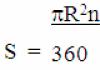When building or purchasing a private house, an electrical supply system will be connected to it, and therefore grounding measures will be needed. We propose to consider how to make a separate external and internal grounding loop, the cost of its installation and PUE standards, as well as the price and where to buy materials.
What is it - a ground loop
The grounding device is a group of horizontal conductors - electrodes, connected by a group; they are installed in close proximity to the object at a certain distance relative to each other.
What is the circuit for?
- protection of electrical devices from voltage surges in premises;
- protection of home residents from electric shock;
- resistance to “spreading” of energy;
- for lightning protection of a cottage, house or apartment.
Inner loop technology
To build such a group, it is customary to use steel angles or reinforcing metal pipes, supports, up to 3 meters long. They are driven into the ground with a sledgehammer and, if necessary, secured with a foundation, but it is advisable not to fill them, otherwise, if repairs are needed, it will be impossible to carry out.
You need to connect them together using a thin steel strip with a thickness of 4 millimeters, which before starting work is laid in a trench up to a meter deep. We fasten everything together by welding.
To save space on the site, these groups are located around the perimeter of the building, or common area. Contour – this is exactly the geometric figure that is formed when assessing the work from above. Absolutely all electrical appliances in the house are connected to this ground electrode, especially those that consume a load above average: from 380 V.
What does the circuit depend on?
Before starting work, it is necessary to take measurements and measure the resistance of the ground loop. This indicator depends on several factors, in particular:
- Condition of the ground flooring;
- Grounding installation depth;
- Soil quality and type (clay, black soil, sand, etc.);
- Number of grounding groups and electrodes in each group;
- Electrode material and its characteristics.
Ideally, you need to place the ground loop in black soil, clay soils and loams. It is strictly forbidden to install electrical resistance in stone covers or rocks; they also conduct current, and the resistance of these materials is very low.
Instructions for circuit design

Installation of a closed circuit is carried out as follows: a trench of the selected depth is dug, the optimal value is 70 centimeters, but if your apartment is filled with various types of power plants, then you can create a ditch up to a meter down. The shape of the trench is an isosceles triangle with a maximum width of a meter and a depth of about 07-1 m; it must first be measured.

A corner is hammered into the vertices of the triangle with a sledgehammer, which will be responsible for the initial resistance of the ground loop of a private house. The optimal pipe length for a regular building is 2-3 meters. If the reinforcement does not fit into the ground well, use a special drill, not a hammer. After this, we begin to install our grounding conductors along the trench.
Tips from an electrician:

After all the electrodes are closed, you need to lay a steel strip up to 4 mm thick, starting from the substation and moving around the perimeter.
You will need a drawing diagram of the site, because... installation of a ground loop for a private house or building is prohibited by SNIP above gas or water pipes. It can be drawn up schematically or using software (for example, the AutoCad program), this document will be needed when the inspection protocol is drawn up in accordance with GOST. In addition, you also need to take into account the permission from the energy supply company.
Video: how to make a ground loop in a house
Grounding loops can be constructed only if there is an act for hidden work.
Testing and evaluation
Afterwards, the ground loop must be connected and tested for resistance. To do this, we connect a multimeter to it in ommert mode, after which we connect all the devices in the room to grounding, and measure the frequency of the pulses. The optimal rate is 60 pulses per minute.
What are the requirements for the grounding circuit:
- It is allowed to choose more wires than indicated in our comparison table, but not less;
- The strip connecting the electrodes must be made of corrosion-resistant alloy steel;
- The connections must be painted (the color is selected according to GOST);
The estimate is drawn up not only for the materials themselves; prices for a typical grounding loop also take into account the work being done, because in any case you will have to invite an employee of the electricity supply company to evaluate the work, he will fill out a passport and issue a protocol.
- Fittings – 1500 rubles;
- Steel tape and its installation – 3000 rubles;
- Painting of connections – 300 rubles;
- Primary documentation – 200 rubles;
- Welding work when connecting to a boiler room - 200 kW (100 rubles);
- Wires used to lay grounding to the house wiring - 500 rubles;
The time frame for creating a circuit like a KTP or TP grounding is 3-5 days. The installation must be approached very responsibly, wear a protective suit and dielectric gloves, and use a mask when working with welding.
When constructing a new residential building, property owners try to provide it with various means of protection, including from lightning strikes. To do this, it is imperative to make the correct grounding loop according to all standards, since otherwise it does not guarantee reliable protection. In this regard, there is a need for a thorough study of the rules and regulations of the PUE.
PUE norms are a collective group of special normative legal acts that were written under the USSR by the Ministry of Energy - rules for the design of power installations. These rules for electrical installations contain a description of how to properly create electrical wiring in residential buildings, factory premises and other structures; they have a description of various devices, as well as the principle of their construction. PUE includes the conditions for laying communications of electrical installations, components, requirements for certain systems and their individual elements.
Very often, PUE standards are used when installing electric lighting in buildings, various premises, as well as streets, towns, and the territories of certain institutions or enterprises. They contain conditions for the installation of ultraviolet irradiation in health-improving structures, advertising with lighting devices, and more. When laying wiring in buildings, refer to a specific section of the PUE standards.

