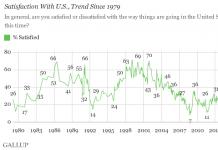
Most often, fused roofing is used to cover flat roofs and surfaces with slight slopes. To create it, a rolled material based on a canvas impregnated with polymer bitumen components is used. The built-up roof is installed as on residential buildings, and in warehouses, hangars, industrial facilities and other structures.
Fused roofing: features and characteristics
A few decades ago, only roofing material was used to create a fused roofing - a material based on cardboard impregnated with bitumen. It performed its functions properly until the bitumen layer lost its properties. After this, the coating had to be changed. Since then, technologies for the production of roofing materials have become more advanced, resulting in new types of rolled roofing with a multilayer structure:
- Bottom layer. This polyethylene film, which, in addition to its protective function, serves as an indicator that allows you to determine the optimal heating temperature during installation.
- Working layer. Work surface made from bitumen or bitumen-polymer compositions, as well as simply from bitumen.
- Warp. The reinforcing fabric acts as the basis of the roll. Now cardboard is no longer used; it has been replaced by polyester, fiberglass or fiberglass.
- Second working layer. To cover the base, the same polymer compounds or bitumen are used.
- External powder. Basalt chips are usually used.
This structure provides high strength, durability and good waterproofing characteristics of the roofing covering. But they only appear if the technology for installing a fused roof is followed.
The multilayer structure of the fused roof ensures its high strength and durability, subject to installation technology
Fused roofing has a number of advantages that provide it with well-deserved popularity:
- light weight - the material is easy to load, transport and deliver to the roof;
- the presence of a layer of mastic on the inside, which greatly simplifies installation;
- reliability - during its service life this coating does not require special care;
- high strength;
- good hydro- and sound-proofing characteristics;
- resistance to temperature changes;
- environmental friendliness - during operation such a roof does not emit harmful substances;
- affordable price.
Materials for built-up roofing
When creating a roll roofing, we use different materials for base, topping and binding components. In order to understand what a particular roofing covering is made of, you need to look at its markings:

The basis of the built-up roof
Unlike paper base, which was used before, modern materials do not rot and do not allow mold to develop. There are several options for creating a base that differ in strength and price:

Binders
Bitumen impregnation is used as a binder, which can be of several types:
- Oxidized bitumen. This is the most cheap material having not much high performance, therefore such roll coverings used only to create the bottom layer of the roof. They are not suitable for regions with frequent temperature changes and require additional protection from ultraviolet radiation.
- Polymerized bitumen. It can be used at air temperatures down to -25 o C. Isotactic and atactic polypropylene can increase the tensile strength and density of the material, but the melting point also increases. The addition of APP is cheaper than PPI, but in terms of its characteristics it is only slightly inferior. Styrobutadiene styrene is used for roof coverings complex shape and located in harsh weather conditions. Such materials have high plasticity; they are often called rubber bitumen.
Sprinkles
To strengthen the top layer, special toppings are used. They help resist solar radiation, precipitation, increase the rigidity of the coating and its service life.
The topping can be of different fractions:
- dusty - used for the bottom layer roofing pie, does not allow the web in the roll to stick together;
- fine-grained;
- middle fraction;
- coarse-grained;
- scaly.
Instead of mineral powder, foil or polymer film can be used.
In order to make the top layer more durable and resistant to external environment, it is sprinkled with mineral chips
To create a built-up roof, the material is laid in 2–5 layers, the width of the roll is usually from 400 to 1050 cm, and the length is from 7 to 20 meters.
Tool for built-up roofing
Installation of a built-up roof, although not particularly complicated, requires a certain set of tools to complete it:

