Gyms, saunas, billiard rooms are often located in the basement, not to mention the fact that sanitary norms many countries allow even bedrooms to be placed in basements. In this regard, the question arises about heat loss through basements.
Basement floors are in conditions where average temperature fluctuations are very small and range from 11 to 9°C. Thus, heat loss through the floor, although not very large, is constant throughout the year. According to computer analysis, heat loss through an uninsulated concrete floor is 1.2 W/m 2 .
Heat losses occur along the lines of stress in the soil to a depth of 10 to 20 m from the surface of the earth or from the base of the building. The installation of polystyrene insulation with a thickness of about 25 mm can reduce heat loss by approximately 5%, which is no more than 1% of the total heat loss of the building.
The device of the same roof insulation allows to reduce heat losses in winter time by 20% or improve the building's overall thermal efficiency by 11%. Thus, in order to save energy, roof insulation is much more efficient than basement floor insulation.
This position is confirmed by the analysis of the microclimate inside the building in summer time. In case the bottom foundation walls building is not insulated, the incoming air heats the room, but the thermal inertia of the soil begins to affect heat loss, creating a stable temperature regime; at the same time, heat loss increases, and the temperature inside basements decreases.
Thus, free heat exchange through the structures contributes to maintaining the summer air temperatures in the premises at a comfortable level. Thermal insulation under the floor significantly violates the conditions of heat exchange between the concrete floor and the ground.
The installation of floor (internal) thermal insulation from an energy point of view leads to unproductive costs, however, at the same time, it is necessary to take into account moisture condensation on cold surfaces and, in addition, the need to create comfortable conditions for a person.
To mitigate the feeling of cold, you can apply thermal insulation, placing it under the floor, which will bring the floor temperature closer to the air temperature in the room and isolate the floor from the underlying layer of the earth, which has a relatively low temperature. Although such insulation can increase the temperature of the floor, in this case the temperature usually does not exceed 23°C, which is 14°C lower than human body temperature.
Thus, to reduce the sensation of cold from the floor in order to provide the most comfortable conditions, it is best to use carpeting or arrange wooden floor on a concrete base.
The last aspect to be considered in this energy analysis concerns the heat loss at the junction of the floor with the wall, which is not protected by backfill. Such a node is found in buildings standing on a slope.
As the analysis of heat losses shows, significant heat losses are possible in this zone in winter. Therefore, to reduce the influence of weather conditions, it is recommended to isolate the foundation along the outer surface.
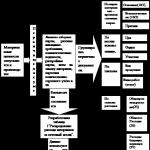
Heat transfer through the fences of a house is a complex process. In order to take into account these difficulties as much as possible, the measurement of premises when calculating heat losses is done according to certain rules, which provide for a conditional increase or decrease in area. Below are the main provisions of these rules.
Rules for measuring the areas of enclosing structures: a - section of a building with an attic floor; b - section of a building with a combined coating; c - building plan; 1 - floor above the basement; 2 - floor on logs; 3 - floor on the ground;
The area of windows, doors and other openings is measured by the smallest construction opening.
The area of the ceiling (pt) and floor (pl) (except for the floor on the ground) is measured between the axes of the inner walls and the inner surface of the outer wall.
The dimensions of the outer walls are taken horizontally along the outer perimeter between the axes of the inner walls and the outer corner of the wall, and in height - on all floors except the lower one: from the level of the finished floor to the floor of the next floor. On the top floor the top of the outer wall coincides with the top of the cladding, or attic floor. On the lower floor, depending on the floor design: a) from the inner surface of the floor on the ground; b) from the preparation surface for the floor structure on the logs; c) from the lower edge of the ceiling over an unheated underground or basement.
When determining heat loss through internal walls their areas are measured along the inner perimeter. Heat losses through the internal enclosures of the premises can be ignored if the air temperature difference in these premises is 3 °C or less.

