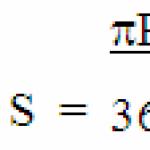Definition. Side edge- this is a triangle in which one angle lies at the top of the pyramid, and the opposite side coincides with the side of the base (polygon).
Definition. Side ribs- these are the common sides of the side faces. A pyramid has as many edges as the angles of a polygon.
Definition. Pyramid height- this is a perpendicular lowered from the top to the base of the pyramid.
Definition. Apothem- this is a perpendicular to the side face of the pyramid, lowered from the top of the pyramid to the side of the base.
Definition. Diagonal section- this is a section of a pyramid by a plane passing through the top of the pyramid and the diagonal of the base.
Definition. Correct pyramid is a pyramid in which the base is a regular polygon, and the height descends to the center of the base.
Volume and surface area of the pyramid
Formula. Volume of the pyramid through base area and height:
Properties of the pyramid
If all the side edges are equal, then a circle can be drawn around the base of the pyramid, and the center of the base coincides with the center of the circle. Also, a perpendicular dropped from the top passes through the center of the base (circle).
If all the side edges are equal, then they are inclined to the plane of the base at the same angles.
The lateral edges are equal when they form equal angles with the plane of the base or if a circle can be described around the base of the pyramid.
If the side faces are inclined to the plane of the base at the same angle, then a circle can be inscribed into the base of the pyramid, and the top of the pyramid is projected at its center.
If the side faces are inclined to the plane of the base at the same angle, then the apothems of the side faces are equal.
Properties of a regular pyramid
1. The top of the pyramid is equidistant from all corners of the base.
2. All side edges are equal.
3. All side ribs are inclined at equal angles to the base.
4. The apothems of all lateral faces are equal.
5. The areas of all side faces are equal.
6. All faces have the same dihedral (flat) angles.
7. A sphere can be described around the pyramid. The center of the circumscribed sphere will be the intersection point of the perpendiculars that pass through the middle of the edges.
8. You can fit a sphere into a pyramid. The center of the inscribed sphere will be the point of intersection of the bisectors emanating from the angle between the edge and the base.
9. If the center of the inscribed sphere coincides with the center of the circumscribed sphere, then the sum of the plane angles at the vertex is equal to π or vice versa, one angle is equal to π/n, where n is the number of angles at the base of the pyramid.
The connection between the pyramid and the sphere

A sphere can be described around a pyramid when at the base of the pyramid there is a polyhedron around which a circle can be described (a necessary and sufficient condition). The center of the sphere will be the intersection point of planes passing perpendicularly through the midpoints of the side edges of the pyramid.
It is always possible to describe a sphere around any triangular or regular pyramid.

A sphere can be inscribed in a pyramid if the bisector planes of the internal dihedral angles of the pyramid intersect at one point (a necessary and sufficient condition). This point will be the center of the sphere.
Connection of a pyramid with a cone
A cone is said to be inscribed in a pyramid if their vertices coincide and the base of the cone is inscribed in the base of the pyramid.
A cone can be inscribed in a pyramid if the apothems of the pyramid are equal to each other.
A cone is said to be circumscribed around a pyramid if their vertices coincide and the base of the cone is circumscribed around the base of the pyramid.
A cone can be described around a pyramid if all the lateral edges of the pyramid are equal to each other.
Relationship between a pyramid and a cylinder
A pyramid is called inscribed in a cylinder if the top of the pyramid lies on one base of the cylinder, and the base of the pyramid is inscribed in another base of the cylinder.
A cylinder can be described around a pyramid if a circle can be described around the base of the pyramid.


A tetrahedron has four faces and four vertices and six edges, where any two edges do not have common vertices but do not touch.
Each vertex consists of three faces and edges that form triangular angle.
The segment connecting the vertex of a tetrahedron with the center of the opposite face is called median of the tetrahedron(GM).
Bimedian called a segment connecting the midpoints of opposite edges that do not touch (KL).
All bimedians and medians of a tetrahedron intersect at one point (S). In this case, the bimedians are divided in half, and the medians are divided in a ratio of 3:1 starting from the top.