Video: tools needed to create a fused roof
The roofing pie of a fused structure is a coating that reliably protects the roof from the negative effects of external factors throughout the entire period of its use. Roll materials are used for roofs with a slope from 1 to 12 degrees.
The composition of the roofing cake for rolled materials is no different from what is made for piece soft coverings:
- vapor barrier - this layer consists of a film or built-up material and is attached with overlapping strips and sealing the seams;
- thermal insulation - slab insulation is usually used, which are glued together using hot bitumen;
The insulation can stick bitumen mastic or fastened with disc dowel nails
- cement-sand screed - performed on top of a layer of thermal insulation, its thickness is usually 5 mm. If the covering area is large, then the screed is made into squares of 6x6 m and separated by expansion joints;
- waterproofing - laid in several layers with an overlap of 150 mm with high-quality sealing of the seams.
The base for a built-up roof can be a profiled sheet, a concrete slab or a wooden floor
When creating a roofing pie, not a single layer can be excluded. For example, if there is no vapor barrier, the thermal insulation material will begin to get wet, which will lead to a deterioration in its qualities. Absence cement screed will increase the load on thermal insulation, and it will also quickly lose its characteristics.
Features of installation of a built-up roof
If you decide to install a built-up roof yourself, you won’t be able to do the job well on your own. In order to do everything quickly and in compliance with technology, it is best to work with three people. In extreme cases, you can get by with just one assistant.
First person using gas burner carries out heating of the lower layer on the rolled material. After this, the second person rolls the material over the roof surface, and the third person immediately behind him levels the coating using a rolling roller. Only by following this sequence of actions can you create high-quality coating, which will protect the roof from the negative effects of external factors over a long period of time.
Features and sequence of installation of the deposited material:
- The base for laying the deposited material must be dried and pre-coated with a primer.
- Before heating the material, it must be unwound and tried on. To cut to size, use a construction knife.
- Using a gas torch, heat the edge of the roll and fix it in the desired place, then roll the roll.
When laying roofing material, both the roll and the base must be heated at the same time.
- Gradually roll out the roll, warm up its inner side and apply it to the roof surface. The burner flame must be directed both at the surface of the roof and at the bottom of the roll in order to simultaneously melt both surfaces.
- Smooth the surface well and roll it with a roller.
- Check the quality of work and correct errors if necessary.
After laying the heated surface, roll it with a roller, then the coating will stick to the base evenly and without bubbles
In order not to spoil the quality and appearance built-up roof, you cannot walk on it immediately after installation; you must give it time to cool.
To perform the work better, you need to take a soft roller and roll out the strip from the middle to the edges. The strips are laid with an overlap to ensure the tightness of the coating. The overlap on the sides should be 8–10 cm, and at the ends of the strips - 12–15 cm. On rolled materials with coarse-grained topping, the edges are deliberately underfilled by a width of 7–10 cm. To ensure a high-quality connection of the ends on the bottom strip, the topping must be removed independently.
Errors when installing a built-up roof
If you do not have the skills to perform similar work, then it is better to turn to professionals. If you have the desire and a certain skill, all the work can be done with your own hands, you just need to strictly follow the developed technologies.
The most common mistakes made when installing a fused roofing yourself:
- wrong choice of material. The roofing covering must be selected taking into account the operating conditions and weather conditions in the region where the building is located;
- installation on a completely flat roof. It is recommended that the slope be at least 1 degree - this will prevent water from accumulating on the roof and it will not seep into the coating;
- the presence of holes and depressions. Not only must the coating have a minimum slope, it must also be level;
- base moisture is more than 4%. Under such conditions, the material will not be able to adhere well;
- fusing onto a surface not treated with a primer. These compositions prime the surface with high quality and provide better adhesion of the material;
- non-compliance with overlap. It should be both at the sides and at the ends, and the transverse overlaps of adjacent strips should be offset by at least 0.5 m;
When laying a built-up roof, the transverse overlaps of adjacent strips must be offset relative to each other by at least half a meter
- laying one layer of fused roofing. The roof to be built up must have at least two layers, and for the first one, ordinary material is used, and for the second, a coating with a protective coating is used;
- insufficient heating. It must be carried out until the indicator pattern located on the inside of the strip begins to deform;
- incorrect design of connections. Vertical overlaps on pipes, chimneys or walls should be made at least 15–20 cm high;
At the junctions it is necessary to arrange vertical overlaps, which can then be covered with an additional layer of material
- incorrect design of the drainage system, which does not allow water to quickly drain from the surface.
If you do not make the mistakes described, you will be able to create a high-quality fused roof on your own that will last at least 10–15 years.
Video: installation of a fused roof
Features of operation of a built-up roof
The operation of a built-up roof involves carrying out scheduled and unscheduled inspections so that the condition of the coating can be assessed.
- During the spring inspection, the presence and size of swellings, the tightness of the coating in its horizontal sections and at junctions are assessed.
- In the summer, the presence of cracks, bubbles and cavities is determined. It is necessary to constantly remove emerging plants so that their roots do not destroy the covering material.
- Periodically it is necessary to clean the surface from leaves, dirt and debris, as water will stagnate in these places. Use a broom or wooden shovel so as not to damage the coating material. Check periodically drainage system so that it can ensure normal drainage of water.
- IN winter time The roof must be cleared of snow and ice. Fused roofing is mainly used on roofs with a slight slope, from which snow cannot naturally fall off. When performing such work, wooden or plastic shovels are also used, everything is done carefully so as not to damage the roof being built up.
- After strong wind, rain or hail, it is advisable to carry out unscheduled inspections. This will allow you to identify damage immediately after it appears, so that you can correct everything in time. During the inspection, you should pay attention to the condition of the coating, since over time this layer is destroyed.
Video: soft roof problems
Service life of a fused roof
The service life of a built-up roof is significantly influenced by both the quality of the materials used and the technology of their installation, which must not be violated.
- If glassine, roofing felt or bicrost are used, the service life of the fused roof is about 10 years.
- The use of linochrome, bicroelast or bipole can increase it to 10–15 years.
- When materials such as uniflex and ecoflex are used, the roof lasts 15–25 years.
- The use of uniflex together with a vapor barrier increases the service life to 25–30 years.
Fused roof repair
Although the built-up roof has high performance characteristics, over time, situations arise when such coverage needs to be repaired.
During inspections, damage may be identified that requires repair:
- cracks and tears in the top layer;
- the presence of vegetation and signs of rotting of the middle layer;
- peeling of material.
It is advisable to carry out repairs when the area of damage does not exceed 40% of the entire roof, otherwise it is necessary to completely replace the roof.
Local damage
Small cuts and cracks can be repaired by applying patches.

Bloating
Bubbles form during a temperature change when air enters the insulating layer and a bulge forms. Bubbles may also appear because the material was laid on a damp base.
To eliminate them, perform the following operations:

Cracking
Roof coverings usually crack due to the action sun rays, as a result of which the protective coating on it disappears. To carry out repairs, the surface is first cleaned of dirt, dried and a layer of mastic is applied. When it hardens, apply a second layer and immediately lay down the coarse-grained topping. You can also install a patch with a coarse-grained coating; it should cover the damaged area by 10–15 cm. If the damage area is large, then the entire coating will have to be replaced.
Separation of the waterproofing layer from the base
The tearing of the canvas most often occurs if, during installation, the base was not well cleaned of dirt and dust, and also if a primer was not used during installation. The peeled area is cleaned of dirt and dust, dried and re-glued using bitumen mastic.
Peeling of the coating mainly occurs in those places where the welded roof is adjacent to vertical elements or wall.

Anyone can install a built-up roof with their own hands. home handyman. To ensure good sealing in difficult places, you can not lubricate the surface with bitumen, but pour it. This solution will be more effective than even three layers of rolled materials. The reliability and durability of a built-up roof will depend on compliance with its installation technology, so if you are unsure of your abilities, it is better to entrust the work to professionals.



















In this article we will tell you what a built-up roof is, why it is called that, what materials it is made from, and we will also analyze the technology for installing this type of roofing. The article will help you understand the materials used and the technology of their installation and be “on the same wavelength” in conversation with the craftsmen who install this type of roofing.