Breakdown of the floor surface (a) and recessed parts of the outer walls (b) into design zones I-IV
The transfer of heat from the room through the structure of the floor or wall and the thickness of the soil with which they come into contact is subject to complex patterns. To calculate the resistance to heat transfer of structures located on the ground, a simplified method is used. The surface of the floor and walls (in this case, the floor is considered as a continuation of the wall) is divided along the ground into strips 2 m wide, parallel to the junction of the outer wall and the ground surface.
The counting of zones starts along the wall from the ground level, and if there are no walls along the ground, then zone I is the floor strip closest to outer wall. The next two strips will be numbered II and III, and the rest of the floor will be zone IV. Moreover, one zone can begin on the wall and continue on the floor.
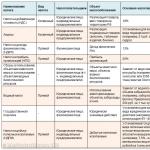
A floor or wall that does not contain insulating layers made of materials with a thermal conductivity coefficient of less than 1.2 W / (m ° C) is called non-insulated. The resistance to heat transfer of such a floor is usually denoted as R np, m 2 ° C / W. For each zone of an uninsulated floor, standard values heat transfer resistance:
- zone I - RI = 2.1 m 2 ° C / W;
- zone II - RII = 4.3 m 2 ° C / W;
- zone III - RIII \u003d 8.6 m 2 ° C / W;
- zone IV - RIV \u003d 14.2 m 2 ° C / W.
If there are insulating layers in the floor structure located on the ground, it is called insulated, and its resistance to heat transfer R unit, m 2 ° C / W, is determined by the formula:
R pack \u003d R np + R us1 + R us2 ... + R usn
Where R np - resistance to heat transfer of the considered zone of an uninsulated floor, m 2 · ° С / W;
R us - heat transfer resistance of the insulating layer, m 2 · ° C / W;
For a floor on logs, the heat transfer resistance Rl, m 2 · ° С / W, is calculated by the formula.
Despite the fact that heat losses through the floor of most one-story industrial, administrative and residential buildings rarely exceed 15% of the total heat loss, and sometimes do not even reach 5% with an increase in the number of storeys, the importance right decision tasks...
The definition of heat loss from the air of the first floor or basement to the ground does not lose its relevance.
This article discusses two options for solving the problem posed in the title. Conclusions are at the end of the article.
Considering heat losses, one should always distinguish between the concepts of "building" and "room".
When performing the calculation for the entire building, the goal is to find the power of the source and the entire heat supply system.
When calculating the heat losses of each a separate room building, the problem of determining the power and number of thermal devices (batteries, convectors, etc.) required for installation in each specific room to maintain the desired indoor air temperature.
The air in the building is heated by receiving thermal energy from the Sun, external sources of heat supply through the heating system and from various internal sources- from people, animals, office equipment, household appliances, lighting lamps, hot water systems.
The air inside the premises cools down due to the loss of thermal energy through the enclosing structures of the building, which are characterized by thermal resistances measured in m 2 ° C / W:
R = Σ (δ i /λ i )
δ i- the thickness of the material layer of the building envelope in meters;
λ i- coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material in W / (m ° C).
Protect the house from external environment ceiling (floor) of the upper floor, external walls, windows, doors, gates and the floor of the lower floor (possibly the basement).
The external environment is outside air and soil.
The calculation of heat loss by the building is carried out at the estimated outdoor temperature for the coldest five-day period of the year in the area where the facility is built (or will be built)!
But, of course, no one forbids you to make a calculation for any other time of the year.
Calculation inexcelheat loss through the floor and walls adjacent to the ground according to the generally accepted zonal method by V.D. Machinsky.
The temperature of the soil under the building depends primarily on the thermal conductivity and heat capacity of the soil itself and on the ambient air temperature in the area during the year. Since the outside temperature varies significantly in different climatic zones, then the soil has different temperatures in different periods years at different depths in different areas.
To simplify the solution challenging task for determining heat loss through the floor and basement walls into the ground, for more than 80 years, the method of dividing the area of enclosing structures into 4 zones has been successfully used.
