Equipping their garden plot, especially from scratch, many gardeners try to do the drainage of the garden plot with their own hands. Until recently, parks and gardens were designed exclusively by landscape designers. Now, very often, the owners themselves plan the placement of plantings on their land, drawing up a site drainage project.
What is drainage for?
Sometimes, in a rainy summer, gardeners have to deal with such a very unpleasant phenomenon as flooding part, or even the entire plot, with water. If such a “wet” period occurs during the ripening of the crop, part of it may die. In addition, some malicious garden pests (slugs, snails) that destroy grown vegetables, berries and even flowers are very fond of moist soil. Therefore, the drainage of a garden plot is an important and sometimes integral part of the care of both newly-made owners of garden acres, and those who have had them for more than one year.
The word "drainage" has several meanings:
- A material that absorbs water well from the soil, usually used when growing plants in closed ground.
- A method of removing and diverting surface or groundwater from a piece of land using a system of pipes, boreholes, and similar devices.

Different soil types absorb moisture differently. Through light porous soils, water passes almost without delay. Plants planted on such soils do not have time to get the amount of water they need for growth and development. Clay, heavy soils, on the contrary, do not allow water to pass to the roots, which again deprives the plants of proper nutrition.
Pro tip: Determine the type of soil in your area. To do this, you need to dig a small hole up to 60 cm deep, pour water into it and notice the time when all the water goes into the soil. Complete absorption of water per day will indicate that the soil in the area is very porous. If the water does not leave for more than two days, the earth is too dense.
In order to somehow remedy the situation in the case of heavy, poorly water-permeable soils, it will be necessary to drain the site - drainage for the removal of groundwater.
How to arrange a drainage system?
Charting
Before starting work, the drainage scheme of the site should be well thought out. You should start with the water intake equipment. Then trenches are prepared for the collector, which collects water from the drainage pipes (drains), and for the entire drain system.

Drainage system rules:
- The diameter of each drain is 6-9 cm, the diameter of the collector is up to 10 cm. In areas of up to 0.5 ha, their diameters can be equal.
- The depth of the trenches intended for the collector and pipes is 1-1.2 m, the width is up to 35-40 cm.

- The depth of open areas in very relief areas is about 1 m, and on relatively flat or with a slight slope - up to 1.5 m.
- The slope of the entire drainage system towards the collector is 2-3 mm per meter of pipe with a diameter of 50-100 mm. For pipes of larger diameter, the slope should be somewhat less. Drainage pipes in the area with clay soil are laid at a distance of 7-10 m from each other, and in the area with light sandy soil - 15-20 m.
- The entire drainage system should be located no closer than 1 m from the foundation of the house and 0.5 m from the fence.
If the land is located in a lowland or on a slope, the question arises: how to properly drain the site so that water does not accumulate and stagnate in the lowest place?
Since the water intake in such cases is usually located above the territory requiring drainage, it is necessary to build a drainage well. A special drainage pump is installed in it, which automatically pumps all the water up into a ditch or ravine, which is a water receiver.
Work order
Work is performed in the following order:
- Make a drainage well 2-3 m deep. You can strengthen its walls with reinforced concrete rings with a diameter of up to 1 m.
- In order for the drainage pipes to serve for a long time without silting - the ingress of clay particles into the pipes, they should be wrapped with a special material before laying, which filters coarse particles. But most often, such pipes are sold already covered with geotextiles that act as a filter.

- Volumetric filters made from rye straw, fibrous peat or weaving waste are also widely used. They protect plastic pipes used in drainage systems well.
Pro tip: The permeability of filters made of straw does not decrease for a long time due to auto-regeneration - the ability to restore its porosity with the inevitable decomposition of the filter material during operation. These filters are well suited for use on loamy and clay soils.
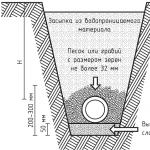
- Drainage pipes are laid in trenches prepared and covered with 5 cm gravel.
- They are sprinkled with gravel or crushed stone (not lime!) for 30-40 cm, and then for another 30 cm - coarse sand, on top of which a layer of fertile soil is laid.

How to extend the life of the drain
The drainage system implemented with the help of drains is quite effective. Drainage of a garden plot, carried out using only crushed stone and broken bricks, will require repair work or a complete replacement within 5-7 years after the start of operation. A system consisting of pipes can last up to 50 years without major repairs.
Here are a few conditions that make up the observance of which will extend the life of the drainage system:
- A complete ban on the movement of heavy vehicles in the area where drains are laid. For the passage of equipment, if necessary, it is best to arrange a temporary road.
- Carrying out loosening of the earth, compacted by the wheels of machines, to make it permeable and loose. This will ensure reliable operation of the entire drainage system.
- Flushing drains to avoid possible clogging of their holes with clay particles or rust every 2-3 years with a strong pressure of water, let out of the hose from the collector into the drainage pipe system.

Any earthwork in the garden is best done when the earth has not yet dried to a “stone” state. Wet soil, although harder than dry soil, in this case you will not break the tools, and the work will be carried out more efficiently. Otherwise, carrying out the described work is unlikely to cause any difficulties.