One of the most important parameters that you should pay attention to when choosing pipes for a sewerage device is, in addition to the pipe material, the diameter of the sewer pipe, because pipes of different diameters are used for various internal sewerage systems. All sewer pipes are manufactured strictly in accordance with the Specifications. At the same time, manufacturers offer a huge selection of products of different sizes. Therefore, it is easy to choose exactly what is required for each specific case. How to do this - the article below will tell.
Influence of diameter on other pipe parameters
As we have already said, one of the main parameters of any pipe is its diameter. It defines the scope of its application:
- to drain water from a free-standing bathtub or sink, use pipes with a diameter of no more than 75 mm;
- pipes that drain waste from the toilet should already have a diameter of 100-110 mm;
- sewer pipes of large diameters are used to divert all collected sewage out of the building.
The diameter of the sewer pipes determines their other parameters:
- Pipe wall thickness. For pipes of large diameter (up to 160 mm), the wall thickness is greater than for pipes with a diameter of up to 110 mm. It is respectively 3.9 and 3 mm.
- Pipe weight. 1 m of pipe with a diameter of 160 mm weighs about 2 kg, while a pipe with a diameter of 110 mm of the same length weighs just over 1 kg.
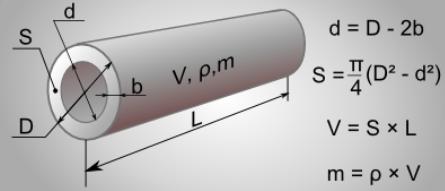
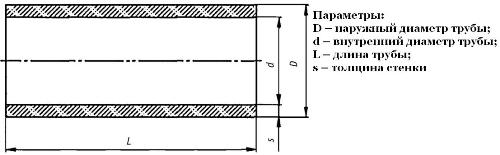
Inner and outer diameter
Usually, the factory marking indicates only the outer diameter of the sewer pipe and its thickness.
Pro tip: In order to determine the inner diameter of the purchased pipe, it is necessary to subtract twice the value of its thickness from the value of the outer diameter.
The inner diameter of the sewer pipe must be known in order not to make a mistake with the selection of pipes to perform certain tasks in the sewer system.
There is an approximate gradation of pipes used in certain cases for internal and external sewage:
- To drain water from a washing machine or dishwasher, pipes with a diameter of 25 mm are used.
- For drainage from a shower cabin, bathtub, sinks, pipes with a diameter of 32 mm are suitable.
- The general sewer wiring in the apartment is pipes with a diameter of up to 40-50 mm.
- To divert all drains to the outside, pipes of the largest diameter are used - from 160 to 200 mm.
Pipes made from various materials are usually used for different types of sewers. So for the device of external sewage, plastic pipes are often used, for example PVC sewer pipes: their diameter is most often 110 mm.
Cast iron pipes are marked, which indicates their nominal (actual) diameter. For example, the designation "DN 100" indicates that the diameter of the "conditional passage" of the pipe is 100 mm. Thus, in order to determine the nominal inner diameter of cast iron sewer pipes, it is enough to check their markings.

Smallest allowable diameters
According to the Sanitary Norms and Rules (SNiP), pipes can be used for various types of sewerage networks, the minimum size of which is:
- for the flow of industrial and domestic water within the quarter - 150 mm;
- for the same street networks - 200 mm;
- for a quarterly network that drains rainwater - 220 mm;
- for street storm network - 250 mm;
- for networks that output silt under pressure - 150 mm.
In some cases, minimum pipe sizes are allowed:
- for settlements, the volume of effluents in which does not exceed 300 cubic meters per day, both for street and quarterly networks that carry out the withdrawal of industrial water, it is possible to use pipes with a minimum diameter of 150 mm;
- for some production networks, if appropriate justification is provided, this diameter may be even smaller.
Determining the exact pipe diameter
Convert mm to inches
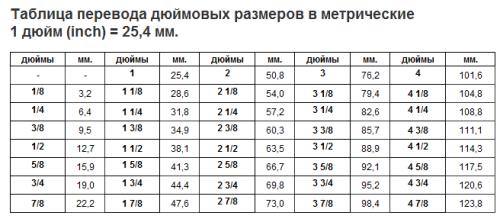
It is not very easy, at times, to determine the diameter of the required pipe, since it is often indicated not in millimeters, but in inches. To move from one unit to another, there are various tables that can be used.
The conversion table shown in the figure above is used if it is possible to measure the diameter (the pipe is not fixed) with a ruler or with a caliper.

Pro tip:
To measure the diameter of an existing (installed) pipe at home, you just need to attach a ruler to it and measure its “thickness”. If the resulting number is about 32 mm, then the bore diameter of the pipe is 1 inch; about 28 mm is already ¾ inch; 16 mm - ½ inch.
Calculation of the required pipe diameter
It is important to know the diameter of the pipes used in the installation of the system. The volume of liquid carrier passing through the pipes is directly related to their diameter. An accurate calculation of the diameter of the sewer pipes can be done independently.
The diameter is calculated by a simple formula:
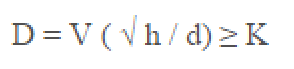
where:
- V is the speed of movement of liquid masses through pipes. The indicator should not exceed the value of 0.7 / s. You can choose from the table below.
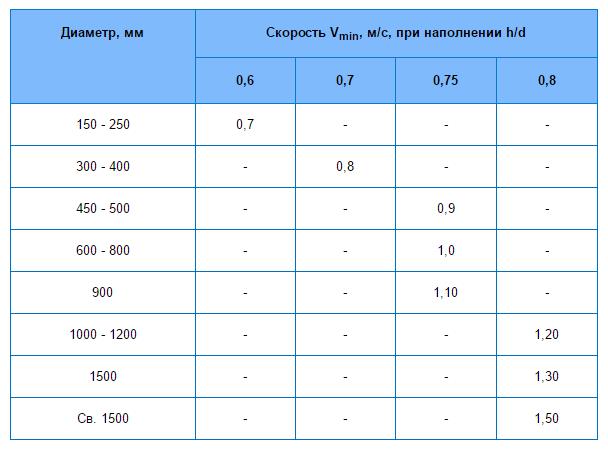
- h / d - indicator of the fullness of the pipeline. It is the ratio of the flow height h (maximum) to the inner diameter of the pipe. The minimum value should exceed 0.3, the maximum should not exceed 0.6.
- K is a coefficient depending on the material of the pipeline. So, for polymer products it is 0.5, for other materials - 0.6.
The most optimal version of the sewer system is easy to create if you adhere to the calculated pipe diameter. Drawing up a preliminary detailed design of the entire sewerage system in the house will allow you to determine the required number and size of pipes purchased for installing the system.