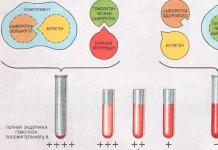
PLAN:
1) The concept of society.
2) What is a system? Society and nature as elements of the system.
3) Society as a system. Subsystems and elements of society.
4) Public relations.
5) Interaction of the main areas public life.
1) The concept of society.
The term "society" has many meanings. The following meanings of this word are usually indicated:
* society as a group of people united for modern activities
for the realization of their common goals and interests (a society of book lovers, a society of beer lovers, a society of sobriety, etc.). In this sense, the word "society" is synonymous with the words "organization", "union", "association". * society as a certain stage in the development of mankind or a country (primitive society, feudal society, French society of the Restoration era, Soviet society of the NEP period, etc.). Here the word "society" is often used together with the words "stage", " stage", "period". * society as a characteristic of the qualitative state of a particular stage in the development of mankind or a country ("consumer society", "information society", "traditional society", etc.). In this case, the word "society "is necessarily preceded by its qualitative characteristics.
* society as an extremely broad concept for designating that part of the material world that has become isolated from nature and interacts with it in a certain way. In this sense, society is the totality of all forms of association and ways of interaction between people both among themselves and with the natural world around them. This last definition is considered the philosophical definition of the concept of society.
Before proceeding to the characterization of the interaction between society and nature, it is necessary to pay attention to the similarity that exists between the various concepts of "society". This similarity can be seen if you look closely at the word itself: "society" - from the words "general", "community " (Latin societas also comes from socius, which means common, joint).
2) What is a system? Society and nature as elements of the system.
If we take into account the origin of the word "society", it becomes necessary for its detailed description introduce the concept of "system" and consider society from the point of view of a systems approach.
System (from the Greek "systema") - a set or combination of parts and elements that are interconnected and interact in a certain way with each other.
They talk about the solar system, the river system, the nervous system. A system is any set of phenomena that are interconnected and interact with each other. In this sense, the system is the unity constituent parts which are society and nature.
The interaction of society and nature shows their inseparable connection with each other.
Society cannot exist outside of nature and without interaction with it, because:
* it arose as a result of the development of the natural world, standing out on
a certain stage from it (this happened in a long and complex process of becoming a person),
* it takes from surrounding nature means and resources necessary for its development (agriculture is impossible without the existence of fertile soils, modern industry cannot exist without a number of natural materials, life modern society unthinkable without the use of various natural sources of raw materials),
* the pace and characteristics of its development are largely determined by the specifics of the natural environment, climatic and geographical conditions. (Northern peoples (Eskimos, Evenks, Chukchi) have harsh climatic conditions in their places of residence, so they are engaged in reindeer herding and hunting.)
(Ancient civilizations of the East (ancient Egypt, civilization ancient China) arise in river valleys, the climate is arid, irrigation irrigation systems are needed. Huge labor costs and therefore always a strong despotic beginning.)
At the same time, society has a huge impact on nature because: * it develops various means of adaptation, adaptation to the surrounding natural elements (a person has learned to use fire, build houses, sew clothes, created artificial materials necessary for the life of society),
* in the process of labor, society modifies natural landscapes, uses certain Natural resources in the interests of further social development (the consequences of this impact can be both destructive and beneficial).
Crimea used to have a more arid climate. They were mainly engaged in fishing, after the annexation of Crimea to Russia (1783), they brought exotic
trees, the climate has changed (the climate has become milder).
There were very few in Holland fertile land, earth constantly flooded. The Dutch created a network of dams, drainage canals, due to these structures significantly increased the area of land suitable for both construction and land use.
An artificial Rybinsk reservoir was created, villages, villages and floodplain meadows were flooded. Now there is a bad environment and everything that is under water is rotting - a negative impact on nature.
Does society become freer, more independent of nature as it develops? Until recently, the answer could only be positive - a person was considered as a being capable of subjugating, subjugating nature (according to the principle: "We cannot wait for mercy from nature, it is our task to take them from nature"). Today, it is obvious that society cannot be independent by nature. In some ways, we are modern world we depend on nature more than ever. This refers to the fact that society today is facing an ecological catastrophe created by a predatory, consumerist attitude towards nature. In this regard, it should be mentioned that the United Nations in 1992 adopted the concept sustainable development, obligatory for all states and proceeding from the need to ensure such a development of society that would make it possible to preserve natural world and ensure the survival of mankind.
