Have you ever held a huge LED in your hands, the size of a human fist? Of course not, because they don't exist. I'll show you how to make such an original thing with your own hands. This LED will be exactly like its smaller brother, except that its brightness will be many times greater.
Will need
- Plastic bottle.
- The board is textolite, foil-coated.
- Thick wire.
- A piece of LED strip.
- Resistor 5-10 Ohm.
- Epoxy resin with hardener.

Making a large LED
So, let’s first figure out what an LED consists of. The first is two pins that go into the body of the LED. Next you can see two pads, one smaller is the anode, and the other larger is the cathode. On the cathode there is a platform with a reflector and a semiconductor crystal. Above all this there is a lens, which is a monolith with an LED body.
First, let's make an imitation of a large semiconductor crystal with a reflector. We take the LED strip and solder the chip elements from it. If you don’t have a hairdryer, heat it up with a soldering iron.

Let's cut out such a board from a piece of foil PCB.

We tin it and solder the LED chip onto it.

We also solder the contact and the current-extinguishing resistor.

Let's check the power supply. The crystal is ready.

For greater visual similarity, we will cut out the cathode and anode from PCB.

The elements are located at the bottom of the body.

We take a thick wire and make contacts from it. We solder them to the pads.

Next, we coat the light module with hot glue and glue it perpendicularly to the largest area - the cathode.


Solder the pins to the board.

Next we need to prepare a mold for pouring epoxy resin. A plastic bottle will serve us for this purpose.

Let's cut it in the middle and put the top part on the bottom.

There is an empty area in the lid area where the epoxy will be poured. In order not to waste extra material, we fill the voids of the neck with foil.

Strictly according to the instructions, mix the hardener with the resin and mix well.

We fix the insides with office clips so that they float in the air. Pour the composition into the mold.

We are waiting 24 hours. After drying, cut the bottle with a scalpel and remove parts of the bottle from the surface.

This is what happened:

Using a mechanical tool, we cut off the foil and polish the surface irregularities.



Sand with fine sandpaper, dipping it in water. This will remove all the smallest scratches.


It's time to polish. Polishing paste can be obtained from motorists. In extreme cases, toothpaste will do.
LED lamps are widely used in household, street and industrial lighting. Their important advantages are efficiency, environmental friendliness, and low maintenance.
A DIY LED lamp will definitely find its application in your home. You will find detailed manufacturing instructions, as well as assembly diagrams, in the presented article.
The basis of the LED lamp is a single-sided semiconductor, the size of which is several millimeters. There is a unidirectional movement of electrons in it, which allows you to convert alternating current into direct current.
An LED crystal consisting of several layers is characterized by two types of electrical conductivity: positively and negatively charged particles.
The side containing the minimum number of electrons is called hole (p-type), while the other with a large number of these particles is called electron (n-type).
When elements at a pn junction collide, they collide, generating light particles called photons. If you keep the system at a constant voltage during this time, the LED will emit a stable stream of light. This effect is used in all LED lamp designs.
Four types of LED devices
Depending on the placement of LEDs, such models can be divided into the following categories:
- DIP. The crystal is arranged with two conductors, above which there is an enlarger. The modification has become widespread in the manufacture of signs and garlands.
- "Piranha". The devices are assembled similarly to the previous version, but have four outputs. Reliable and durable structures are most often used to equip cars.
- SMD. The crystal is placed on top, which significantly improves heat dissipation and also helps reduce the size of the devices.
- OWL. In this case, the LED is soldered directly into the board, which increases the glow intensity and protects against overheating.
A significant drawback of COB devices is the impossibility of replacing individual elements, which is why you have to purchase a new mechanism due to a single failed chip.
Chandeliers and other household lighting products typically use SMD design.
LED lamp device
The LED lamp consists of the following six parts:
- Light-emitting diode;
- base;
- driver;
- diffuser;
- radiator.
The operating element of such a device is an LED, which generates a stream of light waves.
LED devices can be designed for different voltages. The most in demand are small products of 12-15 W and larger lamps of 50 watt.
The base, which can have different shapes and sizes, is also used for other types of lamps - fluorescent, halogen, incandescent. At the same time, some LED devices, for example, LED strips, can do without this part.
An important design element is the driver, which converts the mains voltage into traction on which the crystal operates.
The efficient operation of the lamp largely depends on this unit; in addition, a high-quality lamp with good galvanic isolation provides a bright, constant luminous flux without a hint of blinking.
A conventional LED produces a directional beam of light. To change the angle of its distribution and provide high-quality lighting, a diffuser is used. Another function of this component is to protect the circuit from mechanical and natural influences.
The radiator is designed to remove heat, excess of which can damage the device. Reliable operation of the radiator allows you to optimize the operation of the lamp and extend its life.
The smaller this part, the greater the thermal load the LED will have to withstand, which will affect the speed of its burnout.
Advantages and disadvantages of a homemade lamp
Specialized stores offer a large selection of LED devices. However, sometimes it is impossible to find a device in the assortment that meets the necessary parameters. In addition, LED devices are traditionally high in cost.