Welded type materials
So, the basis of the fused materials is a non-woven frame: fiberglass, fiberglass, cardboard or polyester mesh. It is treated on both sides with modified bitumen or a bitumen-polymer mixture. The second option is increasingly used today as a more efficient look impregnations with long-term operation and improved performance.
The top bitumen layer is sprinkled with stone, sand or mica chips, which serve to protect the roofing material from the negative effects of sunlight. Some manufacturers use special protective films made of polymers for this purpose. The lower bitumen layer acts as a bonding compound. When it heats up, it softens and sticks to the base of the roof. A polymer indicator film is applied on top of it. Its purpose is not only to protect the material during storage and transportation, but also to show when heated that the coating is ready for gluing. That is, when it burns and melts, this is a sign that the roofing covering can be pressed against the roof plane.

Finished soft fused roofing products are rolled material. Manufacturers today offer five of its categories. The materials included in them differ from each other in characteristics, properties and service life.
"Economy" will last on roofs for no more than 10 years.
Related to business class can be used for up to 25 years.
Premium class - up to 30 years.
On our website you can find contacts of construction companies that offer repair services for roofs and roofing coverings of any complexity. You can communicate directly with representatives by visiting the “Low-Rise Country” exhibition of houses.
Construction of a roof made of fused materials
Let's start with the fact that overlay materials can be laid on flat and pitched roofs. With flat roofs everything is clear - the materials were specially invented for these roofs. As for pitched ones, there is a limitation for them - the angle of inclination should not exceed 50°.
Now about the construction of a built-up roof. It is formed only on a strong, even and reliable plane. Therefore, on flat roofs, no matter what material they are built from, the final layer is a cement-sand screed. That is, regardless of whether the roof is being built with an insulated roof or a cold one, the materials being built up are laid on the screed layer.

But we must pay tribute to the manufacturers of thermal insulation materials, who today offer products with a tensile strength of more than 0.06 MPa. These are materials that, under the influence of loads, wrinkle no more than 10% of their original size. Fused surfaces can be laid on such mats and slabs. roofing decking. Of course, it is optimal to choose insulation with a tensile strength of more than 0.15 MPa.
Note! The slabs or mats on the roof are laid in a checkerboard pattern with an offset relative to each other of half the product if the installation is carried out in two layers. Thus, the problem of uniform distribution of loads on the heat-insulating layer is solved, plus the joints between the mats and slabs are covered with solid products.
With cold roofs everything is clear; these are most often six-hollow floor slabs covered with a screed, which forms the slope of the slope. If an insulated roof is being erected, then a thin screed is poured onto the floor slabs to level the surface. Then a layer of thermal insulation material is laid, covered with a vapor barrier on top. And the last layer is screed. And the weld coating is laid on it. If insulation mats with the characteristics described above are used, then the top screed is not poured.

On flat roofs, bulk materials are often used as insulation: expanded clay, perlite, vermiculite. They must be filled with screed.
As for pitched roofs, we must immediately make a reservation that the installation of a built-up roof is carried out only on continuous sheathing. In this case, either moisture-resistant plywood or OSB-3 boards (also moisture-resistant) are used.
Please pay attention to the following nuances:
pitched roofs are insulated under the sheathing elements when thermal insulation material is laid between the rafters;
laid on top of the rafters vapor barrier membrane, which is attached to them with metal staples using a stapler;
over vapor barrier the sheathing is assembled;
the outer plane of the latter is required treated with a fire retardant compound, and on top with a bitumen primer;
covered substrate made of non-flammable material;
fits and the weld material is glued.

Installation process
The technology of installing a soft roof from fused materials is a simple process. The roll is laid at the eaves of the roof, the outer surface is heated with a gas burner, and the material begins to be rolled out, which immediately sticks to the prepared surface. The rolling is carried out from the cornice to the ridge using a poker. The installation is carried out by two workers: one heats the roll and rolls it out, the second presses it to the roof plane with his hands or some tool.
On flat roofs, installation is carried out along the eaves, starting from the bottom. In this case, the next strip is laid on the previous one with a slight overlap.
Video description
The technology for laying the deposited material is shown in the following video:
You need to be careful with a built-up roof (with work on its construction). This is a fire hazardous event where rules and requirements are strictly adhered to. fire safety. For example, the distance from the gas cylinder to the burner during operation should not be less than 5 m. Qualified craftsmen are familiar with the requirements, they comply with them, so there should be no problems.
Soft roof repair
Unfortunately, like many roofing materials, built-up roofing materials fail, and not only at the end of their service life. They do not have increased strength characteristics, for example, like metal ones. Therefore, the roof must be periodically inspected for defects:
peeling edges;
bubbles filled with water or air;
cracks;
disappearance stone topping.

Let's start with the last flaw, which is formed by clearing snow from roofs using shovels. It's easy to fix. For this purpose in hardware store Stone pavement is purchased in the required quantity. The main thing is to match it to the color of the roof. The defective area is coated with bitumen mastic and the coating is evenly applied to it.
Peeling of the edges is also easy to repair. The edge is retracted, the plane underneath is coated with bitumen mastic, the edge of the material is placed in place and pressed firmly.

As for the bubbles.
Using a sharp knife, make a bulge at the site cross cut in the form of an envelope.
Bred triangular edges in different directions.
If there is a need, level out base with cement-sand mortar.
Heat up retracted ends with a burner.
Stacked they are pressed into place.
Making a patch, which should be 10 cm larger than the defective area on each side.
Patch placed on the prepared area after heating. The best option is to lay two patches on top of each other.

Now how to repair cracks. If it is a network of small cracks, then the defective area is treated with bitumen-polymer mastic, to which aluminum powder is first added. And sprinkle stone chips on top. If the crack is one and large, then the technology for repairing it is similar to sealing an air bubble. Only in this case the crack is not opened, but a patch is simply laid on it.