3) Society as a system. Subsystems and elements of society.
Society itself can be considered as a certain system of interacting subsystems and elements.
The main subsystems of society are the spheres of public life. Usually they talk about the existence of four most important social (public) spheres:
economic- | political- |social- |spiritual-
covers relatively | covers relatively | covers relatively | covers from-
scheniya, arising - | niya associated with | scheniya associated with | wearing,
in the process | interaction | interaction | associated with
production, races | states, parties | classes, social | development of
definition, exchange | political org- | layers and groups |
and consumption ma- |izations about | | consciousness, science
material goods | power and management | | | culture,
| Niya | | arts
These subsystems (spheres), in turn, can be represented by a set of their constituent elements:
* economic - production institutions (factories, factories), transport institutions, stock and commodity exchanges, banks, etc.,
* political - the state, parties, trade unions, youth, women's and other organizations, etc.,
* social - classes, strata, social groups and strata, nations, etc.,
* spiritual - church, educational institutions, scientific institutions, etc.
4) Public relations.
To characterize society as a system, it is not enough to single out its subsystems and elements. It is important to show that they are interconnected and can be represented as links between social groups, nations, individuals that arise in the process of economic, political, social, spiritual life society. The term is used to refer to these links. "public relations" .
Kinds public relations:
material: | spiritual:
about the reason - | political,
stva, distribution | legal,
exchange and consumer-|moral,
material | ideological
benefits | and etc.
5) Interaction of the main spheres of public life.
Society, thus, is a certain set of elements interconnected and interacting with each other. The spheres of public life are mutually permeable and interconnected.
Economic difficulties and even more so crises (economic sphere) give rise to social instability and discontent of various social forces (social sphere) and lead to an aggravation of political struggle and instability (political sphere). All this is usually accompanied by apathy, confusion of the spirit, but also - spiritual searches, intensive scientific
research, the efforts of cultural figures aimed at understanding
the origins of the crisis and ways out of it. This is one of the examples illustrating the interaction of the main spheres of public life.
A military coup (political sphere) as a result of the economic crisis, a sharp decline in living standards (economic sphere), disagreement in society (social sphere) and all this affects the spiritual life of society. (Pinochet (1973) (military junta) came to power in Chile As a result of the military-fascist coup, he established a regime of the most severe terror, the economy improved, disagreement in society, the creative intelligentsia went underground.
Basic concepts: society, system, public relations, spheres of public life
Questions and tasks:
1) Define the concepts listed above. Analyze them.
2) Give examples of the beneficial and negative impact of society on nature.
- What are areas of public life?
- What are the areas of public life?
- How are different spheres of society interrelated?
The structure of society has always interested people. Have you thought about it? For many centuries, scientists have tried to create a model, an image with which to reproduce human society for studying. It was represented in the form of a pyramid, clockwork, likened to a branched tree.
Spheres of society
Society is rationally arranged. Each of its spheres (parts) performs its functions, satisfies certain needs of people. Remember what needs are.
Spheres of public life - areas of public life in which the most important needs of people are satisfied.
Scientists identify four main areas of public life: economic, political, social and spiritual. Such a division is conditional, but it helps to better navigate the diversity social phenomena.
The economic sphere includes firms, enterprises, factories, banks, markets, mines, etc. That is, everything that allows society to produce such a quantity of goods and services that will satisfy the vital material needs of people - food, housing, clothing, leisure, etc. .d.
The main task of the economic sphere is the organization of the activities of large groups of people in the production, consumption (purchase and use of the purchased for their own purposes) and distribution of goods and services.
The entire population participates in economic life. Children, pensioners, the disabled, for the most part, are not producers of material goods. But they participate in the exchange - when they buy goods in a store, distribution - when they receive pensions and benefits, and, of course, in the consumption of material goods. You are not yet creating material goods, but you are actively consuming them.