Disadvantages of the products include the lack of a warranty from the manufacturer. In addition, if assembled carelessly, such devices may have an unattractive appearance.
Meanwhile, it is quite possible to save money and get the perfect lamp by assembling it yourself. This is not difficult to do and basic technical knowledge and practical skills will be enough.
A DIY LED device has a number of significant advantages over a store-bought analogue. They are economical: with careful assembly and the use of high-quality parts, the service life reaches 100 thousand hours.
Such devices show a high degree of energy efficiency, which is determined by the ratio of power consumption and the brightness of the light produced. Finally, their cost is an order of magnitude lower than their factory counterparts.
DIY problems
The main issues that have to be resolved in the manufacture of LED lamps are the conversion of alternating electric current into pulsating and its equalization to constant. In addition, it is necessary to limit the power flow to 12 volts, which is necessary to power the diode.

To create an LED lamp yourself, you can use parts purchased in specialized stores, or elements from burnt-out appliances
When thinking through the device, you should also solve a number of design problems, namely:
- how to arrange the circuit and LEDs;
- how to isolate the system;
- how to ensure heat exchange in the device.
Before assembly, it is advisable to think through all these problems, taking into account the requirements for a homemade light source.
LED lamp circuits
First of all, you should develop an assembly option. There are two main methods, each of which has its own pros and cons. Below we will look at them in more detail.
Option with diode bridge
The circuit includes four diodes that are connected in different directions. Thanks to this, the bridge acquires the ability to transform the mains current of 220 V into a pulsating one.
This happens as follows: when sinusoidal half-waves pass through two diodes, they change, which causes a loss of polarity.
During assembly, a capacitor is connected to the positive output in front of the bridge; in front of the negative terminal - a resistance of 100 Ohms. Another capacitor is installed behind the bridge: it will be needed to smooth out voltage drops.
Making an LED element
The easiest way to create an LED lamp is to make a light source based on a broken lamp. It is necessary to check the functionality of the detected parts, which can be done using a 12 V battery.
Defective elements must be replaced. To do this, you should unsolder the contacts, remove the burnt out elements, and put new ones in their place. In this case, it is important to observe the alternation of anodes and cathodes, which are attached in series.
If you need to change only 2-3 pieces of the chip, you can simply solder them to the areas where the failed components were previously located.
For complete self-assembly, you need to connect 10 diodes in a row, observing the polarity rules. Several completed circuits are soldered to the wires.

When making a lamp, you can use boards with LEDs, which can be found in burnt-out devices. It is only important to check their functionality
When assembling circuits, it is important to ensure that the soldered ends do not touch each other, as this can lead to a short circuit in the device and failure of the system.
Devices for softer light
To avoid the flickering characteristic of LED lamps, the circuit described above can be supplemented with several details. Thus, it should consist of a diode bridge, 100 and 230 Ohm resistors, 400 nF and 10 μF capacitors.
To protect the device from voltage surges, a 100 Ohm resistor is placed at the beginning of the circuit, followed by a 400 nF capacitor, after which a diode bridge and another 230 Ohm resistor are installed, followed by an assembled chain of LEDs.
Resistor devices
A similar scheme is also quite accessible to a novice master. To do this, you need two 12k resistors and two chains of the same number of LEDs, which are soldered in series, taking into account the polarity. In this case, one strip on the R1 side is connected to the cathode, and the other to R2, the anode.
Lamps made according to this scheme have a softer light, since the operating elements are lit in turn, making the pulsation of the flashes almost invisible to the naked eye.
Materials for making homemade products
In addition to the body, other elements will be required to create the lamp. These are, first of all, LEDs, which can be purchased in the form of LED strips or individual NK6 elements. The current strength of each part is 100-120 mA; voltage 3-3.3 V.