As you can see, the technology for repairing soft roofs made from fused materials is not the most complicated process. The main task is to detect the formation of a defect in time and not create conditions for the appearance of leaks.
Conclusion on the topic
Fused materials are increasingly being used to cover flat roofs in private housing construction. They cover outbuildings. Houses with flat roofs are becoming fashionable, so in this regard, the demand for soft roofing does not decrease. In civil multi-storey construction, these materials have not lost their popularity. It’s just that roofing felt and bitumen have been replaced by modern materials, which are superior in both quality and service life to old products and technologies.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
One of the most common options for covering flat roofs is the installation of a built-up roof. The use of roll materials allows you to create a roof covering with your own hands quite simply and quickly.
The roof of any building, regardless of its purpose, is created to perform certain protective functions, including:
- protecting the building from precipitation;
- preservation of heat during the cold season;
- protection against overheating in summer.
Thus, any roof must meet very serious requirements for strength, tightness and thermal insulation. All of them are specified in the relevant standards and regulations relating to roofing structures. Currently available on the building materials market huge selection. Each material has its own strengths and weaknesses, service life and cost. Therefore, it is very important to familiarize yourself with all the characteristics of the roofing material you are purchasing before purchasing.
Roof selection
If we talk about the materials that are used to create soft roofs, then they can be classified according to several indicators.
For example, such roofs differ according to the type of base:
- cardboard;
- fiberglass;
- asbestos;
- polymer.

By type of binder:
- polymer;
- bitumen;
- bitumen-polymer.
The previously very popular first generation rolled materials (roofing felt) are today used only as a lining and waterproofing layer. The undoubted advantages of roofing felt include its cost, but, unfortunately, in all other indicators it has unsatisfactory results, which has led to a decrease in its popularity among developers.
Today, to create a truly high-quality roofing covering, materials based on polyester or fiberglass are selected, and bitumen-polymer compositions are used as impregnation. There is no generally accepted GOST for such materials, so each manufacturer has its own specifications.

The largest manufacturers mark their products according to a three-letter designation.
The first letter in the marking indicates the type of base:
- E - polyester;
- T - fiberglass;
- X - fiberglass.
The second is the view outer covering:
- P - polymer protective film;
- M - fine-grained sand;
- K - mineral dressing.

The third letter describes the bottom covering:
- F - foil;
- C - suspension;
- M - fine-grained sand;
- P - protective polymer film.
Fused roofing technology
Before installing a built-up roof, the foundation should be prepared. The first layer of the roofing cake is a vapor barrier, which is laid directly on the floor slabs. For these purposes, welded or film materials are used. Attention! Important to know. In places where the vapor barrier adjoins the vertical elements, the film is applied to the walls, raising it above the level of the future thermal insulation layer. On horizontal surfaces, the vapor barrier film is laid overlapping, and all seams are sealed.

Next comes a layer of thermal insulation, on top of which a layer of cement-sand screed will be placed. The insulation boards also need to be connected to each other using hot bitumen. The screed is made taking into account temperature-shrinkable seams, the width of which should be about 5 mm. The seams should divide the screed into equal squares with a side of 6 m. After 3-4 hours after laying the screed, it is covered with a primer prepared from a mixture of bitumen and kerosene (in proportions 1 to 1).
Last layer roof pie, on top of which the top covering will be laid - this is waterproofing. At the same time, during its installation it is necessary to provide for the organization of funnels for internal water drainage. Their installation is carried out according to project documentation. Where the “pie” joins the walls and pipes, sides are made of asphalt concrete or cement-sand mortar height 10 cm and tilt angle of 45 degrees.
Before you begin laying waterproofing, you must check the moisture level of the screed. Work cannot continue if the cement is not dry enough. Shrinkage seams must be additionally covered with strips of waterproofing 15 cm wide. In this case, it is better to use rolled material with coarse-grained topping, the side of which is placed down.

At the location of the water intake funnels, additional “patches” are laid with square pieces of insulation with a side of 70 cm.
If a roof made of fused materials is being repaired, the base preparation should be carried out according to the following scheme:
- remove debris from the surface;
- remove dust from the surface of the old coating as much as possible;
- carefully inspect the coating to identify bubbles and swellings;
- discovered bubbles must be opened, and then the area must be heated to fuse it.
Required materials
To carry out the work you will need following tools:
Fused roofing - installation technology
As a standard, roof covering with roll material occurs according to the following scheme:

The most difficult aspect of the work that a fused roofing requires is the technology of laying a hermetically sealed junction of the roofing pie to the vertical elements. At such points it occurs highest probability formation of cracks and roof leaks. That is why it is so important to carefully study the issue of organizing “difficult places”. As a rule, two additional layers of waterproofing are glued. The first layer must be placed on the surface wall at least 25 cm, the second layer is placed a little less - 5 cm.
Roofing roll material - we carry out installation "). It is especially easy to lay the material on top of the old base, that is, when repairing a built-up roof.
But at the same time, you must always remember the dangers of working with gas burners. This is why it is so important to follow safety regulations. Taking into account all aspects of the work, having previously studied the instructions for the work, an untrained person will be able to independently lay such a roof for a sufficiently long time. high level(read: " ").
With a slight slope on the roof, especially if it is generally flat, choosing a good roofing covering is a real challenge. After all, most types of tiles, their imitations, and even corrugated sheets are not intended for roofs whose slopes are less than 12°. Then all that remains is either to be content with what the market offers for such cases, or to lay a modern fused roofing on the roof - a breathable, completely environmentally friendly material with excellent waterproofing!
Today, fused roofing is used for almost all types of roof configurations, no matter what climate zone they are located in. And this option is quite suitable for furnishing a private home, and not just industrial buildings. Moreover, there is even the opportunity to choose a stylish design!
So, the built-up roofing consists of bitumen and bitumen-polymer materials. In essence, we are talking about a waterproofing sheet consisting of a polyester or fiberglass base, onto which bitumen or bitumen-polymer binder is applied on both sides.
On top of this binder is covered with a protective layer in the form of sand, film or sprinkling:
Modern built-up roofing is designed for high-quality waterproofing not only of roofs, but also of bridges, foundations and tunnels. Here are its advantages:
- fairly quick installation;
- excellent noise and waterproofing;
- frost resistance, some manufacturers even allow roofing to be laid at temperatures of -20°.
- high maintainability;
- practicality, such a roof can be laid over the old coating;
- durability, ability to withstand high temperatures without changing the composition. For example, SBS bitumen allows you to easily tolerate heating of the coating up to +90-100°C.
If we talk about the composition of the fused roof, then it is a five-layer waterproofing membrane, in which a binder is applied to the base, and on the outer sides there is a stone coating and a low-melting film.
It is precisely, depending on each layer, that types, classes and entire collections of such roofing appear.
Types, types and classes of fused roofing
To choose the right roof for your home, we recommend that you learn to understand its quality, grade, and suitability for a particular climate.
Base: tensile strength
Many are surprised by the fact that among the fused rolled roofings there is a fairly large assortment of choices: both by class and performance qualities, although it would seem that roofing felt would be enough. In fact, almost everything depends on the base, and cardboard, like roofing felt, does not cope with all tasks.
Here are the alternatives:
- Polyester. This is one of the most reliable and expensive materials for fused roofing. It consists of special polymer fibers arranged in a chaotic manner. As a result, according to the standards, this material has the ability to elongate up to 60% and a tensile strength of more than 35 kg/cm. These are really solid specs.
- Fiberglass. This backing consists of interwoven glass filaments, which are more economical than polyester. The elongation here is much less, only 2%, and the tensile strength is up to 80 kg/cm.
- Fiberglass. This material is not as strong as the two previous options, and the quality depends on the binder used. Fiberglass is quite stable, but is not always suitable for structures that are constantly in use. The breaking force here is only up to 30 kg/cm, and there is no possibility of elongation at all, that’s the point.
Fused roofing is also divided into classes based on quality and price. They differ in the base and bitumen binder used, as well as the proportions of SBS and APP modifier.
Bitumen binder: roof durability
The very first welding materials were made using oxidized bitumen. This is a kind of “artificial aging” of bitumen, when it is heated and air bubbles are passed through the mass. All this increases the heat resistance of the material, because raw bitumen lacked it.
Moreover, it began to melt already at a temperature of +50°C, and such a temperature is easy to imagine on the roof of a multi-story building in the heat. And thanks to oxidation, this limit was increased to 80-85°C.
But here another problem arose: due to oxidation, bitumen loses its elasticity, and already aged bitumen will continue to age right on the roof. As a result, the service life of such a roof is no more than 5 years due to its fragility. That is why bitumen began to be further modified in order to restore such important properties to it.
And today, built-up roofing is made from the following modified bituminous materials:
- artificial rubber, officially called SBS, styrene butadiene styrene;
- artificial plastic called APP, atactic polypropylene.
SBS gives bitumen excellent flexibility at low temperatures, although the heat resistance is slightly lower than that of APP, although with the help of special additives the threshold is sometimes increased to 1000°C. The elasticity of such bitumen, if without a base, reaches 1500-2000% and has good adhesion. With the help of SBS, the rolled roofing becomes a so-called polymer matrix, a three-dimensional mesh, where the bitumen itself is distributed in the form of a fine dispersion.
Unlike SBS, atactic polypropylene, or thermoplastic, high temperature melting. Thanks to it, the fused roofing is resistant to destructive ultraviolet radiation, heat, has good flexibility and high heat resistance. But despite all the flexibility, the elasticity of the AMS is less, i.e. loses in stretching, but to some extent this is compensated for by the polyester bases.
That is why SBS-bitumen overlay roofs are more suitable for northern climates, and APP - for hot ones.
The class of material for roll roofing, or rather its quality and price, is determined by the base, the weight of the bitumen (bitumen-polymer) binder and the percentage of SBS or APP modifier.
Let's look at what it offers modern market: what manufacturers of fused roofing, what types and prices, and what are its competitive advantages.
TechnoNIKOL: domestic quality and plenty of choice
TechnoNIKOL was the first to appear on the domestic market, more than 20 years ago. Today it is installed both on the old coating and on the new one.
TechnoNIKOL pleases wide range their weldable coatings, for the most different tasks and with for different periods services. All products are divided into different classes: economy (and sub-economy), standard, business class and premium.
Even for an inexperienced person, it is quite easy to choose the right type that will be optimal in terms of price/quality. In addition, the manufacturer also offers its additional tools and solutions, such as vapor barrier, bitumen primer and more.
What is the advantage and why isn’t it easier to buy all this from different brands? Professional roofers know well that with complex solutions, the final quality is much higher, because all materials are ideally suited to each other, because They were created for each other.
Icopal: a practical solution for any climate
On Russian market building materials, another high-quality fused roofing is supplied - Finnish production Icopal.
A little about the manufacturer. Icopal has gained the trust of the whole world, which is no wonder, because the company was founded back in 1876 and today this concern already has 30 factories in developed countries. And it was this company that at one time developed the technology for modifying bitumen with SBS polymer, which was readily picked up by all other manufacturers.
Icopal fused roofing undergoes complex quality control tests and is guaranteed for 10 years with 40 years of actual use. The whole secret is in high-quality bitumen, which is produced without sulfur, which guarantees the required durability.
It uses a new generation of SBS called synthetic rubber. It is this that gives bitumen high elasticity and heat resistance. As a result, Icopal roofing copes well with roof deformation when the surface is slightly stretched, and heals minor cuts and punctures.
Icopal produces two types of built-up roofing: Ultra Top and Ultra Base, both made from a non-woven polyester base. Icopal Ultra Top is distinguished by its coarse-grained coating, and Ultra Base by the fact that it can be both fused and mechanically fixed.

