The construction of a drainage system, an integral part of any private house, should be based on the requirements of SNiP: drainage that meets all the rules will be able to fully prevent the negative impact of precipitation and groundwater on buildings and plantings on the site, because this is what it is mandatory.
We will talk about these rules, as well as about the design features of the drainage system, in this article.
Drainage system design
What should the project contain
The beginning of the drainage device should be preceded by the development of a system design. The drainage project is created based on engineering hydrological studies of the site. Its purpose is to define and describe the fundamental technical characteristics of a drainage system.
As a rule, the project contains the following data:
- schematic representation of the laying of drainage pipes (deep and surface systems);
- design parameters of drains - section, slope, assembly of the mouth part, depth of laying in the ground and distance relative to each other;
- standard sizes of the components of the drainage system (drains, wells, connecting elements, etc.);
- a list of building materials required for the installation of the structure.

The project must take into account the following factors:
- site landscape;
- the average volume of atmospheric precipitation per year;
- composition and characteristics of the soil;
- ground water level;
- location of nearby natural reservoirs, etc.

What should the budget include
Before the construction of the drainage system, a local estimate for the drainage device is compiled, which consists of the cost of the following operations:
- dismantling of reinforced concrete foundations;
- creating trenches in the soil 2 m deep manually, installing fasteners across the entire width and laying a waterproofing layer from a polymer film;
- installation of a transverse drainage having a two-sided outlet;
- laying a sewer pipeline from polyethylene pipes;
- backfilling of the base for crushed stone pipelines;
- installation of drainage communications, strengthening of the underlying layers and concrete blocks (reinforcement);
- dismantling of existing asphalt concrete pavements;
- creation of new asphalt concrete pavements;
- installation of bridges, passages, floorings, etc. made of wood;
- preparation of soil for crops (filling a layer of soil up to 20 cm thick);
- sowing various lawns and other plantings by hand.

For the device of the drainage system you will need materials:
- crushed stone;
- sand;
- corrugated drainage pipes wrapped with geofabric;
- geotextile (needle-punched non-woven fabric used to create an additional filter, which may be required depending on the characteristics of the soil at the site);
- viewing wells.
Drainage erection
Rules for drainage
It is possible to protect structures and plantings from excess moisture, knowing the rules for drainage:
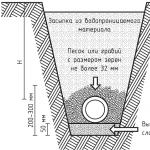
- A closed drainage system involves the creation of a trench in the ground, the depth of which is 70-150 cm, and the width is 25-40 cm. A slope directed to an artificial or natural water intake is required. The slope following which drainage systems are mounted - SNiP describes as follows:
- the slope value is 2 cm per 1 linear meter, if the soil is clayey;
- 3 cm per 1 linear meter if the soil is sandy.

Variant of the drainage system with a slope angle of 2 cm per 1 m (i=0.02)
- The bottom of the resulting recess is covered with a crushed stone pillow. Drains are laid out on it, then everything is again covered with rubble. Next, the system is backfilled with soil.
- Wastewater flows through drainage pipes, collects in a collector and eventually ends up in a water intake (river, ravine, pond, etc.).
- Control over the operation of the drainage system is carried out through manholes built of reinforced concrete or polymer rings.

Pro tip: If the drainage system is installed correctly, the groundwater level does not rise above the permissible point, but, on the contrary, begins to decline. This leads to an increase in soil fertility in the area. If the drainage system is not built, it is possible to oversaturate the soil with moisture, which has a negative impact on buildings and crops.
The construction of the drainage system should be made from high-quality, solid materials. Requirements for their quality are regulated by the following state standards:
- GOST 8411-74. Ceramic drainage pipes. Specifications;
- GOST 1839-80. Asbestos-cement pipes and couplings for non-pressure pipelines. Specifications.
Methodology for the device of the drainage system
The arrangement of the drainage system consists of several stages:
- A trench is dug about 70 cm deep and about 50 cm wide. It should be located on a slope, above the house, in order to collect melted snow and precipitation from the site. Water is discharged outside the territory through drainage pipes.
- The bottom of the trench is previously laid out with gravel, it is carefully compacted.
- Drains are placed on the gravel pad - perforated corrugated pipes with a diameter of 100 mm. At the same time, a slope is observed (2-3 cm per meter), and the pipes are wrapped in geotextiles - it prevents large soil particles from entering the system.

- The drainage is covered with a layer of material that passes water well, for example, expanded clay.
- Backfilling is in progress.
As a result, a drainage system is formed on the site, which effectively collects precipitation and melt water, otherwise they would simply flow down the slope.