Each of the four zones has its own fixed heat transfer resistance in m 2 °C / W:
R 1 \u003d 2.1 R 2 \u003d 4.3 R 3 \u003d 8.6 R 4 \u003d 14.2
Zone 1 is a strip on the floor (in the absence of soil penetration under the building) 2 meters wide, measured from the inner surface of the outer walls along the entire perimeter or (in the case of a subfloor or basement) a strip of the same width, measured down the inner surfaces of the outer walls from soil edges.
Zones 2 and 3 are also 2 meters wide and are located behind zone 1 closer to the center of the building.
Zone 4 occupies the entire remaining central square.
In the figure below, zone 1 is located entirely on the basement walls, zone 2 is partially on the walls and partially on the floor, zones 3 and 4 are completely on the basement floor.

If the building is narrow, then zones 4 and 3 (and sometimes 2) may simply not be.
Square gender zone 1 in the corners is counted twice in the calculation!
If the entire zone 1 is located on vertical walls, then the area is considered in fact without any additives.
If part of zone 1 is on the walls and part is on the floor, then only the corner parts of the floor are counted twice.
If the entire zone 1 is located on the floor, then the calculated area should be increased by 2 × 2x4 = 16 m 2 when calculating (for a rectangular house in plan, i.e. with four corners).
If there is no deepening of the structure into the ground, then this means that H =0.
Below is a screenshot of the calculation program in Excel heat loss through the floor and recessed walls for rectangular buildings.

Zone areas F 1 , F 2 , F 3 , F 4 calculated according to the rules of ordinary geometry. The task is cumbersome and often requires sketching. The program greatly facilitates the solution of this problem.
The total heat loss to the surrounding soil is determined by the formula in kW:
Q Σ =((F 1 + F1y )/ R 1 + F 2 / R 2 + F 3 / R 3 + F 4 / R 4 )*(t vr -t nr)/1000
The user only needs to fill in the first 5 lines in the Excel table with values and read the result below.
To determine heat losses to the ground premises zone areas will have to be calculated manually. and then substitute in the above formula.
The following screenshot shows, as an example, the calculation in Excel of heat loss through the floor and recessed walls. for the lower right (according to the figure) basement room.

The sum of heat losses to the ground by each room is equal to the total heat losses to the ground of the entire building!
The figure below shows simplified circuits standard designs floors and walls.

The floor and walls are considered non-insulated if the coefficients of thermal conductivity of materials ( λ i), of which they are composed, is more than 1.2 W / (m ° C).
If the floor and / or walls are insulated, that is, they contain layers with λ <1,2 W / (m ° C), then the resistance is calculated for each zone separately according to the formula:
Rinsulationi = Rnon-insulatedi + Σ (δ j /λ j )
Here δ j- the thickness of the insulation layer in meters.
For floors on logs, heat transfer resistance is also calculated for each zone, but using a different formula:
Ron the logsi =1,18*(Rnon-insulatedi + Σ (δ j /λ j ) )
Calculation of heat losses inMS excelthrough the floor and walls adjacent to the ground according to the method of Professor A.G. Sotnikov.
A very interesting technique for buildings buried in the ground is described in the article “Thermophysical calculation of heat losses in the underground part of buildings”. The article was published in 2010 in №8 of the ABOK magazine under the heading "Discussion Club".
Those who want to understand the meaning of what is written below should first study the above.
A.G. Sotnikov, relying mainly on the findings and experience of other predecessor scientists, is one of the few who, in almost 100 years, has tried to move the topic that worries many heat engineers. I am very impressed with his approach from the point of view of fundamental heat engineering. But the difficulty of correctly assessing the temperature of the soil and its thermal conductivity in the absence of appropriate survey work somewhat shifts the methodology of A.G. Sotnikov into a theoretical plane, moving away from practical calculations. Although at the same time, continuing to rely on the zonal method of V.D. Machinsky, everyone just blindly believes the results and, understanding the general physical meaning of their occurrence, cannot definitely be sure of the obtained numerical values.
What is the meaning of the methodology of Professor A.G. Sotnikov? He proposes to consider that all heat losses through the floor of a buried building “go” into the depths of the planet, and all heat losses through walls in contact with the ground are eventually transferred to the surface and “dissolve” in the ambient air.
