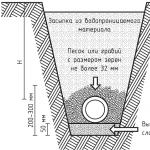
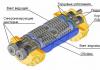
Last year, I took care of choosing a system for removing and cleaning domestic wastewater. First considered autonomous non-volatile wastewater disposal structures on the basis of underground filtration facilities with wastewater discharge into the ground as the most economical and easy to implement. These systems consist of a septic tank and an underground filtration facility:
. for sandy and sandy loamy soils - a filter well or underground filtration fields;
. for light loamy soils - a filter cassette.
But none of these designs worked for me. The fact is that the possibility of using such structures depends primarily on the filtering properties of the soil and the level of groundwater. At the same time, the groundwater level must be at least 1 m deeper than the bottom of the structure (filtering well and cassette) or irrigation pipe tray (underground filtration fields). Unfortunately, in my area, the groundwater level is above this cherished mark of 1 m. In addition, I did not have the conditions for gravity discharge of purified water into a roadside ditch or soil. Therefore, even if I could, for example, arrange the same filter cassette with the help of bulk soil, but considering that my earth is solid clay, I, taking into account the costs of creating a clay castle, a surface filter layer, required significant cash injections. And not only did this not solve the problem with the gravity drainage of treated effluents, I now had to install it in a pump that feeds the settled effluents into the filter cassette. It also became necessary to build an additional storage well with another float-operated fecal pump installed in it for the forced removal of treated water into a roadside ditch, which was almost flush with my site. That is, the system has already turned out to be non-volatile. And when taking into account the costs of a septic tank, earthworks for the arrangement of an underground filtration system and a prefabricated well, the amount turned out to be very significant. In addition, it would also be necessary to find a place for these structures on our not so large site. Therefore, having considered all possible options with non-volatile autonomous structures of natural underground filtration, I was forced to abandon them. I will only say if you have a low groundwater level, sandy or sandy loamy soil on your site, then I advise you to choose a water treatment design based on underground filtration systems. And the most economical design in this case is a septic tank + filter well.
And I began to consider more expensive autonomous biological wastewater treatment systems.
At first, from a large number of existing systems presented on the Russian market, my head was spinning. But, when I understood a little about the principles on which most autonomous treatment systems work, it turned out that there are not so many of them. The names of firms, installations differ, but the principles of operation for most of these installations are similar. The most important thing is to understand what exist or how they are now called local treatment facilities ( VOC) (Tank, Helyx, etc.) and biological wastewater treatment plants(Topas, Unilos, Tver). The main difference between septic tanks and biological wastewater treatment plants is, first of all, in principle and the degree of wastewater treatment.
Septic tanks. Local treatment facilities. (LOS)
Most of the existing septic tanks (VOS) work according to the following principle: wastewater flows by gravity into the first section of the septic tank, where insoluble substances are retained. Solid impurities that can settle accumulate on the bottom in the form of sediment, and fats, oils and surfactants form a film on the surface. Further, the drain alternately passes through the remaining sections of the septic tank, where the drains are subjected to biological treatment processes under the influence of a colony of anaerobic bacteria, which do not need oxygen in the air for life. The appearance and reproduction of bacteria is due to the entry of organic compounds into the septic tank, which serve as a nutrient medium for them. As a result of the "work" of bacteria, the content of harmful substances in the drain is reduced, and due to the additional settling of suspended particles, the drain is clarified. The decomposition of sewage is accompanied by the release of gases, which are removed by ventilation. It is this principle that is laid down in septic tanks. Tank, helyx, Biofilter, SANITEC etc.
 |
An example of a modern septic tank. |
IMPORTANT! Not a single septic tank gives a degree of treatment of more than 85% of wastewater, which is why they are usually used in the chain of construction with underground after-treatment of wastewater, or as storage tanks for periodically pumping out their contents using sewage trucks. Manufacturers of septic tanks, using various structural elements and porous loads, are trying to increase the degree of wastewater treatment, but even the most advanced septic tanks of the " Favorite 2P", this figure does not exceed 90%. From my point of view, this is not enough to tell the owners of neighboring plots that I am dumping practically clean water into a common ditch.
As I wrote above, based on the nature of the soil and the level of groundwater in my area, the construction of underground filtration systems was not possible for me, and pumping out the storage tank every three months is too troublesome and expensive. That is why I immediately closed the topic of septic tanks for myself.
