Edged board is the most common type of lumber. It has an extremely wide range of applications. Its dimensions are very different - from 16 * 8 mm to 250 * 100 mm (but the width is always more than twice the thickness; if less, then such lumber is called a "beam"). Due to the wide distribution and popularity of this material in almost any construction works ah, the question of calculating the required number of boards will arise with a very high probability.
Edged board is an indispensable material in construction. Its required amount is measured in cubic meters.
The edged board is measured, like the rest of the lumber, in cubic meters. Accordingly, the calculation of its cubic capacity is an important practical task, the solution of which is necessary to determine the cost. It is not difficult - enough elementary geometric knowledge.
How to calculate cubic capacity
Unlike an unedged or one-sided edged board, an edged board does not have a wane (parts of the former surface of the log where bark is or was present before). Rather, a small wane is allowed according to the standard, but its quantity is clearly normalized, and in any case it is small. Therefore, in geometric sense we have a simple cuboid. Accordingly, we have 3 parameters: thickness (smaller side of the cross section), width (large side of the cross section) and length. They are traditionally denoted by the letters a, b and l.
According to current standards, edged boards are produced with a thickness (parameter a) of 22, 25, 30, 40, 50 and 100 mm. Sawn timber of other thicknesses is made from standard by longitudinal sawing or planing. Standard Width goes from 100 to 250 mm in 50 mm increments. Standard lengths- 3, 4 and 6 m.
To determine the cubature, we need, in accordance with the formula for calculating the volume cuboid multiply the thickness, width and length.

All three parameters should be considered in meters: that is, the dimensions of 25 mm * 10 cm * 4 m should be written as 0.025 m * 0.1 m * 4 m. Thus, we get the volume - cubic capacity - of one data board of parameters. Now you need to find out how many of them "fit" in one cubic meter. To do this, you need to divide the unit by the calculated volume. Everything, the desired number is found.
Example: let's say we need lumber 6 m long, 3 cm thick, and 25 cm wide. Then the volume of one piece will be 0.03 * 0.25 * 6 m, or 0.045 m³. 1 m³ will contain 1 / 0.045 = 22.222, or, rounding up, 22.2 boards of the indicated sizes.
Having a similar calculation, it is already possible to estimate further how many cubic meters this lumber need to be purchased for construction or repair work. It should only be taken into account that supplier companies like to round all numbers in a favorable direction, and in our example, 0.045 m³ in practice can turn into 0.05 m³, that is, only 20 pieces per cubic meter. Such an “error” can reach several percent, which, at prices of several thousand rubles per cubic meter, is already a noticeable value.
When carrying out construction work on the construction of a residential building, a specialist must perform big number a variety of tasks, some of which are: compilation and calculation estimated cost until the final finishing of the premises of a residential building. AT without fail, calculate the required number of various building materials which is quite difficult to do. Therefore, such knowledge - how many boards are in a cube, has a very importance for a specialist who is engaged in the construction of a residential building and wants to perform the work as efficiently as possible and quickly in time.
Buyer's club: existing types of boards
To calculate exactly how many board pieces are in a cube, you need to know not only what exactly the board cube means, but you should understand important point that there are different types of boards and what is the opportunity to purchase on modern market to carry out various construction works. It should be noted that the cube of almost all materials, regardless of the type of material, is calculated in the same way, that is, according to one specific method. The types of boards have no influence on the calculation of the cubic capacity of this building material.
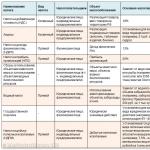
The non-grooved type of lumber is: timber, various edged boards, as well as unedged boards (they are an exception when calculating cubic capacity, because this process is a little different). Grooved types (which have special grooves for the joint) include: modern lining, blockhouse, flooring material, as well as imitation of natural timber. When you choose to buy a tongue-and-groove type of building material, then you need to pay attention to the fact that when making a calculation, only the working width of the board without a spike is used. If we talk about a blockhouse (imitation of a log), then when calculating the cubic capacity, only the thickness at its highest point is taken.