In separate sections you can find recommendations on how to make a grounding loop, how to install electrical protective devices, and other rules for the operation of various electrical equipment. More detailed and precise information about the conditions for using such equipment is written in the Rules for the Technical Operation of Consumer Electrical Installations (PTEEP).
Today, if you follow all the rules of the PUE for installing and connecting different types of wiring, laying a grounding loop or other technical solutions, the cost of such work will be very high. For this reason, these standards are followed superficially, observing only the most important instructions, and for others they try to find an alternative solution. Despite the high cost, these rules make it possible to effectively protect a building of any type from various negative factors.
Video “Making a contour and marking. Part 1"
Standards regarding ground loopa
It is strongly recommended that the installation of the ground loop be done with reference to the PUE standards. This approach will allow you to make all the necessary connections and connect the circuit correctly in compliance with all standards. This will ensure reliable operation of the protection system in the building, preventing the negative consequences of natural or anthropogenic factors. To make a ground loop with your own hands, you should have some knowledge in the field of electrical engineering. Before work, it is recommended to read the necessary literature, as well as sections of the PUE that refer to the installation of the ground loop.
According to the current Rules for Electrical Installations, the secondary circuit must be located at the exit points of any type of building. Natural grounding conductors should be installed in place of the repeated grounding loop. The rules specify some metal structure trimmers that are suitable for grounding. Among them you can find reinforced concrete structures, massive metal parts that must come into contact with the ground with most of their surface. If the circuit is connected in an aggressive environment, then such structures must have a special protective coating. Also suitable for a grounding element are a metal water pipe that is dug deep into the ground, or long rails from non-electrified railways.

You must definitely pay attention to the PUE clause, which indicates elements that cannot be used as a ground loop. These include reinforced concrete structures with metal elements that are energized, as well as pipelines with flammable substances, heating and sewer pipes. If the circuit must be made using a natural grounding device (soil, foundation under a building), then you must first make theoretical calculations and a connection diagram.
Typically, during the construction of a new building, the ground loop is made artificially by burying supports underground. This method is considered more universal and is used much more often in practice. This is dictated by the fact that not all places have suitable conditions for natural grounding.
A very important factor that influences the circuit is soil resistance. So in places with high soil moisture, the resistance will be low. Significant installation problems arise on dry soil. For example, sandy soils, rocky or stone formations are completely unsuitable for such work.
The regulatory documents indicate the exact resistance value that determines the level of current flow, as well as what resistance the circuit should have.

There are two types of grounding used in household electrical installations.
Traditional ground loop. In this case, the main grounding element must be made of several vertical supports and one horizontal one. They must have a round cross-section and be smooth. To do this, you can use steel rods, pipes or thick reinforcement. For ordinary private houses, it is advisable to use large-sized supports. If steel reinforcement is used, then you can take 3 such elements with dimensions starting from 2 meters. They are set so that an equilateral triangle is formed if the installation location of the reinforcement is at the vertices of the conventional figure. Before you begin installing the supports, you need to measure the distance between them. The more space between them, the better. It is desirable that the distance between the grounding elements be at least 1.5 meters. After making sure that the measurements correspond to the norm, you can begin installing the circuit.
When the elements are driven into the ground, a reliable connection should be made between them. Can be attached with separate fasteners at the same height. The connection of all supports is made using horizontal grounding conductors closer to the top of the electrodes. According to PUE standards, connections must be made of steel or copper. Each element can be connected to the transverse electrode by welding. This method is more reliable than movable fasteners (nuts, bolts). As for the sizes of these electrodes, they have standardized smallest values. When installing, preference should be given to longer supports. Their thickness is regulated by the rules for electrical installations in Table 1.7.4.

