The energy of the sun is just a stream of photons. And at the same time, it is one of the fundamental factors that ensure the very existence of life in our biosphere. Therefore, it is quite natural that sunlight is actively used by man not only in the climatic aspect, but also as an alternative source of energy.
Where is solar energy used
The scope of solar energy is very extensive, and every year it becomes more and more. So, until recently, a country shower with a solar heater was perceived as something extraordinary, and the possibility of using sunlight for home electrical networks seemed fantastic. Today, you will not surprise anyone not only with an autonomous solar station, but also with mobile solar-powered chargers and even small appliances (for example, watches) operating on the photovoltaic effect.
In general, the use of solar energy is very much in demand in such areas as:
- Agriculture;
- Energy supply of sanatoriums and boarding houses;
- Space industry;
- Environmental protection and ecotourism;
- Electrification of remote and hard-to-reach regions;
- Street, garden and decorative lighting;
- Housing and communal services (DHW, house lighting);
- Mobile technology (gadgets and solar-powered charging modules).
Previously, solar energy was used mainly in the space industry (power supply for satellites, stations, etc.) and in industry, but over time, alternative energy began to be actively developed in everyday life. One of the first objects equipped with solar installations were southern boarding houses and sanatoriums, especially those located in secluded areas.
Solar installations and their advantages
The successful application of the first solar modules proved that solar energy has many advantages over traditional sources. Previously, the main advantages of solar plants were only environmental friendliness and inexhaustibility (as well as free) of sunlight.
But in fact, the list of advantages is much wider:
- Autonomy, since no external power communications are required;
- Stability of power supply, due to the specifics of the solar current is not subject to power surges;
- Profitability, since the funds are spent only once, during the installation of the installation;
- Solid service life (over 20 years);
- All-weather use, solar installations work effectively even in frosty and cloudy weather (with a slight decrease in efficiency);
- Simplicity and convenience of service, as it is required only occasionally to clean the front sides of the panels from contamination.
The only drawback is the dependence on the sun and the fact that such installations do not work at night. But this problem is solved by connecting special batteries, which accumulate the energy of sunlight generated during the day.
photo energy
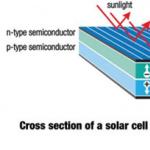
Photovoltaic is one of two ways to use the sun's radiation. This is a direct current generated by the action of sunlight. Such a transformation takes place in the so-called photocells, which, in fact, are a two-layer structure of two semiconductors of different types. The lower semiconductor is p-type (with a lack of electrons), the upper one is n-type with an excess of electrons.
The electrons of the n-conductor absorb the energy of the rays of the sun incident on them and leave their orbits, and the energy impulse is sufficient for them to pass into the zone of the p-conductor. In this case, a directed electron flow is formed, called a photocurrent. In other words, the whole structure works as a kind of electrodes, in which electricity is generated under the influence of the sun.

Silicon is used for the production of such photocells. This is explained by the fact that, firstly, silicon is widespread, and secondly, its industrial processing does not require large expenditures.
Silicon photocells are:
- Monocrystalline. They are made from single crystals and have a uniform structure with a slightly higher efficiency (about 20%), but at the same time they are more expensive.
- Polycrystalline. They have an uneven structure due to the use of polycrystals and a slightly lower efficiency (15-18%), but are much cheaper than monovariants.
- Thin film. They are made by sputtering amorphous silicon onto a thin-film substrate. They are characterized by a flexible structure and the lowest production cost, but they have twice the dimensions compared to crystalline counterparts of the same power.
The fields of application of each type of cells are very extensive and are determined by their operational features.
Solar collectors
Solar collectors are also used as solar energy converters, but the principle of their operation is completely different. They convert the incident light not into electrical, but into thermal energy by heating the liquid coolant. They are used either for hot water supply or for heating houses. The main element of any collector is an absorber, which is also a heat sink. The absorber is either a flat plate or a tubular evacuated system, inside which a coolant circulates (this is either plain water or antifreeze). Moreover, the absorber must be painted black with a special paint to increase the absorption coefficients.

It is by the type of absorbers that the collectors are divided into flat and vacuum. For flat heat sinks, the heat sink is made in the form of a metal plate, to which a metal coil with a coolant is soldered from below. Vacuum absorbers are made of several glass tubes connected to each other at the ends. The tubes are made double, a vacuum is created between the walls, and a rod with a coolant is placed inside. All rods communicate with each other by means of special connectors at the pipe joints.
Absorbers of both types are placed in a durable lightweight housing (usually made of aluminum or impact-resistant plastics) and are reliably insulated from the walls. The front side of the body is covered with transparent impact-resistant glass with maximum photon permeability. This ensures better absorption of solar energy.
Features of functioning
The principle of operation of both types of collectors is similar. Heating in the collector to high temperatures, the coolant passes through the connecting hoses to the heat exchange tank, which is filled with water. Through the tank, it passes through a serpentine tube, giving off its heat to the water. The cooled coolant exits the tank and is fed back to the collector. In fact, this is a kind of “solar” boiler, only instead of a heating coil, a coil is used in the tank, and instead of the mains, sunlight is used.
Structural differences determine the difference in the use of vacuum and flat collectors. The use of solar radiation with the help of vacuum models is possible all year round, including in winter and in the off-season. Flat options work better in the summer. However, they are cheaper and simpler than vacuum ones, so they are optimally suited for seasonal purposes.
Solar energy in cities (eco-houses)
Solar energy is actively used not only for private houses, but also for urban buildings. How a person uses solar energy in megacities is not difficult to guess. It is also used for heating and hot water supply of buildings, and often entire blocks.
In recent years, the concept of eco-houses, fully powered by alternative energy sources, has been actively developed and implemented. They use combined systems that provide efficient production of solar, wind and thermal energy of the earth. Often, such houses not only fully cover their energy needs, but also transfer the surplus to city networks. And more recently, projects of such eco-buildings have appeared in Russia.
Heliostations and their types
In the southern regions with high insolation, not just individual solar plants are being built, but entire stations that generate energy on an industrial scale. The amount of solar energy produced by them is very large, and many countries with a suitable climate have already begun the gradual transition of the entire energy system to such an alternative. According to the principle, the operation of the station is divided into photothermal and photovoltaic. The former work according to the collector method and supply heated water for hot water supply to the houses, while the latter generate electricity directly.

There are several types of solar stations:
- Tower. They allow to receive superheated water vapor supplied to generators. A tower with a water tank is based in the center of the station, heliostats (mirror) are placed around it, which focus the rays on the tank. These are quite efficient stations, their main drawback is the difficulty of accurately positioning the mirrors.