How many boards are in 1 cube: performing a calculation
Any person, since his school days, understands how the cubic capacity is calculated. For this procedure, it is necessary to calculate quantities such as: length, width and height. A similar principle is also used to calculate the cubature of 1 board. It is recommended that when performing such calculations, convert all available values in meters. Cubic capacity of 1 board, which has a section of 150x20 mm. and a length of 6 m., is calculated as follows: 0.15 is multiplied by 0.02 and by 6, so that the cubic capacity of this board will be 0.018 cubic meters.
Apply the volume formula V= L*h*b (where L is the length, h is the height, b is the width).
L=6.0; h=0.02; b=0.15.
Thus, V \u003d 6.0 * 0.02 * 0.15 \u003d 0.018 m 3.
To determine how many boards are in one cube: 1 m 3 is divided by the cubic capacity (the volume of one board).
1 m 3 / V = N pcs.
1 m 3 / 0.018 m 3 \u003d 55.55 pcs.
Thus, the number of boards in one cube is 55.5 pieces.

Find out the cost a certain kind boards, when the values \u200b\u200bof its volume are known quite easily: 0.018 is multiplied by the price of 1 cubic meter. When 1 cube of a certain type of board has, for example, a cost of 5500 rubles, then the cost will be 99 rubles. At this moment of calculation, there is some trick of salesmen and managers in construction stores, because the cubature of the material is rounded up to some integer values.
Such rounding can lead to such a moment that the price of 1 board (when 1 cube costs 5500) will be completely different values. In addition to all this, it should be noted that for various boards for construction, which make up a nominal length of 6 meters, in fact, the length is 6.1 - 6.2 m, which is not taken into account when selling this building material. This also applies to the acquisition of a significant number of boards. This is quite clearly visible if, for example, a 150x20 mm board is used. The number of boards in a cube is a value of 55.5 pieces. But, in a cube, 55 pieces are considered, which, when calculating, will have a value of 0.99 cubic meters. In fact, it follows from this that the overpayment for 1 cubic meter of this popular building material can be 1% of the real price. For example, 5500 instead of 4995 rubles.
To calculate the cubature for a non-cut-off type of board, slightly different methods are used. When it comes to buying 1 board, then measuring its thickness, as well as the total length, is done in the same way as when choosing a cut building material. In this case, the width for calculations is taken as an average - between great value and small.
For example, when at the end the width of the board is 25 cm, and at the other 20, then the average value will be approximately 22 centimeters. When it is necessary to calculate the volume of a significant number of such boards for construction, then it will be necessary to decompose them so that the wide one does not differ from the narrow one, more than 10 cm. The main length of this material in the unfolded stack should be approximately the same. After that, using an ordinary tape measure, an accurate measurement of the height of the entire stack of boards is made, the width is measured (approximately in the middle). The result obtained will then need to be multiplied by a special coefficient ranging from 0.07 to 0.09, in direct proportion to the existing air gap.

How many boards in 1 cube: special tables
To calculate exactly what number of boards of a certain width, length in 1 cubic meter, various tables are used. Below are several such specialized tables, which indicate the cubature of the common and popular types of this material today. It is possible to calculate the volume of various boards having different sizes, for example, material for erecting a fence on your site, using the available formula, which is presented above.