The political sphere includes the state and bodies state power and management. In Russia, these are the President, government, parliament (Federal Assembly), local authorities, army, police, tax and customs services, as well as political parties. The main task political sphere- ensuring order in society and its security, resolving social conflicts, adopting new laws and monitoring their implementation, protecting external borders, collecting taxes, etc.
Social sphere includes day-to-day interactions between citizens, as well as relationships between large social groups society: peoples, classes, etc.
The social sphere also includes various institutions for ensuring the life of people. These are shops, passenger transport, utilities and household service(housing management companies and dry cleaners), catering(canteens and restaurants), healthcare (clinics and hospitals), communications (telephone, post office, telegraph), as well as leisure and entertainment facilities (culture parks, stadiums).
An important place in the social sphere is occupied by the bodies of social protection and social security. They are designed to provide social assistance to those in need: pensioners, the unemployed, large families, the disabled, low-income people. You learned about how social assistance is provided to families in the 5th grade.
The spiritual realm includes science, education, religion and art. It includes universities and academies, research institutes, schools, museums, theaters, art galleries, cultural monuments, national art treasures, religious associations, etc. It is in this area that the accumulation and transfer of the spiritual wealth of society to the next generations is carried out, and people and entire societies find the answer to the question of the meaning of life and their existence.

What areas of public life are depicted in the photographs? Justify your answer.
The relationship of the four spheres of society
So, we have identified four main areas of modern society. But this does not mean that they exist separately from each other. On the contrary, they are closely related and influence each other. For example, if the country's economy does not fulfill its tasks, does not provide the population with a sufficient amount of goods and services, does not expand the number of jobs, then the standard of living drops sharply, there is not enough money to pay wages and pensions, unemployment appears, and crime grows. Thus, success in one, economic, area affects well-being in another, social.

The economy can also have a strong influence on politics, there are many examples of this in history.
Additional reading
The Byzantine Empire and Iran waged long-term wars with each other over which of them would collect duties from merchants who led caravans along the Great Silk Road. As a result, they exhausted their forces in these wars, and the Arabs took advantage of this, who seized most of their possessions from the Byzantine emperors, and conquered Iran entirely.
Explain how given example shows the relationship between economic and political spheres.
The social sphere is directly connected with political life. Changes in the political sphere, such as a shift in power, the arrival of other politicians to rule the state, can worsen the living conditions of people. But it is also possible Feedback. The reason for the change of power was often the indignation of the masses of the worsening of their situation. For example, the Western Roman Empire ceased to exist also because the taxes that the emperor established were unbearably high for his subjects and they preferred the power of the barbarian kings to the imperial one.
Summing up
There are four spheres of public life: economic, political, social and spiritual. The spheres of public life satisfy the basic needs of people and are closely interconnected with each other.
Basic terms and concepts
Spheres of society: economic, political, social, spiritual.
Test your knowledge
- Into what areas can society be divided? Give brief description every area of society. What is their significance for society?
- Explain how different areas of society influence each other. Use the diagram on p. twenty.
- What do you think is the most important area of society? Explain your answer.
Workshop

Quiet my home!
Willows, river, nightingales...
My mother is buried here
During my childhood...
Where I swam for fish
Hay is rowed into the hayloft:
Between river bends
People dug a canal.
Tina is now a swamp
Where I love to swim...
Quiet my home
I haven't forgotten anything.
New fence in front of the school
The same green space.
Like a happy crow
I'm going to sit on the fence again!
My school is wooden!..
The time will come to leave -
The river behind me is foggy
Will run and run...
The main areas of society
In a social system, not only social subjects are distinguished as parts, but also other entities - spheres of society. Society is a complex system of specially organized human life. Like any other complex system, society consists of subsystems, the most important of which are called areas of public life.
Sphere of social life- a certain set of stable relations between social subjects.
The areas of public life are large, stable, relatively independent subsystems of human activity.
Each area includes:
§ certain types human activities (eg educational, political, religious);
§ social institutions (such as family, school, parties, church);
§ established relations between people (i.e. connections that have arisen in the course of people's activities, for example, relations of exchange and distribution in the economic sphere).
