Human life is inextricably linked with water. Therefore, in the construction of housing, one of the first concerns is the construction of a water pipe. But if water is supplied to the house, then you need to take care of the disposal of wastewater. In order to recycle used water and to keep the soil and water clean, wastewater treatment systems must be used. Let's consider what installations can be used for sewerage equipment in a private house.
Today, few people are satisfied with the prospect of living in a house devoid of amenities, even if it is just a dacha. Most owners strive to make their home as comfortable as possible: organize heating, conduct water into the house.
But if there is a water supply system, then a sewerage system is also needed - a system for diverting and processing wastewater. Since far from all suburban settlements have a centralized system for collecting and processing domestic wastewater, a local wastewater treatment system is being built.
Wastewater treatment methods
To clean domestic sewage, as a rule, the following cleaning methods are used:
- Mechanical - settling, filtering.
- Biological - processing of wastewater by microorganisms.
In nature, there are two types of bacteria that can effectively clean drains:
- Anaerobes are microorganisms that carry out their vital activity without oxygen.
- Aerobes are bacteria that do not "work" in an oxygen-free environment.
As practice shows, it is possible to achieve the greatest effect in wastewater treatment if a combination of several treatment methods is used. The modern treatment system provides for the initial settling of wastewater, and then their biological treatment using anaerobes and aerobes.
Anaerobic septic tanks
A septic tank is an installation in which drains go through several phased stages of treatment. The principle of operation of a septic tank is to settle wastewater and process organic matter by anaerobic bacteria. To achieve the best quality of cleaning, septic tanks are made multi-chamber. The main part of the solid waste settles in the first chamber, and pre-purified water flows into the subsequent chambers.

Organic inclusions, which make up most of the pollution of domestic sewage, decompose under the action of anaerobic bacteria. Organics decompose into simple components - methane and water, and insoluble residues settle to the bottom of the chambers.
Treatment of wastewater with aerobic bacteria begins after it leaves the septic tank and enters the aeration fields - devices necessary for post-treatment of wastewater. On aeration fields, wastewater is additionally filtered, passing through a filter made of sand and gravel. Thus, after going through all the stages, the water is purified by almost 100% and does not harm the environment.
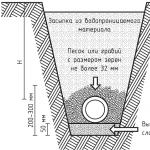
Cleaning steps in an anaerobic septic tank
- Stage one. It is carried out in the primary sump. There is a process that is commonly called clarification of drains. In the first chamber, the contaminated water is separated by specific gravity. Particles that have a heavy weight settle to the bottom, inclusions that are lighter than water rise to the top. In the center of the primary clarifier, where the overflow pipe to the second chamber is located, clarified effluents are collected. Settling continues in the second chamber, only here the sedimentation of smaller inclusions that are in the liquid in suspension occurs.
Advice! Septic tanks are built in such a way that drains from chamber to chamber flow slowly. Only at a low speed of movement is it possible to ensure high-quality sedimentation.
- The second stage is biological. Organic matter that has settled to the bottom undergoes biological processing by anaerobic bacteria. During the fermentation of the sediment, heat is released, so the temperature in the septic tank is always elevated. This circumstance allows the use of septic tanks not only in summer, but also in winter.

- The last stage of cleaning takes place on the filtration fields. The effluents clarified in the septic tank are supplied here through pipes. Holes are made in the pipes through which water seeps into the soil filter. Passing through a layer of sand and gravel, the water is filtered. In addition, it is additionally cleansed with the help of aerobes that live in the soil.
Aerobic type septic tank
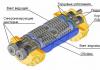
In addition to traditional septic tanks, modern systems of biological wastewater treatment - VOCs, additionally equipped with aerators, are widely used today. In such stations, wastewater is alternately processed by anaerobic and aerobic bacteria, as a result, at the outlet of the treatment plant, the water is 98% purified, so there is no need to build filtration fields.
Water purified in VOCs can be discharged onto the ground or into the nearest body of water without harm to the environment. If necessary, water can be directed to a storage well for domestic use, such as lawn or garden irrigation.
Stages of wastewater treatment in aerobic septic tanks
- The first stage is upholding. Just like in conventional septic tanks, VOC uses such a simple but reliable mechanical cleaning method.
- The second stage is the processing of the sludge by anaerobic bacteria. Organic matter that has fallen in the form of a precipitate is processed by anaerobic bacteria. That is, up to this point, there are no differences in the operation of a simple septic tank and VOCs.
- The third stage is processing with the help of aerobic bacteria. When the aerator is turned on in the chamber, the stage of aerobic cleaning begins. In an environment saturated with oxygen, bacteria efficiently and quickly process most of the organic inclusions.