This seems to be partly true (without mathematical justification) in the presence of sufficient deepening of the floor of the lower floor, but with a deepening of less than 1.5 ... 2.0 meters, doubts arise about the correctness of the postulates ...
Despite all the criticisms made in the previous paragraphs, it is the development of the algorithm of Professor A.G. Sotnikova seems to be very promising.
Let's calculate in Excel the heat loss through the floor and walls into the ground for the same building as in the previous example.
We write down the dimensions of the basement of the building and the estimated air temperatures in the block of initial data.
Next, you need to fill in the characteristics of the soil. As an example, let's take sandy soil and enter its thermal conductivity coefficient and temperature at a depth of 2.5 meters in January into the initial data. The temperature and thermal conductivity of the soil for your area can be found on the Internet.
The walls and floor will be made of reinforced concrete ( λ=1.7 W/(m °C)) 300mm thick ( δ =0,3 m) with thermal resistance R = δ / λ=0.176 m 2 ° C / W.
And, finally, we add to the initial data the values of the heat transfer coefficients on the inner surfaces of the floor and walls and on the outer surface of the soil in contact with the outside air.

The program performs the calculation in Excel using the formulas below.
Floor area:
F pl \u003dB*A
Wall area:
F st \u003d 2 *h *(B + A )
Conditional thickness of the soil layer behind the walls:
δ conv. = f(h / H )
Thermal resistance of the soil under the floor:
R 17 =(1/(4*λ gr )*(π / Fpl ) 0,5
Heat loss through the floor:
Qpl = Fpl *(tin — tgr )/(R 17 + Rpl +1/α in )
Thermal resistance of the soil behind the walls:
R 27 = δ conv. /λ gr
Heat loss through walls:
Qst = Fst *(tin — tn )/(1/α n +R 27 + Rst +1/α in )
General heat loss to the ground:
Q Σ = Qpl + Qst
Remarks and conclusions.
The heat loss of the building through the floor and walls into the ground, obtained by two different methods, differ significantly. According to the algorithm of A.G. Sotnikov value Q Σ =16,146 kW, which is almost 5 times more than the value according to the generally accepted "zonal" algorithm - Q Σ =3,353 kW!
The fact is that the reduced thermal resistance of the soil between the buried walls and the outside air R 27 =0,122 m 2 °C / W is clearly small and hardly true. And this means that the conditional thickness of the soil δ conv. not defined correctly!
In addition, the “bare” reinforced concrete of the walls, which I chose in the example, is also a completely unrealistic option for our time.
An attentive reader of the article by A.G. Sotnikova will find a number of errors, rather than those of the author, but those that arose when typing. Then in formula (3) a factor 2 appears in λ , then disappears later. In the example, when calculating R 17 no division sign after unit. In the same example, when calculating heat loss through the walls of the underground part of the building, for some reason the area is divided by 2 in the formula, but then it is not divided when recording the values ... What kind of uninsulated walls and floor are these in the example with Rst = Rpl =2 m 2 ° C / W? In this case, their thickness must be at least 2.4 m! And if the walls and floor are insulated, then, it seems, it is incorrect to compare these heat losses with the calculation option for zones for an uninsulated floor.
R 27 = δ conv. /(2*λ gr)=K(cos((h / H )*(π/2)))/К(sin((h / H )*(π/2)))
As for the question, regarding the presence of a factor of 2 in λ gr has already been said above.
I divided the complete elliptic integrals by each other. As a result, it turned out that the graph in the article shows a function for λ gr =1:
δ conv. = (½) *TO(cos((h / H )*(π/2)))/К(sin((h / H )*(π/2)))
But mathematically it should be:
δ conv. = 2 *TO(cos((h / H )*(π/2)))/К(sin((h / H )*(π/2)))
or, if the factor is 2 λ gr not needed:
δ conv. = 1 *TO(cos((h / H )*(π/2)))/К(sin((h / H )*(π/2)))
This means that the schedule for determining δ conv. gives erroneous underestimated values by 2 or 4 times ...