Traditionally, there are four main areas of public life:
§ social (peoples, nations, classes, gender and age groups, etc.)
§ economic (productive forces, production relations)
§ political (state, parties, socio-political movements)
§ spiritual (religion, morality, science, art, education).
It is important to understand that people are simultaneously in different relationships with each other, connected with someone, isolated from someone when solving their life issues. Therefore, the spheres of the life of society are not geometric spaces inhabited by different people, but the relationship of the same people in connection with different aspects of their lives.
Graphically, the spheres of public life are presented in fig. 1.2. The central place of man is symbolic - he is inscribed in all spheres of society.
Rice. 1 Areas of public life
Social sphere
Social sphere - these are the relations that arise in the production of direct human life and man as a social being.
The concept of "social sphere" has various meanings, albeit related. In social philosophy and sociology, it is a sphere of social life, which includes various social communities and the connections between them. In economics and political science, the social sphere is often understood as a set of industries, enterprises, organizations whose task is to improve the standard of living of the population; while the social sphere includes health care, social security, public services, etc. The social sphere in the second meaning is not an independent sphere of social life, but an area at the intersection of economic and political spheres, associated with the redistribution of state revenues in favor of those in need.
The social sphere includes various social communities and relations between them. A person, occupying a certain position in society, is inscribed in various communities: he can be a man, a worker, a father of a family, a city dweller, etc. Visually, the position of an individual in society can be shown in the form of a questionnaire (Fig. 1.3).

Rice. 2. Questionnaire
Using this conditional questionnaire as an example, one can briefly describe the social structure of society. Gender, age, marital status determine the demographic structure (with groups such as men, women, youth, pensioners, single, married, etc.). Nationality determines the ethnic structure. The place of residence determines the settlement structure (here there is a division into urban and rural residents, residents of Siberia or Italy, etc.). Profession and education make up professional and educational structures proper (doctors and economists, people with higher and secondary education, students and schoolchildren). Social origin (from workers, from employees, etc.) and social position (employee, peasant, nobleman, etc.) determine the class structure; this also includes castes, estates, classes, etc.
Economic sphere
Economic sphere is a set of relations between people that arise during the creation and movement of material goods.
The economic sphere is the area of production, exchange, distribution, consumption of goods and services. In order to produce something, people, tools, machines, materials, etc. are needed. - productive forces. In the process of production, and then exchange, distribution, consumption, people enter into various relationships with each other and with the goods - relations of production. Production relations and productive forces together constitute the economic sphere of society:
§ productive forces- people ( work force), tools, objects of labor;
§ industrial relations - production, distribution, consumption, exchange.
Political sphere
The political sphere is one of the most important spheres of public life.
Political sphere- this is the relationship of people, connected primarily with power, which provide joint security.
The Greek word politike (from polis - state, city), having appeared in the writings of ancient thinkers, was originally used to denote the art of government. Having retained this meaning as one of the central ones, the modern term "politics" is now used to express social activity, in the center of which are the problems of acquiring, using and retaining power. The elements of the political sphere can be represented as follows:
§ political organizations and institutions- social groups revolutionary movements, parliamentarism, parties, citizenship, presidency, etc.;
§ political norms - political, legal and moral standards, customs and traditions;
§ political communications - relations, connections and forms of interaction between participants in the political process, as well as between the political system as a whole and society;
§ political culture and ideology - political ideas, ideology, political culture, political psychology.
Needs and interests form certain political goals of social groups. On this target basis, political parties, social movements, powerful state institutions arise, carrying out a specific political activity. The interaction of large social groups with each other and with the institutions of power constitutes the communicative subsystem of the political sphere. This interaction is ordered various norms, customs and traditions. Reflection and awareness of these relations form the cultural and ideological subsystem of the political sphere.
spiritual realm
spiritual realm- this is the area of ideal, non-material formations, including ideas, values of religion, art, morality, etc.
The structure of the spiritual realm life of society in the most in general terms is:
§ religion - a form of worldview based on belief in supernatural forces;
§ morality - a system of moral norms, ideals, assessments, actions;
§ art - artistic development of the world;
§ science - a system of knowledge about the patterns of existence and development of the world;
§ law - a set of norms supported by the state;
§ education is a purposeful process of education and training.