For example, if the circuit is made of copper conductor, then it must be at least 1.2 centimeters in cross-section. If it is made of a sheet of black steel, then its thickness should be more than 4 centimeters, and its cross-sectional length should be more than 10.
When a ground loop is considered for residential buildings, it should be located in a place where people rarely visit. It is advisable to choose the north side. Since this part is illuminated less frequently, the earth retains more moisture.
The distance to the walls of the building must be more than 1 meter.
Deep ground loop. This type eliminates most of the disadvantages that are present in the traditional method. This method involves a modular-pin system. This design is made in specialized factories and has a certificate. The modular pin system has a number of advantages. First of all, this is compliance with all technical norms and standards. It has a long service life of more than 30 years. This design always has a stable resistance to the spreading of an electric charge under any weather conditions. The supports are driven 25-30 meters deep into the ground, which ensures reliable grounding of large buildings.

Such a system does not need to be constantly checked, as it is quite simple and reliable. The design and calculation of the grounding conductors of a modular-pin system are simpler than a do-it-yourself protection system.
When a private house or separate room has been equipped, then before connecting it, the actual readings of the entire system should be measured. If after measurements the indicators correspond to the standard data, then the installation and connection of the circuit were done correctly. Measurements of this kind, as well as checking the connection and installation diagram, are checked by a special certified electrical laboratory. After verification, it issues an expert technical report with a separate number, and is then entered into the register. Having made measurements at the main connection points, as well as the resistance, they fill out a technical passport for grounding loops, draw up a test report and sign an acceptance certificate for the corresponding system.
Special sockets must be installed in the premises, which are designed to connect wires with grounding. To make the connection, you need to lay a three-core power cable with a ground wire in advance. In addition to phase and neutral, the ground wire is also connected to the socket. It must be connected to the terminal, which is located between the sockets of the socket.
Before starting work, you need to make a grounding loop diagram, and you also need to take appropriate measurements. For each room or entire house there are rules for calculations. The design of a specific building is carried out separately. For example, let's take into account a small country house. To calculate the ground loop, you need to have the initial data:
- priming. Clay soil with a resistance of 60 Ohm*m.
- grounding elements. Metal corner with dimensions: thickness – 50 mm, length – 2.5 m, width – 5 cm.
- the distance between supports is 2.5 m.
- trench depth for the structure is 0.7 m.
- you need a grounding resistance of 10 ohms.
For calculations, all data must be converted to one unit of measurement (for length in meters). From the PUE tables, coefficients are determined for specific climatic conditions and the length of vertical supports. The actual value of soil resistance will differ from the theoretical value, since the weather in the region affects the calculations. With measurement data we use the 2nd climate zone.

Using these measurements and data, when calculating using the basic formula, we obtain the value R = 27.58 Ohm. Once the resistance value of a single grounding support has been determined, it is used when calculating the number of required grounding elements in the structure. In this case, there should be 3 of them. After the calculation results have been obtained, you need to draw up a conditional diagram. This makes it easier to understand the structure and record the values of all its elements separately. It is advisable to save the diagram after installation in case repeated work with the grounding loop is necessary. Since it is difficult to make calculations and a diagram on your own, you can use the given values. But you need to take into account the soil on which the house is located.
A modern private house is equipped with a large number of household electrical appliances. To connect them to the power supply, it is necessary to ground them for safety reasons. From this article you can learn how to properly make a ground loop in a private house with your own hands.
What is grounding?
This is the name for a specially made connection to the ground of electrical equipment elements. Its main purpose is guaranteed protection against the effects of electric current in the event of failure of a household appliance.
Grounding kit
On sale you can find special grounding kits, the price of which is about 4,600 rubles. You can also purchase separate components for installation, they are inexpensive. For example, a steel rod (electrode) 1.5 m long will cost 500 rubles, a coupling - 200 rubles, a connecting bus - 850 rubles. Each grounding kit has corresponding installation instructions, which take into account the specifics of all products.
However, most of the required elements can be made independently. In addition, the choice of materials is quite wide. You just need to know the requirements that apply to them.
Vertical ground electrode
- Corner 50x50x5 mm.
- A pipeline with a diameter of at least 32 mm, and the wall thickness must be 3.5 mm or higher.
These electrodes can be used with electricity consumption volumes of no more than 15 kW.