The assembly of some circuits involves the use of additional links, for example, a driver, so the set of components for each specific case is considered separately
You also need 1N4007 rectifier diodes or a diode bridge, as well as fuses, which can be found in the base of an old device.
You will also need a capacitor, the capacitance and voltage of which must correspond to the electrical circuit used and the number of LED elements used in it.
If you are not using a ready-made board, you need to think about the frame to which the LEDs are attached. For its manufacture, a heat-resistant material that is not metal and non-conducting electric current is suitable.
As a rule, such a part is made of durable plastic or thick cardboard. To attach the LED elements to the frame you will need liquid nails or superglue.
Assembling a simple LED lamp
Let's consider the implementation of a lamp in a standard base from a fluorescent lamp. To do this, we will have to slightly change the above list of materials.
In this case we use:
- old base E27;
- NK6 LEDs;
- driver RLD2-1;
- a piece of plastic or thick cardboard;
- Super glue;
- electrical wiring;
- soldering iron, pliers, scissors.
Initially, you need to disassemble the lamp. For luminescent devices, the connection of the base to the plate with tubes is carried out using latches. It is important to locate the fastening location and pry the elements with a screwdriver, which will allow you to easily disconnect the cartridge.

The process of assembling a homemade LED lamp is simple. A driver is inserted into the case from the old device, on top of which a board with LEDs is installed
When disassembling the device, extreme care must be taken so as not to damage the tubes that contain a toxic substance inside. At the same time, it is necessary to monitor the integrity of the electrical wiring connected to the base, as well as preserve the parts contained in it.
We use the upper part with connected gas-discharge tubes to make the plate necessary for connecting the LEDs. It is enough to remove the tubular elements and attach the LED parts to the remaining round holes.
To secure them securely, it is better to make an additional plastic or cardboard cover, which will serve to isolate the chips.
The lamp will use NK6 LEDs, each of which consists of 6 crystals with parallel connection. They allow you to create a fairly bright lighting device with a minimum of electricity consumption.
To connect each LED to the cover, you need to make two holes. They should be pierced carefully in strict accordance with the diagram.
The plastic part allows you to firmly fix the LED elements, while the use of cardboard requires additional fastening of the LEDs to the base using liquid nails or superglue.
Since the device is designed to use six LEDs with a power of 0.5 watts each, the circuit must include three elements connected in parallel.