Again, if you lead a suburban lifestyle outside the city, that is, with irregular residence, then it makes sense to take a closer look at options with septic tanks and storage tanks. In my case, with permanent residence outside the city, there was only one option left - these are autonomous stations for deep biological wastewater treatment. These stations are TOPAS, UNILOS, TVER, UBAS etc.
Stations for deep biological treatment of sewage
The principle of operation of all deep wastewater treatment plants is approximately the same. It is based on fine-bubble air aeration with the help of artificial air supply necessary for the oxidation of organic particles in wastewater.
The design solutions adopted to implement this principle of wastewater treatment and used in modern plants differ and sometimes significantly. We will see, how Topas and Unilos cleaning stations work. In them, first, wastewater enters the septic chamber, where primary mechanical wastewater treatment takes place, during which suspended particles are separated. Further, the waters flow into the aerotank, in which organic pollutants that are difficult to oxidize are finally destroyed by the oxidation of activated sludge. The sludge mixture from the aeration tank enters the secondary settling tank, from where the sludge is returned to the aeration tank, and the clarified waste water is removed. Discharge or removal of wastewater treated in this way is carried out by gravity or using a fecal pump with a level indicator (float) and without a check valve.
The design and operation of stations for deep wastewater treatment such as Tver, Yubos, is somewhat different. We will see, how it is implemented in a Tver type installation. First, wastewater enters the septic chamber, where primary mechanical wastewater treatment takes place, during which suspended particles are separated. Further, the waters flow into the bioreactor and then into the aerotank in which organic pollutants that are difficult to oxidize are finally destroyed by the oxidation of activated sludge. The sludge mixture from the aeration tank enters the secondary settling tank, from where the sludge returns to the aeration tank, and the clarified wastewater first enters the aerobic bioreactor, where it is saturated with oxygen and then, after settling in the tertiary settling tank, is discharged to the relief. Discharge or removal of water is carried out by gravity or using a fecal pump with a level indicator (float) and without a check valve.
And in settings like Topas and in settings like Tver A significant factor for me was that the water is discharged onto the terrain, which means that the effluents do not need additional soil post-treatment. Manufacturers of these systems guarantee the degree of wastewater treatment with proper operation of at least 96-98%.
When you choose a system and they tell you that this system is of the Topas type, and this is of the Tver type, then it is advisable to buy not a "type" but Topas or Tver itself. The original, from my point of view, is always better than what is made in its likeness, but this is my subjective point of view, which does not claim to be the ultimate truth.
So, now everything has become much easier - it remains choose between Topas and Tver. And although each of these installations for deep biological wastewater treatment has its own long history and practically has no negative reviews among those who have acquired similar installations in their suburban areas, I still chose the Tver installation. For me personally, the determining factors were not the cost of installing and assembling the station, it was just lower for Topas sellers. The main thing for me was the simplicity, conditions and cost of operating these stations. All these indicators, again from my point of view, turned out to be more attractive for manufacturers of Tver biological treatment plants. The table below shows the comparable characteristics of the two systems that I considered important for me when choosing between these two most reliable biological wastewater treatment plants.
Table Comparison of the parameters and characteristics of the Tver-0.75P and Topas-5 installations
| Parameters and characteristics | Unit rev. | Tver-0.75P | Topas-5 |
| Usable installation volume | cubic meters | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| Number of cleaning steps | --- | 4 | 2 |
| Biological processes in the winter period (water temperature not less than +12 gr.С) | --- | carried out (air supply at room temperature) | no (outside temperature air supply) |
| Scheme of waste water movement | --- | gravity (simple and without electronics) | forced (available for control only by service specialists) |
| Additional measures during installation at a high level of groundwater. | --- | not required (shallow occurrence + loading skirt) | required (concreting) |
| Sensitivity to power fluctuations. | --- | No | a stabilizer is required. |
| Service maintenance | --- | possibly on your own | only service technicians |
| Frequency of service and technical work | --- | 1 time per year | 1 time in 3 months |
Well, in conclusion, a small photo gallery of work on the mounting of the Tver installation in my area. Now only time will tell how right I was in my choice of such an important thing in life outside the city as an autonomous sewage system.