These materials belong to the class of lightweight concrete. Each has its own benefits. It is not a subjective opinion that will help to make a choice when choosing, but knowledge of the basic properties of foam concrete and aerated concrete.
What is the difference between a foam block and a gas block. Characteristics
Cellular concrete, from which foam blocks (foam concrete) and gas blocks (aerated concrete) are made - this is a wall material, small pores are evenly distributed in it over the entire surface. The production technology and the main components affect the characteristics of these largely similar building materials.
Video about the difference between foam concrete and aerated concrete (plus polystyrene concrete), comparison.
How to produce
Lightweight concrete is made from environmentally friendly components. The production method has significant differences, but pores appear as a result of different technological processes.
Foam blocks:
- the components are combined, a special foaming filler is added;
- concrete and foam are mechanically mixed;
- hardening takes place in vivo;
- equipment for production affordable for the entrepreneur " middle class". Foam blocks are often produced in small artisanal industries;
- finished products are often uneven surface. Deviations in size are quite significant, which worsens the quality of the masonry.
gas blocks:
- the cellular structure appears as a result of a chemical reaction between the main components;
- to increase strength ready blocks processed in an autoclave;
- aerated concrete can only be produced in the factory on high-tech, expensive equipment; the quality of the material is much higher than that of artisanal foam blocks;
- the geometry of gas silicate blocks is almost perfect. The installation of the structure is progressing at a high speed, the masonry comes out solid and monolithic.
What are they made from
Both types cellular concrete can be safely attributed to environmentally friendly building materials. Some builders are wary of the aluminum powder required for the production of gas silicate blocks. But, in finished products this component is absent.
For the manufacture of foam blocks lime, water, cement, some types of industrial waste are used: blast-furnace slag, and others. An obligatory component is soap or sulfide lye, which form the foam structure of the material.
Composition of aerated concrete: cement, quartz sand, water, lime. An obligatory component is aluminum paste. In its pure form, this component is harmful to human health, but the particles dissolve during the production process.
Video about the production of gas blocks and foam blocks, the difference between aerated concrete and foam concrete.
How to distinguish aerated concrete from foam concrete
Differences between the foam block and the gas block are clearly visible:
- Foam block: gray shade, smooth surface.
- Gas-block: color - white, surface rough, embossed.
Compare the block structure. The differences are visible to the naked eye. The pores of foam concrete are much larger.
Do an experiment:
- Break off a small piece from the gas block and foam block, put them in two glasses
. - Aerated concrete with open pores will quickly absorb moisture and sink to the bottom.
- Foam concrete practically does not absorb moisture. A piece of material will remain on the surface for several days.
- If we compare the foam block and the gas block: what repels moisture better, then the answer is obvious.

Structure
 Foam concrete - closed cell material. Walls built of foam concrete have excellent heat and sound insulation characteristics. The material absorbs water less than aerated concrete. But, exterior decoration is still needed.
Foam concrete - closed cell material. Walls built of foam concrete have excellent heat and sound insulation characteristics. The material absorbs water less than aerated concrete. But, exterior decoration is still needed.
Fine-meshed pores with microcracks- this is the structure of aerated concrete. The material absorbs water more strongly than foam concrete. This feature of the material requires the obligatory application of a special coating that protects against moisture penetration.
Strength
Aerated concrete or foam concrete - which is stronger? This indicator largely depends on the density of the material. Density of foam concrete– about 650–700 kg/m3, aerated concrete density– 450 kg/m3. Perhaps foam concrete should be stronger.
But, thanks to the use modern technologies and factory production gas silicate blocks with a strength of 35 kgf / cm2 and a density of 400 kg / m3 withstand the same load as foam concrete with a density of 700 kg / m3 and above.
Conclusion: aerated concrete is considered a higher quality and durable material. For the durability of buildings, choose gas silicate blocks. Please note that costs will also increase.
Application features
Gas silicate and foam blocks are used in the construction of low-rise buildings. Erected from foam concrete:
- partitions;
- load-bearing walls (not higher than the third floor);
- various types of fences.
Aerated concrete is suitable for:
- construction of partitions;
- erection of load-bearing walls;
- filling frames in monolithic structures;
- durable gas blocks are used for the construction of buildings with a higher number of storeys using a stiffening belt.
What is warmer?
Foam block or gas block? Gas blocks have lower frost resistance than foam blocks, but thanks to the ideal geometry, it is possible to lay on cement-adhesive compositions. High-quality fitting of gas silicate blocks ensures the solidity of the structure, and "cold bridges" are minimized.
Compare:
- thermal conductivity coefficient of aerated concrete with a density of D 500–0.12;
- coefficient of thermal conductivity of foam concrete density from D 700 and above - 0.24.
Foam blocks have high thermal resistance, they accumulate heat well. This fact reduces heating costs. But, to achieve such a result, foam concrete walls should be almost 2 times thicker than those of a house built from gas blocks.
Conclusion: houses made of aerated concrete are almost twice as warm as those built from foam concrete with the same wall thickness. Insulation of buildings and installation of ventilated facades will provide pleasant microclimate in the house.
What is cheaper foam block or gas block? Prices
 Foam concrete or aerated concrete? The cost of equipment for the production of aerated concrete blocks reaches several hundred thousand dollars. Sophisticated technology for the production of high-quality material also requires considerable costs.
Foam concrete or aerated concrete? The cost of equipment for the production of aerated concrete blocks reaches several hundred thousand dollars. Sophisticated technology for the production of high-quality material also requires considerable costs.
Foam blocks are produced in artisanal conditions, often right on the construction site. Equipment costs several times cheaper. The quality and geometry of the finished foam blocks are inferior to aerated concrete.
Conclusion obvious: aerated concrete is more expensive than foam concrete. But, the costs are fully compensated by the durability of the structure. The consumption and cost of glue for laying aerated concrete blocks with ideal dimensions is much lower than the price of a larger volume of cement mortar, which will have to equalize the errors of the sides of the foam blocks.