Table of the number of edged boards in 1 cubic meter
| Board size | The volume of the 1st board (m 3) | The number of boards in 1m 3 (pcs.) | The number of square meters in 1m 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| twenty | |||
| Board 20x100x6000 | 0.012 m 3 | 83 pcs. | 50 m2 |
| Board 20x120x6000 | 0.0144 m 3 | 69 pcs. | 50 m2 |
| Board 20x150x6000 | 0.018 m 3 | 55 pcs. | 50 m2 |
| Board 20x180x6000 | 0.0216 m 3 | 46 pcs. | 50 m2 |
| Board 20x200x6000 | 0.024 m 3 | 41 pcs. | 50 m2 |
| Board 20x250x6000 | 0.03 m 3 | 33 pcs. | 50 m2 |
| twenty-five | |||
| Board 25x100x6000 | 0.015 m 3 | 67 pcs. | 40 m2 |
| Board 25x120x6000 | 0.018 m 3 | 55 pcs. | 40 m2 |
| Board 25x150x6000 | 0.0225 m 3 | 44 pcs. | 40 m2 |
| Board 25x180x6000 | 0.027 m 3 | 37 pcs. | 40 m2 |
| Board 25x200x6000 | 0.03 m 3 | 33 pcs. | 40 m2 |
| Board 25x250x6000 | 0.0375 m 3 | 26 pcs. | 40 m2 |
| Thirty | |||
| Board 30x100x6000 | 0.018 m 3 | 55 pcs. | 33 m2 |
| Board 30x120x6000 | 0.0216 m 3 | 46 pcs. | 33 m2 |
| Board 30x150x6000 | 0.027 m 3 | 37 pcs. | 33 m2 |
| Board 30x180x6000 | 0.0324 m 3 | 30 pcs. | 33 m2 |
| Board 30x200x6000 | 0.036 m 3 | 27 pcs. | 33 m2 |
| Board 30x250x6000 | 0.045 m 3 | 22 pcs. | 33 m2 |
| Thirty-two | |||
| Board 32x100x6000 | 0.0192 m 3 | 52 pcs. | 31 m2 |
| Board 32x120x6000 | 0.023 m 3 | 43 pcs. | 31 m2 |
| Board 32x150x6000 | 0.0288 m 3 | 34 pcs. | 31 m2 |
| Board 32x180x6000 | 0.0346 m 3 | 28 pcs. | 31 m2 |
| Board 32x200x6000 | 0.0384 m 3 | 26 pcs. | 31 m2 |
| Board 32x250x6000 | 0.048 m 3 | 20 pcs. | 31 m2 |
| Sorokovka | |||
| Board 40x100x6000 | 0.024 m 3 | 41 pcs. | 25 m2 |
| Board 40x120x6000 | 0.0288 m 3 | 34 pcs. | 25 m2 |
| Board 40x150x6000 | 0.036 m 3 | 27 pcs. | 25 m2 |
| Board 40x180x6000 | 0.0432 m 3 | 23 pcs. | 25 m2 |
| Board 40x200x6000 | 0.048 m 3 | 20 pcs. | 25 m2 |
| Board 40x250x6000 | 0.06 m 3 | 16 pcs. | 25 m2 |
| fifty | |||
| Board 50x100x6000 | 0.03 m 3 | 33 pcs. | 20 m2 |
| Board 50x120x6000 | 0.036 m 3 | 27 pcs. | 20 m2 |
| Board 50x150x6000 | 0.045 m 3 | 22 pcs. | 20 m2 |
| Board 50x180x6000 | 0.054 m 3 | 18 pcs. | 20 m2 |
| Board 50x200x6000 | 0.06 m 3 | 16 pcs. | 20 m2 |
| Board 50x250x6000 | 0.075 m 3 | 13 pcs. | 20 m2 |
Table of the amount of timber in 1 cubic meter
| Beam size | Volume of 1 piece (m³) | The number of timber in 1m³ (pcs.) |
|---|---|---|
| 100×100×6000 | 0.06 m 3 | 16 pcs. |
| 100×150×6000 | 0.09 m 3 | 11 pcs. |
| 150×150×6000 | 0.135 m 3 | 7 pcs. |
| 100×180×6000 | 0.108 m 3 | 9 pcs. |
| 150×180×6000 | 0.162 m 3 | 6 pcs. |
| 180×180×6000 | 0.1944 m 3 | 5 pieces. |
| 100×200×6000 | 0.12 m 3 | 8 pcs. |
| 150×200×6000 | 0.18 m 3 | 5.5 pcs. |
| 180×200×6000 | 0.216 m 3 | 4.5 pcs. |
| 200×200×6000 | 0.24 m 3 | 4 things. |
| 250×200×6000 | 0.3 m 3 | 3 pcs. |
Table of the number of unedged boards in 1 cubic meter
It makes no sense to make the same calculations several times if the original data does not change. A rounded log with a diameter of 20 cm and a length of 6 meters will always have the same volume, regardless of who and in which city conducts the count. Only the formula V=πr²l gives the correct answer. Therefore, the volume of one OCB will always be V=3.14×(0.1)²×6=0.1884 m³. In practice, in order to exclude the moment of holding standard calculations, cubes are used. Such useful and informative tables are created for various kinds lumber. They help to save time and find out the cubic capacity of round timber, boards, CBM, and timber.