- Dish-shaped. They consist of a solar energy receiver and a reflector. Reflector - a dish-shaped mirror that concentrates radiation at the receiver. Such solar energy concentrators are located at a small distance from the receiver, and their number is determined by the required power of the installation.
- Parabolic. Tubes with a coolant (usually oil) are placed at the focus of a long parabolic mirror. The heated oil gives off heat to the water, which boils and rotates the generators.
- Balloon. In fact, these are the most efficient and mobile solar stations on Earth. Their main element is a balloon with a photovoltaic layer filled with water vapor. It rises high into the atmosphere (usually above the clouds). The heated steam from the ball is fed through a flexible steam pipeline to the turbine, at the outlet of it it condenses and the water rises back into the ball with a pump. Once in the ball, the water evaporates and the cycle continues.
- On photobatteries. These are solar-powered installations that are already familiar to everyone, which are used for private houses. They provide electricity and water heating in the required volumes.
Today, various kinds of solar stations (including combined ones, combining several types) play an increasing role in the energy production of many countries. And some states are restructuring their energy in such a way that in a few years they will almost completely switch to alternative systems.
In recent years, scientists have been particularly interested in alternative energy sources. Oil and gas will run out sooner or later, so we have to think about how we will survive in this situation now. Windmills are actively used in Europe, someone is trying to extract energy from the ocean, and we will talk about solar energy. After all, a star that we see in the sky almost every day can help us save and improve the ecological situation. The value of the sun for the Earth is difficult to overestimate - it gives heat, light and allows all life on the planet to function. So why not find another use for it?
A bit of history
In the middle of the 19th century, the physicist Alexandre Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect. And by the end of the century, Charles Fritts created the first device capable of converting solar energy into electricity. For this, selenium coated with a thin layer of gold was used. The effect was weak, but this invention is often associated with the beginning of the era of solar energy. Some scholars do not agree with this formulation. They call the founder of the era of solar energy the world famous scientist Albert Einstein. In 1921 he received the Nobel Prize for explaining the laws of the external photoelectric effect.
It would seem that solar energy is a promising way of development. But there are many obstacles for it to enter every home - mainly economic and environmental. What makes up the cost of solar panels, what harm they can do to the environment and what other ways to generate energy, we will find out below.
Accumulation methods
The most urgent task associated with the domestication of the energy of the sun is not only its receipt, but also its accumulation. And that is what is most difficult. Currently, scientists have developed only 3 ways to fully tame solar energy.
The first is based on the use of a parabolic mirror and is a bit like playing with a magnifying glass, which is familiar to everyone since childhood. Light passes through the lens, gathering at one point. If you put a piece of paper in this place, it will light up, because the temperature of the crossed sun rays is incredibly high. A parabolic mirror is a concave disk resembling a shallow bowl. This mirror, unlike a magnifying glass, does not transmit, but reflects sunlight, collecting it at one point, which is usually directed to a black pipe with water. This color is used because it best absorbs light. The water in the pipe is heated by the sun's rays and can be used to generate electricity or to heat small houses.
flat heater
This method uses a completely different system. The solar energy receiver looks like a multilayer structure. The principle of its work looks like this.
Passing through the glass, the rays fall on the darkened metal, which, as you know, absorbs light better. Solar radiation turns into and heats the water, which is under the iron plate. Further, everything happens as in the first method. The heated water can be used either for space heating or for generating electrical energy. True, the effectiveness of this method is not so high as to be used everywhere.
As a rule, the solar energy obtained in this way is heat. To obtain electricity, the third method is much more often used.
Solar cells
Most of all, we are familiar with just this way of obtaining energy. It involves the use of various batteries or solar panels, which can be found on the roofs of many modern houses. This method is more complicated than previously described, but is much more promising. It is he who enables the sun to produce electricity on an industrial scale.

Special panels designed to capture rays are made from enriched silicon crystals. Sunlight, falling on them, knocks the electron out of orbit. Another one immediately strives to take its place, thus a continuous moving chain is obtained, which creates a current. If necessary, it is immediately used to provide devices or accumulates in the form of electricity in special batteries.
The popularity of this method is justified by the fact that it allows you to get more than 120 watts from just one square meter of solar panels. At the same time, the panels have a relatively small thickness, which allows them to be placed almost anywhere.
Types of silicon panels
There are several types of solar panels. The first are made using single-crystal silicon. Their efficiency is about 15%. These are the most expensive.
The efficiency of elements made of polycrystalline silicon reaches 11%. They cost less, since the material for them is obtained using a simplified technology. The third type is the most economical and has a minimum efficiency. These are panels made of amorphous silicon, that is, non-crystalline. In addition to low efficiency, they have another significant drawback - fragility.
Some manufacturers use both sides of the solar panel to increase efficiency - the back and front. This allows you to capture light in large volumes and increases the amount of energy received by 15-20%.
domestic producers
Solar energy on Earth is becoming more widespread. Even in our country, they are interested in studying this industry. Despite the fact that the development of alternative energy is not very active in Russia, some success has been achieved. Currently, several organizations are engaged in the creation of panels for solar energy - mainly scientific institutes of various kinds and factories for the production of electrical equipment.
- NPF "Kvark"
- JSC "Kovrovsky Mechanical Plant"
- All-Russian Research Institute of Electrification of Agriculture.
- NPO of mechanical engineering.
- JSC VIEN.
- JSC "Ryazan plant of metal-ceramic devices".
- AOOT Pravdinsky Experimental Plant of Power Sources "Posit".
This is only a small part of the enterprises that are actively involved in the development of alternative
Environmental impact
The rejection of coal and oil sources of energy is connected not only with the fact that these resources will run out sooner or later. The fact is that they greatly harm the environment - they pollute the soil, air and water, contribute to the development of diseases in people and reduce immunity. That is why alternative energy sources must be safe from an environmental point of view.

Silicon, which is used for the production of photovoltaic cells, is itself safe, since it is a natural material. But after cleaning it, waste remains. They can harm humans and the environment if used improperly.
In addition, in an area completely filled with solar panels, natural lighting may be disturbed. This will lead to changes in the existing ecosystem. But in general, the environmental impact of devices designed to convert solar energy is minimal.
Economy
The biggest costs associated with the high cost of raw materials. As we have already found out, special panels are created using silicon. Despite the fact that this mineral is widely distributed in nature, there are big problems associated with its extraction. The fact is that silicon, which makes up more than a quarter of the mass of the earth's crust, is not suitable for the production of solar cells. For these purposes, only the purest material obtained by an industrial method is suitable. Unfortunately, it is extremely problematic to obtain the purest silicon from sand.