A spectacular lamp can be created using LED strip. This element is inserted into a tube used for fluorescent lighting
In a design that will operate from a 220 V power supply, you need to provide an RLD2-1 driver, which you should purchase in a store or do it yourself.
To avoid short circuits, it is important to insulate the driver and board from each other using plastic or cardboard before starting assembly. Since the lamp barely heats up, there is no need to worry about overheating.
Having selected all the components, you can assemble the structure according to the diagram, and then connect it to the electrical network to check the glow.
The device, operating from a standard 220 V power supply, has low energy consumption and a power of 3 Watts. The latter figure is 2-3 times less than that of fluorescent devices and 10 times less than that of incandescent lamps.
Although the light output is only 100-120 lumens, the dazzling white color makes the lamp appear much brighter. The assembled lamp can be used as a table lamp or to illuminate a compact room, for example, a corridor or closet.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
In the video below you can see a detailed description of a specialist about self-assembly of an LED lamp:
LED lamps, made independently, have high technical characteristics. They are almost as good as factory models in terms of qualities such as strength, reliability, and durability.
The assembly of such devices is accessible to almost everyone: to successfully complete it, you just need to strictly follow the diagrams and carefully carry out all the prescribed manipulations.
Perhaps you have already assembled an LED lamp with your own hands and can you give valuable advice to visitors to our site? Or did you have any questions after reading the article? Please leave your comments in the block below.
LEDs and products based on them are becoming increasingly popular. LED light bulbs and lamps are systematically displacing traditional light sources from store shelves. This semiconductor device also cannot leave radio amateurs indifferent, and the question increasingly arises: how to make an LED with your own hands?
The LED itself is quite complex to manufacture, and it is impossible to repeat the technological process outside of production conditions. Growing a crystal, packaging, applying phosphor - all this requires complex, expensive equipment. However, the further life path of an LED out of production can be very diverse. LEDs are used in monitor backlighting, display, lighting and many other areas. They open up enormous opportunities for both professional developers and ordinary DIY enthusiasts.
In order for the LED to work, it needs to be soldered onto the board; such a unit will already be called an LED module. The module may include one or more light-emitting diodes.
Unlike indicator LEDs, which have long pins for soldering into holes, high-power lighting LEDs are primarily manufactured in surface-mount packages. Therefore, soldering them onto a board with your own hands is much more difficult, and the printed circuit boards themselves for such LEDs come in different types.
Fiberglass can only be used if the power is low, no more than a watt per LED, to avoid overheating. In this case, the space near the diode must be metalized, and sometimes “studded” with vias to quickly dissipate heat to the second side of the board. Although the radiator from such a board turns out to be unimportant, it has a significant advantage - you can easily make it yourself using the good old “printer and iron” technology.
For optimal heat dissipation, a high-power LED is usually mounted on an MCPCB (Metal Core Printed Circuit Board) board.
It is an aluminum plate that has copper printed conductors on the surface, separated from the base by a thin dielectric oxide film. Such boards usually have a thickness of 1.5-2 mm, they are much more expensive than textolite ones and, as a rule, they can only be obtained in finished form, already wired for specific types of LEDs. You won’t be able to make such a board yourself - you need to have specialized production. However, recently, almost all domestic manufacturers of printed circuit boards have begun to provide services for the production of MCPCBs, and if there is a strong desire to produce your own unique LED module, then today you can realize it. It won't be cheap.
Soldering an LED onto an MCPCB board presents certain difficulties:
- when you try to solder a diode with a regular soldering iron or soldering station, the board becomes a significant hindrance - a radiator that removes heat from the contact pad, preventing it from heating up properly, so you have to use a powerful soldering iron;
- In addition to the cathode and anode, a powerful LED usually also has a terminal for heat removal, which is a flat platform located at the bottom of the LED housing, i.e. inaccessible to the soldering iron tip.
A typical board for such LEDs is shown in the figure below.

Because of its bizarre shape, this board is called a “star”. In the center is a LED seat, in this case XPE from CREE. The LED itself looks like this

Soldering the LED to the star can be done using a hot air gun, but this must be done with great care so as not to damage the lens. You should also make sure that the air flow does not dislodge the LED. You should not overuse solder paste; if you apply too much, the body may “float” and you will end up with a skew.
If you need to solder a large number of LEDs, for example, a module in the form of a long ruler, then a hair dryer is definitely not the best option.
There is a more efficient installation method. An old flat iron can be an ideal tool for “baking” LED modules. It is installed with the sole up and heated to about 230 degrees. Then an aluminum board with pre-applied flux, solder paste and installed LEDs is carefully installed on it. You can visually see when the board heats up, the solder paste melts and clear solder joints form. The main thing is not to overexpose it - the LED can be exposed to such temperatures only for a few tens of seconds, otherwise it can be damaged or lose a significant share of the luminous flux. In this way, you can solder several dozen LEDs simultaneously.
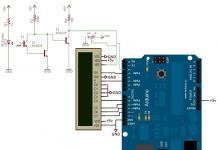
8x8 LED Matrix Displays come in a variety of sizes and are fun to work with. Large industrial assemblies measure around 60 x 60 mm. However, if you are looking for much larger LED matrices, they are difficult to find.
In this project we will be building a really large LED matrix LED display that is made up of several large 8x8 LED modules connected in series with each other. Each of these modules measures approximately 144 x 144 mm.
The special thing about this display is that you can look at the background behind it if necessary. This gives you the freedom to use these displays creatively, such as placing them in front of glass panels so you can see what's happening behind the display.

For this project we will use 10mm. You can use other sizes. Commonly available sizes are 3mm, 5mm, 8mm, and 10mm.

Although the display is not designed to work with any microcontroller, we will use popular Arduino boards and connect it via SPI using only 3 signal wires.

To build this project, basic knowledge of electronics and component soldering is required, as well as some knowledge of using Arduino. Firmware .

Here you need to solder the LEDs together using the long LED legs. You can use any size and color of LED, but the leg length (more than 23mm) must be long enough to bend and solder them together. The LEDs are arranged in an 8x8 matrix, where the cathodes are soldered together for the rows, and the anodes are soldered together for the columns.