Name of this building guide due to the fact that the volume physical quantity measured in cubic meters (or cubic meters). For a simpler explanation, they say "cubature", respectively, the table was called "cubature". This is an ordered matrix, which contains data on the volume of one product for various initial parameters. The base column contains sections, and the row contains the length (molding) of the material. The user only needs to find the number located in the cell at their intersection.
Consider specific example- cubic yard of roundwood. It was approved in 1975, is called GOST 2708-75, the main parameters are diameter (in cm) and length (in meters). Using the table is very simple: for example, you need to determine the V of one log having Ø20 cm with a length of 5 m. At the intersection of the corresponding row and column, we find the number 0.19 m³. A similar cube for round timber exists according to another standard - ISO 4480-83. Reference books are very detailed in increments of 0.1 m, as well as more general, where the length is taken in 0.5 m.
little secrets
The very use of the cube is not difficult, but the main nuance is the correct data. Round wood is not a cylinder, but a truncated cone, in which the lower and upper cuts are different. One of them can be 26 cm, and the other - 18. The table assumes an unambiguous answer for a particular section.
Various sources suggest doing it in two ways: calculate the average value and take the volume from the reference book for it, or take the size of the upper cut as the main section. But if the tables were compiled according to certain standards, then they must be used in accordance with the accompanying instructions. For a cubature GOST 2708-75, the diameter of the upper saw cut of the log is taken. Why is the raw data moment so important? Because with a length of 5 meters for Ø18 cm we get 0.156 m³, and for Ø26 cm - 0.32 m³, which is actually 2 times more.
Another nuance is the correct cubes. If the GOST 2708-75 table used complex formulas for truncated cones, calculations were carried out, and the results were rounded to thousandths, then modern companies that make up their own cubes allow themselves “liberties”. For example, instead of 0.156 m³, there is already the number 0.16 m³. Often, frankly erroneous cubic meters are posted on Internet sites, in which the volume of a log 5 meters long with Ø18 cm is indicated not 0.156 m³, but 0.165 m³. If an enterprise uses such directories, implementing round wood consumers, then it makes a profit by actually deceiving customers. After all, the difference in 1 product is significant: 0.165-0.156=0.009 or almost 0.01 m³.

The main problem of round timber is different section. Sellers offer to resolve issues with calculations in the following ways:
- calculation of the volume of each unit and summation of the obtained values;
- storage method;
- finding the average diameter;
- method based on the density of the wood.
1. It must be said right away that the first of the indicated options gives the correct results. Only the calculation of the volume of each log and the subsequent addition of the numbers ensures that the buyer will pay for the timber that he will receive from the company. If the length is the same, then it is enough to find the cross-sectional areas of all the trunks, add them up, and then multiply by the length (in meters).
2. Warehousing method.
It is assumed that the stored round timber occupies a part of the space that has the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped. In this case, the total volume is found by multiplying the length, width and height of the figure. Given that there are voids between the stacked trunks, 20% is subtracted from the resulting cubic capacity.
Minus - the acceptance as an indisputable fact that the tree occupies 80% of the total space. After all, it may well happen that the bars are folded inaccurately, thereby the percentage of voids is much greater.

3. Density based method.
In this case, you need to know the mass of the forest and the density of the wood. The cubature is easily found by dividing the first number by the second. But the result will be very inaccurate, since a tree of the same species has a different density. The indicator depends on the degree of maturity and humidity.
4. Average method.
If the trunks of harvested trees are appearance almost identical, then choose any 3 of them. Measure the diameters, and then find the average value. Further, according to the cubature, the parameter for 1 product is determined and multiplied by right amount. Let the results show: 25, 27, 26 cm, then the average is Ø26 cm, since (25 + 26 + 27) / 3 = 26 cm.
Given the disadvantages of the considered methods, the only the right way calculation of cubature can be considered as finding the volume of each log using a cubature GOST 2708-75 or ISO 4480-83 and summing up the data obtained.
