1. Before the onset of cold weather, it is necessary to conduct a thorough inspection of the garden: cut down damaged branches, remove moss and lichens from the trunk.
2. If you find a hollow in a tree, then you need to clean it, and also do not forget about disinfection.
3. It should be remembered that many insects and pests can settle in the bark of trees for the winter, so even before the onset of cold weather, the trunks should be thoroughly treated with slaked lime or simply painted.
4. Take care of the birds: build feeders and hang them on trees or in other suitable places. This way you can accustom birds to your garden and save them from hunger.
5. To protect trees from rodents, you should tie the bases with matting or special burlap. Young seedlings need to be covered with a plastic mesh and sprinkled with earth on top.
Garden work in winter
1. The garden must be periodically cleaned in winter, and fallen snow must be removed.
2. Heavy snowfall can damage the branches of trees and shrubs in the garden, so gardeners recommend shaking off the snow. This should be done with extreme care, since the branches of trees and shrubs are very delicate.
3. With the onset of the first cold weather, roses, hibiscus, hydrangeas and other shrubs must be carefully wrapped with agrofibre.
4. If you find a tree with a broken branch in your garden plot, this place should be treated with garden varnish.
5. Lack of snow can damage trees and shrubs, so you should rake the snow to the base of the trees in a small mound.
6. In winter, don’t forget about lawn care. The most important rule is to reduce the load, i.e. It is better not to walk on the lawn. Otherwise, with the onset of spring, you will find bald spots on it.
In the fall, after harvesting, many novice gardeners limit themselves to cleaning the area, collecting and burning old leaves. And it’s completely in vain, you shouldn’t relax. There are few nice sunny days left, and you need to make the most of them. A long winter is ahead - the most difficult time for many plants, and the gardener’s task is to prepare them as best as possible for this harsh period.
Caring for a garden in the fall is a whole complex of activities, during which the foundations of the harvest for the next year are laid, and in this short time before the onset of cold weather, a lot needs to be done.
What can you plant in the fall?
Autumn is a time not only to harvest, but also to sow. During this period, some vegetables and herbs are planted, for example:
- winter onion;
- garlic;
- celery;
- basil;
- parsley;
- mustard.
Overwintered crops enter the active growth phase much earlier and produce higher yields. In autumn, it is also necessary to plant fruit trees and fruit bushes. Before winter, seedlings are planted:
- apple trees;
- pears;
- plums;
- cherries;
- currants;
- gooseberries;
- raspberries and many others.
The best time for planting new seedlings and replanting young trees and bushes is immediately after the end of leaf fall. The plant has gained strength and prepared for winter; right now it has the greatest immunity and can most easily withstand the stress of moving. There is no point in delaying it, since a crop that does not have time to take root well before frost will most likely die.
If for some reason the deadlines for autumn planting are missed, it is better not to take risks, but to limit ourselves to preparing for spring planting - choosing places and digging holes. In the spring, this will reduce the time for seedlings to adapt to new conditions and increase their survival rate.
Why is pruning and cleaning necessary?
A fine autumn day is an excellent reason to do some spring cleaning in the garden. You can start by pruning fruit trees and shrubs. At this time, sanitary treatment is carried out, broken, dry and damaged branches are removed.

All cuts must be treated with garden varnish.
For additional protection, the trunks and lower branches can be wrapped in artificial material, for example, roofing felt, and the crops can also be fenced with a chain-link mesh. Along with fruit trees, shrubs are also pruned. All two-year-old shoots of raspberries are pruned; sanitary pruning is done on currants, gooseberries, and honeysuckles, removing dry and broken branches, and root shoots are also removed. The tree trunk circles need to be dug up. If autumn is not rainy, then it is worth watering once and mulching the soil around the plants with peat or humus.