In terms of price, this resource is comparable to uranium used in nuclear power plants. That is why the cost of solar panels currently remains at a fairly high level.
Modern technologies
The first attempts to tame solar energy appeared a long time ago. Since then, many scientists have been actively engaged in the search for the most efficient equipment. It should be not only cost-effective, but also compact. Its efficiency should strive to the maximum.

The first steps towards an ideal device for receiving and converting solar energy were made with the invention of silicon batteries. Of course, the price is quite high, but the panels can be placed on the roofs and walls of houses, where they will not bother anyone. And the effectiveness of such batteries is undeniable.
But the best way to increase the popularity of solar energy is to make it cheaper. German scientists have already proposed replacing silicon with synthetic fibers that can be integrated into fabric or other materials. The efficiency of such a solar battery is not very high. But a shirt interspersed with synthetic fibers can at least provide electricity to a smartphone or player. Work is also being actively carried out in the field of nanotechnology. It is likely that they will allow the sun to become the most popular source of energy this century. Scates AS specialists from Norway have already stated that nanotechnologies will reduce the cost of solar panels by 2 times.
Solar energy for home
Self-sufficient housing is the dream of many: there is no dependence on centralized heating, no problems with paying bills, and no harm to the environment. Already, many countries are actively building housing that consumes only energy obtained from alternative sources. A striking example is the so-called solar house.

During the construction process, it will require more investments than the traditional one. But on the other hand, after several years of operation, all costs will pay off - you will not have to pay for heating, hot water and electricity. In a solar house, all these communications are tied to special photovoltaic panels placed on the roof. Moreover, the energy resources obtained in this way are not only spent on current needs, but also accumulated for use at night and in cloudy weather.
Currently, the construction of such houses is carried out not only in countries close to the equator, where it is easiest to obtain solar energy. They are also built in Canada, Finland and Sweden.
Advantages and disadvantages
The development of technologies that allow the use of solar energy everywhere could be more active. But there are certain reasons why this is still not a priority. As we said above, during the production of panels, substances harmful to the environment are produced. In addition, the finished equipment contains gallium, arsenic, cadmium and lead.
The need to recycle photovoltaic panels also raises many questions. After 50 years of operation, they will become unusable and will have to be destroyed somehow. Will it cause enormous harm to nature? It should also be borne in mind that solar energy is a fickle resource, the efficiency of which depends on the time of day and weather. And this is a significant disadvantage.
But there are also advantages, of course. Solar energy can be mined almost anywhere on Earth, and the equipment to produce and convert it can be small enough to fit on the back of a smartphone. More importantly, it is a renewable resource, that is, the amount of solar energy will remain unchanged for at least another thousand years.
prospects
The development of technologies in the field of solar energy should lead to a reduction in the cost of creating elements. Glass panels are already appearing that can be installed on windows. The development of nanotechnology has made it possible to invent a paint that will be sprayed onto solar panels and can replace the silicon layer. If the cost of solar energy really drops by several times, its popularity will also grow many times over.

Creating small panels for individual use will allow people to use solar energy in any environment - at home, in the car or even outside the city. Thanks to their distribution, the load on the centralized power grid will decrease, since people will be able to independently charge small electronics.
Shell experts believe that by 2040 about half of the world's energy will be generated from renewable resources. Already now in Germany, the consumption of solar energy is actively growing, and the battery power is more than 35 Gigawatts. Japan is also actively developing this industry. These two countries are the leaders in the consumption of solar energy in the world. The United States is likely to join soon.
Other alternative energy sources
Scientists do not stop puzzling over what else can be used to produce electricity or heat. Let us give examples of the most promising alternative energy sources.
Windmills can now be found in almost every country. Even on the streets of many Russian cities, lanterns are installed that provide themselves with electricity from wind energy. Surely their cost is above average, but over time they will make up for this difference.

Quite a long time ago, a technology was invented that allows you to get energy using the difference in water temperatures at the surface of the ocean and at depth. China is actively going to develop this direction. In the coming years, off the coast of the Middle Kingdom, they are going to build the largest power plant operating on this technology. There are other ways to use the sea. For example, in Australia they plan to create a power plant that generates energy from the force of the currents.
There are many others or heat. But against the background of many other options, solar energy is a really promising direction in the development of science.
Have you become a participant in discussions of alternative energy? Almost everyone has at least heard something about it. And many even had the opportunity to observe solar panels or wind farms with their own eyes. Now the development of this sphere of energy supply is very important for the further comfortable existence of mankind.
Since we have almost exhausted the main part of traditional resources, such as minerals, we have to look for more durable sources. One such non-traditional energy source is solar energy. This resource is one of the most common and easily accessible, since there is sunlight in one quantity or another in any corner of our planet. Therefore, developments related to the accumulation of solar energy began quite a long time ago and are actively carried out to this day.
As an energy source, sunlight is an excellent alternative to traditional resources. And with proper use, it may well displace all other energy resources in the future.
To find the most efficient methods for converting solar energy, scientists needed to understand what kind of conversion is the source of solar energy. To answer this question, a huge number of experiments and studies have been carried out. There are various hypotheses to explain this phenomenon. But experimentally, in the course of long studies, it was proved that the reaction, during which hydrogen is converted into helium with the help of carbon nuclei, thus acts as the main source of solar energy.
We already know that hydrogen and helium are the source of solar energy, but solar energy itself is a source for certain processes. All earthly natural processes are carried out thanks to the energy received from the Sun.

Without solar radiation it would be impossible:
- The water cycle in nature. It is due to the influence of the Sun that water evaporates. It is this process that starts the circulation of moisture on Earth. Temperature rises and falls affect cloud formation and precipitation.
- Photosynthesis. The process by which the balance of carbon dioxide and oxygen is maintained, the substances necessary for the development and growth of plants are formed also occurs with the help of sunlight.
- Atmospheric circulation. The sun influences the processes of movement of air masses and heat regulation.
Solar energy is the basis for the existence of life on Earth. But its beneficial effect does not end there. For humanity, solar energy can be useful as an alternative source of energy.
At present, the active development of technology has made it possible to convert solar energy into other forms used by man. As a renewable energy source, solar energy has become widespread and is actively used, both on an industrial scale and locally in small private plots. And every year there are more and more areas where the use of solar thermal energy is commonplace.

Today, sunlight as a source of energy is used:
- In agriculture, for heating and power supply of various outbuildings such as greenhouses, hangars and others.