Horizontal ground electrode
- Steel wire with a cross-section of at least 10 mm 2.
- Strip mm.
Conductors
You can use a metal strip or copper wire as conductors. For example, a SIP wire with cores of the appropriate cross-section and without insulation. When laying in a trench - at least 25 mm 2, when laying openly - at least 16 mm 2.
Features of the scheme

Marking and choosing a location
Installation of the ground loop should be carried out closer to the house, taking into account the distances indicated above. The length of the connecting “line” in this case will be minimal, which will reduce material consumption. And most importantly, in the future it will not interfere with business activities - laying utility lines, planting flower beds.

Calculation
It is beyond the power of a person who does not have deep knowledge to make an accurate calculation. Since the calculation uses a complex form, which contains many coefficients characterizing the properties of the soil, soil moisture, as well as the climatic conditions of the zone. These coefficients can only be obtained through complex additional analyzes and calculations, which requires certain qualifications and, accordingly, will not be cheap.
For this reason, we will consider how to make a ground loop in a private house with your own hands in a simpler way. Taking into account the fact that household equipment operates within a certain range of circuit resistance in which it will function normally.
Installation
Making a grounding loop in a private house with your own hands is not so easy. This process is quite labor-intensive and includes the following steps:

How to bring it into the house?
The ground loop is connected to the metal strip that was used to connect the electrodes as follows:

Checking the ground loop
For an accurate contour, special equipment will be required. In its absence, you can use the folk method, which will allow you to determine the performance of the resulting circuit.
It is necessary to take a powerful consumer (from 2 kW) and connect it in this way: to the phase in the apartment - one end of the supply wire, to the ground - the other, and the device should work. Then you should measure the voltage in this network with the equipment turned off and on. A slight voltage difference (5-10V) indicates that you have made the correct ground loop, which is completely ready for operation.

If the test shows a significant voltage difference, then you will need to add more electrodes. From the top of the triangle, another trench 2.5 m long is dug in any direction and at its end an additional corner is driven into the ground, which is connected to the strip, and the test is carried out again. If everything is normal, then the ground loop (diagram above) can be considered ready.
Prohibited
- Connect conductors to metal pipelines of any utilities.
- Coat the elements of the circuit with paints and varnishes.
- Use the “neutral” wire to connect the ground.
- Place horizontal grounding conductors and connectors at the top (ground laying is used in rare cases).
1. Before starting work, it is recommended to draw up a temporary circuit diagram, which it is advisable to save. After all, over time, a lot is forgotten, and in order not to later guess where the connector goes and in what place the electrodes are placed, you will always have a circuit diagram at hand.
2. Electrodes can be placed not only at the vertices of the triangle. They can be placed in an arc, on a line. It is important that the total resistance of the grounding system does not exceed 3 Ohms (voltage circuit up to 500 V) and 4 Ohms (up to 1 kW). If necessary, this indicator is reduced by installing 1-2 more rods.
3. If it is not possible to take measurements yourself, then for absolute confidence in the quality of installation of the circuit, it is advisable to invite a specialist. This service will cost on average 400-500 rubles.
Very often, this service is literally imposed on the energy sector, convincing that only licensed organizations have the right to carry out this type of work. However, none of the regulatory documentation contains any instructions prohibiting self-installation of the circuit.
Naturally, you can order installation from power engineers, accept the finished work and pay for it. But if you are confident in your own abilities, why not install the ground loop yourself.
The electricity supply system is connected through the distribution board to the internal wiring of the premises and provides power to all existing household appliances and equipment. During operation, it is quite possible that malfunctions and emergency situations may occur, leading to... In this regard, protective measures are carried out in every home, among which an important role is played by the grounding loop, installed separately or together with residual current devices.
These systems are installed in accordance with the PUE, protecting people and equipment from the damaging effects of electric current.
General information about the ground loop
A standard grounding loop is a complex of metal structures placed in the ground, at certain distances from each other and at a slight distance from the protected object.
This circuit performs the following functions:
- They protect people from electric shock, and devices and equipment from voltage surges.
- Due to resistance, energy is prevented from spreading uncontrollably in the environment.
- Provide protection from the effects of lightning strikes.
If it is necessary to make an external grounding loop, in this case most structures are made of steel pipes, angles, smooth rods and other profile materials. The length of each element does not exceed 3 meters. They are driven with a sledgehammer into hard ground, covered with earth and compacted. It is undesirable to use concrete, since future repair of such structures will be impossible.
The clogged electrodes are connected to each other with a thin steel strip, at least 4 mm thick. Fastenings are carried out by welding or bolted connections. Next, the structure is connected with a special grounding cable to all devices located in the house, primarily those with high load consumption. To improve the quality of system operation, an internal grounding loop is often installed at the site.