Icopal uses slate or ceramic chips as a finishing coating. It is painted in different colors, and securely attached to the bitumen mass. As a result, the percentage of loss during the service life is no more than 5%.
Another difference between the welded blood core and Icopal is the unique technology for profiling the bottom surface, called “Quick Profile”. It greatly simplifies installation, saving up to 25% of gas and a third of the time for the entire installation process. In addition, such rolls have a 40% increase in the heated area, which is also a plus for adhesion to the base.
Thanks to all this, Icopal fused roofing can be used for any type of roof, and all climatic zones. Such roofing has been implemented as single-layer and double-layer.
Safety SBS from Tegola: reliable waterproofing
Safety SBS fused roofing is produced by the well-known company Tegola. These rolls have high strength characteristics and are suitable vapor and waterproofing for flat roofs, foundations and interfloor ceilings:

Safety SBS is based on non-woven polyester fabric or glass fiber impregnated with styrene butadiene styrene or a modified polymer. On top and bottom there is a heat-sensitive polymer film, which acts as a sensor during installation, namely, it is deformed in the desired way.
Construction of a fused roof: single-layer and multi-layer
Bitumen roll roofing they are fused in one layer, two or three – the amount depends on the type of coating itself. Place strips of material along the long side of the slope on roofs up to 15° and across with a large slope:
- if the angle of inclination of the slope is more than 15°, two layers are deposited, usually they differ in markings: lower P, upper K;
- if the slope angle is from 5 to 15°, then three layers are made;
- and as many as four layers are required for a roof with a slope of up to 5°.
By the way, some manufacturers today are working on premium materials that can be applied to any roof in only one layer.
The welded roof is laid on reinforced concrete floors, even slabs, if their seams are sealed with a moisture-resistant mortar, and on a solid leveling screed made of M150 concrete. But it is forbidden to fuse a roof onto a wooden base, although this mistake can still be encountered, and it is 100% fire unsafe!
Laying technology: achieving high quality
Let's tell you one secret: when it comes to a built-up roof, the technology for laying it is not so simple, and conventional construction knowledge it won't be enough here.
As experts note, even experienced builders, which are excellent at building foundations and walls, taking a torch and a roll usually do not cope with this task. Therefore, it is recommended to either call special brigade, or really understand all the intricacies of a built-up roof.
Flat roof: proper waterproofing
So, let's list the main stages of installing a fused roof on flat roof. Whatever the roll, no matter what special properties it has, the technology for carrying out the work is still the same.
Step 1: Surface Cleaning
How responsibly you approach this step will determine the service life of the entire coating. After all, the adhesion of the deposited material directly affects the tightness of the roof, its durability and the resistance of the coating itself to various damages. And also how often the roof will need repairs.
Therefore, before starting work, completely clean and level the entire roof, treat the screed with a primer solution - this will improve the adhesion of the new material. And if there is already old roofing carpet, repair and restore it.
Fill all irregularities, potholes and seams between the slabs with M150 concrete, which is moisture resistant. The main rule is not to clean the surface with mechanical brushes or grinding discs, because they form grooves on the surface.
Professionals also advise priming the surface with bitumen mastic, armed with a roller. Then you get a sticky film, which is good for promoting the adhesion of the roof and the base:

Step 2. Trying on the material
As soon as the primer has dried, the roll material is unwound and tried on. Where necessary, adjust using a roofing knife. Then the roof is rolled back onto the roofing roller.
Step 3. Deposition of material
The bottom glued layer is heated, and the roll is rolled out and pressed tightly to the base. The side overlaps should be from 7 to 10 cm, and the end overlaps should be from 10 to 15 cm. To obtain such overlaps, a 7-10 cm wide edge is specially left on the material with sprinkling along the entire canvas. If the manufacturer did not leave one, heat the desired area and remove the sprinkles.
To get started, choose clear, sunny weather. When it is windy, working with a gas burner is especially dangerous, and on a cloudy day the surface of the roof will be slightly damp, which will negate all your efforts.
Fusing with a gas burner begins from the fixed edge of the panel. Attachment of the building material occurs during the heating of the primer and partial melting of the bitumen of the lower layer. The movement of the burner should resemble the letter G - this is how you can achieve high-quality heating of the overlap zone.
After forming a small roll of molten bitumen, the roll is gradually unwound, straightening and pressing the coating to the base of the roof using a soft roller. The roller moves in a herringbone pattern - from the center to the edges. After passing each strip, you need to check the quality of the seam. If necessary, it is lifted with a spatula and re-fused. Defects are pierced with an awl and treated with mastic or special glue(the Ruflex plant, for example, offers its customers a full range of related materials).
The main indicator that you are heating the material to the desired temperature is a change in the indicator pattern. Usually, for most manufacturers, it melts and changes contours. If there is no such thing at all, then the roll simply darkens:

The roof is fused onto vertical surfaces as follows:


Step 4: Reheat
Once the bottom layer has been laid, reheat the resulting joint and make sure it is tight. But only the lower one, the upper one does not need to be heated again, otherwise you will damage the roof! Additionally, you can seal the seam with a primer.

Step 5. Checking the quality of the seam
How well the installation of the fused roof was performed is assessed visually using the following two important parameters:
- The entire surface of the laid roll material should not have any wrinkles or folds.
- In the place where the deposited mother comes into contact with the base or old layer, a “bitumen bead” is formed.
This is what it looks like:

It is this roller that guarantees complete tightness of the overlap. But if the bitumen binder flows out from under the side edge, or it is not there at all, or it is burned out - all this is a defect.
By the way, when fusing, the edges of the roll are rolled with a roller or with a hand wearing a protective glove, but you can also use your foot if you are careful:

Roof with slopes: reliable fastening
On the slope, the first strip is laid from the very bottom of the roof, along eaves overhang. Each subsequent strip is laid with a mandatory overlap of up to 10 cm. And transverse overlaps of at least 15 cm.
With a transverse vertical overlap, the top layer is shifted by no less than 500 mm, and with a longitudinal overlap, this layer is shifted by 300-700 mm.
Skates need to be protected with welded strips in the transverse and longitudinal direction, up to four pieces.
The first welded strip has minimum width, and each next one should be wider than the previous one by the amount of the overlap itself. If you are making a transverse overlap, throw it over the ridge and fasten it on that side of the slope with an overlap of 250 mm for the top layer and 200 mm for the bottom layer.
It is also important to protect narrow valleys that are less than 60 cm. Strips are laid along them. If the valleys are wider, then protective coating then it is applied crosswise, with the same overlaps as the main layer.
The strips also protect the grooves. These are connected by melting directly on the slope, if its angle of inclination does not exceed 15°. And if the junction has a steep angle, the roof is fused in the upper part of the junction.
Found ideal option for your roof? We're glad we could help!
- Preparing the base
- Application of primer (primer):
The surface is cleaned of dirt, dust, cement laitance and other particles that prevent the adhesion of the welded material to the base, all sharp and protruding elements are removed - sharp corners and edges.
- increases adhesion of built-up waterproofing to the base;
- binds dust, small particles, fills pores and small cracks,
making the base more durable; - moisturizes the surface, which increases the speed of waterproofing work.
Primer drying time ranges from several minutes to 24 hours, depending on the type of primer, temperature and humidity of the surrounding air.
The primed surface is considered dry if it is not sticky.
Gluing of rolled material is carried out in the process of melting the lower surface of the rolled roll with the flame of a gas burner while simultaneously heating the surface of the base, gradually rolling out the roll and pressing it to the base.
Bases for waterproofing
The base for the roof can be flat surfaces:
- reinforced concrete load-bearing slabs, the seams between which are sealed with cement-sand mortar of a grade of at least 150;
- mineral wool thermal insulation boards with a compressive strength at 10% deformation of at least 0.06 MPa;
- monolithic thermal insulation with a compressive strength of at least 0.15 MPa from lightweight concrete, as well as materials based on cement or bitumen binder with an effective filler - perlite, vermiculite, etc.;
- leveling monolithic screeds made of cement-sand mortar and asphalt concrete with a compressive strength of at least 15 (M150) and 0.8 MPa, respectively, as well as prefabricated dry screeds made of flat asbestos-cement sheets, cement-bonded particle boards, glass-magnesium sheets and others with a thickness of at least 8 mm, laid in two layers.
Screeds made of sandy asphalt concrete are used in the autumn-winter period over monolithic and slab insulation. It is not allowed to use asphalt concrete screeds over compressible (mineral wool, etc.) and backfill (expanded clay gravel, perlite sand, etc.) insulation materials, as well as when gluing rolled materials onto cold roofing mastics.
The installation of screeds made of cement-sand mortar in roof structures with a load-bearing base made of profiled sheets is not allowed.
Cement-sand screeds 50 mm thick are installed over backfill insulation (expanded clay gravel, perlite sand, etc.) with obligatory reinforcement with road mesh.
When forming a prefabricated screed, the sheets must be laid with seams staggered so that the sheets of the top layer overlap the seams of the bottom layer by at least 500 mm. The sheets are fastened to each other using rivets along the perimeter and in the center of the sheet. The number of fasteners is selected based on at least 14 pieces. per sheet measuring 3000 x 1500 mm. Connection with self-tapping screws is allowed. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the self-tapping screw does not destroy the prefabricated screed sheet. To do this, you should first drill a hole for the self-tapping screw. Connecting sheets of prefabricated screed is necessary to create a “monolithic” base. For roof slopes greater than 10%, it is necessary to mechanically fix the prefabricated screed to the load-bearing base. For smaller slopes, the need for fixation to the base is checked by calculating the wind load.
Vertical surfaces of structures protruding above the roof and made of piece materials (brick, foam concrete blocks, etc.) must be plastered with cement-sand mortar M150 to the height of the edge of the roofing carpet, but not less than 350 mm. Parapet walls made of piece materials should be plastered similarly.
The basis for waterproofing can be:
- flat surface concrete base;
- leveling layer made according to concrete base if it is not even enough.
Slope-forming layer
To ensure maximum durability of the roofing, it is recommended to provide a slope under the base of the waterproofing.
Can be used as a slope-forming layer backfill insulation (expanded clay gravel, perlite and others), light concrete mixtures (foam concrete, expanded polystyrene concrete, expanded clay concrete, perlite concrete), cement-sand compositions or wedge-shaped insulation slabs. If necessary, it is possible to use sand filling in cases where the fraction of the slope-forming layer exceeds the required minimum thickness and the formation of a “step” is possible.
Prohibited use bulk materials, as well as concrete and cement-sand compositions as slope-forming layers along load-bearing foundations made of steel profiled flooring.
Preparing the base
- The base surface should not have protruding reinforcement, shells and potholes, concrete sagging, cracks, irregularities with sharp edges, oil stains and dust.
- The base for built-up waterproofing must be level and smooth.
- In newly installed screeds, temperature-shrinkable seams with a width of about
5 mm, dividing the cement-sand mortar screed into sections of no more than 6x6 m, the asphalt concrete screed into 4x4 m cards. - The surface to be waterproofed must be dry
- In places adjacent to vertical roofing structures(walls, parapets, ventilation shafts etc.) it is necessary to make inclined sides (fillets) at an angle of 45° and a height of 100 mm from cement-sand mortar, asphalt concrete or hard mineral wool slabs. For bases made of prefabricated screeds or rigid mineral wool slabs, the sides must be made of rigid mineral wool insulation or use ready-made stone wool elements.
- Before the actual installation of the built-up waterproofing, all contaminants and materials that impede adhesion (dirt, dust, cement laitance film, etc.) are removed.
- The prepared surface must be primed
Concrete sagging, ends of reinforcement, sharp corners and chamfers are cut down and cleaned; oil stains burn off.
Sinks, cracks, and irregularities are sealed with cement-sand mortar M150.
Small potholes and cracks can be filled with hot bitumen mastic.
The evenness of the base is checked with a 2-meter lath. The presence of gradually increasing irregularities of no more than 10 mm across the slope and no more than 5 mm along the slope is allowed on the base for laying the deposited material. In this case, the number of irregularities should be no more than two per 4 m2 of base area. For foundations made of piece materials, unevenness across and along the slope should not exceed 10 mm.
Temperature-shrinkage seams must coincide with the end seams of the load-bearing slabs and be located above the seams in monolithic thermal insulation.
Permissible humidity concrete or cement-sand screed (including deep moisture) should not exceed 4% by weight, and asphalt concrete screeds - 2.5%.
Determination of base moisture values is most often carried out using instruments - surface moisture meters.
The simplest test for moisture involves laying a 1 x 1 m polyethylene film on the prepared concrete surface. If condensation does not appear under it within 4-24 hours, then laying overlay materials is possible.
To reduce the humidity of a waterproofed surface, various techniques are used: 1) wipe the wet surface with a rag soaked in acetone and then dry it with hot air from an industrial hair dryer; 2) arrange greenhouses and install them in heat guns; 3) blow on the surface compressed air from a compressor with an oil trap; 4) heating electric cords are installed in expansion joints.
It is recommended to remove the laitance film by dry or wet blast-abrasive cleaning. Dust removal, depending on the situation, is carried out using a dry or wet method. To do this, use sweeping with brushes, blowing with air from a compressor, industrial vacuum cleaners, and rinsing with water. Surface treatment with milling cutters that form grooves in concrete, as well as mechanical brushes and grinding, is not allowed.
For surfaces made of concrete slabs, cement-sand screeds are used as a primer (ready-made bitumen primer). The primer can also be prepared from bitumen (grades BN 70/30, BN 90/10, BNK 90/30) and fast-evaporating
solvent (gasoline, nefras), diluted in a ratio of 1:3-1:4, by weight or bitumen mastics with heat resistance above 80 ° C, diluted to the desired consistency.
Bituminous primer is applied using brushes, brushes or rollers.
In the case of fusing the material onto a base of mineral wool insulating boards, the surface of the top layer of insulation must be primed with hot bitumen mastic with a heat resistance of at least 85 ° C or bitumen BN 70/30, BN 90/10, BNK 90/30 with a consumption of 1.5- 2.0 kg/m2.
Installation of a built-up roof
- Robots for installing a fused roof are carried out in a certain technological sequence:
- Pasting funnels of internal drains
- Pasting valleys and eaves areas
- Laying the roofing carpet on the main roof plane
- Arrangement of junctions.
- The bonded roll material should be applied in the following sequence:
- A roll of material is rolled out onto the prepared base.
- Set the required direction and provide overlap between adjacent panels
- Roll the roll towards the middle (from both end sides)
- In the process of heating the lower surface of the roll with simultaneous heating of the adjacent base zone, the panel is sequentially re-rolled and glued to the underlying layer.
- Rolling out and gluing of panels of welded roll material must be carried out after achieving the required parameters for melting the cover layer of a low-melting polymer film, namely: in the process of melting, rolling and pressing, it is necessary to ensure the required heating of the cover layer and heating of the base along the entire width of the gluing and synchronous movement rolling out material with a melting device; the melting temperature of the coating layer should be in the range of 140 - 160 °C. A sign of such heating is the transition of the coating layer to plastic, but not liquid state and the absence of blackening and bubbles on the outer surface of the guided web.
- The polyethylene film on the lower surface of the material must be completely melted along with the bitumen mass.
- One of the signs of proper heating of the material is the flow of bitumen mass from under the side edge of the material in a continuous roller, approximately 5-10 mm, which also guarantees the tightness of the seam.
- The deposited rolls should not have folds, wrinkles or waves. To prevent these defects, if necessary, the panels are rolled with soft brushes or rollers, the movements of which should be from the axis of the roll diagonally to its edges while the substrate is softened.
- Rolling of rolls on the roof slope is carried out along or perpendicular to the slope (for slopes of more than 15% - only along the slope).
- Cross sticking of panels of rolls of the first and second layers of roofing is not allowed.
- Laying of rolled material must begin from low areas of the roof (adjacent to drainage funnels, along the valley), across the slopes.
- Temperature-shrinkage seams in screeds must be covered with strips of rolled material 100-150 mm wide. In this case, material with sprinkles is used, laid with the topping down.
- The bonded roll material should be applied with an overlap between adjacent panels 80-100 mm wide (lateral overlap), with an overlap across the web 150 mm wide (end overlap) with preliminary cleaning of the coating strip from the overlap strip of the panel wire brush or with a heated spatula.
- The distance between the side joints of roofing panels in adjacent layers must be at least 300 mm. The end overlaps of adjacent panels of roofing material should be offset relative to each other by 500 mm.
Rolling out the roll must be done in the direction “towards you”, additionally rolling it with a roller. Places of overlap are rolled with special care.