- To provide electricity to medical centers and sports buildings.
- For the supply of electricity to settlements.
- To provide cheaper lighting on city streets.
- To maintain the smooth operation of all communication systems in residential buildings.
- For the daily household needs of the population.
Based on this, we see that solar energy can actually become an excellent source of power in almost every area of human activity. Therefore, continued research in this industry can change the usual current existence in the roots.
Today, thanks to various developments and methods, solar energy as an alternative energy source can be converted and accumulated in many ways. Now there are systems for the active use of solar energy, and passive systems. What is their essence?

- Passive (selection of building materials and design of premises for the maximum use of solar energy) are mostly focused on the use of direct solar energy. Passive systems are buildings in which the design took place in such a way as to receive as much light and heat energy as possible from the Sun.
- Active (photovoltaic systems, solar power plants and collectors), in turn, mean really processing the received solar energy into other types necessary for a person.
Both types of such systems are used in certain cases, depending on the needs that they must satisfy. Whether it is the construction of an environmentally friendly solar house or the installation of a collector on the site, this will in any case give its result and be a profitable investment.

What is a solar power plant? This is a specially organized engineering structure, thanks to which the processes of converting solar radiation for further generation of electricity take place. The designs of such stations can be completely different depending on which processing method will be used.
Varieties of solar power plants:
- SES, at the heart of the construction of which is the tower.
- The station, which is being built on a plate type.
- Based on the operation of photovoltaic modules.
- Stations operating with the use of parabolic trough concentrators.
- With the Sterling engine taken as the basis for the work.
- Aerostat stations.
- Combined type power plants.
As we can see, the solar power plant as an energy source has long ceased to be a part of utopian science fiction novels and is actively used all over the world to meet the energy needs of society. There are clear advantages and disadvantages to her work. But their correct balance makes it possible to obtain the desired result.
Pros and cons of solar power plants
Advantages:
- Solar energy is a renewable energy source. At the same time, it is publicly available and free of charge.
- Solar installations are quite safe to use.
- Such power plants are completely autonomous.
- They are economical and have a fast payback period. The main costs occur only for the necessary equipment and require minimal investment in the future.
- Another distinguishing feature is stability in work. There are practically no power surges at such stations.
- They are not whimsical in maintenance and are quite easy to use.
- Also, for SPP equipment, a characteristic long operating period is characteristic.
Flaws:
- As a source of energy, the solar system is very sensitive to climate, weather conditions and time of day. Such a power plant will not operate efficiently and productively at night or on a cloudy day.
- Lower productivity in latitudes with strong seasons. They are most effective in areas where the number of sunny days per year is closest to 100%.
- Very high and inaccessible cost of equipment for solar installations.
- The need for periodic cleaning of panels and surfaces from contamination. Otherwise, less radiation is absorbed and productivity drops.
- A significant increase in air temperature within the power plant.
- The need to use the terrain with a huge area.
- Further difficulties in the process of disposal of plant components, in particular photocells, after the end of their service life.
As in any industrial field, solar energy processing and conversion has its strengths and weaknesses. It is very important that the advantages cover the disadvantages, in which case the work will be justified.
Most of the developments in this industry are now focused on optimizing and improving the performance and use of existing methods and on developing new, safer and more productive methods.
Solar energy is the energy of the future
The further our society steps in its technical development, the more sources of energy may be required with each new stage. But traditional resources are becoming less and less, and their price is rising. Therefore, people began to think more actively about alternative energy supply options. This is where renewable sources come to the rescue. The energy of wind, water or the Sun is a new round that allows society to continue to develop, supplying it with the necessary resources.
Floating solar panels came to the attention of experts back in 2011, when the French firm Ciel & Terre developed its first "floater" - the Hydrelio Floating PV system, the website EVWind notes.
The floating island-panel has proved to be in demand in the clean energy market, many countries have adopted this method of generating electricity. For example, in Chile, where mining requires a constant expenditure of energy and water: by putting a solar panel on the surface of numerous lakes, the government has reduced the cost of mining and reduced the carbon footprint.
Floating battery panels are still being tested at the Los Bronques mine, near which an experimental energy island has been created - the Los Tortolas project is funded by companies from the UK and the USA, the area of \u200b\u200bsolar panels is still 112 square meters, Chilean Mining Minister Baldo Prokuritsa. Tortolas was inaugurated in April, the floating battery cost $250,000, but if successful, the area will be expanded to 40 hectares.
According to experts, solar energy has great prospects in Chile. There are about 800 ponds in the country that can be used to install floating solar power plants (SPPs). As conceived by the engineers, the float battery is placed in the center of the body of water, which is used to store "tails" (waste from mining). This achieves a triple benefit:
- shade lowers the temperature of the pond water;
- water evaporation is reduced by 80%;
- production is cheaper many times, working on solar energy.
Ecologists applaud such a plan, because there is much more water left in the mine for natural balance, this approach can reduce the regional consumption of already scarce fresh water.
Through this system, Chile is rationalizing fresh water consumption in line with its goal of improving the mining process and reducing fresh water consumption by 50% by 2030. The carbon footprint is automatically reduced also through the production of clean energy.
Chile is gradually increasing its share of clean energy
The Los Bronques mine is located 65 km from the capital of Chile at an altitude of 3.5 km above sea level. Almost 20% of the energy that is produced and used in the Latin American country in 2019 is clean. In 2013, the indicator was equal to only six percent, which demonstrates a steady increase in the share of green energy in the national economy of the country and its commitment to the goals of the Paris Climate Agreement (2015).
The developments of engineers from Ciel & Terre, as well as financial assistance, gave Chile the opportunity to expand the horizons of the energy market and break out of the vicious circle in which electricity is obtained by burning minerals. Floating solar panels are easy to install, maintain and manage. High density thermoplastic, installed at 12 degrees, completely eco-friendly and recyclable. Floating solar power plant does not harm nature, it is cost-effective and flexible in settings.
According to Chilean engineers, this is a simple and affordable alternative to ground-based solar energy facilities. It is ideal for water intensive industries with limited water consumption or land area.
Hevel will build a solar power plant with a capacity of 100 MW in Kazakhstan
Cold energy: "anti-solar battery" works at night
Engineers have created a device that can be called a reverse solar cell: it generates current not when it absorbs photons, but when it emits them. Such an energy source could power various equipment at night, giving off the heat stored by the Earth's surface into space.