You should not save fallen leaves of trees, since this is a real breeding ground for pests and their larvae, deposited for the winter in the tree trunks. It is better to burn the fallen leaves and treat the ground around the trunk with a solution of copper sulfate.
It is not necessary to burn cut dry branches; you can chop them up and use them as a heat-insulating layer when creating “warm” beds.
How to care for greenhouses in the off-season?
After harvesting crops growing under cover, it’s time to restore order in the greenhouses themselves. From them it is necessary to remove all remnants of vegetation along with the roots: cucumber vines, tomato shoots, weeds. If the plants were not sick in the summer, all this can be taken to the compost pit, otherwise burning is necessary.
The next stage will be soil reclamation. Increased plant growth greatly depletes the soil. In addition, under conditions of high humidity and temperature, not only the crops themselves, but also fungi develop rapidly. To prevent disease and replenish the supply of nutrients, the top layer 10-15 cm thick must be completely replaced.
If no cases of disease have been noted, reclamation can be carried out partially by digging a furrow in the middle of the beds, laying peat in it and covering it with earth. After this, the soil should be thoroughly watered with a urea solution at the rate of 50 grams per 10 liters of water. Once every five years, it is recommended to completely change the soil or move the greenhouse to another location.
The greenhouse can be disinfected by fumigating with a sulfur bomb or spraying with special solutions. The first option is suitable for tall structures with a wooden frame. Metal greenhouses rust badly under the influence of sulfur, so it is better to treat such greenhouses with copper sulfate (75 grams per 10 liters of water), 4% lime solution or 2% creolin.
If polyethylene was used as a covering material, it must be removed, washed with detergent, dried and stored until next year. Polycarbonate and glass greenhouses are not disassembled, but only opened wide. In winter, they must be covered with snow and the soil must be covered. It is better to strengthen the metal frame with supports made of wooden beams; this will protect it from possible deformation under the weight of the snow cover.

To destroy cocoons of codling moths, all trees need to be sprayed with a 5% solution of carbamide (urea); the drug Fury is suitable for leaf rollers and silkworms. To prevent fungal diseases, plantings are treated with solutions containing copper (copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture). To protect against scab, use Strobi or Impact.
Feeding before wintering
After the fruiting season, the plants are severely exhausted, but they should go into hibernation with a full supply of energy. Autumn feeding will help trees and shrubs gain strength for a good winter. Nutrients (mainly humus) are introduced into the soil by the root method. This is usually done while digging tree trunk circles. The recommended application rate for each fruit tree no older than 8 years is 30 kg, 50 kg for older ones.
For pears and apple trees, you can apply bait in liquid form, along with watering the near-root zone. For this you need 300 gr. superphosphate and 200 gr. potassium sulfate, which are diluted in 40 liters of water. For cherries and plums, the fertilizer rate can be reduced by 2-2.5 times.

When applying fertilizing, you need to take into account the nature of the soil. Heavy clay soils retain nutrients well, while in light sandy soils they are quickly washed out. In this case, the norms may be increased.
Nitrogen fertilizers stimulate shoot growth, so they should not be used in the fall.
Berry bushes also need autumn feeding. You can use both organic matter and complex mineral fertilizers for this. A tablespoon of double superphosphate and potassium sulfate is added to each berry bush. The use of potassium sulfate (15-20 grams per square meter) has worked well. After application, you can water. From organic matter, it is most advisable to use rotted manure.
How to take care of perennial flowers?
Hardly any garden is complete without a flower bed. But there is also a lot of work there in the fall. Overwintering perennials need to be prepared for the coming cold, while non-wintering ones need to be dug up, processed and stored.

Non-frost-resistant tuberous and bulbous flowers are dug up at the first frost, and it is better to store gladioli before the first drop in temperature below zero degrees occurs. Dahlias can be pulled out of the ground a little later. The dug up rhizomes should be treated with fungicides or a solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection, dried and placed in a dry place.
Some wintering perennial flowers are pruned in the fall. For example, peonies, asters and tradescantia are cut almost to the root. Clematis are cut to a height of 20 cm, and only bloom on this year's shoots. Ferns, violets, chrysanthemums and lilies of the valley are not touched at all. Before winter, the flower garden needs to be cleared of weeds, faded shoots and debris.
What about shelter for the winter?
Plants with insufficient winter hardiness must be covered, otherwise they may die in severe frost. They hide the grapevine from the cold; it is worth taking special care of. The lashes are removed from the trellises and placed in a specially dug ditch, which is then covered with boards, covered with roofing felt, film or other materials and filled with earth.

