 m.
If moisture meets some obstacle in the lifting zone, say, a concrete floor, then it is gradually saturated with liquid droplets and water vapor. Salts from the soil dissolved in water slowly corrode the concrete and destroy the structure of the wood, thereby reducing the operational life of the floors.
Moreover, the moisture that has entered the pores of concrete expands by about 9% when it freezes and breaks it. The resulting microcracks open the way for active penetration of moisture. In addition, alternating cycles of "freeze-thaw" slowly turn the tree into dust, and the concrete completely cracks.
This problem is not new at all, and there are many ways to solve it, but in any case, this requires competent floor waterproofing, which primarily requires the presence of a “cushion” under the structure.
Layered "pillow" under the dirt floor
The layering of the base avoids the formation of pits and failures - undesirable consequences, which is fraught with natural subsidence of the soil. The structure of such a structure is determined by the characteristics of the soil under the house under construction.
The sequence of layers in the "pie"
 "Bottom up" materials are arranged in the following sequence.
"Bottom up" materials are arranged in the following sequence.
Dense soil. At this stage, the natural earth foundation. These works use special tools e.g. level.
Bedding. It is performed in two layers, each about 10 cm. Crushed stone is used as a material, preferably a coarse fraction and sand - without any restrictions. Everything should be compacted as much as possible. The backfill does not allow water to penetrate capillary into the higher layers and provide for further work leveling base. If the distance from the GWL (groundwater level) to the base is more than two meters, then crushed stone can be replaced with expanded clay.
But replacing it with broken bricks or similar material is unacceptable.
Having laid all three layers, proceed to the next steps. What they will be depends on the type of future floor, whether it will be wooden or concrete.
Floor in basement
Proper basement floor waterproofing involves a number of activities that include foundation work and installation around the house. drainage system. First of all, they study the features of the soil for the structure, that is, the relief and its saturation with groundwater.
Device at low groundwater level
 Most often carefully packed sand and gravel pad 10-15 cm is enough to keep penetration groundwater Into the basement. The sub-base is cleaned and leveled. Clay can also be laid and compacted. Further poured reinforced screed from concrete, which is kept for about two weeks. The screed is covered with mastic and rolled waterproofing is laid with an overlap on the walls. Insulation sheets are laid with an overlap of 10 s and welded with a gas burner.
Most often carefully packed sand and gravel pad 10-15 cm is enough to keep penetration groundwater Into the basement. The sub-base is cleaned and leveled. Clay can also be laid and compacted. Further poured reinforced screed from concrete, which is kept for about two weeks. The screed is covered with mastic and rolled waterproofing is laid with an overlap on the walls. Insulation sheets are laid with an overlap of 10 s and welded with a gas burner.
Device at high groundwater level
When raising water from the ground higher than the floor level in the basement, their pressure increases and approaches to implementation finishing works in the basement, respectively, change.
GWL up to 20 cm from the basement floor. Coating waterproofing is applied to the walls of the basement and a “castle” of clay is arranged. Under preparation concrete base oily crumpled clay is also used.
Today, another technology is used for the “lock” device - bentonite. The bentonite clay underlying it has high colloidal properties, which makes it possible to limit the height of the protective layer to 1-2 cm. Concrete is laid between the geotextile or cardboard.
 GWL at a height of 20–50 cm from the floor. The floor surface in the basement is leveled with cement screed, and then, in preparation from concrete, roll material is laid in two layers. From below, the structure is under high hydrostatic pressure. To balance it, concrete must be laid on top of the waterproofing.
GWL at a height of 20–50 cm from the floor. The floor surface in the basement is leveled with cement screed, and then, in preparation from concrete, roll material is laid in two layers. From below, the structure is under high hydrostatic pressure. To balance it, concrete must be laid on top of the waterproofing.
UGV at a height of more than 50 cm. In this case, three layers of rolled materials or waterproofing are used and a reinforced concrete slab is arranged. It must be embedded in the basement wall, which perceives the hydrostatic pressure created by groundwater, as it works in bending. In addition, along the walls of the basement, the places of their junction with the base are insulated with bitumen-polymer tapes.
To increase the hydrophobicity of cement-sand bases, it is also recommended to use penetrating materials. They contain additives from chemical active substances. Through capillary moisture through open pores, they enter the thickness of the substrate. When they interact with the components of concrete, filamentous crystals are formed, narrowing, they reduce water permeability.
Use of liquid rubber
Liquid rubber allows you to get a seamless surface that is completely insulating from water. Considering the insufficient strength of rubber to mechanical damage, geotextiles are laid on top of it for protection and poured with reinforced concrete screed. In this case, it performs two functions: it protects against damage and pressurizes when groundwater rises.
Ground waterproofing concrete floor
 When constructing a concrete floor, the same three base layers of the “pie” are needed. However, it requires a serious approach. This is due to the contradiction between the structure of soil and concrete: the first is mobile, and the second is a monolith. It is necessary to take into account and combine both of these factors, usually two possible methods are used.
When constructing a concrete floor, the same three base layers of the “pie” are needed. However, it requires a serious approach. This is due to the contradiction between the structure of soil and concrete: the first is mobile, and the second is a monolith. It is necessary to take into account and combine both of these factors, usually two possible methods are used.