As you know, heated bodies emit radiation. This is easy to verify by raising your hand to a hot battery (preferably on the side so that the upward flow of warm air does not interfere). If an object does not receive as much thermal energy from the external environment as it radiates, it cools down. In order for an object to be cooled more efficiently, it is necessary to allow it to freely exchange photons with the coldest possible environment.
Back in the 20th century, physicists theoretically calculated, and in recent years experimentally demonstrated, the effect of negative illumination. It lies in the fact that a photodiode can generate electricity not only by absorbing photons coming from the external environment (as in a conventional solar battery), but, on the contrary, giving them away and cooling due to this. This process consumes energy stored in the device in the form of heat.
To operate such a device, a cold environment is needed, in which photons will leave without returning back. And we have such an environment at our fingertips, or rather, above our heads: this is open space.
Of course, if such an emitter is simply launched into orbit (and not allowed to heat up from the Sun, keeping it in the shade), it will quickly highlight all its heat, equalize in temperature with the vacuum of space and stop generating energy.
However, on Earth, it is possible to provide him with thermal contact with the surface of the planet. As soon as the photocell becomes colder than the surrounding bodies, the energy deficit will be replenished due to thermal conductivity. Thanks to this, photons will still regularly fly into icy outer space through the atmosphere, which is quite transparent at wavelengths from 8 to 13 micrometers (narrow band in the mid-infrared range). Part of the energy of the radiation leaving the installation will be converted into electrical energy.
It is this device that the authors of the new work created. They chose a compound of mercury, cadmium and tellurium (HgCdTe) as the material for the photodiode. This substance effectively radiates precisely in the desired wavelength range. Passing through a hemispherical gallium arsenide (GaAs) lens and a barium ferride (BaFe2) window, the photons hit a parabolic mirror that sends them straight up into the sky. To get to the diode from the external environment, the radiation needs to go the same way in the opposite direction. All these tricks are needed in order for the installation to exchange photons almost exclusively with space, and receive energy from the Earth due to heat conduction.
The experimental setup in Fan's group's experiments generated 64 nanowatts per square meter of surface. Of course, devices cannot be powered from such power. However, as the authors calculated, the theoretical limit, taking into account the influence of the atmosphere, is 4 watts per square meter. This is much less than modern solar panels (100-200 watts per square meter), but quite enough to power some devices.
To bring the installation power closer to this mark, it is necessary to choose a material for the photodiode with a more pronounced negative illumination effect. Researchers are currently looking for such a substance.
2018
The EU solar energy market grew by 36% in a year
Preliminary data on the development of solar energy in European countries have been published. Germany is still in the lead, with Turkey in second place and the Netherlands in third.
According to statistics from the Solar Energy Association SolarPower Europe, the European market grew significantly in 2018. In 28 EU countries, 8 GW of solar power plants were commissioned, which is 36% more than in 2017. At the same time, 11 countries have already exceeded their obligations to introduce renewable energy sources and reached the level of 2020. The wider European market, including Turkey, Russia, Ukraine, Norway, Switzerland, Serbia, Belarus, also showed an increase of 11 GW, up 20% from a year earlier.
Germany once again became the largest solar energy market on the European continent in 2018 with new solar power plants with a total capacity of 3 GW. Turkey, due to the high pace of market development over the past two years, took second place (1.64 GW). The Netherlands, which also set a national record of 1.4 GW of SPPs put into operation, was ranked third at the end of the year.
According to experts, in 2019 the industry will grow even more - factors such as the abolition of duties on Chinese solar panels and the competitiveness of industrial photovoltaic solar power plants will affect the development of solar energy in Europe.
An iron-based molecule has been created that can "capture" the energy of sunlight
On December 4, 2018, it became known that some photocatalysts and solar cells are based on technology that includes molecules containing metals. Their task is to absorb the rays and use their energy. For December, 2018 metals in these designs are rare and expensive are, for example, ruthenium, osmium and iridium.
Together with colleagues, he worked to find an alternative for expensive metals. The researchers focused on iron, which is much easier to mine. Scientists have created their molecules based on iron, its potential for use in solar energy has been proven in previous studies.
As of December 2018, this research has taken it one step further and developed an iron-based molecule that can "capture" and use sunlight energy for long enough that it can react with another molecule.
The study is published in the journal Science. According to the researchers, the molecule can be used in the following types of photocatalysts for the production of solar energy. In addition, the results open up other potential applications for iron molecules, such as materials in LEDs.
Researchers bring solar cell efficiency closer to conventional
On October 5, 2018, it became known that the researchers brought the efficiency of the solar battery closer to the usual one. Solar energy is considered the most sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, but the technology to convert it into electricity must be very efficient and cheap. Scientists at the Energy Materials Department of the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology believe they have found a formula for making low-cost, high-efficiency solar cells.
To do this, Professor Yaobing Qi, leader of the study, identified three conditions that will lead the technology to be introduced to the market and successfully commercialized. According to him, the rate of conversion of sunlight into electricity must be high, inexpensive, and also durable.
For October, 2018 the majority of commercial photocells which are used in batteries are made of crystal silicon. It has a relatively low efficiency - about 22%. Ultimately, this leads to the fact that the product is expensive for the consumer, and his only motivation for buying is concern for nature. Japanese scientists propose to solve the problem with the help of perovskite.
SoftBank to build largest solar power plant in Saudi Arabia
The corresponding memorandum of intent was signed in New York by Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman Al Saud and SoftBank CEO Masayoshi Son. The prince is on a three-week official visit, the channel notes.
The planned capacity of the cascade of solar panels is 200 GW, which is many times more than any existing solar power plant. By comparison, California's Topaz Solar Farm, one of the largest of its kind, peaks at about 550 MW. Energy is stored there by 9 million thin-layer photovoltaic modules.
Dutch startup Oceans of Energy, which specializes in the development of floating renewable energy systems, has teamed up with five large companies to build the world's first offshore solar power plant. "Such power plants are already operating on water bodies in the mainland of different countries. But no one has built them on the sea - this is an extremely difficult task. We have to deal with huge waves and other destructive forces of nature. However, we are convinced that by combining our knowledge and experience, we can handle this project," said Allard van Hoeken, head of Oceans of Energy.
According to preliminary calculations, the floating power plant will be 15% more efficient than existing installations. The Energy Research Center of the Netherlands (ECN) will select the most suitable solar modules. Its experts believe that it is possible to use standard solar panels for the project, which also work at ground-based solar stations. "Let's see how they behave in sea water and in adverse weather conditions," said ECN spokesman Jan Kroon.
