Sewer drains in the house must be collected and sent to the central sewer or to or to.
This task is performed by the piping system inside and outside the house - internal and external sewage.
How to lay sewer pipes in a private house
The sewerage diagram shows two vertical pipes crossing the house from the basement to the roof − these are sewers, in which drains from nearby sanitary appliances are collected.
Drains from sanitary appliances move by gravity to the sewer risers, and from there to the horizontal sewers and further to the outlet of the external sewer.
Features of the movement of effluents through sewer pipes
When developing a sewerage scheme, be guided by the following.
With a volley discharge of water through the toilet, a portion of water filling all, or almost all, the section of the sewer pipe, moving along the pipe, acts like a piston. Behind the flow of water, a vacuum is created in the pipe, which, if there is no ventilation, sucks water from the siphons of sanitary appliances connected to the pipe downstream.
BUT pressure builds up ahead of the water flow, which pushes water out of the siphons of sanitary appliances connected upstream.
The effect of pressurizing the pipe is usually less pronounced, since the sewer pipe at the front end usually has an open outlet. The vacuum in the pipes with an improper sewage system in the house often leads to the suction of water from the siphons of sanitary appliances and smell in the house.
Similar processes in sewer pipes can occur:
- When emptying the tub or draining the washing machine under pressure from the pump.
- In very long supply pipes from sanitary appliances to the riser.
- With a large difference in height between the beginning and end of the supply pipe.
Rules for laying sewerage in the house
When developing a sewerage scheme for a private house, the following rules are observed:
1. The toilet must have a separate connection to the riser. No other sanitary appliances should be connected to the pipe between the toilet bowl and the riser. Failure to comply with this rule may lead to the fact that when flushing the toilet over the full cross section of the pipe, water will be sucked out of the siphons of other sanitary appliances.
2. Connection to the riser on the floor of other sanitary appliances should not be lower than the connection point of the toilet bowl. Otherwise, when flushing the toilet, sewage may appear in the drain hole of adjacent appliances.
Other sanitary appliances, except for the toilet, may have one common pipe to the riser.
3. When choosing the diameter of the pipes, they are guided by the rule - the diameter of the pipe leading to the riser should not be less than the diameter of the drain pipe of the sanitary appliance. If several devices are connected to one supply pipe, then the diameter of the pipe is taken according to the largest section of the branch pipe of the connected devices.
The diameter of the riser pipe should not be less than the diameter of the toilet drain pipe - 100mm .; or 50 mm. - for a riser without a toilet bowl.
4. The length of the supply pipe to the riser from the toilet should be no more than 1 m. The length of the pipe connections from other sanitary appliances is not more than 3m. For longer pipes (up to 5 meters), it is necessary to increase the pipe diameter to 70-75mm. Liners with a length of more than 5 m are made from pipes with a diameter of 100-110 mm. It is not necessary to increase the diameter of the inlet pipes if the upper ends of the inlets are ventilated with an aeration vacuum valve or by connecting the inlet to the riser vent pipe. The length of the piping to the toilet can be increased provided that the end attached to the toilet is ventilated.
5. The slope of the pipes for effective self-cleaning should be within 2 - 15% (2 - 15 cm per meter of length). The height difference between the beginning and the end of the piping to the toilet should not exceed 1m. For other eyeliners - no more than 3m. If the height difference is greater, then ventilation of the upper end of the liner is necessary.
6. Avoid installing corner fittings with an angle of 90 degrees at pipe bends. The angles of rotation and connection of pipes must be formed smoothly, from standard parts with an angle of 135 degrees along the flow of the liquid.

7. Sewer pipes are laid with a socket in the direction - towards the flow.
8. Be sure to ventilate the risers. To do this, the pipes of the risers are brought up, at least 0.5 m. above the roof surface. The lack of ventilation leads to the appearance of a vacuum in the pipes when draining water, emptying the siphons of sanitary appliances and the smell of sewerage in the house and on the site. Ventilation of the sewer riser should not be associated with the channels of natural ventilation of the premises.
9. For ventilation of risers and piping, in the cases indicated above, an aeration vacuum valve is installed at the upper end of the room. The aeration valve only allows air to enter the pipe, but does not release gases to the outside. The operation of the valve prevents the occurrence of a vacuum in the pipe, which leads to the emptying of the siphons of sanitary appliances. If an aeration valve is installed, it is not necessary to ventilate such a riser. But ventilation of at least one riser in the house should be done without fail.