- Stage four - again upholding. After aerobic treatment of wastewater, water enters the secondary clarifier, where the insoluble sediment - sludge - settles. Purified water enters the outlet, and activated sludge is reused in the purification process. As excess sludge accumulates, it will need to be removed from the sump.
Simple septic tank or VOC?
What kind of wastewater treatment system should be preferred when building a local sewerage system? There is no single answer to this question. When choosing an installation, local conditions will need to be taken into account. Let's conduct a small comparative analysis of septic tanks and VOCs:
- Space required for installation. To install a modern VOC, as a rule, one or two square meters of area is sufficient. If you need to install a septic tank, you will need a large area. The septic tank itself is somewhat larger than the VOC, but the main area will be required for the construction of filtration fields necessary for the post-treatment of wastewater.
- Geological characteristics of the site. If it is decided to install a VOC, then the geological characteristics of the site can only affect the choice of VOC modification. But the arrangement of filtration fields on clay soils is an intractable task.
Advice! If soil water is high on the site, then you should purchase a VOC with forced drainage, that is, equipped with an additional pump.
- Autonomy. If the septic tank is a completely autonomous installation, then the VOC requires power to work.
Advice! If the local sewerage system is equipped with a volatile wastewater treatment plant, then during a power outage it is necessary to reduce the use of water to a minimum. Otherwise, overflow of the chambers may occur, since the pumps pumping wastewater do not work.
- Service. Both a conventional septic tank and VOCs need regular maintenance. The septic tank will have to be cleaned of accumulated sediment about 1-2 times a year using sewage equipment. The cleaning of the sludge collector in the VOC should be carried out more often - about once a quarter, but this work can be easily done on your own.
Advice! When choosing a place to install a septic tank, you need to take into account the need to clean it and leave free passage for the sewer truck.
- Price. A conventional septic tank is cheaper than VOCs. However, it is necessary to take into account the cost of building filtration fields, as well as the fact that filtration fields last no more than 10-12 years, after which they need to be changed.
Design
Having decided on the type of treatment plant, you can begin designing drainage systems for a country house. Most often, the project is made simultaneously with the project of the house. But if a building that has already been put into operation is being improved, then a sewerage project for a private house is drawn up separately.

When designing a wastewater disposal system, local conditions must be taken into account. Therefore, prior to the start of design work, it is recommended to carry out geological exploration, during which the following points will be clarified:
- features of the relief of the site;
- characteristics of the soil, to select the method of water drainage, it is necessary to assess the absorbency of the soil;
- the level of location and seasonal rises of groundwater.
Before the development of a project for a drainage system for a home is started, the following points need to be clarified:
- average daily water consumption in the house;
- frequency of use - year-round or periodically.
After collecting information, you can begin to draw up a project.
Tilt angle
An important point is the angle of inclination of the pipeline. This point is important in the construction of gravity systems. If it is impossible to comply with the required angle of inclination, it is necessary to plan the construction of a pressure system in which wastewater is pumped using a fecal pump.
Many home masters who undertake self-assembly underestimate this moment, and meanwhile, errors in both directions reduce the efficiency of the system.

If the angle is not large enough, then the flow will move through the pipeline at a low speed. At the same time, some of the large inclusions will have time to precipitate in the pipes, and this is fraught with the formation of blockages. An angle that is too large will also disrupt the normal movement of the conveyed medium. Water will drain too fast, not having time to carry away heavy inclusions that will linger in the pipes, forming blockages.
The optimal angle of inclination depends on the diameter of the pipe that is used to create the pipeline. The smaller the diameter, the larger the slope angle should be. So, if pipes with a diameter of 50 mm are selected, then a slope of 3 cm per meter should be observed. When using 100 mm pipes, the slope should be 2 cm.
System elements
When creating a project, a diagram of internal and external networks is created. The internal networks include all the elements that are located in the house, these are:
- a riser connected to a fan pipe led to the roof;
- elements of plumbing (sinks, bathtubs, toilets, etc.);
- pipes connecting plumbing elements with a riser.
The boundary separating the internal and external networks is the pipe outlet through the foundation. External networks include:
- a pipeline connecting the output with a treatment plant;
- revision wells for network maintenance;
- cleaning plant.
When constructing a local sewage system, one cannot do without a local treatment plant. Depending on local conditions and the capabilities of the owners, this can be a simple anaerobic type septic tank or a modern local bio-treatment station.