Definition. Acute angled pyramid- a pyramid in which the apothem is more than half the length of the side of the base.
Definition. Obtuse pyramid- a pyramid in which the apothem is less than half the length of the side of the base.
Definition. Regular tetrahedron- a tetrahedron in which all four faces are equilateral triangles. It is one of the five regular polygons. In a regular tetrahedron, all dihedral angles (between faces) and trihedral angles (at the vertex) are equal.
Definition. Rectangular tetrahedron is called a tetrahedron in which there is a right angle between three edges at the apex (the edges are perpendicular). Three faces form rectangular triangular angle and the faces are right triangles, and the base is an arbitrary triangle. The apothem of any face is equal to half the side of the base on which the apothem falls.
Definition. Isohedral tetrahedron is called a tetrahedron whose side faces are equal to each other, and the base is a regular triangle. Such a tetrahedron has faces that are isosceles triangles.
Definition. Orthocentric tetrahedron is called a tetrahedron in which all the heights (perpendiculars) that are lowered from the top to the opposite face intersect at one point.
Definition. Star pyramid called a polyhedron whose base is a star.

Pyramid is a multifaceted figure, the base of which is a polygon, and the remaining faces are represented by triangles with a common vertex.
If the base is a square, then the pyramid is called quadrangular, if a triangle – then triangular. The height of the pyramid is drawn from its top perpendicular to the base. Also used to calculate area apothem– the height of the side face, lowered from its top.
The formula for the area of the lateral surface of a pyramid is the sum of the areas of its lateral faces, which are equal to each other. However, this method of calculation is used very rarely. Basically, the area of the pyramid is calculated through the perimeter of the base and the apothem:

Let's consider an example of calculating the area of the lateral surface of a pyramid.
Let a pyramid be given with a base ABCDE and apex F. AB=BC=CD=DE=EA=3 cm. Apothem a = 5 cm. Find the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid.
Let's find the perimeter. Since all the edges of the base are equal, the perimeter of the pentagon will be equal to:
Now you can find the lateral area of the pyramid: ![]()
Area of a regular triangular pyramid

A regular triangular pyramid consists of a base in which lies a regular triangle and three side faces that are equal in area.
The formula for the lateral surface area of a regular triangular pyramid can be calculated in different ways. You can apply the usual calculation formula using the perimeter and apothem, or you can find the area of one face and multiply it by three. Since the face of a pyramid is a triangle, we apply the formula for the area of a triangle. It will require an apothem and the length of the base. Let's consider an example of calculating the lateral surface area of a regular triangular pyramid.
Given a pyramid with apothem a = 4 cm and base face b = 2 cm. Find the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid.
First, find the area of one of the side faces. In this case it will be:
Substitute the values into the formula: ![]()
Since in a regular pyramid all the sides are the same, the area of the side surface of the pyramid will be equal to the sum of the areas of the three faces. Respectively: ![]()
Area of a truncated pyramid

Truncated A pyramid is a polyhedron that is formed by a pyramid and its cross section parallel to the base.
The formula for the lateral surface area of a truncated pyramid is very simple. The area is equal to the product of half the sum of the perimeters of the bases and the apothem: ![]()
Let's consider an example of calculating the lateral surface area of a truncated pyramid.
Given a regular quadrangular pyramid. The lengths of the base are b = 5 cm, c = 3 cm. Apothem a = 4 cm. Find the area of the lateral surface of the figure.
First, let's find the perimeter of the bases. On a larger basis it will be equal to: ![]()
In a smaller base: ![]()
Let's calculate the area:
Triangular pyramid is a polyhedron whose base is a regular triangle.
In such a pyramid, the edges of the base and the edges of the sides are equal to each other. Accordingly, the area of the side faces is found from the sum of the areas of three identical triangles. You can find the lateral surface area of a regular pyramid using the formula. And you can make the calculation several times faster. To do this, you need to apply the formula for the area of the lateral surface of a triangular pyramid:
![]()
where p is the perimeter of the base, all sides of which are equal to b, a is the apothem lowered from the top to this base. Let's consider an example of calculating the area of a triangular pyramid.
Problem: Let a regular pyramid be given. The side of the triangle at the base is b = 4 cm. The apothem of the pyramid is a = 7 cm. Find the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid.
Since, according to the conditions of the problem, we know the lengths of all the necessary elements, we will find the perimeter. We remember that in a regular triangle all sides are equal, and, therefore, the perimeter is calculated by the formula:
Let's substitute the data and find the value:
Now, knowing the perimeter, we can calculate the lateral surface area: ![]()
To apply the formula for the area of a triangular pyramid to calculate the full value, you need to find the area of the base of the polyhedron. To do this, use the formula: 
The formula for the area of the base of a triangular pyramid may be different. It is possible to use any calculation of parameters for a given figure, but most often this is not required. Let's consider an example of calculating the area of the base of a triangular pyramid.
Problem: In a regular pyramid, the side of the triangle at the base is a = 6 cm. Calculate the area of the base.
To calculate, we only need the length of the side of the regular triangle located at the base of the pyramid. Let's substitute the data into the formula: 
Quite often you need to find the total area of a polyhedron. To do this, you will need to add up the area of the side surface and the base. ![]()
Let's consider an example of calculating the area of a triangular pyramid.
Problem: Let a regular triangular pyramid be given. The base side is b = 4 cm, the apothem is a = 6 cm. Find the total area of the pyramid.
First, let's find the area of the lateral surface using the already known formula. Let's calculate the perimeter:
Substitute the data into the formula: ![]()
Now let's find the area of the base: 
Knowing the area of the base and lateral surface, we find the total area of the pyramid: ![]()
When calculating the area of a regular pyramid, you should not forget that the base is a regular triangle and many elements of this polyhedron are equal to each other.
Surface area of the pyramid. In this article we will look at problems with regular pyramids. Let me remind you that a regular pyramid is a pyramid whose base is a regular polygon, the top of the pyramid is projected into the center of this polygon.
The side face of such a pyramid is an isosceles triangle.The altitude of this triangle drawn from the vertex of a regular pyramid is called apothem, SF - apothem:

In the type of problem presented below, you need to find the surface area of the entire pyramid or the area of its lateral surface. The blog has already discussed several problems with regular pyramids, where the question was about finding the elements (height, base edge, side edge).
Unified State Examination tasks usually examine regular triangular, quadrangular and hexagonal pyramids. I haven’t seen any problems with regular pentagonal and heptagonal pyramids.
The formula for the area of the entire surface is simple - you need to find the sum of the area of the base of the pyramid and the area of its lateral surface:
![]()
Let's consider the tasks:
The sides of the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid are 72, the side edges are 164. Find the surface area of this pyramid.

The surface area of the pyramid is equal to the sum of the areas of the lateral surface and the base:
*The lateral surface consists of four triangles of equal area. The base of the pyramid is a square.
We can calculate the area of the side of the pyramid using:

Thus, the surface area of the pyramid is:
Answer: 28224
The sides of the base of a regular hexagonal pyramid are equal to 22, the side edges are equal to 61. Find the lateral surface area of this pyramid.

The base of a regular hexagonal pyramid is a regular hexagon.
The lateral surface area of this pyramid consists of six areas of equal triangles with sides 61,61 and 22:
Let's find the area of the triangle using Heron's formula:

Thus, the lateral surface area is:
![]()
Answer: 3240
*In the problems presented above, the area of the side face could be found using another triangle formula, but for this you need to calculate the apothem.
27155. Find the surface area of a regular quadrangular pyramid whose base sides are 6 and whose height is 4.

In order to find the surface area of the pyramid, we need to know the area of the base and the area of the lateral surface:
The area of the base is 36 since it is a square with side 6.
The lateral surface consists of four faces, which are equal triangles. In order to find the area of such a triangle, you need to know its base and height (apothem):
*The area of a triangle is equal to half the product of the base and the height drawn to this base.
The base is known, it is equal to six. Let's find the height. Consider a right triangle (highlighted in yellow):

One leg is equal to 4, since this is the height of the pyramid, the other is equal to 3, since it is equal to half the edge of the base. We can find the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem:
![]()
This means that the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid is:

Thus, the surface area of the entire pyramid is:
Answer: 96
27069. The sides of the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid are equal to 10, the side edges are equal to 13. Find the surface area of this pyramid.
27070. The sides of the base of a regular hexagonal pyramid are equal to 10, the side edges are equal to 13. Find the lateral surface area of this pyramid.
There are also formulas for the lateral surface area of a regular pyramid. In a regular pyramid, the base is an orthogonal projection of the lateral surface, therefore:
P- base perimeter, l- apothem of the pyramid
*This formula is based on the formula for the area of a triangle.
If you want to learn more about how these formulas are derived, don’t miss it, follow the publication of articles.That's all. Good luck to you!
Sincerely, Alexander Krutitskikh.
P.S: I would be grateful if you tell me about the site on social networks.