Spiritual sphere - this is the sphere of relations that arise in the production, transfer and development of spiritual values (knowledge, beliefs, norms of behavior, artistic images, etc.).
If the material life of a person is connected with the satisfaction of specific daily needs (for food, clothing, drink, etc.). then the spiritual sphere of human life is aimed at meeting the needs for the development of consciousness, worldview, and various spiritual qualities.
spiritual needs unlike material ones, they are not biologically defined, but are formed and developed in the process of socialization of the individual.
Of course, a person is able to live without satisfying these needs, but then his life will not differ much from the life of animals. Spiritual needs are met in the process spiritual activity - cognitive, value, prognostic, etc. Such activities are aimed primarily at changing the individual and public consciousness. It manifests itself in art, religion, scientific creativity, education, self-education, upbringing, etc. At the same time, spiritual activity can be both producing and consuming.
spiritual production called the process of formation and development of consciousness, worldview, spiritual qualities. The product of this production are ideas, theories, artistic images, values, the spiritual world of the individual and spiritual relations between individuals. The main mechanisms of spiritual production are science, art and religion.
Spiritual consumption called the satisfaction of spiritual needs, the consumption of products of science, religion, art, for example, visiting a theater or a museum, obtaining new knowledge. The spiritual sphere of the life of society ensures the production, storage and dissemination of moral, aesthetic, scientific, legal and other values. She covers various forms and levels of social consciousness - moral, scientific, aesthetic, religious, legal.
The relationship of spheres of public life
The spheres of public life are closely interconnected. In the history of the social sciences, there have been attempts to single out any sphere of life as determining in relation to others. So, in the Middle Ages, the idea of the special significance of religiosity as part of the spiritual sphere of society dominated. In modern times and the Age of Enlightenment, the role of morality and scientific knowledge was emphasized. A number of concepts assign the leading role to the state and law. Marxism asserts the defining role economic relations.
Within the framework of real social phenomena, elements of all spheres are combined. For example, the nature of economic relations can influence the structure of the social structure. Place in the social hierarchy forms certain Political Views, opens appropriate access to education and other spiritual values. The economic relations themselves are determined by the legal system of the country, which is very often formed on the basis of the spiritual culture of the people, their traditions in the field of religion and morality. Thus, on various stages historical development influence of any sphere can be amplified.
The complex nature of social systems is combined with their dynamism, i.e., mobile, changeable character.
Most right approach to the study of society is systems approach , which involves the analysis of social structures, including the study of the elements of society and the relationships between them, as well as the analysis of the processes and changes taking place in society and reflecting the trends of its development.
Structural analysis of the system is logical to begin with the allocation of the largest complex parts, called subsystems. Such subsystems in society are the so-called spheres of social life, which are parts of society, the limits of which are determined by the influence of certain social relations. Traditionally, social scientists distinguish the following main areas of society:
1. Economic sphere- a system of economic relations that arises and is reproduced in the process material production. the basis of economic relations and the most important factor, which determines their specificity, is the method of production and distribution of material goods in society.
2. Social sphere- a system of social relations, i.e. relations between groups of people occupying different positions in social structure society. The study of the social sphere involves consideration of the horizontal and vertical differentiation of society, the allocation of large and small social groups, the study of their structures, forms of implementation social control in these groups, analysis of the system of social ties, as well as social processes occurring at the intra- and intergroup level.
It should be noted that the terms "social sphere" and "social relations" are often used in a broader interpretation, as a system of all relations between people in society, reflecting not the specifics of this local sphere of society, but the integrative function of social science - the unification of subsystems into a single whole.
3. Political (political and legal) sphere - a system of political and legal relations that arise in society and reflect the attitude of the state towards its citizens and their groups, citizens towards the existing state power, as well as relations between political groups (parties) and political mass movements. Thus, the political sphere of society reflects the relationship between people and social groups, the emergence of which is determined by the institution of the state.
4. spiritual realm- a system of relations between people, reflecting the spiritual and moral life of society, represented by such subsystems as culture, science, religion, morality, ideology, art. The significance of the spiritual sphere is determined by its priority function of determining the value-normative system of society, which, in turn, reflects the level of development of social consciousness and its intellectual and moral potential.