Which is better: foam or aerated concrete?
In recent years, non-traditional building materials such as gas and foam concrete, or, as they are also called, porous blocks, have become widespread. These are two types of concrete blocks with a cellular structure.
Cellular concrete, due to its pores, has high thermal insulation properties.
The cellular structure of these types of concrete is characterized by high energy-saving qualities. In addition, ease of manufacture and use in construction, relative cheapness in comparison with brick and reinforced concrete brings gas and foam concrete to the forefront of their use in private construction.
Foam and aerated concrete, for all their similarities, have some differences.
Types of concrete
Cellular concrete is fake diamond, which is based on a mineral binder and a silica component with pores distributed throughout the entire volume of the material.

The main components of cellular concrete are cement, lime, sand, water and foaming agents.
The binder may be cement, gypsum, lime, or compositions of these materials. Ground or unground sand or TPP ash is used as a dispersed filler.
They differ in manufacturing technology. Pores in foam concrete are formed when foaming agents are introduced, and in aerated concrete, porization is carried out due to hydrogen, which is released as a result of the reaction between metallic aluminum and alkali.
In the manufacture of porosity is relatively easy to regulate and this allows you to get concrete mixes of different density and purpose.
Concrete density is divided into three groups:

The scope of blocks from cellular concrete is defined by their density (D).
- a group of heat-insulating concretes, the density of which in dried form is 200-500 kg / m³, is used as a heater for floors, walls, roofs;
- a group of structural and heat-insulating concretes with a density of 500-900 kg / m³, used in the construction of enclosing structures and buildings up to three floors high;
- a group of structural concretes with a density of 900-1200 kg/m³, which are used in the production of reinforced concrete.
Materials used in the production of cellular concrete:
- astringent components and additives to them;
- silica component and additives;
- additives that form .
As the main binder in the production of gas and foam concrete with a cellular structure, it is recommended to use low-aluminate Portland cement grade 400 and higher.

Calcium quicklime is used for the production of mortars and concretes.
In the production of foam silicate concrete, cements with short terms setting. The end of setting should be no later than 4-5 hours after pouring.
In the preparation of silicate cellular foam and aerated concrete, calcium quicklime is used. If the quality of the cement used in the production of cellular concrete is low, caustic soda NAOH is added to the aerated concrete.
With an increased concentration of chromium in cement in gas concrete mix add water solution iron sulfate.
The quality of cellular concretes significantly depends on the type of finely ground silica component, which is used as sand, TEC fly ash, and on heat treatment conditions.
The use of finely ground sand makes it possible to reduce the consumption of a binder foam and gas former, but this process requires additional equipment. Grinding fineness is adjustable normative documents and depends on the size of the products.

Aluminum powder is small silver-gray lamellar particles that are used in the manufacture of cellular concrete.
As an additive that provides porosity to aerated concrete, aluminum powder and perhydrol are used. Currently, aluminum powder is introduced into aerated concrete in the form of a water-aluminum suspension, which provides a much better uniform distribution of the gas generator than the introduction of dry calcined aluminum powder into the mixture. To obtain a water-aluminum suspension, surfactants are used that facilitate the mixing of the components: rosin soap, creosote soap or sulphite-alcohol stillage.
The use of perhydrol also involves the use of catalysts or inhibitors. Chlorine is used as a catalyst, and salts of phosphoric acid are used as an inhibitor.
Foam concrete has several foam formers, which are formed from the following materials:
- glue-rosin - glue, rosin, caustic soda;
- aluminosulfonaphthene - kerosene contact, alumina sulfate, caustic soda;
- emolo-saponin - soap root and water.
The foaming agent is prepared in an emulsifier equipped with rotating blades.
Autoclave production method

Aerated concrete combines the best properties of building materials made of stone and wood.
Aerated concrete, like foam concrete, is an artificial porous stone with first-class thermal insulation and energy-saving properties, and low weight.
It is made from a mixture of Portland cement, a silica component and a blowing agent. According to the chemical reactions caused, gas generators are divided into the following types:
- substances that react with the binder component - aluminum powder;
- substances that decompose with the release of gas - perhydrol;
- substances that enter into exchange reactions with each other. As a result of these reactions, a large amount of gas is released - ground limestone and hydrochloric acid.

Gas blocks are easy to process: they can be cut, sawn, drilled and milled with both electric and hand tools.
A standard gas block weighing 30 kg replaces 30 bricks. And the light weight of the blocks allows construction without the use of special lifts, which reduces the cash costs for renting equipment. Aerated concrete blocks are easy to cut and process.
To obtain aerated concrete mix, use:
- water;
- lime;
- cement;
- quartz sand.
The production of cellular concrete is carried out on semi-automatic or fully automated production lines, the cutting of blocks is carried out using wire strings.