Some varieties of raspberries that are not frost-resistant also need to be covered for the winter. When planting bushes in a row, they are sequentially bent towards each other, and then the entire ribbon is covered with straw. Single bushes are simply tilted to the ground or tied into a single whole.
Severe frosts can lead to freezing of young seedlings, and mice and hares will happily gnaw the bark on trees and bushes. Let's figure out what can be done to prevent these troubles.
Protecting the garden from frost
To better understand the freezing process, it is necessary to understand what cambium is. Cambium- this is a transparent slippery layer that can be seen between the wood and the bark of any tree. Cambium is a so-called building material that plays an important role in the development of a young seedling. The health of the tree and its ability to produce good harvests depend on its structure and quality. That is why it is so important to protect the cambium from various types of damage and, above all, from frost. When severe cold unexpectedly sets in, unprepared trees can develop frost breakers, that is, damage to the cambium in certain places.
Frost damage most often occurs on trunks (trunks), since the winter hardiness of this part of the tree is always much lower than that of the crown. Damage to the cambium can also occur on branch forks, especially if they are located at an acute angle.
Frostbite is not easy to notice; the bark can remain in the damaged area for two to three years. This is dangerous because next winter, even with less cold, the frost damage can greatly increase. Therefore, in the spring after severe frosts, it is necessary to carefully examine the bark in order to be able to take timely measures, since increasing frost holes will sooner or later lead to the death of the tree.
To protect the trunk from freezing, it can be completely covered with snow, which is a natural insulator and will prevent even extreme cold from damaging the cambium.
However, winters are not always snowy. In this case, tree trunks must be wrapped in various breathable materials. For these purposes, you can use newspapers, thick cotton fabric, burlap, and the like. Under no circumstances should you wrap the trunks with polyethylene, as the tree will simply freeze under it. Experienced gardeners recommend tying young seedlings with coniferous spruce branches on top of newspapers, which are tied with the needles down. Such protection will protect the plant not only from the winter cold, but also from unexpected guests - mice and hares.
Not only the trunks, but also the root system of fruit trees need to be protected from severe frosts. This is especially true in late autumn or snowless winter, when severe cold can occur in the absence of thick snow cover.
Mulching the tree trunk circle with various materials - sawdust, fallen leaves, well-ripened compost, peat chips - helps to effectively protect the roots. The mulch layer should be at least 6–8 centimeters, and it should be laid on slightly loosened soil. You can insulate the root system by simply covering the trees well with soil.
When preparing the garden for winter, you should remember that it is necessary to begin work on insulating the trunks after the onset of slight but stable frosts. If such work is carried out early (in September-October), then a greenhouse effect can be created under the insulation, the trunk begins to warm up and peel off, the surface layer of bark is damaged, which significantly reduces the frost resistance of the tree.
It is necessary to insulate not only trees, but also shrubs for the winter. Small bushes and young seedlings of fruit trees can be completely covered with breathable material or tied with coniferous spruce branches, as mentioned above. It is recommended to mulch the soil under the plants, or hill up the bushes higher. If autumn is dry, the soil needs to be watered. Damp soil freezes much more slowly than soil dried by cold winds.
Protecting your garden from rodents
In winter, fruit trees and shrubs can be damaged not only by severe frosts, but also by rodents - mice and hares, which make their way closer to human habitation in search of food. The damage caused by these animals often leads to death, especially for young plants. Hares eat large branches and completely gnaw through thin branches; mice can gnaw off sections of bark in a ring around the entire branch. Such circular lesions are especially dangerous, as they lead to disruption of sap flow, the tree does not receive the necessary nutrients and dies very quickly. Experienced gardeners know many ways to protect themselves from these “intruders.” Let's take a closer look at the most effective of them.
How to protect your garden from mice
Today there are two main ways to protect the garden from rodents - mechanical And chemical. The essence of the mechanical method is that the trunks and branches are tied with various materials. It is best to use coniferous spruce branches and special rodent protection nets for these purposes, which can be purchased in specialized stores.
Some people use roofing felt or roofing felt for tying, laying the canvas tightly and burying it slightly into the ground. It should be noted that it is recommended to remove this material during thaws, since at elevated temperatures during the day condensation can form under it, which negatively affects the condition of the trunk bark.

A fairly effective way to protect trees and shrubs from mice is to compact the snow cover around them. In winter, mice move under a layer of loose snow, and if it is trampled down, they have significant difficulties.
A good result when fighting mice is obtained by treating trees and the space around them with various chemical compounds that repel animals. For this, you can use a mixture of clay and cow dung. Clay and manure are taken in equal parts and diluted with water until the consistency of thick sour cream is obtained. You need to add one tablespoon of carbolic acid to a bucket of the mixture, then mix everything thoroughly. The resulting solution is lubricated on the trunks and skeletal branches of trees.
The following recipe will help protect the garden from rodents: 4 kg of clay, 4 kg of fresh mullein, 100 g of creolin, 90 g of karbofos (concentrate). All this is mixed well and diluted with water until it becomes sour cream, then the trunks and large branches of plants are coated.