It turns out that until everyone has nothing else to do, how to continue to either “count”, or “determine” heat losses through the floor and walls into the ground by zones? No other worthy method has been invented in 80 years. Or invented, but not finalized?!
I invite blog readers to test both calculation options in real projects and present the results in the comments for comparison and analysis.
Everything that is said in the last part of this article is solely the opinion of the author and does not claim to be the ultimate truth. I would be glad to hear the opinion of experts on this topic in the comments. I would like to understand to the end with the algorithm of A.G. Sotnikov, because it really has a more rigorous thermophysical justification than the generally accepted method.
I beg respecting the work of the author to download a file with calculation programs after subscribing to article announcements!
P.S. (02/25/2016)
Almost a year after writing the article, we managed to deal with the questions raised a little higher.
Firstly, the program for calculating heat losses in Excel according to the method of A.G. Sotnikova thinks everything is correct - exactly according to the formulas of A.I. Pehovich!
Secondly, the formula (3) from the article by A.G. Sotnikova should not look like this:
R 27 = δ conv. /(2*λ gr)=K(cos((h / H )*(π/2)))/К(sin((h / H )*(π/2)))
In the article by A.G. Sotnikova is not a correct entry! But then the graph is built, and the example is calculated according to the correct formulas!!!
So it should be according to A.I. Pekhovich (p. 110, additional task to item 27):
R 27 = δ conv. /λ gr\u003d 1 / (2 * λ gr ) * K (cos((h / H )*(π/2)))/К(sin((h / H )*(π/2)))
δ conv. =R27 *λ gr =(½)*K(cos((h / H )*(π/2)))/К(sin((h / H )*(π/2)))
According to SNiP 41-01-2003, the floors of the floor of the building, located on the ground and logs, are delimited into four zones-strips 2 m wide parallel to the outer walls (Fig. 2.1). When calculating heat losses through floors located on the ground or logs, the surface of the floor sections near the corner of the outer walls ( in zone I ) is entered into the calculation twice (square 2x2 m).
Heat transfer resistance should be determined:
a) for non-insulated floors on the ground and walls located below ground level, with thermal conductivity l ³ 1.2 W / (m × ° C) in zones 2 m wide, parallel to the outer walls, taking R n.p. . , (m 2 × ° С) / W, equal to:
2.1 - for zone I;
4.3 - for zone II;
8.6 - for zone III;
14.2 - for zone IV (for the remaining floor area);
b) for insulated floors on the ground and walls located below ground level, with thermal conductivity l c.s.< 1,2 Вт/(м×°С) утепляющего слоя толщиной d у.с. , м, принимая R c.p. , (m 2 × ° С) / W, according to the formula
c) thermal resistance to heat transfer of individual zones of floors on logs R l, (m 2 × ° C) / W, determined by the formulas:
I zone - ![]() ;
;
II zone - ![]() ;
;
III zone - ![]() ;
;
IV zone - ![]() ,
,
where , , , are the values of thermal resistance to heat transfer of individual zones of uninsulated floors, (m 2 × ° С) / W, respectively, numerically equal to 2.1; 4.3; 8.6; 14.2; - the sum of the values \u200b\u200bof thermal resistance to heat transfer of the insulating layer of floors on logs, (m 2 × ° С) / W.
The value is calculated by the expression:
 , (2.4)
, (2.4)
here is the thermal resistance of closed air spaces
(Table 2.1); δ d - the thickness of the layer of boards, m; λ d - thermal conductivity of wood material, W / (m ° C).
Heat loss through the floor located on the ground, W:
 , (2.5)
, (2.5)
where , , , are the areas of I, II, III, IV zones-bands, respectively, m 2 .
Heat loss through the floor, located on the logs, W:
 , (2.6)
, (2.6)
Example 2.2.
Initial data:
- first floor;
- external walls - two;
– floor construction: concrete floors covered with linoleum;

– design temperature of internal air °С;
Calculation order.