The consortium emphasizes that a floating solar power plant can be installed directly between offshore wind turbines. There are calmer waves and all power lines have already been laid. In the next three years, the consortium will work on a prototype with the financial support of the State Agency for Entrepreneurship of the Netherlands. And the University of Utrecht will provide the startup with the materials of its research.
The cost of solar energy in Australia has fallen by 44% since 2012
This renewable energy craze has led people to actually start paying less for electricity. On the plus side, the cost of electricity itself has also come down. Since 2012, the cost of installing and operating solar panels has fallen by almost half.
In 2017, private homeowners and businesses in the country installed panels with a total capacity of 1.05 GW. This assessment is given by the agency responsible for clean energy in the country. Authorities say that this is a record figure in history. At the beginning of this decade, renewable energy growth was reportedly linked to lucrative subsidies and tax proposals, but 2017 growth is different: the country's residents have decided to fight rising electricity tariffs in this way, and the movement has become massive.
BNEF predicts that Australia will become the world leader in the introduction of solar panels. By 2040, 25% of the country's electricity needs will be covered by rooftop solar panels. This will become possible due to the fact that today the payback period for such solutions has been reduced to the minimum since 2012. While this does not mean that traditional power plants in Australia are a thing of the past, but people are becoming freer in matters of providing themselves with electricity.
2017
South Korea to increase solar generation by 5 times by 2030
South Korea's Minister of Commerce, Industry and Energy unveiled the government's plan to quintuple solar power generation by 2030.
The announcement came shortly after this year's President-elect Moon Jae-in vowed to end government support for the construction of new nuclear power plants and move towards clean energy sources. The government has already canceled the construction of six nuclear reactors in South Korea.
In total, the country plans to receive by 2030 a fifth of the generated electricity from renewable sources. Last year this figure was 7%. To this end, it is planned to add 30.8 GW of solar power and 16.5 GW of wind power by the appointed date. Additional energy will come from major projects as well as private households and small businesses, Minister Paik Ungyu said. "We will fundamentally change the way renewable energy is developed by creating an environment where citizens can easily participate in the renewable energy trade," he said.
This means that by 2022, approximately 1 in 30 households should be equipped with solar panels, according to Clean Technica.
Nevertheless, while South Korea ranks fifth in the world in terms of the use of nuclear energy. The country has 24 operating reactors, providing about a third of the country's electricity needs.
BP invests $200 million in solar energy
The Atacama Desert in Chile is one of the sunniest and driest places on the planet. It is logical that it was there that they decided to build the largest solar power plant in Latin America, El Romero. Giant solar panels cover 280 hectares of area. Its peak capacity is 246 MW, and the power plant generates 493 GWh of energy per year - enough to power 240,000 homes.
Surprisingly, just five years ago, there was almost no use of renewable energy sources in Chile. The country was dependent on energy supplier neighbors who inflated prices and forced Chileans to suffer exorbitant electricity bills. However, it is precisely the lack of fossil fuels that has led to a massive flood of investment in renewables, especially solar energy.
Now Chile produces almost the cheapest solar energy in the world. The companies hope that the country will become "Saudi Arabia for Latin America". Chile has already joined Mexico and Brazil in the top 10 renewable energy producing countries and is now set to lead the clean energy transition in Latin America.
"Michelle Bachelet's government has made a quiet revolution," said sociologist Eugenio Tironi.
Now that Chile's oligopolistic energy market is open to competition, the government has set a new goal: by 2025, 20% of the country's energy must come from renewable sources. And by 2040, Chile is going to completely switch to "clean" energy. Even to experts, this does not seem like a utopia, since the country's solar power plants, with current technologies, produce electricity twice as cheap as coal-fired power plants. Solar energy prices fell 75% to a record 2,148 cents per kilowatt hour.
Manufacturing companies face another problem: too cheap electricity does not bring much profit, and the maintenance and replacement of solar panels is not cheap. "The government will have to build long-term strategies so that the miracle does not become a nightmare," said José Ignacio Escobar, CEO of the Spanish conglomerate Acciona.
Google is completely switching to solar and wind energy
The company has become the world's largest corporate buyer of renewable energy, reaching a total capacity of 3 GW. Google's total investment in clean energy has reached $3.5 billion, writes Electrek in November 2017.
Google is officially moving to 100% solar and wind power. The company signed a contract with three wind farms: Avangrid in South Dakota, EDF in Iowa and GRDA in Oklahoma, with a total capacity of 535 MW. Now Google offices around the world will consume 3 GW of renewable energy.
The company's total investments in the energy sector reached $3.5 billion, and 2/3 of them are in facilities in. Such interest in "clean" sources is connected, first of all, with the fall in the cost of solar and wind energy by 60-80% in recent years.
Google first signed a partnership with a 114 MW solar farm in Iowa back in 2010. By November 2016, the company was already a participant in 20 renewable energy projects. It was going to completely switch to solar and wind energy back in December 2016. Google is now the world's largest corporate buyer of renewable energy.
Smart glass for windows was invented in Sweden
Scientists have been exploring this area for a long time and are looking for applications for the development. In the modern world, this technology is relevant, since the heat loss of houses due to windows is approximately 20%. Scientists believe that their invention can also be used for thermal insulation of various objects.
Villages in Iran sell electricity to the state
As of autumn 2017, there are more than 200 "green" villages in Iran. It is expected that by the spring of 2018 their number will reach 300. Iran today reports that solar panels have been installed in some settlements of the country for ten years. It is noted that the largest volumes of energy from the sun are produced in the provinces of Kerman, Khuzestan and Lorestan.
Initially, the emergence of alternative energy sources in the villages of Iran was due to the impossibility of delivering electricity to them from cities. Now they sell their own energy to the Iranian Ministry of Energy. It is planned to develop legislative norms, according to which the purchase of electricity in the villages will become permanent.
By 2030, Iran expects to produce 7,500 MW of "green" energy, today this figure is only 350 MW. However, the country has good prospects for the development of solar energy, because the sun shines on 2/3 of the territory 300 days a year.
British scientists have invented solar-powered glass bricks
A team of scientists at the University of Exeter in England have developed glass wall units with built-in solar panels. This is written by the architectural portal Archdaily. Blocks can be used in the construction of houses instead of ordinary bricks.
The building material was called "Solar Squared" ("Solar Square Tile"). As tests in the laboratory of the university showed, in addition to generating electricity, the blocks have a number of other useful properties. In particular, the walls constructed in this way let sunlight into the building well and keep the heat in the rooms.
To promote the product, scientists created an innovative company, The Build Solar. The search for investors is currently underway. The launch of the "solar tile" on the market is tentatively scheduled for 2018.