Data for structural calculations can be obtained by carrying out the necessary studies. In accordance with the type and nature of the soil, the depth of the electrodes, their number and other parameters are determined. The most suitable material for the manufacture of structural elements is selected. Clay soils, loams and chernozems are considered ideal options for the contour of the grounded object.
It is prohibited to install grounding in rocky or rocky soils, since they are current conductors and have low resistance.
PUE requirements for the ground loop
Before designing and implementing a grounding loop in practice, you should carefully study the requirements of the PUE on this issue. This will allow you to avoid mistakes, make high-quality connections and connections, observing all regulations and standards. Having studied the regulatory documentation, it is quite possible to independently manufacture an external grounding loop, if you have theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
In accordance with the PUE, each exit from the building must have a repeated grounding circuit. For these purposes, it is recommended to use natural grounding conductors from nearby metal and reinforced concrete structures. Most of their surface should be in contact with the ground. If the grounding loop of a house is connected to structures located in an aggressive environment, they must be protected with a special coating.

The rules also define those elements that cannot serve as a ground loop. First of all, these are energized reinforced concrete products, pipelines for transporting flammable substances, sewerage and heating pipes. If you can’t do without natural grounding conductors, you need to perform preliminary calculations and decide how to choose the right design, after which the most optimal connection scheme is selected.
When constructing new buildings, artificial grounding loops are used, installed during the construction process. This grounding method is used most often, since it is not always possible to take advantage of natural factors locally. It is also necessary to take into account soil resistance, which directly affects the performance of systems, including the grounding loop of the transformer substation.
If the soil is constantly wet, its resistance will always be below the acceptable level. These and other parameters must be taken into account when developing the design of the grounding loop.
Types and designs of grounding
In private homes, PUE requirements allow the use of various types of grounding. The design of a conventional circuit includes vertical electrodes and one horizontal jumper. All elements must be the same size and have a circular cross-section. They are usually made from thick reinforcement, pipes or steel rods.

The classic figure is a ground loop with a triangle configuration, consisting of 3 reinforcing rods, measuring 2 meters or more. The greater the distance between the bars, the more efficient the system will work. The minimum distance is 1.5 m.
After the electrodes are driven into the ground, they are connected to each other. A separate strip is installed on each side, fixed at the same height. These are copper or steel horizontal grounding conductors installed on the top of the pins.
The place to install the circuit in a private house is chosen where people very rarely enter. Preference is given to the north side, which is poorly lit and helps retain a large amount of moisture in the soil. The distance from the contour to the wall of the house must be at least 1 meter.

In another embodiment, the grounding has a deep-type design. It has virtually no disadvantages characteristic of the conventional method, since a modular-pin system is used. The entire assembly kit, made at the factory, is technically confirmed by a certificate. The main advantage of these systems is their compliance with standards; they have an increased service life - from 30 years and above.
The electric charge spreads steadily, regardless of weather conditions. The depth of the electrodes reaches 30 meters, ensuring the quality and reliability of grounding, and the entire assembled circuit does not require constant checks.
Tools and materials
To calculate the materials, the necessary measurements are taken, after which a detailed circuit diagram is drawn up with reference to a specific building.
Then you need to prepare the tools. You will definitely need a shovel, a sledgehammer, a set of wrenches, a hammer drill, an angle grinder with cutting wheels, a welding machine with electrodes, and measuring instruments for measuring current, voltage and resistance.

