If country estates have a personal plot, then, most likely, it is used either for agricultural or for decorative and floricultural purposes. And in fact, and in another case, you can not do without the regular conduct of certain agrotechnical work. And irrigation will always be in the foreground - without effective irrigation, especially in dry summers, it is hardly possible to achieve a high yield, beautiful flowering flower beds or even just a juicy green lawn.
Even in the case when a water main is connected to the site, using water from it for irrigation is by no means the best solution. Firstly, it is very wasteful, and secondly, such water undergoes certain processing, including chlorination, and is not very useful for plants. For irrigation, it is better to use some natural source, but to use it you will need special equipment - a pump.
However, if the buyer goes to the store or enters the online catalog unprepared, he may encounter a lot of questions that make the optimal choice extremely difficult. Pumping equipment is very "many-sided" and differs not only in technical characteristics, but also in operational capabilities. It is necessary to take into account many criteria in advance in order to leave your choice on the model that is most suitable for the existing conditions. This publication is dedicated to this - we buy a pump for watering the garden: varieties, selection, installation, basic operating rules.
Where will the water come from?
It is impossible to choose the right pump if you do not decide in advance where the water will be taken from for irrigation. There may be many options here.
- The most successful "layout" is when the site has its own or located in the immediate vicinity of a reservoir of natural origin - a pond or lake, fed from underground sources or a stream and having a sufficient debit of water. It is possible to carry out watering from the river flowing nearby. In any of these cases, a surface pump or a submersible (semi-submersible) drainage type may be required.

If the site has an artificial reservoir - a pond or pool, then it can also become a source of water for irrigation. All the same, the water in it should change regularly, and these two operations can be combined - supply fresh water to the pool, pumping it out to the garden that already needs to be replaced. True, on one condition - that no chemical reagents were used.
- Even a somewhat swampy reservoir can serve as a source of water for irrigating the site, but in this case you will have to purchase a special kind of drainage pump, which is designed to pump dirty water.
However, such ideal conditions are rare. Most often, one has to resort to artificially created water sources.
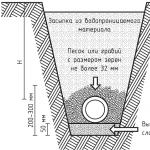
- For irrigation, you can use water from a well or well. For wells, both surface pumps (with a shallow aquifer) and submersible pumps can be used. For wells where water is usually found at great depths, only submersible pumps of a special type are suitable.
Water intake from wells requires special pumping equipment
To raise water from a great depth and at the same time provide it with sufficient pressure and the required flow rate for further use - not any equipment can handle this. How to approach - read in a separate publication of our portal.
However, an important note should be made immediately. Any experienced gardener or gardener will say that using water directly from their well or well for irrigation is highly undesirable, since such irrigation of plants can do them more harm than good. The best option is that the required volume for regular watering is pumped in advance into containers installed on the plot. The water will warm up in a day, get rid of the chemical compounds dissolved in it, and become quite suitable for irrigation. By the way, this approach opens up wide opportunities for the competent use of fertilizers and dressings with strict adherence to the recommended proportions of dilution of the compositions.

For a set of containers, the already mentioned well or borehole pumps are used. But directly for irrigation, it will be possible to acquire a compact surface-type garden pump or special submersible models designed specifically for taking water from containers (barrels, eurocubes, home-made tanks, etc.).
- A good owner should not lose anything, including rainwater, the collection of which in garden containers is very often organized from drainage systems. And besides, if a competent storm sewer is organized on the site, then a storage storm collector can also become a source of water for irrigation. In this case, the submersible drainage pump will again become an assistant.
How is storm sewer arranged?
Unfortunately, not everyone remembers this system for draining water from the local area, or they ignore its creation in the hope that everything will somehow “dissolve” by itself. Why this approach is wrong, and how to create it correctly - read in a separate article on our portal.
So, the choice of a pump for irrigation in the first place will depend on the type of water source used.
What performance and pressure ratings are required?
Whatever type of pump is chosen, this unit must fully cope with the functions assigned to it.
- Firstly, it must ensure the pumping of the required volume of water at a certain time - this is an indicator of performance.
It is not difficult to calculate this parameter. They proceed from the fact that according to the existing rules, for high-quality irrigation of one square meter of land, from 3 to 6 liters of water is required (depending on local climate conditions, characteristics of crops grown, and steady weather). It is best to calculate to the maximum - this will create a certain reserve of productivity, but everyone is free to decide this issue on their own.
Of course, only the area of \u200b\u200bthe site that is allocated for crops that require regular watering is taken into account. If lawn or flower beds are cultivated, their area is also taken into account.
The next value required for the calculation is the time that is planned to be spent on watering the entire area. Usually this event is held in the evening, after the subsidence of the heat of the day and the aggressiveness of direct sunlight, so an hour or two will probably be enough.
To find the required productivity (usually it is indicated in the technical documentation by the symbol Q), it remains to multiply the area of the irrigated area and its irrigation rate, and divide the resulting value by the time allocated for irrigation.
Q=S uch ×N/t
S uch – irrigated area (m²).
N- the accepted watering rate is from 3 to 6 l / m² (for individual crops it may be more).
t- the time allotted for watering the site.
For ease of calculation, you can use the proposed calculator. The area in it is indicated in acres - so many gardeners are more familiar.