Water supply is a prerequisite in the engineering support of a residential building. The system is formed by several functional blocks, including the supply and output infrastructure. Moreover, at the stage of wastewater disposal, a crucial stage of cleaning is provided. This is the most important condition for maintaining the regulatory environmental background, not only within the home, but also in the urban environment as a whole. The sanitary and hygienic indicators of the area also depend on how well the wastewater treatment plant in the communications of a separate facility will be performed. In multi-apartment buildings, this task is solved by managing organizations, and in a private house it is taken on directly by the owner.
Wastewater and treatment standards
Contaminated household waste water is far from homogeneous. It is formed by many groups of elements, most of which are hazardous to health to varying degrees. First of all, these are mineral substances that fill drains both at home and in the external environment. For example, a storm water treatment plant, which involves the installation of coarse filters, is just focused on combating this kind of pollution. They are of inorganic origin, may include salts and soil particles, and in rare cases, chemical compounds. Much more dangerous are organic inclusions, which are based on decaying remains of animal and plant origin. Chemical elements, including household polymers, also make up a large proportion of this group of contaminants. Why should wastewater treatment get rid of? Each filtering step takes on a specific category of unwanted items. For example, in accordance with the regulations, a complete cleaning cycle must pass through the drains at least 0.1 mg of iron per 1 liter.
Mechanical Methods

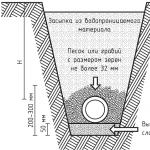
The simplest, but important stage of treatment, during which wastewater is disposed of coarse elements. In particular, it can be leaves, food debris, soil particles, sand and small stones. To eliminate such inclusions, coarse filters are used, which are installed on the sewer line. This may be an on-site surface wastewater treatment plant that will serve both the domestic drainage line and the utility channels. Despite the external primitiveness of such cleaning, it performs a multi-stage filtering. At a minimum, even simple installations provide for the implementation of three stages of purification, including sedimentation, filtration and straining. At the last stage, sand traps come into play, which rid the drain of small but visible foreign bodies.
biological methods

Bioinstallations are not always used in the domestic sphere, but their presence significantly improves the quality of water treatment, and in some cases endows wastewater with qualities that improve further treatment processes. Various systems are used to solve the problems of biological filtration. For example, biofilters act like microdrainage. The membranes installed in them contain sand and gravel, which allows them to perform an aerobic function. In the industrial sector, a biological wastewater treatment plant is used in the form of a closed tank into which oxygen is supplied. An important condition for the operation of such facilities is the production of activated sludge, which decomposes organic compounds. In the sludge layer itself, there are different groups of bacteria with properties that are useful for cleaning. The principle of operation is similar to this method. Their peculiarity lies in providing natural conditions for wastewater treatment without technological maintenance of filtration by artificial means.
Physical and chemical methods

Also a group of methods that is not common in the domestic sphere, but in the industrial economy it is used quite widely. Coagulation is considered to be the most effective technology for physical and chemical treatment. It allows you to build up the sedimentation processes, which facilitates the work of an already mechanical filtration system. The chemical effect is expressed in the "sticking" of small particles into larger ones, and the physical means of cleaning just remove the elements formed by coagulation. Domestic wastewater absorption plants are also popular in large facilities, but are more commonly used as an auxiliary filtration technique. This method can be called a point method - it is optimally suited for removing certain types of contaminants, including dyes, fertilizers, etc. Coarse chemical cleaning methods include treatment with potassium permanganate and chlorine. This is the simplest method of getting rid of pathogenic inclusions, which has proven itself well in the household.
Waste water disinfection
With varying degrees of efficiency, disinfection can be performed with the same chemistry, but such agents are of little use for regular use. Modern disinfection is increasingly provided by equipment with ultraviolet rays. This light spectrum destroys microorganisms without leaving behind harmful traces. It is the safety of the method that has led to its widespread use - from the treatment of domestic and sewage effluents to the maintenance of factory waste. Directly at the facility, the ultraviolet wastewater treatment plant is mounted in the wastewater channels. Provides passive exposure without the need for additional structural solutions. However, ultraviolet lamps only work with drains prepared for fine cleaning. That is, the same stage of rough mechanical cleaning follows first, and then the stage of disinfection can be organized.
Sludge removal

The passage of wastewater through the filtration channels is in itself the engine of the treatment process. But also, as the operation of water communications, sediment accumulates. These are the most harmful and sometimes toxic elements that must not only be removed, but also disposed of in special ways. First of all, centrifuges are used to extract the sediment, which also perform dehydration. As a rule, local wastewater treatment plants contain decanter mechanisms for loading and unloading sludge. The collected material then undergoes a series of preparations for disposal, including pasteurization, conditioning, drying, thermophilic stabilization and composting.
Technical organization of cleaning
Before installing the equipment, a project of an integrated solution is developed. It specifies the means by which the cleaning will be carried out, the configuration of the placement, the requirements for installation operations, etc. Typically, the entire installation process is implemented in three basic steps. First of all, communications are mounted. This may be a piping system, power supply, sometimes ventilation and climate control devices. Next, the working equipment is directly introduced into the created infrastructure. Depending on the chosen principle of operation, the wastewater treatment plant may provide for direct installation in the circulation channel or the placement of a separate reservoir unit with active elements in which the serviced liquid will accumulate, filter and be discharged. The third stage is the performance of commissioning operations, in which the equipment is checked and adjusted.

Installation work
The installation method depends on the scale and technical conditions for organizing the cleaning system. At large enterprises, the principle of local construction of process units is often used, which are assembled by functional elements - membranes, motors, control relays, etc. As an alternative solution, manufacturers of treatment equipment offer the placement of ready-made monolithic blocks on the output channels, for which it is enough just to prepare the foundation . In everyday life, a compact wastewater treatment plant is mainly used, which is integrated into the channel by ordinary plumbing operations. The filter is installed and fixed with mounting fittings, and during operation, the user only needs to replace the membranes with a certain frequency.
Automation of cleaning systems
Complex ones, which include several stages of water treatment and filtration, are provided by software controllers. These are devices that allow you to work in automatic mode without user intervention. The cleaning parameters are fixed by sensors that send data to the control unit. Further, according to the previously entered threshold values, decisions are made to turn off, turn on or change the operation parameters of a particular device. The installation of complex wastewater treatment is not complete without emergency signaling systems. As a rule, they are triggered in the event of a power outage, overflow of individual nodes, or when a certain component fails.
Conclusion

Systems should be selected on the basis of many parameters - from the nuances of the design to the way they are controlled. But the main criterion is still the principle of filtration. In the simplest versions, the wastewater treatment plant provides only a superficial mechanical screening of unwanted inclusions. This equipment is suitable for household use. But for industrial facilities, it is desirable to choose complex solutions that provide for multi-stage cleaning.