The production of aerated concrete in industrial conditions is carried out from Portland cement, lime and sand with the addition of aluminum powder by the autoclave method.
The casting technology for the production of gas-cell concrete provides for pouring the finished cellular mixture into block molds.
The starting materials are dosed and fed into a self-propelled mixer, in which the mixture is mixed for 4-5 minutes. An aqueous suspension of aluminum powder is added, and after thorough mixing, the mixture with aluminum powder is poured into metal molds not to the very top. Leaves space to fill the form to the top after swelling.
Heat treatment of aerated concrete is carried out in autoclaves with saturated steam.
The technological process of production includes the following operations:
- mixing the solution in a concrete mixer;
- pouring the solution into molds;
- swelling of concrete in molds under the action of a chemical reaction;
- removal of "pink salmon" with a string;
- autoclaving to obtain a building material with a set of predetermined properties and characteristics.
non-autoclave method

Foam concrete blocks continue to gain strength over time.
Foam concrete is produced using several technologies. The most widespread is the production of foam concrete in a steam generator and in cavitation plants.
Foam concrete is obtained from a mixture consisting of cement, sand or fly ash, water and foam. Foam is formed in the foam generator from a solution of a foaming agent and water. Changing the ratio of components in the mixture, application different technologies preparations allow you to control the ratio of solid and air phases in the mixture. As a result, it is possible to obtain foam concrete of all three groups: structural, structural and heat-insulating, heat-insulating.
In cavitation plants mixing source materials is carried out in a pressure mixer, without the use of a foam generator, which allows the production of foam concrete in small volumes.
Has a wide range of applications. They build from it:

Foam concrete is made from sand, cement, water and special foam by a mechanical method.
- bearing walls in private construction;
- external enclosing structures in the construction of high-rise monolithic buildings;
- internal partitions;
- thermal insulation of pipelines;
- thermal insulation of technological equipment;
- sound insulation of floors;
- for roof insulation;
- to fill voids for various purposes;
- for the manufacture of building blocks, fences and balcony railings;
- for the manufacture of wall panels, ceilings, various partitions.
Foam concrete has the following advantages: environmental friendliness, durability, absorbs a small amount of moisture, fire safety, and provides good sound insulation.
The production of foam blocks is carried out in three ways:
- in cassette metal molds.
- Cutting foam concrete arrays on cutting machines.
- Pouring concrete mixture into special shapes followed by automatic stripping.
Comparison of types of cellular concrete

Aerated concrete differs in production technology: aerated concrete is autoclaved, and foam concrete is non-autoclaved or mechanical method production.
- Density and strength. Aerated and foam concrete have the same density, and in terms of strength, the indicators are better for aerated concrete.
- In terms of frost resistance and thermal conductivity, both materials have similar characteristics.
- The water absorption capacity of aerated concrete is higher, but it does not affect the quality of the material in construction.
- Cost of materials. This indicator is better for foam concrete, its cost is 20-25% lower than. This is achieved by the low cost of foaming additives.
- Price production equipment. Equipment for the production of cellular gas and foam concrete has a high cost, but the cost of equipment for gas concrete is an order of magnitude higher than the cost of foam concrete.
- The production of foam blocks can be arranged at the construction site.
- The closed cell structure of foam concrete allows it to be used for construction in areas of potential flooding by flood waters.
- The geometry and structure of the blocks is better for gas-cell concretes.
- The properties of gas silicate to absorb and release water are comparable to those of natural wood.
- Gradual construction of structures according to specially developed projects. This indicator characterizes aerated concrete better. It allows you to easily build on and complete the house at any time.
- Aerated concrete requires plastering works, and foam concrete, these works are not required.
The popularity of cellular concrete in the form of blocks is growing from year to year. Foam and aerated concrete are valued for high specifications. In recent years, other products made of cellular concrete have also been in demand: lintels, floor slabs, stair steps.
Didn't find the answer in the article? More information
When erecting buildings, the question of the choice of building material almost always arises. In this article, we will consider two types of materials for building walls: foam blocks and gas blocks, and we will try to find out what to build a house from and which is better - foam block or gas block.
Production technology of gas blocks and foam blocks
These are two types of building materials that are made from different components and in different ways.
Foam blocks
Foam blocks are made of foam concrete - a porous material consisting of cement, sand, water and foam. Sometimes some other ingredients, such as ash, may be added to them. Acquires porous, thanks to the special chemical reagents that are part of the solution. This foamy solution is poured into special molds and, after hardening, finished products are obtained, including foam blocks. Due to the porous structure, foam blocks are lightweight, have low thermal conductivity and good sound insulation. This building material is very durable and strong.
gas blocks
Now, to answer the question of which is better - a foam block or a gas block, consider