Dubai launches world's largest solar power plant
The installation of each solar panel cost 6,000 euros, including rent for a year, repairs and technical equipment. It is planned that solar panels will operate at public transport stops for about a year, after which they will be transferred to schools and kindergartens.
According to Piotr Switalski, head of the EU delegation to Armenia, the EU is interested in developing alternative energy in the country. He called the stop with solar panels "the solar stop of the European Union".
There have been disputes and discussions about solar energy and the prospects for its development for many years. Most consider solar energy to be the energy of the future, the hope of all mankind. A large number of companies are investing heavily in the construction of solar power plants. Solar energy is being developed in many countries of the world, considering it the main alternative to traditional energy carriers. Germany, being far from a sunny country, has become a world leader in this area. The total capacity of SES in Germany is growing year by year. Seriously engaged in developments in the field of solar energy in China. According to the optimistic forecast of the International Energy Agency, by 2050 solar power plants will be able to produce up to 20-25% of the world's electricity.
An alternative view of the prospects for solar power plants is based on the fact that the costs required for the manufacture of solar panels and battery systems are many times higher than the profit from the electricity produced by solar power plants. Opponents of this position claim that the opposite is true. Modern solar batteries are able to work without new investments for tens and even hundreds of years, the total energy produced by them is equal to infinity. That is why, in the long term, electricity generated using solar energy will become not just profitable, but super-profitable.
Where is the truth? Let's try to figure it out together with you, dear readers. We will look at modern approaches in the field of solar energy and some of the most brilliant ideas that have already been implemented to date. We will try to establish the efficiency of solar panels that are currently operating, to understand why today this efficiency is rather low.
The efficiency of solar panels in Russia
According to modern research, solar energy is about 1367 watts per square meter (solar constant). At the equator, only 1020 watts reach the earth through the atmosphere. On the territory of Russia, with the help of solar power plants (assuming that the efficiency of solar cells is 16% today), an average of 163.2 watts per square meter can be obtained.
In taking into account weather conditions, the duration of the day and night, as well as the type of installation of solar panels (the efficiency of the solar battery is not taken into account).
If a square kilometer of solar panels is installed in Moscow at an angle of 40 degrees (which is optimal for Moscow), then the annual volume of electricity generated will be 1173 * 0.16 = 187.6 GW * h. With an electricity price of 3 rubles per kWh, the notional value of the generated electricity is 561 million rubles.
The most common ways to generate electricity using the sun:
Solar thermal power stations
The huge mirrors of such solar power plants, turning, catch the sun and reflect it onto the collector. The principle of operation of such power generating stations is based on the conversion of the thermal energy of the sun into the mechanical electrical energy of a thermodynamic machine, either with the help of a gas-piston Stirling engine, or by heating water, etc.
As an example, consider the Ivanpah power plant (capacity 392 megawatts), in which the almighty Google has invested. More than two billion US dollars have been invested in the construction of a solar power plant located in California's Mojave Desert. 5612 dollars were spent for 1 kW of the installed capacity of the solar power plant. Many believe that these costs, while higher than those of coal-fired power plants, are much lower than those of nuclear power plants. But is it? First, a nuclear power plant costs between $2,000 and $4,000 per kilowatt of installed capacity, which is cheaper than the cost of building Ivanpah. Secondly, the annual electricity generation of the solar power plant is 1079 GWh, therefore, its average annual capacity is 123.1 MW. In addition, the solar power station is able to generate solar energy only during the daytime. Thus, the "average" cost of building a solar power plant comes to 17,870 dollars per 1 kW, and this is a rather significant price. Perhaps it would be more expensive to generate electricity in outer space. The construction costs of conventional power plants operating, for example, on gas, are 20-40 times lower. At the same time, unlike solar power plants, these power plants can operate continuously, producing electricity when there is a need for it, and not only during those hours when the sun is shining.
But we know that modern solar thermal power plants are capable of generating electricity around the clock, using for this a large volume of coolant heated throughout the daylight hours. Only the cost of building these stations is being tried not to advertise too much, probably because it is significant. And if batteries are included in the cost of designing and building solar power plants, especially the construction of pumped storage power plants, then the amount will increase to fantastic proportions.
silicon solar panels
Today, for the operation of solar power plants, semiconductor photocells are used, which are semiconductor diodes of a large area. A light quantum flying into the pn junction generates an electron-hole pair, while a voltage drop (of the order of 0.5V) is created at the outputs of the photodiode.
The efficiency of a silicon solar battery is about 16%. Why is the efficiency so low? In order to form an electron-hole pair, a certain energy is required. If the arriving light quantum has a low energy, then the generation of a pair will not occur. In this case, a quantum of light will simply pass through silicon, as through ordinary glass. This is why silicon is transparent to infrared light beyond 1.2 µm. If a light quantum arrives with more energy than is required for generation (green light), a pair is formed, but the excess energy will simply go nowhere. With blue and ultraviolet light (whose energy is very high), the quantum may not have time to reach the very depths of the p-n junction.
![]()
In order for sunlight not to be reflected from the surface of the solar battery, a special anti-reflective coating is applied to it (such a coating is also applied to the lenses of photographic lenses). The surface texture is made uneven (in the form of a comb). In this case, the light flux, reflected from the surface once, returns again.
The efficiency of photocells is increased by combining photocells based on different semiconductors and with different energies required to generate an electron-hole pair. For three-stage silicon photocells, an efficiency of 44% and even higher is achieved. The principle of operation of a three-stage photocell is based on the fact that a photocell is placed first, which effectively absorbs blue light, and transmits red and green. The second photocell absorbs green, the third absorbs IR. However, three-stage photovoltaic cells are very expensive today, therefore, cheaper single-stage photocells are widely used, which, due to the price, are ahead of three-stage ones in Watt / $.
China is developing the production of silicon solar cells at a gigantic pace, due to which the cost of one watt is reduced. In China, it is about 0.5 dollars per watt.
The main types of silicon solar cells are:
Monocrystalline
Polycrystalline
The efficiency of monocrystalline solar cells, which are more expensive, is slightly higher (by only 1%) than the efficiency of polycrystalline ones. Polycrystalline silicon solar cells today provide the cheapest cost per watt of electricity generated.
Silicon solar cells cannot last forever. Over 20 years of operation in an aggressive environment, the most advanced of them lose up to 15 percent of their original power. There is reason to believe that further degradation of solar panels slows down.