It should be noted that an unambiguous division of the spheres of society is possible and necessary within the framework of its theoretical analysis, however, empirical reality is characterized by their close interconnection, interdependence and intersection, which is reflected in terms such as socio-economic relations, spiritual and political, etc. That is why the most important task of social science is to achieve the integrity of scientific understanding and explanation of the laws governing the functioning and development of the social system.
The structure of society interested people at all times. For many centuries, scientists have tried to find a model, an image with which to reproduce human society. It was represented in the form of a pyramid, a clockwork, a branchy tree.
Modern scientists argue that society is a holistic, naturally functioning and developing system. The word "system" is of Greek origin and means a whole made up of parts, a set. So, A system is a set of interconnected elements, each of which performs a specific task.
Society as a social system is a holistic entity, the main element of which are people, their connections, interactions and relationships., which are sustainable and pass from generation to generation.
In this case, society can be compared to a giant organism, and just as a living organism has a heart, arms, legs, brain, nervous system, so in society there are certain mechanisms of influence on environment- its own control center for diverse processes and means of communication. And just as various life support systems function in a living organism, so in society each of its “organs” performs only its own function. Finally, how can several interrelated levels of its vital activity be distinguished in the body, depending on the significance of each of them for the whole organism ( nervous system, circulatory and digestive systems, metabolism, etc.), and in society it is possible to isolate specific levels (in the scientific literature more often - “spheres”) of its life activity - economic, social, political and spiritual.
Economic sphere is the area of implementation economic activity society, the area of wealth creation. Being one of the main subsystems of society, it can also be considered as independent system. The elements of the economic sphere are material needs, economic benefits (goods) that satisfy these needs, economic resources(sources of production of goods), business entities (individuals or organizations). The economic sphere is firms, enterprises, factories, banks, markets, flows of money and investments, capital turnover, etc. In other words, what allows society to put into production the resources at its disposal (land, labor, capital and management ) and create such a quantity of goods and services that will satisfy the vital needs of people for food, shelter, leisure, etc.
50–60% of the population, who are called the economically active population, directly participate in the economic life of society: workers, employees, entrepreneurs, bankers, etc. Indirectly, 100% of the people living in the given territory participate in it, since everyone is a consumer of goods and services created directly participants in the economic process. Pensioners have already left production, and children have not entered it yet. They do not create material values, but they consume them.
Political sphere- this is the area of realization between people of relations of power and subordination, the area of \u200b\u200bmanaging society. Main elements political system society are political organizations and institutions (the state, political parties, public organizations, the media), the norms of political behavior and political culture, political ideologies. The main elements of the political system of the modern Russian society are the President and the Office of the President, the Government and the Parliament (Federal Assembly), their Office, local authorities (provincial, regional), the army, the police, the tax and customs Service. Together they make up the state.
The political sphere also includes political parties that are not part of the state. The main task of the state is to ensure social order in society, to resolve conflicts between partners, for example, between workers, trade unions and employers, to establish new laws and monitor their strict implementation by all structures, to prevent political upheavals, to protect the external borders and sovereignty of the country, to collect taxes and ensure money institutions of the social and cultural spheres, etc. The main function of the political sphere is to legitimize the ways of fighting for power and protecting it. The task of parties is to express the diversity of political interests of various, often opposing, groups of the population through channels established by law.
Social sphere- is the area of occurrence and functioning of interrelations of people with each other. The social sphere is understood in two senses - broad and narrow - and, depending on this, covers different volumes of social space.
The social sphere of society in a broad sense is a set of organizations and institutions responsible for the welfare of the population. In this case, this includes shops, passenger transport, public utilities and consumer services (housing offices and dry cleaners), public catering (canteens and restaurants), healthcare, communications (telephone, post office, telegraph), as well as leisure and entertainment facilities (culture parks, stadiums ). In this sense, the social sphere covers almost all strata and classes - from the rich and middle to the poor.