Properties also have a porous structure and the same properties that are inherent in foam blocks, but they are made using a different technology. The composition of aerated concrete includes cement, lime, sand, aluminum powder and water. Pores appear when aluminum powder reacts with cement. The mixture is stirred and kept certain time until it reaches the desired condition. Then the resulting array is cut into blocks using special strings. Then they are placed in an autoclave, where all excess water evaporates from them, they acquire their final form and properties, and become ready for consumption. They are light and have good soundproofing characteristics, as well as foam blocks. Gas blocks have high strength and low thermal conductivity. These figures are slightly higher than those of foam concrete, but still it is not easy to determine which is better - a foam block or a gas block due to the many advantages of foam concrete.
Differences between foam blocks and gas blocks

In search of an answer to the question of which is better - foam block or gas block, it must be said that these materials have only one difference - the high hygroscopicity of aerated concrete. Foam concrete, on the contrary, has low hygroscopicity.
What is the best to build
Both materials have many similar benefits. So what is the best way to build a house? The foam block is just as good for this as the gas block. Both materials make excellent one-story and They have thermal conductivity indicators that compete with wood and in many ways surpass ceramic brick. Because they do not include harmful substances, they are environmentally friendly for humans. But gas blocks have one drawback, due to which it is inferior in efficiency to foam blocks - this is the complexity of the technology for building walls from this material, due to its hygroscopicity. Gas blocks are delivered from the factory with a high level of humidity, so after the construction of the house it is impossible to carry out immediately exterior finish. It is necessary to wait several seasons until the walls are completely dry or to equip a ventilated facade, and this leads to an increase in construction costs. So, when determining which is better - a gas block or a foam block, the scales tipped towards the latter because of its efficiency.
A fairly common question on the net is aerated concrete or foam concrete, which is better? Why does he care so much land owners who develop a project for a future home and decide on the choice of materials for its construction? How fundamental is the difference between these very similar materials?
It should be noted right away that both aerated concrete and foam concrete belong to the group of cellular concrete, that is, building materials that have many tiny air cavities in their structural structure, reducing the density and increasing the thermal insulation qualities of the blocks. They are united general concept"gas silicates". However, these materials still differ significantly from each other in their characteristics, which should be studied before choosing one.
Production of building materials from cellular concrete
To understand the differences between aerated concrete and foam concrete, for a start it is worth considering the technology of their production. The fact is that it is during the manufacture of the material that its specific qualities are formed.
Production of aerated concrete
Aerated concrete is an artificially created mineral with a uniform cellular structure.

Due to their structure, aerated concrete blocks are light in weight, so the construction of the walls of a house or other structures may well be carried out without the involvement of lifting equipment. Blocks lend themselves well to processing, and if necessary, reduce their size - the material is easily sawn with a hand saw. In some cases, to speed up this process, a "grinder" or an electric jigsaw can be used.

The process of manufacturing aerated concrete blocks is as follows:
- Materials prepared in certain proportions (sand, cement, lime) are poured and mixed in a dry state in a special mixer for 4-5 minutes. Then a suspension of aluminum powder, made on a water basis, is added there.
- In the process of mixing, lime enters into an active reaction with aluminum, as a result of which hydrogen is formed in a free state. Due to the abundant gas formation throughout the volume of the mixture, bubbles appear in the raw mass, having a size of 0.5 to 2 mm, which are evenly distributed in the solution.
- The finished solution is poured into special forms preheated to 40 degrees. Filling is carried out approximately ½ of the volume of the mold capacity.
- After the solution is poured into the mold, it is sent to the ripening chamber, where the final pore formation occurs, as a result of which the mass in volume almost doubles and gains transport strength. In order to activate the reaction in the solution and to better distribute the composition, the molds are subjected to vibration loads.
- After the solution has reached preliminary hardening, with the help of stretched wire strings, the resulting irregularities are cut off from the surface of the solidified mass.
- After pouring, the finished array is sent from the maturation chamber to the cutting line.
- The next stage of work, the hardened products are sent to the autoclave.
Aerated concrete is often abbreviated AGB, that is, autoclaved aerated concrete, since its production is carried out using this equipment. And the autoclave itself, figuratively speaking, is a kind of "pressure cooker" large sizes, in which a pressure of 12 atmospheres and a temperature of 185 ÷ 190 degrees are injected and then maintained. In such an atmosphere, aerated concrete blanks are within 12 hours.
Aerated concrete prices
aerated concrete

- After ripening in an autoclave, the blocks are additionally separated, since during their processing they can connect in some places.
- Further, the finished products are packed in a heat-shrinkable material or polyethylene - this is necessary to maintain a certain moisture content in the aerated concrete structure before construction begins.

- Finished material can be stored until it arrives at the construction sites within two - three years.
Here it is necessary to clarify that aerated concrete is also produced in a non-autoclave way. In this manufacturing option, the mortar is cured in natural conditions, so high-tech modern equipment is not required for the manufacture of blocks.
However, such material will not have the characteristics that manufacturers of autoclaved aerated concrete claim. The shrinkage of the material during the operation of the built house will be 3 ÷ 5 mm / m, while the blocks that have been processed with the desired temperature and pressure have indicators of only 0.3 ÷ 0.5 mm / m. If we compare the strength, then this parameter for autoclave blocks is 28÷40 kgf / m² against products made in a non-autoclave way, which have a value of 10÷12 kgf / m².
So when choosing aerated concrete blocks, it will never be superfluous to clarify what technology it is produced by.
Production of foam concrete
The production of foam concrete blocks occurs according to a simpler technology. However, to obtain a product with high performance, it is necessary to use quality materials.
Foam concrete, as well as aerated concrete, has a homogeneous porous structural structure, which is formed by artificially creating air bubbles in the mixture. This effect is achieved through the use of special substances that make up the foam concentrate.