If there are a lot of mice on the site, then you can destroy them using poisoned baits, which are prepared from bread or grain, soaking them in poisons. However, this method is extremely dangerous for domestic animals, so it is recommended to place the prepared baits in roofing felt tubes, and only then lay them out in the garden. To prevent the death of domestic animals and birds, it is best to use various traps, traps, and mousetraps to kill mice.
How to protect your garden from hares
Hares are timid, charming creatures that act as positive heroes in many folk tales. However, despite this image, these animals can cause irreparable damage to your garden by eating everything that does not grow well. These animals are especially dangerous in winter, when there is not enough food for them in their usual habitats.
You can protect fruit trees from hares by tying the trunks and branches with spruce branches or netting. A good defense against these “intruders” can be a reliable high fence made of solid material, which will make it much more difficult for them to enter your garden plot. Such fences must be buried at least 30 centimeters into the soil; the height of the fence must be at least 1.2 meters so that the animal cannot undermine it or jump over it.

Hares cannot stand the smell of wormwood stems, so they can be used to line the trunks of trees and shrubs. These animals do not like the smell of blood and rancid lard, pieces of which just need to be rubbed along the trunk and large branches. To protect against hares, you can coat shrubs and trees with a mixture of fish oil and naphthalene in a ratio of 8:1. To repel rodents, there is a special product “Carnofer”, the solution of which is sprayed on the garden in the winter.
You can scare away hares by scattering ash, sawdust or peat chips soaked in kerosene under the trees at the rate of 1 liter per bucket of water. Some gardeners use to fight hares by spraying the garden with a solution of the following recipe: 10 liters of water, 300 g of naphthalene, 2 liters of vegetable oil or diesel fuel, 100 g of copper sulfate, 400 g of turpentine and 350 grams of washing powder. All these ingredients are thoroughly mixed and used for spraying trees and bushes in winter.
As you know, hares are extremely cautious animals; any small movement can frighten them. Therefore, rustling garlands or black paper circles hung on branches are an effective way to scare away animals. Pieces of dog hair and dog droppings are a great way to repel hares.
To prevent hares from visiting your property, you can simply get a cat. Maine Coon cats cope well with this role. These very large pets have a powerful hunting instinct. They will not only drive away the hares, but also destroy the entire population of mice and rats on your and your neighbors’ territories.
How to save damaged trees
If trouble does happen and the trees are damaged by frost or rodent attacks, you need to be able to provide them with the necessary help.
In order to determine the degree of freezing of the trunk, it is necessary in the spring with a well-sharpened knife to cut the bark and outer wood at the bottom, in the middle and at the top of the trunk, and also, if necessary, at the base of the skeletal branches. A healthy tree will have a light green color to its wood. If the wood is dark brown (pear is black), then the plant has suffered significant frost damage. Such a tree is not pruned and its growth is carefully monitored. If in the spring or during the summer it does not produce shoots, or blooms weakly, then the tree will have to be uprooted.
If the wood of the tree being examined is light brown, it means that it is not very frozen. Such trees are pruned not before the buds open, but at the moment of shoot growth, when the frozen parts of the plant are already clearly visible.

Pruning of frozen trees must be done correctly - the wounds should not be more than 5 cm in diameter. Large cuts are much worse overgrown; such trees often develop cytosporosis and cancer, which leads to the death of the plant.
Another important feature of pruning frozen trees is that all cuts with a diameter of more than 1 cm must be thoroughly coated with garden varnish, but in no case with paint. Garden varnish can be bought in the store, or you can prepare it at home. To do this you will need 50 grams of pine resin, 200 grams of wax and 250 grams of grease. All these components must be heated separately until completely dissolved, then mixed thoroughly and poured into a glass container. If the broth turns out to be too thick, you can dilute it with sunflower oil, and if it is too liquid, thicken it with well-sifted ash. After pruning, garden varnish is applied to the wound and rubbed over the surface. Healing after such treatment usually occurs quickly and the tree recovers.