The social sphere in a narrow sense means only socially unprotected segments of the population and institutions serving them: pensioners, the unemployed, the low-income, those with many children, the disabled, as well as social protection and social security agencies (including social insurance) of both local and federal subordination.
social system consists of social groups, social ties, social institutions, social norms, values of social culture.
To spiritual realm include morality, religion, science, education, culture. Its constituent parts are schools, museums, theatres, art galleries, mass media, cultural monuments and national artistic treasures, churches.
Society consists of a huge number of elements and subsystems that are in constant interaction.. You can illustrate the connections between subsystems and elements of society various examples. Thus, the study of the distant past of mankind allowed scientists to conclude that moral relations people in primitive conditions were built on collectivist principles, i.e., speaking modern language, priority has always been given to the collective, and not to the individual.
It is also known that the moral norms that existed among many tribes in those archaic times allowed the killing of weak members of the clan - sick children, the elderly, and even cannibalism. Have the real material conditions of their existence influenced these ideas and views of people about the limits of the morally permissible? The answer is clear. The need to jointly obtain material wealth, the doom to an early death of a person who has broken away from the clan - this is where we should look for the origins of collectivist morality. Also, from the standpoint of the struggle for existence and survival, people did not consider it immoral to get rid of those who could become a burden for the team.
The connection between legal norms and socio-economic relations is well traced. Let's go to the famous historical facts. In one of the first codes of laws Kievan Rus, which is called "Russian Truth", provides for various punishments for murder. At the same time, the measure of punishment was determined primarily by the place of a person in the system of hierarchical relations, his belonging to one or another social stratum or group. So, the fine for killing a tiun (steward) was huge: it was equal to the cost of a herd of 80 oxen or 400 rams. The life of a serf or a serf was valued 16 times cheaper.
Society is in constant motion and development. Thinkers from ancient times have thought about the question in what direction is society developing? Can its movement be likened to cyclical changes in nature?
Development direction, which is characterized by a transition from lower to higher, from less perfect to more perfect, is called progress. Accordingly, social progress is a transition to more high level material condition of society and spiritual development personality. An important sign of social progress is the tendency towards the liberation of man.
Allocate the following criteria social progress:
1) growth of welfare and social security of people;
2) weakening of confrontation between people;
3) the establishment of democracy;
4) the growth of morality and spirituality of society;
5) improvement of human relations;
6) the measure of freedom that society is able to provide to the individual, the degree of individual freedom guaranteed by society.
If we attempted to graphically depict the development of society, we would get not an ascending straight line, but a broken line reflecting ups and downs, accelerated forward movement and giant leaps back. We are talking about the second direction of development - regression.
Regression - downward development, transition from higher to lower. For example, the period of fascism was a period of regression in world history: millions of people died, were enslaved various peoples destroyed many monuments of world culture.
But it's not just these twists and turns in history. Society is a complex organism in which various spheres function, many processes take place simultaneously, and various activities of people unfold. All these parts of one social mechanism and all these processes and types of activity are interconnected and at the same time may not coincide in their development. Moreover, individual processes, changes taking place in different areas of society can be multidirectional, i.e. progress in one area may be accompanied by regression in another.
Thus, throughout history, technological progress is clearly traced - from stone tools to the most complex machine tools with program control, from beasts of burden to cars, trains and aircraft. At the same time, technological progress leads to the destruction of nature, to the undermining natural conditions the existence of mankind, which, of course, is a regression.
In addition to directions, there are also forms of development of society.
The most common form of social development is evolution - gradual and smooth changes in social life that occur naturally. The nature of evolution is gradual, continuous, ascending. Evolution is divided into successive stages or phases, none of which can be skipped. For example, the evolution of science and technology.
Under certain conditions, public changes occur in the form of a revolution - these are rapid, qualitative changes, a radical upheaval in the life of society. Revolutionary changes are radical and fundamental. Revolutions can be long-term or short-term, in one or several states, in one sphere. If the revolution affects all levels and spheres of society - economy, politics, culture, social organization, everyday life people, it is called social. Such revolutions cause strong emotions and mass activity of people. An example is the Russian Revolution of 1917.
Social changes also take place in the form of reform - this is a set of measures aimed at transforming, changing certain aspects of public life. For example, economic reform, education reform.
Similar information.