The list of materials consists of the following items:
- Steel corners for electrodes with shelves 50x50 or 60x60 mm, length from 2 meters and above. The technical requirements of the PUE allow the use of steel pipes instead as a grounding conductor, with a diameter of at least 32 mm. The average wall thickness is 3-4 mm or more.
- Materials for horizontal grounding conductors in the amount of 3 metal strips. The length corresponds to the size of the side of the triangle, thickness - 4-6 mm, width - from 4 to 6 cm.
- Stainless steel connecting strip connecting the ground loop to the building's porch. The cross-sectional dimensions are 40x4 or 50x5 mm.
- Copper current conductor, with a cross-section of at least 6-7 mm 2.
- Set of bolts M8, M10.
Technical characteristics of conductors are selected according to special tables. Their dimensions must be no less than those indicated; all deviations are allowed only in a larger direction.
Installation work
After the installation location of the grounding loop has been determined, a drawing has been drawn up, all calculations and preparatory work have been completed, you can begin the direct installation of structures and decide how to make a grounding loop under the given conditions.
First, you need to dig a trench with a depth of 70 to 100 cm. At the vertices of the triangle, using a sledgehammer, hammer in the corners that provide the initial resistance of the system. The average driving depth is 2-3 m. If the soil is too hard and the electrodes do not penetrate into it well, it is necessary to use a special drill, drill holes and insert ground electrodes into them.


Before installation, it is recommended to sharpen the ends of the metal electrodes so that they penetrate into the ground more easily. The pins do not need to be driven completely into the ground; approximately 30 cm should remain above its surface for fastening. Next, the horizontal and vertical parts are welded together, and the entire structure is connected to a metal strip, which, in turn, is connected to the grounding conductor.
This ground wire is then connected to a busbar installed in the distribution panel. The joints are treated with anti-corrosion compounds.
Checking the ground loop
After deciding how to make a ground loop, you should check the functionality of the resulting structure. The check begins with the connections. For this purpose, the welds are tapped with a hammer, and the bolted joints are checked with wrenches.
Qualified specialists are hired to draw up a report based on the results of the inspection. In the TT system this indicator should be low, and in the TN-C-S system, on the contrary, with a higher value.

If there are no opportunities for official verification, it can easily be done on your own. In this case, you should find out whether household appliances can operate normally at the maximum current for the installed circuit breaker. For this purpose, a special circuit is used when a portable socket is taken, from which one wire is connected to the phase, and the second to the ground loop.
After this, the specified load of power within 2 kW is connected to the outlet. If it works stably, and the voltage drop between the phase and grounding conductor does not exceed 10V, then the grounding is good and fulfills the requirements of the PUE and fulfills its functions in full. This operation requires caution and compliance with electrical safety measures, especially in areas where the protective circuit is directly located.
The main element of ensuring the safety of electrical installations is protective grounding. Related systems: automatic protective switches, fuses, lightning protection cannot function in its absence and become useless.
What is grounding
This is a complex consisting of metal structures and conductors, which ensures electrical contact of the electrical installation housing with the physical ground, that is, with the ground. The system begins with a ground electrode: a metal electrode grounded into the ground. These elements cannot be single; for reliability, they are combined into a grounding loop.
How it works
The external ground loop (which is located directly in the ground) is connected using a reliable conductor to the internal loop in the room, or to the grounding panel. Next, using an internal network of protective conductors, a connection is made to the housings of electrical installations and to the grounding contacts on switching devices (distribution boards, boxes, sockets, etc.).
Devices that generate electricity also have a grounding system to which the zero bus is connected. If an emergency occurs (a phase is connected to the electrical installation body), an electrical circuit arises between the phase conductor and the neutral bus along the ground line. The current strength in the emergency circuit spontaneously increases, the residual current device (circuit breaker) trips or the fuse insert burns out.
The result of a working system:
- the power cable does not ignite (fire hazard);
- The possibility of electric shock when touching the emergency housing of the electrical installation is prevented.
The resistance of the human body is tens of times higher than the grounding resistance. Therefore, the current strength (if there is a phase on the electrical installation body) will not reach a life-threatening value.