Frozen wood impedes the flow of water and nutrients from the roots to the trunk and crown. Therefore, all damaged trees must be well watered, especially in May-June, when the growing season takes place.
An effective agronomic technique for maintaining frozen trees is to mulch the tree trunk with mature compost or rotted cow manure. This activates the vital activity of beneficial microorganisms and earthworms, which improves the structure and fertility of the soil. This mulch also perfectly retains moisture. Such improved conditions contribute to the rapid recovery of frost-damaged trees.
Experienced gardeners do not recommend feeding frozen plants with mineral fertilizers, since a sharp increase in the concentration of the soil solution greatly impedes the flow of moisture from the root system to the leaves, and the process of tree restoration slows down.
If the garden has suffered from a rodent invasion, a decoction made from linden bark will help speed up the healing of wounds. To do this in the spring, you need to grind linden bark (half a bucket) and fill it to the top with cold water, boil for 30–40 minutes. The resulting broth should be cooled and strained, then the resulting jelly-like mass should be lubricated on all wounds on trees and shrubs damaged by rodents. It is best to wrap the damage on top with thick paper and tie it tightly. The bandage is not removed for one to two months, until the wounds on the tree heal.

Some gardeners use so-called plastic bandages to heal damage, that is, they tie the gnawed areas with plastic film. The main advantage of this method is that the film transmits sunlight and heat well, thereby creating favorable conditions for the rapid restoration of damaged trees.
Methods to protect your garden from frost and rodents are quite simple and accessible to everyone. You just need to devote a little time and attention to ensure that your trees and shrubs remain unharmed and pay for your care with a generous harvest for many years.
The frost is crackling outside the window. The ground is covered with snow. It seems that trees and shrubs do not need care. But this is not true at all. At any time of the year, plants require attention. Caring for a garden involves many very important tasks. Their implementation affects the future harvest and the full development of garden crops. But before this, the plants must overwinter. At this time there are many moments that should not be missed.
Protecting plants from freezing
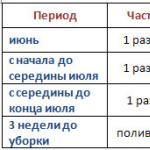
In early December, attention is paid to young trees and shrubs.
In order for them to overwinter well, you should ensure that the plants are insulated. Snow can be used as insulation, which is distributed under trees, around bushes and compacted. It will provide protection from frost and rodents. Hilling of plants with snow continues throughout the winter.
Rodents are pests of dormant plants
Garden care in winter and spring involves various activities. And each of them has its own deadlines. In winter, attention is paid to protecting trees from rodents. Mice and hares can damage tree bark. Annual and biennial crops are especially affected. The tree trunk is protected in the autumn. It is wrapped in various materials. At the end of winter, drugs are used that will repel rodents. They are placed around trees.
Garden care in spring: spring work
With the onset of March, a busy time for gardeners begins. This is a crucial period. With the beginning of the snow melting and the first streams of water, work on personal or summer cottage plots intensifies. How to properly organize garden care in spring? What to do in the first days of March? During this period, the snow becomes loose. It gradually melts, and there is no need to speed up this process. The exception is snowdrifts that completely cover the bushes. To prevent the snow from damaging the branches when it melts, it is raked, freeing the plants.
Tree pruning
The main condition for this event is the air temperature. You should not carry out work if it is frosty outside. In the case when the thermometer recorded readings below minus ten degrees Celsius, trees should not be pruned. Peculiarities of climatic zones make their own adjustments to garden care in the spring.

Proper pruning is carried out before the buds swell. It is performed on sunny days at zero air temperature.
The first to be pruned are fruit-bearing trees, whose flower buds precede the awakening of leaf ones. This event involves the removal of:
Damaged, frozen shoots;
Branches growing inside the crown;
Branches that interfere with crown development.
At the same time, they adhere to the rule, which provides for the maximum pruning of large branches. In this case, no stumps are left. When removing branches with a diameter of more than fifteen centimeters, garden varnish is used. It is used to treat the cut site. After all the trees have been cultivated, it is the turn of the young plants that do not bear fruit. For such trees, this technique involves, first of all, the formation of a crown. The annual gradual removal of branches that are undesirable for proper growth allows you to grow a productive healthy tree within several years, which will reward you with a high harvest.

Caring for a garden in early spring involves pruning not only trees, but also shrubs. Old shoots of currant berry bushes, as well as raspberries and gooseberries must be removed. Frozen, damaged branches are cut off at the base. Fruiting shoots are shortened by ten or fifteen centimeters.
Tree grafting
Caring for a garden in early spring involves a lot of work. One of the important measures is the grafting of fruit crops, which is performed before the buds swell.

