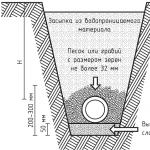
Which can be used in the construction of sewerage networks in a suburban area.
As you now know, wastewater can be discharged using a filtration well, a septic tank, or local treatment facilities. But for the construction of sewerage this is not enough.
You need to know which pipes are preferable to use for the installation of the sewer network. To do this, you need to answer the following questions: “How to choose the material and diameter of the pipes? What is better to use - HDPE, polypropylene or high density pipes?
Let's figure out in this article how one material differs from another and what determines the choice of diameter.
Sewer pipe material
Today, various materials are used in construction, including when laying engineering networks, which include sewerage networks.
Depending on the purpose and operating conditions, sewer pipes made of the following materials are used:
- ceramic;
- concrete;
- asbestos-cement;
- cast iron;
- polymeric (PP, PVC, PVC-U, etc.).
All sewage can be conditionally divided into domestic (fecal sewage) and surface runoff of melt and rainwater. Depending on the purpose of the sewer network, the conditions for its laying, the diameter and material of the pipes are selected.
About which pipes, in which case it is better to choose, read on.
Pipes for internal sewerage
Internal sewerage is laid inside buildings and is intended to divert effluents from plumbing fixtures to the external network outside the building.
In this case, the wastewater flow rate is determined according to SP 30.13330.2012 "Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings" (updated version of SNiP 2.04.01-85*).
For the calculation, data are used on the number of plumbing fixtures, the second flow rates of wastewater from these devices, as well as the probability of their simultaneous use in order to ensure the free passage of the maximum possible flow rates by sewer pipes.
This takes into account the climatic region and the degree of improvement of the building.
To check the diameters obtained by calculation, one should use the tables of capacity of ventilated and non-ventilated risers made of polymeric materials and cast-iron pipes (Tables 6-12 of SP 30.13330.2012), depending on the height of the riser and the angle of connection of floor outlets.
Such calculations are quite complex and are used in the design of multi-apartment residential buildings and industrial enterprises.
To select the diameters of pipes in a country private house or a bath, you can use a simpler method - tables of water disposal standards from plumbing fixtures based on equivalent costs. In this case, the value of the second flow rate (l / s) from the sink, equal to approximately 0.33 l / s, is taken as 1 equivalent.
Based on the table, the diameters of pipelines are accepted depending on the number of installed plumbing equipment.
How such a table looks like is shown in the figure below (click to enlarge):

As you can see, the largest diameter (100 mm) is required to connect the toilet. To connect sinks, sinks and washbasins to the sewerage, pipes with a diameter of 40-50 mm are enough.
For laying internal sewerage, the following materials are used:
- Polyethylene;
- Polypropylene;
- PVC;
- Polybutene;
- Cross-linked polyethylene;
- Fiberglass.
As a rule, pipes for internal sewerage are gray in color, by which they can be distinguished from pipes for outdoor laying, which are orange.
The features of different materials will be considered below.
PVC sewer pipes (PVC) and PVC-U
Pipes made of polyvinyl chloride and PVC-U (non-plasticized polyvinyl chloride) are widely used in the construction of sewers due to the following advantages:
- light weight;
- low cost of manufacture and transportation;
- ease of machining;
- ease of installation of PVC pipelines.
But they also have disadvantages. These include:
- deformation under the influence of elevated temperatures;
- poor resistance to some chemically active substances in sewage;
- combustibility with the release of toxic substances during combustion.

HDPE pipes
The abbreviation HDPE means low-pressure polyethylene, which characterizes the manufacturing method of this material, which is popular in modern drainage systems. HDPE pipes are produced in accordance with GOST 22689.2-89 "Polyethylene sewer pipes and fittings for them."
The notable advantages of polyethylene pipes include:
- high tensile strength;
- increased rigidity;
- temperature range from -50 to 130 degrees;
- high smoothness of the inner walls of the pipe;
- long service life;
- ease of transportation and installation.
The disadvantages include a slightly lower resistance to direct exposure to ultraviolet rays than pipes made of other materials.
Polypropylene pipes
Pipes made of polypropylene are distinguished by the best resistance to elevated temperatures and due to this they can even be used in the installation of heating systems.