Silicon photocell and parabolic mirror
Inventors all over the world are making all sorts of attempts to increase the economic viability of solar power plants. If, for example, we take a small efficient silicon photocell and a parabolic mirror (concentrated photovoltaics), we can achieve an efficiency of 40% instead of 16, while the mirror is much cheaper than a solar battery. But in order to follow the sun, reliable mechanics are required. A huge mirror swivel dish must be securely fastened and protected from powerful wind gusts and aggressive environmental factors. The second problem is that parabolic mirrors cannot focus scattered light. If the sun has set even behind thin clouds, the power generation from the parabolic system will drop to zero. In conventional solar panels under these conditions, the generation of thermal energy is also seriously reduced, but not to zero. Solar panels with parabolic mirrors are too expensive in terms of installation cost and costly to maintain.
Round solar cells on rooftops
The American company Solyndra, with the support of the government, designed solar cells with a round shape. They were mounted on roofs painted white. Circular solar arrays were made by sputtering a conductive layer (in the case of Solyndra, Copper indium gallium (di)selenide was used) onto glass tubes. The actual efficiency of round batteries was about 8.5%, which is lower than cheaper silicon ones. Solyndra, which received state guarantees on a huge loan, went bankrupt. In technology, the cost-effectiveness of which was very doubtful from the very beginning, the American economy has invested a lot of money. “Successful” lobbying of inefficient technologies is not only Russian know-how.
The Big Problem of Solar Energy!
It is known that solar power plants generate electricity during the day, while a huge need for electricity arises just the same in the evening. This means that without batteries, solar power plants will not be effective. During the evening peak of electricity consumption, alternative (classical) sources of electricity will have to be used. During the daytime, some traditional power plants will have to be turned off, and some will be kept on standby in case of bad weather. If clouds hang over the solar power plant, the missing electricity should be provided by the backup. As a result, classical generating capacities stand in reserve and lose profit.

There is another way. It is reflected in the Desertec project - the transmission of electricity from Africa to Europe. With the help of power lines in the evening peak of electricity consumption, it is possible to transmit electricity from solar power plants, which are located in those areas of the globe where at that time the sun is at its height. But this method, before switching to superconductors, requires huge financial costs, as well as all sorts of agreements between different states.
Battery use
We found that the average cost per watt produced by a solar panel is $0.50. During the day (8 hours), the battery is able to generate within 8 Wh. This energy must be conserved until the evening peak of electricity consumption.
Lithium batteries developed in China cost approximately $0.4 per Wh, so for a $0.5 solar panel, $3.2 batteries per watt would be needed, which is six times the cost of the battery itself. . Considering that a lithium battery is designed for a maximum of 2000 charge-discharge cycles, which is three to six years, we can conclude that a lithium battery is an extremely expensive solution.
The cheapest batteries are lead-acid. The wholesale price of these far from the most environmentally friendly systems is about $ 0.08 per Wh. Lead-acid batteries, as well as lithium batteries, are designed for 3-6 years of operation. The efficiency of a lead battery is 75%. This battery loses a quarter of its energy in the charge-discharge cycle. To save a day's solar energy production, you will need to purchase lead-acid batteries for $0.64. We see that this is also more than the cost of the batteries themselves.
Pumped storage power plants have been developed for modern solar power plants. During daylight hours, water is pumped into them, and at night they function like ordinary hydroelectric power plants. But the construction of these power plants (90% efficiency) is not always possible and extremely expensive.
We can draw a disappointing conclusion. Today, batteries are more expensive than solar power plants themselves. For large solar power plants, they are not provided. As electricity is generated, large solar power plants sell it to distribution networks. In the evening and at night, electricity is generated by conventional power plants.
Solar energy - what is its price today?
Take, for example, Germany - the world leader in the use of solar energy. A kilowatt of solar energy that is generated (even during the daytime, and such electricity is cheaper) is bought in this country at a price of 12 to 17.45 euro cents per kWh. Since gas-fired power plants in Germany are still under construction, operating or on hot standby, solar power plants in this country are actually just helping to save Russian gas.
The cost of Russian gas today is $450 per thousand cubic meters. From this volume of gas (generation efficiency 40%), approximately 4.32 GW of electricity can be generated. Consequently, for 1 kWh of electricity generated from the sun, Russian gas is saved in the amount of 0.104 dollars or 7.87 euro cents. Here is the fair value of solar unregulated generation. Thus, currently in Germany, solar energy is 50% subsidized by the state. Although, it should be noted that Germany is rapidly reducing the cost of generating electricity from the sun.
Drawing conclusions
The most economical solar electricity (0.5 dollars per 1 watt) is produced today with the help of solar polycrystalline batteries. All other methods of generating electricity using solar energy are much more expensive.
The problem that is key for solar energy is not the efficiency of solar panels, not the price, and not the EROEI, which is theoretically infinite. The main problem is to reduce the cost of ways to generate solar energy received during the daytime and save this energy for the evening peak consumption. Indeed, at present, battery systems, the service life of which is from three to six years, are several times more expensive than the solar panels themselves.
Solar generation on a significant scale is considered today only as a way to save a small part of traditional fossil fuels during the daytime. Solar energy is not yet able to fully take on the load during the evening peak hours of energy consumption and reduce the number of nuclear power plants, coal, gas and hydroelectric power plants, which should stand in reserve during the daytime, and take on a significant energy load in the evening.
If, as a result of tightening tariffs (which, for example, it would be profitable for producers of hydrogen and aluminum to start their electrolysis production during the daytime), the peak of electricity consumption shifts to daytime hours, then solar energy will have more serious prospects for development.
The cost of solar generation, which is "unregulated", is incomparable to the cost of generating electricity in conventional power plants, which are free to generate it at any time when it is needed.
The cost of solar electricity should not exceed the cost of fossil fuels saved with its help. If, for example, gas in Germany costs $450, then the price of solar generation in this country should not exceed $0.1 per kilowatt hour, otherwise solar energy in this country is unprofitable. As long as fossil fuels remain cheap and readily available, solar power generation is not economically viable.
Currently, the use of solar energy and expensive solar battery systems is economically justified only for those regions and objects where there are no other options for connecting to the power grid. For example, at a lonely standing, remote cellular station.
However, do not forget the following important factors that inspire optimism when considering solar energy:
1. The cost of fossil fuels is steadily rising as its supply decreases.
2. Reasonable government policy makes the use of solar power plants more profitable.
3. Progress does not stand still! The efficiency of solar power plants is increasing, new technologies are being developed in the generation and accumulation of electricity.
Therefore, I would like to believe that in 3-5 years it will be possible to write a much more positive review of this energy sector!