Almost everything in our world has its own measurement value. We measure oil in barrels, coal in tons, the population of countries in thousands, millions.
We take as a basis a value that can specifically designate the object that we measure. When the question arises of how to calculate the cubature of a board, it is already underway not about the mass of the object, since wood has a completely different density, and one tree has differences from another. In addition, boards of the same breed will have different weight considering their moisture content.
For the convenience of calculating the cubature of the board, volume measurement formulas are used.
Suffice it to recall school mathematics and necessary formula, by which to multiply the width, length and height. For the calculation to be correct, it is necessary to adjust all parameters to one value, for example, in centimeters or decimeters. It is most convenient to take meters as a basis. Thus, having multiplied three times in meters, we get m³ or cubic capacity.
Note. To calculate the cubature of the board, special formulas are used.
cubature boards
 Boards may have differences in width, length, thickness. In addition, they are sold unedged and edged. Often, lumber has its own generally accepted standards, which make it easier to calculate cubic capacity.
Boards may have differences in width, length, thickness. In addition, they are sold unedged and edged. Often, lumber has its own generally accepted standards, which make it easier to calculate cubic capacity.
For ordinary material sizes, there are already calculated volumes, which are systematized in tables for measuring the cubature of boards. Therefore, to determine the volume of the material, you simply need to open the table with the indicated dimensions and calculate the volume.
But, in order to do this, you must have these tables with you. Otherwise, in the absence of such, the cubature of the edged board is calculated, having previously determined the thickness and length. These are the main dimensions that meet the requirements for lumber. Each individual material is different. For example, a board with a thickness of 25 mm is used to create a crate, and 50 mm for subfloors. Next, you need to measure the width of the board.
In the case of a cut board, everything is simple, since the material is cut to give one width. Further, using a calculator, all values \u200b\u200bare multiplied among themselves. With a board length of 5 m, a thickness of 50 mm and a width of 25 cm, the volume of the material will be:
5 x 0.050 x 0.25 = 0.0625 m³
After multiplying the resulting number by the number of boards, we get the total volume of material.
The formula for calculating the cubature of boards
V = L x h x b
L - length
h - height
b - width
Determination of the number of boards in a cubic meter
1 m 3: V = N
In order to determine the cost of a particular type of board, with known values volume: V x price 1 m 3.
There is one more point that you need to pay attention to when determining the cubature of boards - the nominal length is exactly 6.1 - 6.2 m, but this is not taken into account when selling. Often this matters in the case of a purchase. a large number material. For example, let's take a board with dimensions of 150 x 20 mm.
Having made simple calculations, we get the number of boards in 1 m 3 - 55, 5 pieces. So, in the cubature of the board 6 m there are exactly 55 pieces, in total, when calculating, we get the value of 0.99 m 3. In essence, the overpayment for the cubature of the board will be 1% of exact price. For example, at a cost of 4,995 rubles, we pay 5,500 rubles.
Unedged board
Calculation features
The calculation of the cubature of an unedged board is somewhat complicated, since the material does not have one width between various boards, but also in each board individually. This is explained quite simply - the tree does not have the same diameter.
It is clear that it is wider at the bottom, narrower at the top. Thus, the width of the edged board does not fall under any standards. How to be in this case? Use for calculation different formulas. The width of the board is measured for convenience in the middle of the length. This is how you get the average width. This method counting works well if the batch of material is small.
For industrial volumes
This method is not suitable, because the work will be very slow, and this is not profitable. For such cases, experts have developed the so-called unedged board cubature. The volume in it is obtained by measuring and experimenting, in other words, using many measurements and calculating the average value of the width.
Of course, it can not be called super exact way, but the deviations are so small that they are not worth paying attention to.
Some wood processing companies use the stack measurement method in practice. To do this, it is not necessary to pre-sort the wood according to width. Specialists take measurements of the length of the board, the average width and height of the stack. The obtained values are multiplied among themselves, and the result is multiplied by a coefficient for calculating the cubature of the board, which has an average value of 0.67.
Weighing method
 In order to measure the cubic capacity of an unedged board, having obtained the most accurate result possible, the weighing method is used.