There are two ways to manufacture foam blocks - this is cassette and sawing. The cassette method involves pouring the finished solution into separate forms. And sawing technology, therefore, consists in the processes of filling with a mixture of one large capacity, and after it hardens - cutting this resulting array into separate blocks of the desired size.
So, for the manufacture of foam concrete, cement grades M 400 ÷ M500, sand purified from clay impurities, certified foaming agent, calcium chloride and water are used. The foaming agent mainly determines the quality of the foam, therefore, a carefully dosed, proven composition is used for the manufacture of blocks. Poor foaming can not only slow down, but even completely stop the process of hardening the finished solution. In addition, the composition of the foaming agent must comply with the requirements of sanitary and hygienic standards, that is, it cannot contain toxic components.
The production process for manufacturing blocks by the cassette method includes the following steps.
- The first step is kneading cement-sand mortar. Its preparation is not much different from kneading conventional concrete.
- Further, a foaming agent is added to the concrete solution, after which the entire composition is well mixed until homogeneous. It is important to achieve the required air entrainment for quality education foam.

- At the next stage, the foamed concrete solution is poured into molds under pressure.
- Hardening of foam concrete occurs in natural conditions, but the duration of this process, unlike ordinary concrete, is twice as long. It will take even several months for foam concrete to gain final strength. If curing takes place at a temperature below +10 degrees, then the process will take much longer. On the production line blocks can be pulled out of the molds only after two to three days. To speed up the hardening process, calcium chloride is added to the solution in the amount of 1 ÷ 2% of the amount of cement involved in the mixture.
The second version of foam concrete blocks, as well as aerated concrete ones, is produced by cutting or sawing. Cutting the finished foam concrete according to linear dimensions is carried out using special equipment.
Prices for foam blocks
foam block
This version of foam block manufacturing technology has a number of advantages, which include the following:
- The edges and corners of the blocks have a clear geometry, without chips or flaws, which reduces labor costs for their "commodity" processing.
- Ideal geometry simplifies masonry work when building walls.
- There is no lubricant on the surfaces of the blocks, which is used to lubricate each of the forms when concrete is poured into them. This approach significantly improves the adhesion of the material with the masonry mortar, as well as with the finishing material.
- It is possible to cut blocks of different parameters, as the equipment can be adjusted to the required step.
It is these factors that contribute to the fact that many manufacturers are switching to this technology for the production of foam blocks.
So let's highlight fundamental difference in manufacturing aerated concrete and foam concrete:
- aerated concrete - the porous structure is provided by the active release of gas caused by a running chemical reaction. The resulting gas tends to get to the surface, "punching its way", which leads to the open, non-isolated nature of the cells. An increase to a predetermined volume occurs after filling out the forms.
- foam concrete - the porous structure is provided by the light of foam formation with air entrainment (something similar happens when using soap or detergents). The bubble is isolated from the "neighbors", that is, it is created closed cell air-filled structure. The solution immediately reaches the desired volume, and after pouring into molds, it may rather sag rather than rise.
Characteristic features of materials
In this section, we will try to compare the features of materials due to the specifics of their production, and talking about some of their advantages and disadvantages.

- First, let's talk about the quality of the products themselves. Of course, it is impossible to sign for all manufacturers, and for all batches of material, but nevertheless ...
The production of aerated concrete blocks in most cases is carried out in the factory, since this process requires special equipment. Therefore, production technology is under control.
Foam concrete products can be produced both on high-tech equipment and in practically artisanal conditions. Naturally, very often, there is completely no proper control over how the solution is made, what material is used to mix the mixture, they are not maintained set by technology terms of foam concrete maturation.

- Density of materials. The structural density of foam concrete and aerated concrete is classified by the grade of the material. For both materials, this parameter varies from 300 to 1200 kg/m³.
It must be remembered that the higher the density of the material, the lower its thermal insulation qualities, respectively, the higher the thermal conductivity. The density of gas silicates, related to thermal insulation, does not exceed grade 600. Next come thermal insulation-structural and structural block products. Structural blocks high density are made for special purpose objects.
- Strength for compression. The strength of foam blocks can vary and be 0.75 ÷ 12.5 kg / cm², while for aerated concrete this figure is in the range of 1.5-3.5 kg / cm². the specific value depends on the brand of density.
Aerated concrete has the same strength throughout the block. And the foam blocks may also have a heterogeneous internal structure - due to the uneven distribution of the foam concentrate when the solution is mixed. Both materials have low bending strength. Therefore, if they are chosen to build a house, special requirements are placed on the reliability and stability of the foundation - it is necessary to prevent uneven shrinkage of the structure.
Prices for gas silicate blocks
gas silicate blocks
- Maturation (hardening). Aerated concrete. due to features chemical composition and autoclaving, reaches maximum strength already in the first stages of manufacture. But as the storage, as well as the operation of the erected walls, it becomes lower.
Foam concrete gains the necessary strength after 28 days from the date of manufacture - this factor is very important to start construction works. To be sure that the material has good strength, it is recommended to purchase blocks in advance, a month before the start of construction and store them on site. Walls built from fresh foam concrete, not gaining strength, after construction will give significant shrinkage and may crack. If, having already gained the necessary strength, then it will increase during its operation - the older the walls of this material, the stronger.
- Block sizes
It is impossible to say unambiguously about the sizes of both one and the other blocks, since each manufacturer can produce them in different linear parameters. Although there are certain standards. For masonry external walls most often, blocks of 200 × 300 × 600 mm are used, and for internal partitions - products with a size of 100 × 300 × 600 mm.