10. It is necessary to provide soundproofing of sewer risers. To do this, it is better to place the risers in the niches of the walls, cover them with a layer of mineral wool, and sheathe the niches with drywall.
11. The riser pipe at the floor level is fixed rigidly. On the floor, between the ceilings, the pipes are connected and fixed in such a way as to ensure movement during temperature deformations. On the lower floor of the house in an accessible place, a hatch is installed in the riser - a revision.
12. Horizontal pipes connecting the risers and the outlet of the external sewage system are laid in the basement of the house along the walls, in the ground under the floor. Every 15m. and at each turn in the pipes they install a revision hatch.
13. The diameter of the horizontal pipes must not be less than the diameter of the riser pipes. The angles of rotation and connection of pipes are made at an angle of not more than 60 degrees. Pipes laid in the unheated part of the house are insulated.
 Doing so is dangerous! A horizontal strobe in the wall for sewer pipes reduces the strength of the walls. The possibility of installing a horizontal strobe in the wall must be confirmed by the designer's calculation.
Doing so is dangerous! A horizontal strobe in the wall for sewer pipes reduces the strength of the walls. The possibility of installing a horizontal strobe in the wall must be confirmed by the designer's calculation.
A device for laying sewer pipes in a vertical niche in the wall, to the entire height of the floor, or a horizontal strobe, leads to a weakening of the strength of the wall. You should not make niches and strobes anywhere, at your own peril and risk. Niches and strobes with a depth of more than 3 cm for laying communications in the walls should be provided in the project of the house.
It is allowed, without agreement with the designer, to arrange vertical strobes in the lower part of the wall to a height of not more than 1/3 of the floor height.
Outside sewer outlet
Sewerage outlet - the outer section of the pipe from the house, is connected to the well of the central sewerage system of the village (if any), or to a drainless storage septic tank for the removal of wastewater by a sewage machine, or to the septic tank of local treatment facilities on the site.
Outside, directly at the house, it is recommended to install an inspection well on the outlet pipe. It is recommended to install a check valve in the well in the pipe. The valve will prevent flooding of the underground part of the building (for example, when the septic tank overflows) and prevent rodents from entering the house through sewer pipes.
The outer pipe at the outlet of the revision well is connected to the central sewerage system or to the septic tank of the autonomous sewerage system of a private house.
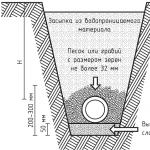
The outer pipe to the septic tank is laid with a slope of 2.5 - 3%, at a depth of about 0.4 m. If the release length is more than 5 m., then the pipe along the entire length is insulated with a shell made of polystyrene foam or extruded polystyrene foam.
The exhaust pipe must not be buried- otherwise, it will lead to the need to install a septic tank at a great depth, which will cost more and make it difficult to operate the septic tank.
Siphon in the sewer
The drain pipe of each sanitary appliance is connected to the supply pipe through a siphon. The siphon is a U - shaped elbow, in the lower part of which there is always a layer of drained liquid.
Some sanitary appliances, such as the toilet, have a built-in siphon. The layer of water in the siphon serves as a barrier to gases, preventing them from escaping from the sewer pipe into the room.
The siphon of a sanitary appliance may not be filled with water and pass gases into the room in the following cases:
- With prolonged inactivity of the sanitary appliance, the water in the siphon dries up. During inactivity (more than two weeks), it is recommended to close the drain holes of sanitary appliances.
- When water is sucked out of the siphon as a result of the vacuum created in the pipes. The risk of water suction from siphons increases with an increase in the length and a decrease in the diameter of the supply pipe, as well as in the absence of ventilation of risers and long supply pipes.
Fecal pumps with grinder for home
Drains move in sewer pipes by gravity, due to the laying of pipes with a slope.
However, situations sometimes arise in the house when it is difficult to create the necessary slope of pipes from sanitary appliances. For example, if a sanitary room is equipped in the basement of a house. Or it is necessary to move the drains a considerable distance (from the bath), and the required pipe slope cannot be created.
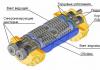
 A fecal pump with a grinder is attached to the toilet. The pump also accepts drains from the washbasin.
A fecal pump with a grinder is attached to the toilet. The pump also accepts drains from the washbasin. For the reception and forced movement of wastewater, special electric fecal pumps are installed. The fecal pump has a device for grinding the contents of wastewater and pumping them into the pipes of the sewer system located above. A fecal pump is installed after each sanitary appliance or for pumping effluent from a group of closely spaced sanitary facilities.