In addition, polypropylene has other advantages - plasticity, resistance to mechanical damage, ease of assembly and high durability of sewer networks made of this material.
Requirements for internal sewerage
When laying internal sewerage, the requirements of SP 30.13330.2012 “Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings” should be taken into account in terms of connecting the fittings of pipelines and indenting devices.
So, for example, it is recommended to connect sanitary appliances to risers using oblique crosses and tees.
As a pipe material for internal lining, it is recommended to use pipes made of modern polymeric materials that have a guaranteed service life without changing their physical and chemical characteristics for at least 25 years.
In buildings, sewerage is laid hidden - in mines, channels and ducts made of non-combustible and low-combustible materials (G2). At the same time, it is not allowed to lay sewers under the ceiling, in the walls and in the floor of living rooms, bedrooms and kitchens.
The sewer riser is displayed at least 20 cm above a pitched or flat unexploited roof and has a distance of at least 4 meters from opening windows, vents and balconies.

Requirements for internal drainage
If you are building a house in which the project involves the installation of internal drains, then you should know the requirements that apply to them:
- It is allowed to mount internal gutters from polyethylene and metal pipes.
- The estimated flow of rainwater and the number of drains is determined by the climatic characteristics of the design area and depends on the intensity of rain in the area.
- Gutters are calculated for the hydrostatic pressure that may occur in the event of a blockage. Also, when installing fasteners, it is necessary to take into account the weight of the drain filled with water.
- Passage of internal drains through residential premises is not allowed.
- Audits on drains should be installed on the first floors of buildings before release.
Pipes for outdoor sewage
External sewerage performs the function of draining wastewater to treatment facilities or filtration wells.
According to the material of the external sewer pipe, there are:
- cast iron;
- Concrete;
- Asbestos-cement;
- Polymer.
Cast iron pipes
Cast iron pipes were not so long ago the most popular choice for both internal and external sewer networks.
Cast iron has excellent physical and chemical properties that make it popular today. And, if today cast iron can be found in internal sewage systems in houses built several decades ago, then cast iron is still used today as pipes for outdoor laying.

The clear advantages of cast iron pipes include the following qualities:
- do not rust;
- have high strength, which allows them to be laid in the ground without fear that the pipes are deformed under the influence of the weight of the soil or the loads from passing vehicles;
- cast iron pipes are very durable and have a service life of up to 80 years.
But they also have disadvantages. The main disadvantages are:
- heavy weight, making it difficult to transport and stack;
- increased fragility - the pipe can be split by hitting it with a hammer or inadvertently hitting a stone;
- the inner surface of cast-iron pipes is not as smooth as that of polymer pipes, and various contaminants gradually grow on it, which leads to a narrowing of the pipe diameter and the appearance of blockages;
- significant cost compared to plastic pipes.
Ceramic pipes
In the economic justification for external sewage networks, pipes made of ceramics are used, manufactured in accordance with GOST 286-82 "Ceramic sewer pipes".

Ceramic pipelines have high strength to physical stress, are resistant to the chemical composition of wastewater and have a significant service life.
The disadvantages include the fragility and complexity of installation. With a product diameter of up to 600 mm in length, ceramic pipes are produced in lengths of only 1500 mm.
A very popular choice for the installation of sewer outlets of small diameter is asbestos-cement pipes according to GOST 1839-80 “Asbestos-cement pipes and couplings for free-flow pipelines”.

They are easy to install, weigh less than pipes made of ceramic or cast iron, and are also resistant to aggressive chemical environments and have good wall smoothness, which reduces the likelihood of blockages.
Asbestos-cement pipelines are assembled using couplings.
For laying external sewerage networks, modern polypropylene or polyethylene pipes can also be used.

You can distinguish them from pipes for internal laying by the characteristic stiffeners, thanks to which the pipe looks like a corrugation. Double walls and ring reinforcements give such pipes strength sufficient to bear the weight of the soil when laying at the standard depth.
Plastic pipes are much easier to install than cast iron, ceramic or asbestos-cement pipes.
The video below shows the installation of plastic corrugated polypropylene pipes.