By the way, the assortment is not limited to thicknesses of 200 and 100 mm. The table below shows other sizes of standard blocks.
| Linear parameters of blocks, mm | Number of blocks in 1 m³, pcs | Number of items on a pallet, pcs |
|---|---|---|
| 100×300×600 | 55 | 80 |
| 120×300×600 | 46 | 64 |
| 150×300×600 | 37 | 48 |
| 200×300×600 | 27 | 40 |
| 250×300×600 | 22 | 32 |
The mass of products made of foam concrete and aerated concrete is almost the same, and the weight differences of the blocks depend on the brand of material. The table below shows the mass of standard wall and partition blocks for reference:
| Block sizes, mm | D300 | D400 | D500 | D600 | D700 | D800 | D900 | D1000 | D1100 | D1200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200×300×600 | 11.7 | 15.6 | 19.4 | 23.3 | 27.2 | 31.7 | 35.6 | 39.6 | 43.6 | 47.5 |
| 100×300×600 | 5.8 | 7.8 | 9.7 | 11.7 | 13.6 | 15.8 | 17.8 | 19.8 | 21.8 | 23.8 |
To know the exact dimensions of the material, they must be requested from the manufacturer who purchase of building materials. In addition to the sizes indicated in the table, other options can be produced. Accordingly, the weight of block products will also depend on the linear dimensions.
- Quality and precision linear forms . Materials made by cutting or sawing have more accurate dimensions - this applies to both foam blocks and gas blocks. This quality allows you to reduce the thickness of the masonry joint to a minimum, literally up to 2-3 mm. Highly useful quality, since masonry joints become cold bridges, since the mortar has a significantly higher thermal conductivity.

- moisture absorption . Due to the fact that aerated concrete has a structural structure with open pores, it is a hygroscopic material, that is, it absorbs moisture well. Unlike aerated concrete, foam concrete absorbs moisture 8-9 times less.

So if you lower two materials into water for a while, then aerated concrete will absorb moisture by 45 ÷ 47% of the total volume of the block, while foam concrete will be moistened by no more than 5%. This method can be used for exact definition what material the seller offers, since at first sight sometimes it is impossible to determine that it is aerated concrete or foam concrete.
Aerated concrete will become much heavier, foam concrete will practically not change its mass. Naturally, it will be difficult to check the material in the conditions of a retail outlet, therefore, in order to check the honesty of the seller, it is worth buying one block, placing it in water at home, leaving it for a day, and then splitting it. If it is aerated concrete, then it will be saturated with water halfway into the depth of the block. Foam concrete will get wet no more than 15 ÷ 20 mm.
With a sharp change in the weather, for example, if after long autumn rains that saturate the aerated concrete with moisture, the temperature drops sharply, the moisture in the structure of the material will turn into ice. As a result, an unprotected structure may become covered small cracks. And such damage is quite capable of becoming the “beginning of the end”, that is, erosion and destruction of the wall.

Therefore, it is necessary immediately after solidification masonry mortar cover with plaster. Such a finish should protect the surface of the walls from moisture penetration.
- Porosity of materials. Active moisture absorption aerated concrete is explained by the fact that the pores of the material remain open. Often its surface on the cut resembles a sponge. Closed pores form in foam concrete, which makes the material hydrophobic, and if it is immersed in a container of water, it will stay on the surface like a float for a long time.

- Thermal conductivity. With the same brand of block products, they have different thermal conductivity. Thus, aerated concrete is a more effective thermal insulation than foam concrete. For example, for a house that is planned to be built in middle lane In Russia, it will be enough wall thickness (if you do not use other thermal insulation layers) built from D 500 brand blocks from aerated concrete - 450 mm, but from foam concrete it should have a thickness of at least 600 mm.
- Vapor permeability. A high level is characteristic of both types of gas silicate, but still it is not the same. Vapor permeability contributes good air exchange in the premises of the house, as a result of which a favorable environment for the appearance of fungal or mold colonies is not created on the inner surfaces of the walls.
Aerated concrete has a higher permeability. When building a house from foam concrete blocks, it is necessary to provide effective system ventilation, since the vapor permeability of this material is slightly lower.
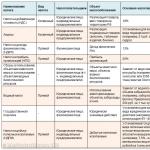
This comparative table presents the absolute various parameters of aerated concrete and foam concrete. Based on them, you can determine which of these materials is more suitable for building a house:
| Name of parameters | aerated concrete | foam concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Foaming components | Fine aluminum and lime. | Wood-saponified resin, classified as a moderately hazardous substance. |
| Manufacturing methods | block cutting | Cassette and rifled |
| Place of manufacture | Factory production only | Factory or handicraft production |
| Structural structure | Uniformly porous with open pores of equal size. | Heterogeneously porous with closed pores, with a spread in their sizes. |
| Material density, kg/m³ | 200÷1200 | 200÷1200 |
| Compressive strength, for grade D400, MPa | 2 | 1.2 |
| Curing time from the moment of manufacture | Immediately upon freezing | Not less than 28 days after manufacture, followed by permanent curing. |
| Frost resistance, cycles | 25 | 35 |
| Thermal conductivity W/(m K) | 0.1÷0.19 | 0.2÷0.36 |
| Moisture absorption, % per day of constant contact with water. | Up to 47% | 0.05 |
| Linear dimensional accuracy | Minimum errors | When sawing a whole solid filled block - minimal errors, when manufacturing in a cassette way - significant flaws in the "geometry" are possible. |
| Masonry shrinkage, mm/m² | 0.5 | 2÷3 |
| Vapor permeability, mg/m×h×Pa | 0.16÷0.23 | 0.9÷0.11 |
Requirements for laying materials and surface finishes
In addition to the characteristics of each of the materials, it is necessary to have information about the features of the construction of walls and partitions from foam blocks and aerated concrete.
- Building foundation requirements, erected howfrom foam concrete, and aerated concrete, are the same, since both materials have a small weight. However, the base for the walls must be strong enough, especially what hygroscopic aerated concrete, even covered with a plaster layer, becomes almost twice as heavy at high humidity, which increases the load on the foundation. Although foam concrete does not significantly change its weight when wet, it, like aerated concrete, rather fragile material, so a reliable basis for it will also not be superfluous.

The horizontal surface must be covered with a waterproofing layer. In this way, the masonry material can be protected from capillary entry of moisture into it from the side of the concrete base, which is in direct contact with moist soil. As a waterproofing, the well-known roofing material is most often used, laid on inflicted bituminous mastic on the concrete surface.
- Cutting, drilling holes, chasing cellular materials are produced in the same way - cutting can be carried out using a conventional hand saw, and drilling holes using a drill and a crown drill of the required diameter. Due to the fact that the material is porous, the cutting process is quite easy.
- Construction speed. Both materials are light in weight, and the linear parameters are much larger than the dimensions of a brick. In addition, the surfaces of the blocks have a sufficiently high adhesion, so the walls can be raised quickly. Especially in those cases when the work will be carried out with the involvement of assistants.

- Block mortar. For laying foam concrete, ordinary concrete mortar or special masonry glue can be used. Aerated concrete is placed on an adhesive mixture specially designed for this material - this will help to significantly reduce the consumption of the solution, since a 3 ÷ 4 mm seam will be enough to fasten the blocks.
- Construction conservation. If necessary, stop work on building a house on winter period, the object is conserved. Moreover, foam concrete walls will last this period without compromising their strength, while aerated concrete must be covered with a waterproof film so that the material does not absorb even atmospheric moisture from environment. It is also necessary to clarify here that aerated concrete during conservation of a construction site requires protection against moisture at any time of the year. But the greatest damage can be caused to the material by autumn rains, a sharp drop in temperature, as well as spring snowmelt.
Prices for ceramic blocks
ceramic block

- Retention of fasteners. Both materials require a special approach in this matter. However, d for porous building materials today in specialized stores you can find a wide range of special self-tapping screws, hardware, " chemical anchors» and other mounting options.
- Finishing materials for porous surfaces. For finishing facades built of gas and foam blocks, plaster mortars, lining, siding, etc. In this matter, with the correct layout of the "facade pie", there are no restrictions.

- Warming materials. Due to the porous structure of these materials, they themselves are very good heat insulators. Therefore, in many cases additional insulation the walls of the house are not even required. However, if such a need nevertheless arises, for example, a house is being built in a region with cold winters, then a heater is used for thermal insulation. And for external insulation it is best to use basalt mineral wool with excellent vapor permeability.