The MAX7219 driver controls the dynamic display of the LED matrix. When designed, each 8x8 LED matrix will be based on a circuit using the following components:
- 1 x MAX7219
- 1 x 10uF 16V electrolytic capacitor
- 1 x 0.1 UF ceramic capacitor
- 1 x 12 kOhm resistor (0.25 W)
- 1 x 24-pin female DIP IC

Note that you may need to select a different resistor value to suit the LED you will be using. This resistor limits the maximum current on the MAX7219 that will be output to the LEDs.

And this video clearly shows how to install an LED matrix, an electronic control board and a simple test to run it using the popular Arduino UNO/Nano board.
|
|
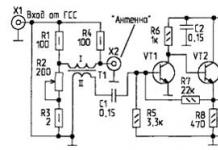
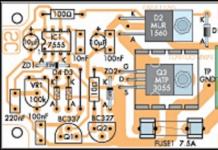
Greetings to all novice electronics engineers and radio engineering enthusiasts and those who like to do something with their own hands. In this article, I will try to kill two birds with one stone: I will try to tell you how to make a printed circuit board of excellent quality yourself, which will be no different from the factory analogue, thereby we will do it with you. This device can be used in a car to connect LEDs. For example, as in .
For work we will need:
- Transistors – IRF9540N and KT503;
- Capacitor 25 V 100 pF;
- Rectifier diode 1N4148;
- Resistors:
- R1 – 4.7 kOhm 0.25 W;
- R2 – 68 kOhm 0.25 W;
- R3 – 51 kOhm 0.25 W;
- R4 – 10 kOhm 0.25 W.
- Screw terminal blocks, 2 and 3 pins, 5 mm
- One-sided textolite and FeCl3 – ferric chloride
Progress.
First of all, we need to prepare the board. To do this, mark the conventional boundaries of the board on the PCB. We make the edges of the board a little larger than the trace pattern. Once you have marked the edges of the borders you can start cutting. You can cut with metal scissors, and if you don’t have them on hand, you can try cutting with a stationery knife.
After cutting out the board, it needs to be sanded. To do this, use sandpaper with a grain size of P800-1000 to sand the board under water. Next we dry and degrease the surface with solvent 646. After which it is not recommended to touch the board.
Next, download the program that is at the end of the article, SprintLayout, and using it, open the board diagram and print it on a laser printer on glossy paper. It is important that when printing, the printer settings are set to high definition and high image quality.
Then you will need to heat the prepared board with an iron and attach our printout to it and iron the board thoroughly for several minutes.
Next, let the board cool a little, then lower it into a cup of cold water for a few minutes. Water will make it easy to tear off the glossy paper from the board. If the gloss has not come off completely, then you can simply roll off the remaining paper slowly with your fingers.
Then you will need to check the quality of the paths; if there are minor damages, you can touch up the bad places with a simple marker.
So, the preparatory stage is completed. Left . To do this, we place our board on double-sided tape and glue it to a small piece of foam plastic and lower it into a ferric chloride solution. To speed up the etching process, you can shake the cup with the solution.
After the excess copper is removed, you will need to wash the board in water and use a solvent to clean the toner from the tracks.
All that remains is to drill the holes. For our device, drills with a diameter of 0.6 and 0.8 mm were used.
It is important not to overheat the tracks, otherwise you may damage them.
All that remains is to assemble our device. It is recommended to first print out the diagram with symbols on plain paper and, using it as a guide, arrange all the elements on the board.
After everything is soldered, you need to completely clean the board of flux. To do this, thoroughly wipe the board with that 646 solvent, wash thoroughly with a brush and soap, and dry.
After drying, we connect and check the functionality of the assembly. To do this, we connect the “constant plus” and “minus” to the power supply and instead of the LEDs, connect a multimeter and check if there is voltage. If there is tension, it means that the flux is not completely disturbed.
As you can see, the board manufacturing process is not a very complicated process. This method of making a board is called LUT (laser ironing technology). As mentioned above, this assembly can be used for ( , , , ), or in any other places where LEDs and 12 volt power are used -
Thank you all for your attention! I will be happy to answer all your questions!
Good luck on the roads!!!
NECESSARILY!!!
Connect devices whose actions and properties are little known to you, especially homemade ones, using fuses.
 The classic circuit of an ionizer is a therapeutic generator of negative ions for the home.
The classic circuit of an ionizer is a therapeutic generator of negative ions for the home.