Connection device
The main roofing carpet in places where it abuts vertical surfaces should be placed on the vertical part above the transition side. At the junctions with vertical surfaces, two additional layers of roofing carpet with a base of fiberglass or polyester are glued to the design mark on the vertical surface.
The first additional layer of roofing carpet must extend onto the vertical surface by at least 250 mm. The second layer of material with sprinkling should overlap the first one by at least 50 mm on a vertical surface.
On vertical surfaces, additional layers are mechanically fixed to the base using an edge strip or washers with a diameter of 50 mm. Fastening is carried out using dowels or self-tapping screws on concrete with a pitch of 200 mm.

If rolls of roofing material of the main layers of the roofing carpet are laid parallel to the parapet wall, then the arrangement of the layers changes.
The main layers of roofing material are laid close to the transition side. Additionally, a layer of reinforcing roofing material is laid on the transition side, extending 100 mm onto the horizontal surface.

When the height of the parapet wall is less than 500 mm, additional layers of roofing carpet are placed on the parapet wall. The top additional layer should extend onto the façade of the building by 50–100 mm.

When attaching a parapet apron, the distance between the attachment points is determined by the rigidity of the profile, but should not exceed 600 mm.
The joints of parapet slabs must be sealed with thiokol (polysulfide) or polyurethane sealant.

It is possible to install material on parapet walls up to 1 m high by additionally fixing panels of roofing material to the parapet wall every 500 mm. The top of the parapet wall should also be covered with a galvanized steel apron or parapet slab.
Climatic (weather) conditions
- When working with fused rolled materials, the ambient air temperature and the temperature of the material itself should not be lower than the flexible temperature of the material (indicated by the material manufacturer).
- If work is performed at sub-zero temperatures, it is recommended to keep the rolls in a warm room for at least 1 day at a temperature not lower than +15 °C. Otherwise, the material compressed in the cold will expand under the influence of the sun, which will lead to the formation of waves on the roof.
- Fusing waterproofing is not allowed during fog or when there is frost or frost on the surface of the building structure. In such weather conditions, the base must be dried, for example, using propane torches.
- If it is necessary to carry out work under unfavorable weather conditions (rain, snow), it is necessary to use special greenhouses, awnings, canopies, etc., providing the required working conditions.