In order to measure the cubic capacity of an unedged board, having obtained the most accurate result possible, the weighing method is used.
Before doing this, it is necessary to measure the moisture content of the material and dense wood. Given that the edged board is the most cheap material used on objects with least degree responsibility, then complex calculations are not too justified.
Also, it should be noted that the result that you get will not be much different from the one that can be obtained using the cube.
During the construction of residential buildings
Here, professionals in their field are required to perform many tasks, including: calculation and budgeting before completion finishing premises. In addition, it is necessary to calculate required amount building materials. It should be noted that this task is quite difficult. Given this, determining the cubature of the board is an important point.
Note. A cubic meter of lumber is calculated using a single method. The type of board does not affect the result.
To non-grooved types wood include: edged board, unedged board.
tongue-and-groove types- these are those that have special grooves for the perfect joining of the boards: flooring, lining, . Please note that when purchasing a grooved board, the calculation is carried out using the working width of the material, without spikes.
Regarding the calculation of the cubature of an unedged board, with the values \u200b\u200bof the width of one end 25 cm, and 20 cm - the other, average value it will turn out - 22 cm. To calculate a large amount of material, it is laid out in such a way that the wide part does not differ from the narrow one by more than 10 centimeters.
The main length of the board in the unfolded bundle should be approximately the same. Then, using a tape measure, measure the height of the stack of boards and the width in the middle. The result, which is obtained during measurements, is multiplied by a coefficient with a value of 0.07 - 0.09, which depends on the air gap between the boards.
Repair and construction work often involves the use of lumber. But shops, timber trading bases sell them more often not in pieces, but in cubes.
Everything is very simple and fast.
Method for calculating edged lumber
- caliper, tape measure or folding m, with known parameters of the length of wood products, you can limit yourself to a regular ruler;
- calculator is fine mobile phone, a smartphone, if there may be problems with the account “in the mind”;
- a piece of paper and a pencil - to record the results of the calculations, how many boards are in the cube.
- Volume = Length × Height (product thickness) × Width.
To prevent confusion when converting cubic centimeters to Cubic Meters it is more convenient to record the measurement results immediately in meters.
For example, 0.132 cu. m = 6 m × 0.022 m (2.2 cm) × 0.10 m (10 cm).
Now, to determine the number of boards in a cube, you need 1 cube. m divided by 0.132. The result obtained (7, 5757) when purchasing timber must be rounded up to 8 pieces.
This method of calculating cubic capacity is also suitable for timber. So you can determine how many cubes of timber you need to purchase if you know the required number of products, or, conversely, determine the required number of cubes.
Back to index
How to calculate the cube of an unedged board?
To determine the required volume of timber, the easiest way is to carry out calculations similar to the above method. Only the final result needs to be multiplied by 1.2 - a correction factor. From unedged boards you can get no more than 70-80% edged.
The width and thickness of each product is measured taking into account its further processing. The technique will help determine the number of cubes wooden products necessary for work, if the final result is planned for their further processing - cropping.
When buying, the widest and thinnest boards are measured to obtain an average width. If the width of the lumber at the butt is wider than at the top, the arithmetic mean of their dimensions is used without taking into account the bast layer or bark, rounded up to 10 mm. In this case, fractions from 5 mm are rounded up to full 10 mm, and fractions up to 5 mm are not taken into account. The length and thickness of lumber are measured in the usual way. The volume of timber is determined according to the usual scheme:
- the volume of one product is calculated;
- the total cubic capacity of the purchased timber is determined; according to GOST, correction factors are used: 0.96 - for lumber from conifers, 0.95 - for sawn hardwood.
In addition to the piece-by-piece method for determining the volume of unedged lumber, a geometric method can be used.
Requirements for a package of unedged timber:
- lumber is laid tightly, without overlaps, in horizontal rows;
- on one side the ends of the boards are aligned;
- all sides of the package are strictly vertical: according to GOST, the displacement of individual products outward, inward should not exceed 0.10 m;
- the entire length of the lumber package must be of the same width.
Then the volume of the package is calculated, the result is multiplied by the coefficient: