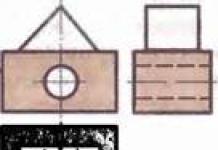
The set of rules for foundations and earthworks SP 45.13330 regulates the backfilling of foundations. Technical standards TR 73-98 provide rules for compacting the materials used. General principle is to apply inert materials from the outside, any from the inside.
The question of how to fill the foundation inside is relevant both for floors on joists and for floors on the ground. The choice of material and compaction technology depends on the following factors:
- type of operation - in buildings permanent residence heating is year-round, the soil under the base of the house does not freeze, so you can even fill it with clay, which will not swell in the absence of moisture and freezing;
- ceiling/floor structure - if the project includes a ceiling on beams, it is cheaper to fill inner part clay, for the footing of a floating floor on the ground, sand is necessary to level the base at least in the upper level (minimum 10 cm layer);
- the height of the base part - for large volumes it is more rational to use soil from the building site, taken out of the trenches; to fill the concrete footing, the very top should be filled with sand;
- GWL level – at high groundwater It is preferable to fill with crushed stone, if the aquifer (“upper water”) is 1 m from the base of the foundation, sand should be used to save the construction budget.
Attention: Clay castles prohibited outside, although the technology was described in the old SNiP. Clay does not allow moisture to pass through, but absorbs intensely, which is dangerous due to uneven swelling, not only when freezing, but also when swelling.

When backfilling, layer-by-layer (20 cm) soil compaction is required.
Don't neglect filling out internal space strip foundation cells in the manufacture of floor joists:
- the underground is too low for normal operation;
- the soil inevitably releases vapors that are harmful to power structures buildings;
- ventilation is required, heat loss through the floor of the lower floor increases;
- Harmful radon is often released from pits, from which the home will have to be protected with foil materials.
Backfilling before the ceiling will allow you to solve all the problems comprehensively and improve the quality of operation.
Materials
Almost any soil is allowed in the internal backfill, but large stones (more than 25 cm) must be excluded from them and, if necessary, longitudinal drains must be laid, including them in the general contour located around the perimeter of the house (only with high groundwater level). Depending on the heating mode, groundwater level, freezing depth, the width of the shell of non-metallic material around concrete structures is:
- heating is constant - there are no restrictions; with proper compaction, backfilling with clay is allowed;
- periodic heating - a 20 cm layer of sand or ASG is enough interior walls foundation;
- freezing 1 m, no regular heating - sinuses 20 cm filled with inert material;
- freezing 1.5 m, without heating - 30 cm layer of non-metallic material near the tape;
- freezing 2.5 m – width of the sinuses 50 cm minimum.

The depth of filling the sinuses is calculated from the planning mark (usually the blind area), and is ¾ of the depth of the base of the strip foundation.
Technologies
Compaction of clay, sand, sandy loam and other materials is not required inside the foundation tape in the only case - when making floors on joists. If you plan to pour a screed, any of these materials must be compacted to a density of 0.95 units. To do this, you need to use manual rammers or vibrating plates.
You can determine the quality of the compaction visually - as soon as traces are no longer imprinted on the soil, you can pour 5-10 cm of the “concrete footing” screed. It is not recommended to spill sand, sandy loam, or loam with water, so as not to saturate the underlying horizons. Instead, the backfill material is moistened to the following values:
- 15 – 23% heavy soils (including dusty ones), waterlogging no more than 1%;
- 12 – 16% – light loams, waterlogging coefficient Kp 1.15%;
- 9 – 14% – light sandy loam, Kp 1.25%;
- 7 – 12% – coarse sandy loam, Kp 1.35%.
You can pour the screed after the soil has completely dried. When filling any monolithic foundation footing is used. This structural element allows:
- reduce the height of the protective layer;
- prevent the leakage of cement laitance into the lower layer with high drainage characteristics;
- protect the waterproofing layer of the foundation base.
Therefore small sand layer on top of loam, sandy loam, crushed stone or clay will further level the base and reduce concrete consumption.
Backfilling outside
Unlike the internal perimeter, which cannot freeze (with a heated building), the soil adjacent to the outer edges of the foundation is not protected from the cold. It swells unevenly and tends to pull out the concrete structure by tangential forces. The problem is solved by the following methods:
- backfilling of the foundation cavities with non-metallic material (minimum 20 cm sand, crushed stone shell);
- insulation of the blind area - 60 - 1.2 m tape around the building pushes back the freezing zone;
- sliding-creased thermal insulation – rigid fixation of extruded polystyrene foam high density EPPS to the outer walls of the foundation, covering with two layers of a plinth fixed at the level polyethylene film, installation of sheets of PSB 25 (minimum density of polystyrene) vertically close to the film without fastening (held by sand powder).

When heaving forces occur, soft polystyrene crumples and rises up a perfectly smooth film without causing damage to the underlying layer of thermal insulation. In the spring, structural elements arrive original appearance after reducing the soil volume.
Materials
The possibility of freezing of the soil adjacent to the foundation from the outside is always present. Therefore, despite the insulation of the blind area, the sinuses of the trenches are filled from the outside with sand, ASG or crushed stone, depending on the groundwater level. For normal operation of concrete structures, a shell density of 0.95 units is required, so non-metallic materials are poured in layers of 10 - 20 cm, compacted with a vibrating plate, hand tools. Spilling sand is not recommended, because... there is a danger of erosion of the lower layers (relevant for silty soils).

Therefore, when backfilling with sand, it is necessary to moisten the material abundantly before placing it in the sinuses. Natural shrinkage takes time, so it is better to rent or make a vibrating plate yourself, reducing the compaction time to a minimum.
If the groundwater level is high or there is a possibility of its seasonal rise, crushed stone should be used. The gravel material is inferior to this non-metallic product in terms of its main characteristic - flakiness. Therefore, shrinkage during operation is possible, leading to deformation of the blind area.
Technologies
Filling the sinuses from the outside with sand or crushed stone allows you to completely eliminate swelling of the layer adjacent to the foundation. However, all non-metallic materials have excellent drainage properties. Therefore, ring drains at the level of the foundation base are prerequisite normal operation.

Scheme of ring drainage around the base of the foundation.
When filling the sinuses, it is necessary to ensure that there is no shrinkage during operation. This is only possible by compacting materials with vibrating plates and hand rammers. The maximum effect is observed when preventing mutual penetration of inert materials and neighboring soils. The technology looks like:
- laying geotextiles or dormite on the walls of the sinus;
- backfilling the outside with sand or crushed stone in a 10–20 cm layer;
- compaction with a tamper or vibrating plate.
If a deep foundation strip is being poured, horizontal thermal insulation (5 cm sheets of high-density extruded polystyrene foam) must be laid at an area of 30–40 cm from the surface, after which the work must continue.
In MZLF tapes, the depth usually does not exceed the specified level, so thermal insulation is laid outside along the bottom of the trench by default. Backfilling is done on top of it.
Advice! If you need contractors, there is a very convenient service for selecting them. Just submit in the form below detailed description work that needs to be done and you will receive offers with prices from construction teams and companies by email. You can see reviews about each of them and photographs with examples of work. It's FREE and there's no obligation.
The foundation is not only the basis of any building, but also the guarantor of the durability and strength of the building. Exactly right choice and compliance with a strict sequence of work, as well as the competent selection of materials used in the construction of the foundation guarantee its reliability and compliance with the required quality standards. The main purpose of this part of the house is to provide the future structure with a stable and strong platform. Properly prepared and packed sand and gravel cushion under the foundation is able to provide it with less settlement. Thus, a reliable pillow helps to significantly improve its quality performance.
 In the event that the construction of the foundation is carried out without observing the necessary building codes and contrary to existing and time-tested rules, the building was built in a very short terms may become completely uninhabitable. In this case, cracks appear on the surfaces of the walls, window frames become warped and the doors stop closing tightly. All this leads to the appearance of mold, dampness, and drafts.
In the event that the construction of the foundation is carried out without observing the necessary building codes and contrary to existing and time-tested rules, the building was built in a very short terms may become completely uninhabitable. In this case, cracks appear on the surfaces of the walls, window frames become warped and the doors stop closing tightly. All this leads to the appearance of mold, dampness, and drafts.
The renovations and decoration of the premises lose their attractiveness. Owners of such unsuccessful buildings have to invest additional funds, time and money in unexpected repair work.
Compliance with all requirements for foundation construction will help you avoid disappointment. And its correctness depends on how exactly the sand and gravel cushion under the foundation was made. It is rightfully considered the key to a strong and durable foundation. The cushion ensures the complete absence of contact between building materials and construction objects and the foundation itself, which, in turn, eliminates the occurrence of various deformations. Thanks to the presence of a properly selected and prepared cushion, the building (at its very bottom) rises high in relation to groundwater.
A mixture of sand and gravel is one of the most popular and frequently used building materials. Both of these components, mixed in exact accordance with the recommended proportions, are very often used for construction residential buildings, shops and other buildings. This seemingly simple composition is one of the most best options basics. It guarantees the strength of the concrete or cement mixture.
Why do you need a pillow under the foundation?
Those who are thinking about making the foundation for the building themselves should pay attention to clearly formed building regulations regarding this issue. First of all, it is important to comply with all the requirements for such a stage of work as the installation of a sand and gravel cushion. In addition to a cushion made of a combination of sand and gravel, foundation cushions made of concrete and crushed stone are common. As a rule, a concrete pad is required only when used under FBS blocks reinforced belt or with additional expansion of the foundation walls. 
The sand-gravel cushion is made on construction sites with weak-bearing soil. It is important to remember that under no circumstances should you use sand dust or fine-grained sand to form it. The ready-to-use mixture must consist of gravel and sand, which have medium particle sizes. After a pillow made from this composition is laid, it will give minimal shrinkage, to ensure which it is necessary to carefully compact it. Such a base for the foundation will perfectly withstand the load of not only a medium-sized house built from frame building materials, timber or logs, but also large buildings, for example, with an attic or second or third floor.
When constructing a sand and gravel support, you can use the following work option:
- dig a trench of the required width and depth down to the level of dense layers of soil;
- in the ditch, which thus turns out, it is necessary to fill river sand coarse grade;
- sand should be poured in layers and in small portions. Each layer should be 15 cm thick;
- after laying each new layer, it must be spilled with water;
- all layers are compacted using special tamping equipment;
- the finished support should have a width 10 mm greater than the planned width of the future building.
The need for a sand-gravel cushion in construction, not only of low-rise buildings, but also of larger ones, is determined by its relatively affordable cost, high degree of durability and the ability to carry out the work with one’s own efforts, without the help of professional builders. However, it should be taken into account that such little things as cleaning the trench after an excavator, filling sand and gravel with buckets or a wheelbarrow, and manually watering all layers with water will require workers to invest serious physical effort. It may be entirely justified to try to involve family members or friends in the process.
DIY sand and gravel pillow
Every experienced master builder knows why a sand and gravel cushion is needed. Such a base for the foundation can ensure full functioning of the subsequently constructed building without defects or damage. It must be remembered that layers of sand-gravel mixture are laid layer by layer, but in different thickness each such layer. The fact is that this issue is fundamental for each individual type of soil. In no case should the layer of sand and gravel be less than 5 cm thick. Many builders do not welcome a cushion thickness of more than 25 cm.
It is advisable to install a cushion under the entire area of the building. It is this method of installation that ensures the most uniform settlement of the structure. The width of such a cushion should be no less than 30 cm wider than the width of the foundation base. Thus, the structure is supported over its entire surface area. When laying a sand-gravel cushion, it should be compacted so intensively that it acquires a density equal to 1.6 g/cm3 of the density of the soil layers.
When doing this work yourself, monitor the quality of the building materials used. So, for example, the presence is not even large quantity Clay impurities in sand can lead to serious unpleasant consequences. If water gets into such a pillow, it will begin to swell. Therefore, monitor the composition and condition of the materials used, and also be sure to follow the recommendations and step by step instructions at all stages of work. 
Many novice builders think about when and how to make a sand and gravel pillow with their own hands. The solution to this problem is quite accessible to anyone who wants to do it. And since laying the foundation is the first step towards the construction of any building, a serious and responsible approach is required to its implementation. The depth of the foundation is primarily determined by the level of water flow in the ground. With a large foundation laying depth, a sand and gravel cushion cannot be used.
Having decided what a sand and gravel cushion is, you can begin installing it, which basically boils down to the following:
- it resembles a kind of “pie” with layers of sand and gravel (you can use crushed stone);
- the first layer in the dug trench (pit) is rubble, which will provide additional strength;
- the second layer is coarse river sand, which, after spreading over the entire surface, must be leveled, watered and compacted;
- the third layer, at least 20 cm thick, is gravel. After laying, it is compacted using a vibrating plate;
- the finished layers are covered with a layer of sand equal to 20 cm. After it is watered, it settles onto the gravel.
This technology must be followed layer by layer until the wet sand has nowhere to settle. After finishing the work on making the pillow, you can begin building the foundation.
Subtleties of constructing a shallow foundation
The shallow foundation is a monolithic strip, mainly made of reinforced concrete. The height of such a tape is from 40 to 60 cm, and its width is 35 – 50 cm. These indicators depend on the thickness of the walls and the materials from which they are built. Laying such a foundation under the building is carried out under all external and internal load-bearing walls.
Very important point The construction of such a foundation can be called the installation of the correct pillow, in which only components that are not subject to heaving should be used. Ideal ingredients for her sand and gravel will become. In this case, the ratio of these components may be approximately as follows:
- river sand of large fractions – 60%;
- gravel – 40%.
This mixture replaces the soil and is placed at the bottom of the prepared trench. Most often, the depth of the trench is about 50 cm. All laid materials are subject to compaction. This bedding significantly reduces the impact of heaving forces on the foundation during frosts. The sand-gravel mixture neutralizes and springs the impact on the base of the structure from below.
To the benefits shallow foundation include its low cost and lack of high labor intensity. However, with this choice, the size of the future building is limited, for example, the walls should not exceed 7 m. Regarding the device basements, then with this type of foundation they are not provided.
Laying the foundation of a house is the first and most important stage of construction, but this is preceded by preparing the foundation under the entire building area on the site.
The type of foundation, its design and characteristics depend on the bearing capacity of the soil at the construction site, as well as the strength of the house that will be built subsequently.
Even at the design stage, it is necessary to determine the properties of the soil and determine which backfill for the foundation, sand or crushed stone, will be relevant as preparation.
It is somewhat incorrect to raise the question of choosing a backfill for a foundation made of sand or crushed stone. The key to a strong and stable home is a strong and reliable foundation, which must meet a number of requirements:
- High strength and density of the soil, capable of withstanding the distributed load of further development;
- Groundwater should not linger under the foundation, therefore the high drainage capacity of the soil is important;
- When wet or dry, the base should not lose its basic characteristics.
- It should not contain organically active components;
- The presence of flammable or plant residues capable of rotting is not allowed.
- Cold heaving of the soil is not allowed;
- Uneven shrinkage or deformation is not allowed.
In progress construction work the foundation should not deform even under the load of the involved construction equipment or the activity of builders.
The strength of the surface layer should be sufficient to accommodate all necessary elements, such as reinforcing frame, formwork, etc.

bedding device
Since it is not possible to select the type of soil on the site in advance, you should work with what you actually have. If the soil does not meet the specified requirements, a foundation filler is used from:
- sand;
- gravel;
- sand and gravel mixture (SGM);
- wood chips (crushed rock fragmentation type);
- crushed stone;
- skinny concrete.
Since the properties of each of the listed materials differ, as do the methods of their use, the choice of backfill should be made based on the final requirements for the base under the foundation.
The main conclusion: backfilling the foundation with sand or gravel is needed to adjust the properties of the soil on which the house will be built. It is part of the foundation preparation activities and is not an absolute component.
Anyway the type of soil is first determined optimal type foundation(tape, pile, monolithic slab, etc.) and after that, if necessary, select the type of bedding that will be required.
High-quality training under strip foundation or monolithic slab is pouring the bottom of the pit with lean concrete to level the level and prepare a solid foundation. Sand or gravel are for the most part a cheap alternative to reduce total costs for construction.
Sand
Simple and enough effective option foundation fillers. Well compacted mechanically the sand cushion is capable of taking on the same strength and density as the main soil, and at the same time is easily molded to accommodate all the unevenness of the bottom of the pit. 
Advantages of sand for backfilling:
- With high-quality compaction, you can achieve a foundation strength equal to the original value for the soil;
- Fills all the unevenness of the pit well and transfers the load evenly;
- Sand retains drainage properties;
- Easily shaped and leveled;
- Does not require the use of heavy construction equipment.
Flaws:
- Weak mechanical strength transverse point load.
- Sand is washed away by groundwater over time.
Sand for backfilling is ideal when using ready-made reinforced concrete blocks and slabs, allowing the load to be transferred evenly over the entire base.
Sand for backfilling is selected from coarse and medium fractions without clay inclusions. Even with complete compaction, the drainage properties of the base are preserved, and cold heaving has almost no effect on the strength of the base.
The thickness of the bedding can range from 10 to 60-70 cm depending on the properties of the soil. The depth of soil freezing in many regions of the country exceeds 30 cm, and cold heaving can appear even under a well-insulated foundation during prolonged winter cold spells.
The optimal height for adding sand is considered to be 45-60 cm. Such a layer of sand is difficult to compact at a time, so the material is gradually filled in layers 5 cm thick and gradually compacted and necessarily moistened.
It is quite difficult to determine the required amount of water to moisten the sand. A common mistake is excessive moistening of the sand, from which the entire mass becomes plastic and diverges more to the sides of the tamper than becomes compacted.
The volume of liquid should be determined individually so that the sand is easily crushed in your hands, maintaining the shape of a cake. On the other hand, during mechanical compaction, water should not come out on top of the sand.
The degree of sand compaction is determined quite simply. If there are no traces left on the prepared sand cushion when walking on it, then the base is ready for further work.
Gravel
 Medium and coarse gravel is used for backfilling in situations where the maximum throughput of the drainage layer should be ensured under the base of the foundation in combination with distributed drainage system, aimed at draining groundwater from the base of the foundation.
Medium and coarse gravel is used for backfilling in situations where the maximum throughput of the drainage layer should be ensured under the base of the foundation in combination with distributed drainage system, aimed at draining groundwater from the base of the foundation.
Gravel is often used as a cheap substitute for lean concrete when preparing and strengthening the soil for a foundation. To do this, it is compacted and mixed with the soil mechanically or manually.
However this is not best solution, since without a binder, which can be cement, such a base is susceptible to erosion by groundwater with subsequent loss of load-bearing strength.
More often in demand is ASG - a sand and gravel mixture to form a level area under the foundation. In combination with sand, the mixture is easier to impart density and strength comparable to that of the parent soil on construction site, while maintaining the drainage capabilities of the bedding.
Advantages of gravel backfill:
- The water capacity of the substrate is low, liquid is poorly retained in it, and the surface area of gravel for wetting is much lower than that of sand;
- Bedding strength and high load capacity and resistance to erosion or lateral loads.
Flaws:
- Under heavy loads, even distributed, gravel bed can “sink”, reducing its own strength and the strength of the parent soil;
- It is difficult to level the bedding surface;
- When pouring concrete, part of the laitance falls aimlessly through the bedding, weakening the main body of the foundation.
If gravel is used for backfilling under a strip foundation or monolithic slab, then, of course, it should be pre-insulated to prevent the concrete from weakening. However, this often entails more costs than when using initially lean concrete.
Which is better sand or crushed stone
The requirements for preparing the foundation pit for the foundation require strict instructions in the construction project based on an analysis of the bearing capacity and properties of the parent soil.
The best preparation for a strip foundation or monolithic slab is lean concrete and only in some cases is it possible to replace concrete with sand, gravel or ASG to reduce overall costs. At the same time, sand has a wide range of advantages and is more practical. 
Gravel is suitable only in cases where high throughput if necessary, arrange a drainage layer with low water capacity. At the same time, it is difficult to isolate the bedding from the volume in which the foundation will be poured.
The gravel backfill goes well with pile foundations, where it is enough to remove excess moisture from under the foundation of the house, and at the same time there will not be a significant load on the bedding itself.
Under strip foundation
By definition, sand bedding is needed only if ready-made reinforced concrete slabs and blocks to distribute the load evenly along the base plane.
With the help of sand it is easier to level the bottom of the pit, and tamping gives the sand the necessary density and load-bearing capacity.
However, this is only relevant if it is possible to place a massive vibrating plate in the trench for mechanical compaction of sand. In most cases, it is safer to use a lean concrete footing to level the base and prepare it.
Sand is also relevant in case of significant differences in height along the bottom of the prepared trench. To reduce costs and reduce the volume of solution for the concrete base, sand or crushed stone is added with layer-by-layer compaction and moistening.
Under a monolithic slab
It is important to strictly level the base of the pit and prepare the soil for installation of the reinforcing frame and pouring. Either lean concrete or sand compacted in layers is used.

stages of construction of a monolithic foundation
Sand is mainly used in cases where it is necessary to significantly raise the bottom of the foundation pit after removing the entire fertile soil layer to the base of the parent soil.
When forming the bedding, it is important to pre-distribute trays for water drainage, communication lines that will pass through the foundation slab, and also mark the required planes of the future foundation.
According to the requirements under monolithic slab the base is formed not strictly in one plane, but with a slight elevation in the center of the building and with a slope of 2-3% in all directions, for effective removal of moisture from the substrate of the future foundation.
Particular attention is paid to the quality of sand compaction. So, the density of the backfill for the foundation should be from 1.65 t/m3 and preferably not less than the density of the parent soil with an error within 0.05 t/m3.
The height of the backfill is determined as the difference between the level of the bare base of the soil after removal of the fertile layer and the design level of the foundation base.
Under a pile foundation
The backfill primarily performs the function of drainage to drain groundwater, and also acts as a substitute for the fertile layer of soil in order to remove the volume of material containing organic or combustible inclusions from under the foundation.

backfill device for pile foundation
For these purposes, it is best to use large and medium gravel and crushed stone. Expanded clay bedding is often used, which further increases thermal insulation properties grounds.
Sand and gravel mixture is one of the most common inorganic materials, used in the construction industry. The composition of the material and the size of the fractions of its elements determine what type the extracted mixture belongs to, what its main functions are, and where it is more suitable for use.
Sand-gravel mixture is used in construction for filling in the lower layers various reasons , for example, asphalt or other road surface, and for the manufacture of various mortars, for example, concrete with added water.

Peculiarities
This material is a universal ingredient, that is, it can be used in different types activities. Since its main components are natural materials(sand and gravel), this indicates that the sand-gravel mixture is an environmentally friendly product. Also, ASG can be stored for a long time - there is no expiration date for the material.
The main condition for storage is to keep the mixture in a dry place.
If moisture does get into the ASG, then when using it, a smaller amount of water is added (for example, when making concrete or cement), and when the sand-gravel mixture is needed only in dry form, you will first have to dry it thoroughly.


Due to the presence of gravel in the composition, a high-quality sand-gravel mixture should have good resistance to temperature changes and not lose its strength. One more interesting feature This material lies in the fact that the remnants of the used mixture cannot be disposed of, but can be further used for their intended purpose (for example, when laying a path to a house or when making concrete).
Natural sand and gravel mixture is low cost, while enriched PGS has high price, but this is compensated by the durability and quality of buildings made from such environmentally friendly material.

Specifications
When purchasing a sand-gravel mixture, you need to pay attention to the following technical indicators:
- grain composition;
- the volume of sand and gravel in the mixture;
- grain size;
- impurity content;
- density;
- characteristics of sand and gravel.


Technical characteristics of sand and gravel mixtures must comply with accepted standards state standards. General information You can learn about sand-gravel mixtures from GOST 23735-79, but there are also others regulatory documents regulating technical specifications sand and gravel, for example, GOST 8736-93 and GOST 8267-93.
The minimum size of sand fractions in ASG is 0.16 mm, and gravel - 5 mm. The maximum value for sand according to the standards is 5 mm, and for gravel this value is 70 mm. It is also possible to order a mixture with a gravel size of 150 mm, but not more than this value.


In enriched ASG, the amount of gravel content is on average 65%, the clay content is minimal - 0.5%.
Based on the percentage of gravel content in enriched ASG, materials are classified into the following types:
- 15-25%;
- 35-50%;
- 50-65%;
- 65-75%.
Important characteristics of the material are also strength and frost resistance. On average, PGS should withstand 300-400 freeze-thaw cycles. Also, the sand and gravel composition cannot lose more than 10% of its mass. The strength of the material is affected by the number of weak elements in the composition.


Gravel is divided into categories based on strength:
- M400;
- M600;
- M800;
- M1000.
Gravel of the M400 category has low strength, and M1000 has high strength. Intermediate level strength is present in gravel of the M600 and M800 categories. Also, the amount of weak elements in gravel of category M1000 should contain no more than 5%, and in all others - no more than 10%.
The density of PGS is determined in order to find out which component of the composition is contained in more, and decide on the scope of use of the material. On average specific gravity 1 m3 should be approximately 1.65 tons.


Has great value not only the size of the sand, but also its mineralogical composition, as well as the fineness modulus.
The average compaction coefficient of the ASG is 1.2. This parameter may vary depending on the amount of gravel content and the method of compacting the material.
The Aeff coefficient plays an important role. It stands for the coefficient of total specific activity efficiency of natural radionuclides and is available for enriched PGS. This coefficient indicates the rate of radioactivity.
Sand and gravel mixtures are divided into three safety classes:
- less than 370 Bq/kg;
- from 371 Bq/kg to 740 Bq/kg;
- from 741 Bq/kg to 1500 Bq/kg.


The safety class also determines which area of application a particular ASG is suitable for. The first class is used for small construction activities, such as manufacturing products or repairing a building. The second class is used in construction automotive coatings in cities and villages, as well as for the construction of houses. The third safety class is involved in the construction of various sites with high load(these include sports and children's playgrounds) and large highways.
The enriched sand-gravel mixture is practically not subject to deformation.


Species
There are two main types of sand and gravel mixtures:
- natural (PGS);
- enriched (OPGS).
Their main difference is that an enriched sand-gravel mixture cannot be found in nature - it is obtained after artificial processing and the addition of a large amount of gravel.
Natural sand and gravel mixture is mined in quarries or from the bottom of rivers and seas. Based on place of origin, it is divided into three types:
- mountain-ravine;
- lake-river;
- sea
The difference between these types of mixture lies not only in the place of its extraction, but also in the area further application, the amount of volumetric content of the main elements, their sizes and even shapes.


Main features of natural sand and gravel mixtures:
- the shape of the gravel particles - the mountain-ravine mixture has the most pointed corners, while the sea ASG does not have them (smooth rounded surface);
- composition - a minimum amount of clay, dust and other polluting elements is contained in the marine mixture, while in the mountain-ravine mixture they predominate in large quantities.
The lake-river sand-gravel mixture has intermediate characteristics between the marine and mountain-ravine AGS. Silt or dust can also be found in its composition, but in small quantities, and its corners have a slightly rounded shape.


In OPGS, gravel or sand can be excluded from the composition, and crushed gravel can be added instead. crushed gravel- this is the same gravel, but in processed form. This material is obtained by crushing more than half the original component and has sharp corners and roughness.
Crushed gravel increases the adhesion of building compounds and is perfect for the construction of asphalt concrete.
Crushed stone compositions (sand-crushed stone mixtures - SSH) are divided according to the particle fraction into the following varieties:
- C12 – up to 10 mm;
- C2 – up to 20 mm;
- C4 and C5 – up to 80 mm;
- C6 – up to 40 mm.
Compositions with crushed stone have the same characteristics and features as compositions with gravel. Most often, a sand-crushed stone mixture with a fraction of 80 mm (C4 and C5) is used in construction, since this type provides good strength and stability.

Scope of application
The most common types of construction in which sand and gravel mixtures are used are:
- road;
- housing;
- industrial.
Sand-gravel mixtures are widely used in construction for backfilling pits and trenches, leveling the surface, building roads and laying a drainage layer, producing concrete or cement, laying communications, filling foundations for various sites. They are also used in the construction of railway tracks and landscaping. This one is affordable natural material participates in the construction of one-story and multi-storey buildings(up to five floors), laying the foundation.
The sand-gravel mixture as the main element of the road surface ensures the road’s resistance to mechanical impact and performs water-repellent functions.



When producing concrete (or reinforced concrete), in order to eliminate the possibility of the formation of empty spaces in a structure, it is enriched ASG that is used. Its factions various sizes They perfectly fill voids and thereby ensure the reliability and stability of structures. The enriched sand-gravel mixture makes it possible to produce several grades of concrete.
The most common type of sand-gravel mixture is ASG with a gravel content of 70%. This mixture is highly durable and reliable; it is used in all types of construction. Natural ASG is used much less frequently, since its strength properties are reduced due to the content of clay and impurities, but it is ideal for backfilling trenches or pits due to its ability to absorb moisture.


Most often, natural ASG is used for arranging the entrance to a garage, pipelines and other communications, constructing a drainage layer, garden paths and landscaping of homestead areas. The enriched composition is used in the construction of high-traffic highways and houses.
How to make a foundation cushion from a sand-gravel mixture, see below.