What does grounding consist of?
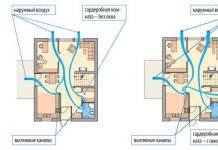
- External ground loop. It is located outside the premises, directly in the ground. It is a spatial structure of electrodes (grounding conductors) connected to each other by an inseparable conductor.
- Internal ground loop. A conductive bus located inside a building. Covers the perimeter of each room. All electrical installations are connected to this device. Instead of an internal circuit, a grounding shield can be installed.
- Grounding conductors. Connecting lines designed to connect electrical installations directly to the ground electrode, or internal ground loop.
Take a closer look at these components.
External or outer contour
The installation of the ground loop depends on external conditions. Before starting the calculation and completing the design drawing, you need to know the parameters of the soil in which the ground electrodes will be installed. If you have built a house yourself, these characteristics are known. Otherwise, it is better to call surveyors to obtain an opinion on the soil.
What types of soils are there, and how do they affect the quality of grounding? Approximate resistivity of each soil type. The lower it is, the better the conductivity.
- Plastic clay, peat = 20–30 Ωm m
- Plastic loam, ash soils, ash, classic garden soil = 30–40 Ohm m
- Chernozem, shales, semi-hard clay = 50–60 Ohm m
This is the best environment to install an external ground loop. The current flow resistance will be quite low even with low moisture content. And in these soils the natural humidity is usually above average.
- Semi-solid loam, mixture of clay and sand, wet sandy loam - 100–150 Ohm m
The resistance is slightly higher, but at normal humidity the grounding parameters will not exceed the standards. If there is prolonged dry weather in the installation region, it is necessary to take measures to forcibly moisten the installation sites of ground electrodes.
- Clay gravel, sandy loam, wet (constant) sand = 300–500 Ohm m
Gravel, rock, dry sand - even with high general humidity, grounding in such soil will be ineffective. To comply with standards, deep grounding will have to be installed.

Important! Incorrect calculation of the grounding loop, ignoring the parameters, often lead to disastrous results: electric shock, equipment failure, cable fire.
Many facility owners, saving on matches, simply do not understand why a grounding loop is needed. Its task, when connecting a phase to the ground, is to ensure the maximum value of the short circuit current. Only in this case will the protective shutdown devices operate quickly. This cannot be achieved if the current flow resistance is high.
Having decided on the soil, you can choose the type, and most importantly, the size of the ground electrodes. Preliminary calculation of parameters can be performed using the formula:

The calculation is given for vertically installed grounding conductors.
Decoding the formula values:
- R0 is the resistance of one ground electrode (electrode) obtained after calculation in ohms.
- Rekv - soil resistivity, see information above.
- L is the total length of each electrode in the circuit.
- d is the diameter of the electrode (if the cross-section is round).
- T is the calculated distance from the center of the electrode to the surface of the earth.
By setting known data, as well as changing the ratio of values, you should achieve a value for one electrode of the order of 30 Ohms.
If the installation of vertical grounding electrodes is not possible (due to the quality of the soil), the resistance value of horizontal grounding electrodes can be calculated.
Important! Installation of a horizontal contour is more labor-intensive and is associated with increased material consumption. In addition, such grounding is highly dependent on seasonal weather.
Therefore, it is better to spend more time driving vertical rods than to monitor the barometer and air humidity.

And yet we present the formula for calculating horizontal grounding conductors.