The sequence in the first variant is as follows:
- Behind the sandy part another of fine gravel is laid.
- As a rough screed, gravel is not poured with a thick layer of a solution of cement and sand.
- The maximum height difference for every 2 m is 3 mm.
- Next, roll material is laid - two layers. More often, roofing felt or roofing material is used for this. The joints are insulated with a gas burner.
Waterproofing materials must be free of powder.
- After laying the thermal insulation, a finishing screed is performed.
In the second variant, the first hydrobarrier is created using a polyethylene film laid on top of the sandy one. All joints must be insulated with adhesive tape or other adhesive-based impervious material.
Even minimal damage is enough for the film to cease to serve as an insulator.
 Next, a rough screed is laid from a standard cement-sand composition. Its thickness is limited to 50-70 mm. By subfloor lay waterproofing. Any rolled material is suitable for it - whether it be a membrane or roofing material. Then in order - thermal insulation and finishing screed. With a surface location of groundwater, it makes sense to additionally arrange waterproofing on the ground.
Next, a rough screed is laid from a standard cement-sand composition. Its thickness is limited to 50-70 mm. By subfloor lay waterproofing. Any rolled material is suitable for it - whether it be a membrane or roofing material. Then in order - thermal insulation and finishing screed. With a surface location of groundwater, it makes sense to additionally arrange waterproofing on the ground.
In principle, the purpose of waterproofing is clear: it is carried out in order to protect the structure as a whole or its individual parts from moisture: precipitation, groundwater, and other things. When is ground waterproofing necessary? The answer is quite simple: when building basements and cellars, arranging floors not on the foundation, but on the ground (this is true for small wooden summer cottages or country houses) and other facilities.
In this article, we will see what are the features of arranging such waterproofing and what materials can be used.
Ground waterproofing: materials
Note that waterproofing on the ground can be performed different materials: roofing felt, film waterproofing, bitumen, clay and others. The choice of material depends on the type of structure, soil moisture, groundwater level, etc.
Note that for more high-quality waterproofing in buildings where it is carried out on the ground and not only, it is very often recommended to build a drainage that will drain excess water.
Besides, in different parts buildings can be provided with different waterproofing. For example, in bathrooms, in addition to waterproofing made directly on the ground, additional pasting waterproofing. The fact is that the first will protect the structure from capillary water, the second - from Wastewater.
Ground waterproofing
Waterproofing directly on the ground may be necessary when constructing floors in buildings without a foundation. There are many ways to perform such protection from water: from the flooring of film insulation to the creation of so-called "clay castles" (which retain moisture).
When arranging the floor on the ground, you can apply the following method of waterproofing:
- Soil preparation. Before equipping the floor and, in fact, waterproofing, the soil is carefully tamped. Before tamping, the soil is leveled using a laser or optical level.
- Filling the soil with sand. It is recommended to add a layer of sand to the natural compacted soil. For these purposes, coarse river sand is usually used. This layer is also compacted. Note that the already compacted layer of sand should be approximately seven to ten centimeters thick.
- Filling the soil with crushed stone. This stage is necessary for capillary waterproofing. For backfilling, crushed stone is used twice spilled with bitumen. The crushed stone layer is also carefully compacted. Note that such waterproofing is effective only if they do not come close to the base of the building. ground water i.e. the soil is quite dry. The thickness of the bedding with such rubble should also be about ten centimeters.
- Filling a rough screed. It is poured onto a layer of crushed stone (treated with bitumen). This screed is necessary for the next stage of waterproofing (which will protect the rear from groundwater and sewage). For screed use cement-sand mortar with crushed stone of fraction 5-20. The thickness of the rough screed is usually about 5 centimeters. As for evenness, it is advisable not to allow differences of more than 3 millimeters per 2 meters of the floor. Note that when using a polyethylene film as a waterproofing (if the soil is dry), a rough screed can be omitted. In this case, the waterproofing is laid on top of the compacted rubble.
- Waterproofing with bituminous roll material . Rough coupler pre-coated with bitumen, on which the rolled waterproofing material is laid. It must be laid with an overlap of 10 centimeters.

- Floor arrangement. Then the floor is insulated and filled with a finishing screed. After cleaning and priming the screed, leveling compounds are poured, and the floor covering is laid.
The second method of floor waterproofing on the ground is suitable for floors on logs. Since it is impossible to lay logs on the ground, brick columns are preliminarily built (there may also be wooden ones, only treated with bitumen). Note that before this, the soil must be carefully compacted. After that, waterproofing spreads. In this case, roofing material, polyethylene, roofing felt can be used. And only then can you lay the logs directly and perform the rest of the work on arranging the floor.
Basement waterproofing on the ground
Talking about the construction of cellars, we also mentioned waterproofing. Recall that in such cases it is created " clay castle". To do this, the soil in the cellar is pre-rammed. Next, clay is laid in a layer of 20 centimeters. This is our castle. Clay will absorb and retain capillary moisture. In addition to such waterproofing, after arranging the floor with concrete or other materials, the cellar floor is also treated with bitumen.
Do not neglect the waterproofing of structures, even if, for example, you are sure that the soil is dry. Approach responsibly to the creation of waterproofing, and your building, cellar, and other structures will last much longer.