There are several such methods. Among them, grafting with cuttings into a split or behind the bark is popular and often used. They are harvested at the beginning of winter, before the onset of severe frosts. Shoots of annual growths are suitable for grafting. The cuttings used for this activity have three or four buds. As a rule, stone fruits will come first, followed by pome crops. For young trees, the grafting zone is no more than two meters above the soil surface, and for shoots - one and a half meters from the trunk. Branch cutting diameter:
For stone fruit crops - 3 cm;
For pome crops - 5-6 cm.
All operations are performed on the day of vaccination. The junction of the cutting with the tree branch is wrapped with insulating tape, which can be removed three or four weeks after the operation or left until next spring.
Planting trees and shrubs
Caring for a garden in early spring is not only about activities that ensure excellent growth of planted plants. At this time, young trees and shrubs can be planted. This event is carried out before the buds open. In the spring, crops that have insufficient winter-hardy qualities are planted. After planting, ensure constant soil moisture.
Preventive actions
One of the important agricultural practices is pest and disease control. Caring for your garden in early spring is the best time of year for this. Chemical treatment of plants will require gardeners to have practical skills and knowledge. Without plant protection, it is impossible to grow a healthy and full-fledged crop.
Spraying fruit and berry crops can be divided into three stages:
Before the buds begin to swell;
Before flowering;
A week after flowering.
The garden is treated with special preparations. When working with them, you should strictly follow the instructions.

In addition, caring for the garden in early spring includes another very important event - whitewashing tree trunks with a solution of slaked lime.
After the snow melts and stable warm weather sets in, fallen leaves are removed and burned.
It’s getting cooler outside, and autumn is about to give way to winter, but you must admit, it’s so nice to keep a “piece of summer” at home. An excellent solution for such purposes would be a home winter garden. By definition, a winter garden is an architectural element with a glass roof, artistically decorated with ornamental plants planted in the ground or displayed in pots.
Providing competent care for this oasis of summer is not an easy task, especially when it comes to caring for a winter garden in an apartment, but by using our advice, you can make your life much easier.
The most popular and necessary type of garden care is, of course, daily winter garden care. It includes the usual light garden cleaning: dusting, removing wilted or dead leaves on plants, sweeping the floor, necessary cleaning of window sills and other surfaces. So, let's look at the basic care tips. 
During such daily garden care, plants are also watered with the necessary regularity. It should be remembered that the need for water is proportional to the intensity of plant growth, and the main task facing households is not to dry out or flood the plants.
Since there is a large concentration of various plants in the winter garden - both moisture-loving plants and those that do not like moisture or are completely undemanding, it is worth designating those flowerpots that should be watered more often than others - do this using small stickers or a marker. This will be especially useful for beginning gardeners.
Once a week, garden care should be accompanied by wet cleaning, which will not only improve the overall microclimate of the winter garden, but also give it a neat, clean look.
Wet cleaning should cover not only window sills and stands, but also the plants themselves.
Particular attention should be paid to the leaves - they must be wiped on both sides. Cleaning plants, as a rule, is required once every 1-2 weeks. To do this, use a sponge or soft cloth or napkin, soaked in warm water and wrung out thoroughly so that no streaks remain after wiping. 
In order for the plant to grow better and not get sick, you should use a variety of fertilizers. The choice of fertilizer type depends on many factors, in particular, on the type of plants in the winter garden. And if your knowledge is not enough, then in this matter it is better to take the advice of a professional, and also read the instructions on the fertilizer bags. 
A prerequisite for maintaining the ideal state of “operability” of the winter garden is the correctly selected temperature regime. The temperature is maintained at the level required by the plants, so either different temperature conditions are created or plants are selected with similar temperature requirements.
The second option is, of course, less labor-intensive and more versatile. By selecting plants with similar temperature conditions and the same watering requirements, you will greatly simplify the care of your winter garden and provide comfortable conditions for indoor plants.
The higher the temperature, the higher the humidity, otherwise serious problems cannot be avoided. Almost all plants love regular spraying and washing of leaves, and sometimes polishing. 
As needed, be it a year, two or three, “general repairs” should be carried out in the winter garden. The fact is that over time, difficulties may arise associated with ensuring a favorable microclimate; maintaining humidity, temperature, lighting, drainage, ventilation, protection from sun or plant diseases. Then all broken parts should be replaced to restore the functionality of the oasis.