Accordingly, decoding of additional quantities:
- Rв - the resistance of one ground electrode (electrode) obtained after calculation in ohms.
- b - width of the electrode - grounding conductor.
- ψ - coefficient depending on the weather season. The data can be taken in the table:

- ɳG is the so-called demand coefficient for horizontally located electrodes. Without going into details, we get the numbers from the table in the illustration:


Preliminary calculation of resistance is necessary not only for proper planning of material purchases: although it will be a shame if you don’t have enough electrode to complete the work, and the store is several tens of kilometers away. A more or less neatly drawn up plan, calculations and drawings will be useful for resolving bureaucratic issues: when signing documents on acceptance of an object, or drawing up technical specifications with an energy sales company.
Of course, no engineer will sign papers only on the basis of even beautifully executed drawings. Spread resistance measurements will be taken.
Work technology
We select the location of the grounding conductors. Of course, not far from the house (facility), so that you do not have to lay a long conductor, which will have to be mechanically protected. It is advisable that the entire contour area be located on the territory that you control (you are the owner). So that one fine moment, your protective “ground” will not be dug up by a drunken excavator operator. So we won’t drive the fence pins.
A vegetable garden (with the exception of a potato bed), a front garden, or a flower bed near the house will do. Cultivated areas are preferable and are regularly watered. And additional moisture in the ground will benefit grounding. If your soil has low resistivity, you can install grounding on the site, which will then be covered with asphalt or tiles. Under artificial turf, the ground does not dry out. And the risk of damaging the ground loop is minimal.
Of course, future plans must be taken into account. If a garage with an inspection hole appears in the place where the circuit is installed in a year, it is better to immediately choose a quieter place.
Depending on the shape of the site, we choose the order of arrangement of the electrodes: in a line or in a triangle.
Important! Regardless of the location, there must be at least three vertical grounding conductors.
If a triangle is selected, we mark out a site of the appropriate shape with sides of 2.5–3 meters. We dig a trench in the shape of an equilateral triangle to a depth of 70–100 cm, a width of 50–70 cm. We know that all ground electrodes are connected to each other. The conductor must be deepened to a distance of at least 50 cm, taking into account the minimum ground level (for example, digging a bed). If a coating is laid on top, its thickness is not taken into account. Only clean soil.
You can select all the soil, not just around the perimeter of the trench. The result will be a triangular pit 0.7–1.0 m deep. The finished circuit can be filled with soil with low resistivity. For example, ash or ashes. The salts will penetrate into the ground and will help reduce the overall resistance to current flow.

After which, in the corners of the pit (trench) we begin to hammer in the electrodes.
Parameters of grounding conductors (considering a vertical arrangement)
- Steel without galvanic coating:
Circle - diameter 16 mm.
Pipe - diameter 32 mm.
Rectangle or corner - cross-sectional area 100 mm².
- Galvanized steel
Circle - diameter 12 mm.
Pipe - diameter 25 mm.
Rectangle or corner - cross-sectional area 75 mm².
Circle - diameter 12 mm.
Pipe - diameter 20 mm.
Rectangle or corner - cross-sectional area 50 mm².
The soil should tightly adhere to the metal surface of the ground electrode. It is prohibited to paint electrodes!
But what if, according to calculations, the length of each of the three electrodes exceeds 1.5–2 meters? There are little secrets.

We connect the electrodes with a conductor. If the reinforcement is steel, welding is best. The copper rods are connected with a bolt tie; the conductor must have a cross-section of at least 30% of the cross-section of the electrodes.
After assembling the circuit, we measure the current flow resistance. Requirements for the grounding loop for individual housing are 10 ohms. It is better to entrust the measurement to certified specialists who have the appropriate equipment. Moreover, when receiving specifications from power engineers, you will still have to provide a grounding system for measurements. If the resistance is higher than normal, we add electrodes and weld them to the circuit. Until we get the norm.

Ground loop inside the object
As a rule, this is a steel bus laid openly along the inner surface of the walls, near the floor.

In individual residential buildings, installation of an internal grounding loop is not carried out. Due to the low hazard class of the premises and the small number of electrical installations. Instead of the internal circuit, a grounding shield, or main grounding bus (GGB), is installed.

The shield is connected either to the internal circuit (as in the illustration) or using a conductor to the external ground circuit. Directly from the panel, protective grounding conductors are routed through electrical installations. Often, instead of a grounding shield, a “PE” contact block can be used, directly in the entrance panel of the apartment.

Bottom line
We examined in detail what a ground loop is, why it is needed, and what it should be according to the PUE. Self-installation does not reduce your responsibility: your life and the lives of your household depend on compliance with safety requirements.
Video on the topic