- plaster mixes. Not all materials will fit here. For finishing porous materials, special plaster mixes that keep them high level breathability. With aerated concrete surfaces, such mixtures have good adhesion, but before applying them on foam concrete a reinforcing mesh is fixed on the wall surface, which ensures higher adhesion of the mortar with the smooth surface of the blocks.
What and how are walls made of gas silicate blocks plastered with?
This work requires special care. how plan preparation of surfaces, and in the choice of plaster and adherence to the technology of its application. Details can be found by clicking on the link to the article of our portal.
The cost of gas silicate building materials
An important issue is the price of building materials. Quite understandable - any future owner At home, during its construction, he is trying to find the most acceptable option, that is, the optimal price-quality ratio.
Therefore, you need to know that aerated concrete will cost on average 20% more than foam concrete. The latter is a more affordable material, since its production is not so complicated and energy-intensive, and does not require high-tech equipment. However, due to the possibility of manufacturing foam concrete even in "garage" conditions, with all the necessary components, a very large number of handicraft materials are found on the construction market. Accordingly, such products do not have all the qualities of blocks manufactured in compliance with the technology in the factory.
When calculating the cost of materials for building a house, it is necessary to immediately take into account not only the price of the blocks themselves, but also the cost of the components of the solution or the finished mixture, the consumption of which will directly depend on the quality of the block products. In addition, when using , you may need steel mesh for reinforcing wall surfaces, and for aerated concrete - waterproofing materials so that at any time you can create protection from the weather. Only by counting everything necessary for the construction, you can accurately determine which of the materials will cost less.
Now, knowing the qualities of both materials and taking into account the peculiarities of the local climate, you can choose the option that is more suitable for specific conditions operation.
And to determine the required number of gas silicate blocks, perhaps the calculator below will help many.
The choice of building material - milestone pre-training building a house. Comfort, coziness, warmth of the structure depend on it. Lightweight, porous materials are popular in modern construction. It remains to choose - aerated concrete or foam concrete. Gas blocks and foam blocks are cellular materials. The main difference is the way air bubbles are formed inside, their technical characteristics. It is worth comparing two materials, identifying similarities and differences between them.
aerated concrete
The name of the gas comes from the manufacturing process. You can distinguish aerated concrete block by white color, rough surface with fine pores. Gas composition:
- quartz sand;
- Portland cement;
- water;
- aluminum shavings, lime.
The result of a chemical reaction is a gas that promotes the formation of aerated concrete. When released, the gas forms pores (small cracks). Advantages:
- Lungs, big size elements allow you to quickly, without the necessary heavy equipment, erect partitions of the building.
- Correct geometric shape.
- Good thermal insulation keeps the heat in in the winter and keeps the room cool in the summer.
- Due to the porous structure, the material has good breathability.
- Easily amenable to external processing.
- Environmentally friendly product. Natural components are not harmful to health. The aluminum included in the composition is a harmful component, but during the process it dissolves in total mass, loses harmful properties.
Flaws:
- High moisture absorption. By placing aerated concrete blocks on the street, having correctly made a system of ebbs, nothing critical happens when moisture is absorbed, the material is not inferior to foam concrete.
- Insufficient density in aerated concrete makes the elements brittle.
Despite the stated disadvantages, correctly selected parameters will allow you to build not only partitions, but also any type of building walls.
Production
On the initial stage the components included in the composition are measured by required quantity mixed in a special mixer. The resulting mixture is poured into a mold, left to acquire the primary setting. According to the method of acquiring strength, blocks are divided into the following types:
- Autoclave. Hardening is facilitated by high pressure, with the addition of water vapor.
- Non-autoclave. Cures the material in natural conditions. It is possible to use steam, heating with electricity, but the pressure does not increase.
Aerated concrete blocks belong to the first type. The strength of the autoclaved material is much higher than that obtained strength in natural conditions. The autoclave method is used only in the factory. For the appearance of porosity, aluminum paste is used. The interaction of aluminum, water leads to an increase in the volume of the mass. After pre-setting, special tool raw materials are cut into equal gas blocks. Construction material placed in an autoclave, where the effect of pressure, temperature, steam, finally adds strength to aerated concrete.
Foam blocks
 Signs of foam material: grey colour, smooth surface, closed porous cells. The composition of foam concrete includes:
Signs of foam material: grey colour, smooth surface, closed porous cells. The composition of foam concrete includes:
- Portland cement;
- water;
- special chemical additives.
Advantages:
- High frost-resistant, heat-shielding characteristic.
- The closed pore structure does not allow moisture to pass through.
- Has good durability. Although in comparison with aerated concrete, the strength is lower.
- Chemical blowing agents are used to form porosity.
- Imperfect geometry.
- The structure of the foam block lends itself to temporary changes.
Production
First, using an industrial mixer, prepare the usual cement mortar, the ratio of components is maintained, according to the future strength. Foam is added to the mixed mixture, thoroughly mixed. After that, the finished solution is distributed into molds. Foam concrete blocks gain strength, harden in natural conditions. The initial setting of the mixture occurs in the first hours after the distribution of the solution. Then the foam blanks are loaded onto a pallet and removed for subsequent drying. The drying process takes 2 to 3 weeks. This time is enough to be able to use . The final strength of the foam block is gaining in six months.
Comparative technical indicators

Foam concrete or aerated concrete is produced according to the same building standards deviating from them is strictly prohibited. It would seem that the difference should be minimal, and technical specifications the same. Let's try to compare, distinguish indicators and find out what is more reliable - aerated concrete or foam concrete?
Strength
The density of materials ranges from 300 to 1200 kg per m³. A comparison of gas and foam concrete of similar density shows that the second option is less durable. The quality of the chemical blowing agent directly affects the strength of the product. Many manufacturers save on it, since the price of foaming additives is high. In addition, it does not differ in the same strength of the material over the entire area. Aerated blocks are homogeneous, the same strength at different points of the material.
Hygroscopicity, cold resistance
These indicators are influenced by the dissimilarity of production methods. Aerated concrete strongly absorbs water, in foam concrete water absorption is lower. In practice, the outer part of the materials can be processed - they are covered with plaster, tiles, so they do not always pay attention to the hygroscopicity index. In this indicator, gas blocks lose before foam concrete.
Safety
In the autoclave method, a chemical reaction takes place between lime and aluminum paste, as a result of which hydrogen is released. In the process of hardening, it does not completely evaporate from the materials, it partially disappears during the construction process. This gas is not considered bad, it does not bring harm to health.
Used do not contain harmful substances, and the pores are hermetically closed. It follows that the two construction products are not harmful. When choosing a material, the safety criterion should not be used as a determining factor.