Rice. 2.2. Fragment of the plan and the location of the floor zones in the living room No. 1
(to examples 2.2 and 2.3)
2. Only the 1st and part of the 2nd zone are placed in the living room No. 1.
I-th zone: 2.0´5.0 m and 2.0´3.0 m;
II zone: 1.0´3.0 m.
3. The areas of each zone are equal to:
4. We determine the resistance to heat transfer of each zone according to the formula (2.2):
(m 2 × ° C) / W,
(m 2 × ° C) / W.
5. According to formula (2.5), we determine the heat loss through the floor located on the ground:
Example 2.3.
Initial data:
– floor construction: wooden floors on logs;

- external walls - two (Fig. 2.2);
- first floor;
– construction area – Lipetsk;
– design temperature of internal air °С; °C.
Calculation order.
1. We draw a plan of the first floor on a scale indicating the main dimensions and divide the floor into four zones-strips 2 m wide parallel to the outer walls.
2. Only the 1st and part of the 2nd zone are placed in the living room No. 1.
We determine the dimensions of each zone-band:
Usually, floor heat losses in comparison with similar indicators of other building envelopes (external walls, window and door openings) are a priori assumed to be insignificant and are taken into account in the calculations of heating systems in a simplified form. Such calculations are based on a simplified system of accounting and correction coefficients for the resistance to heat transfer of various building materials.
Given that the theoretical justification and methodology for calculating the heat loss of the ground floor was developed quite a long time ago (i.e. with a large design margin), we can safely say that these empirical approaches are practically applicable in modern conditions. The coefficients of thermal conductivity and heat transfer of various building materials, insulation and floor coverings are well known, and other physical characteristics are not required to calculate heat loss through the floor. According to their thermal characteristics, floors are usually divided into insulated and non-insulated, structurally - floors on the ground and logs.
The calculation of heat loss through an uninsulated floor on the ground is based on the general formula for estimating heat loss through the building envelope:
where Q are the main and additional heat losses, W;
BUT is the total area of the enclosing structure, m2;
tv , tn- temperature inside the room and outside air, °C;
β - share of additional heat losses in total;
n- correction factor, the value of which is determined by the location of the enclosing structure;
Ro– resistance to heat transfer, m2 °С/W.
Note that in the case of a homogeneous single-layer floor slab, the heat transfer resistance Ro is inversely proportional to the heat transfer coefficient of the uninsulated floor material on the ground.
When calculating heat loss through an uninsulated floor, a simplified approach is used, in which the value (1+ β) n = 1. Heat loss through the floor is usually carried out by zoning the heat transfer area. This is due to the natural heterogeneity of the temperature fields of the soil under the floor.
The heat loss of an uninsulated floor is determined separately for each two-meter zone, the numbering of which starts from the outer wall of the building. In total, four such strips 2 m wide are taken into account, considering the soil temperature in each zone to be constant. The fourth zone includes the entire surface of the uninsulated floor within the boundaries of the first three strips. Heat transfer resistance is accepted: for the 1st zone R1=2.1; for the 2nd R2=4.3; respectively for the third and fourth R3=8.6, R4=14.2 m2*оС/W.
Fig.1. Zoning of the floor surface on the ground and adjacent recessed walls when calculating heat losses
In the case of recessed rooms with a soil base of the floor: the area of the first zone adjacent to the wall surface is taken into account twice in the calculations. This is quite understandable, since the heat losses of the floor are added to the heat losses in the vertical enclosing structures of the building adjacent to it.
Calculation of heat loss through the floor is made for each zone separately, and the results obtained are summed up and used for the thermal engineering justification of the building design. The calculation for the temperature zones of the outer walls of recessed rooms is carried out according to formulas similar to those given above.
In calculations of heat loss through an insulated floor (and it is considered as such if its structure contains layers of material with a thermal conductivity of less than 1.2 W / (m ° C)) the value of the heat transfer resistance of an uninsulated floor on the ground increases in each case by the heat transfer resistance of the insulating layer:
Ru.s = δy.s / λy.s,
where δy.s– thickness of the insulating layer, m; λu.s- thermal conductivity of the material of the insulating layer, W / (m ° C).