If you are reading this, chances are you are in trouble. Agree, until we are affected by a problem of this kind, we will never begin to learn information about prevention or ways to get rid of insects from your living quarters or office.

After reading our article, you will be able to get rid of them as soon as possible by adopting the best methods of insect control. So, let's begin.

The method of controlling insects depends directly on the type of pests and their biological characteristics.






Photos of domestic insect species can be found in the review below, although they are already known to everyone. We list the main ones:

Tarkans
The most common “domestic” insect is the cockroach.

From experience - it is most problematic to bring them out. They carry diseases and get along in almost any climate. They can appear even in a clean apartment. How? For example, they are tired of living with your not entirely clean neighbors.

How to deal with insect pests - only complex solutions will help here, consisting of the use of several means at once and extreme cleanliness.

Fleas
An equally unpleasant sight is fleas.

They also carry diseases, often very dangerous not only for pets, but also for humans. Their main disadvantage is that they multiply very quickly. Pets bring them into the home. Getting rid of them is extremely problematic, but, like others, perhaps with some effort.






bedbugs
Very tenacious, nasty, blood-sucking insects. The worst thing about them is that they bite people at night, which can affect, for example, even children. They live in your bedding, behind wallpaper and baseboards.


mosquitoes
Nobody needs to explain who they are and why they are bad. They also carry diseases, feed on our blood. However, fighting them is not as difficult as with other types of bloodsucking.

Recently, a lot of tools have appeared that specifically fight against mosquitoes - it's worth trying in the complex.

mole
It is very unpleasant when someone eats your material possessions: a fur coat, a sweater, a carpet, furniture, or even your food - cereals, for example. In this regard, a sufficient amount of resources has been allocated for the fight against moths, respectively, there are a huge number of drugs on sale.

house ants
Yes, and it happens. They can be called small cockroaches. Only they are even more tenacious and, so to speak, thick-skinned. They are not inferior in the transfer of diseases and harmfulness to bedbugs and fleas. Most often they tend to appear in corner apartments and private houses, they love country houses and makeshift houses.






flies
So-called kitchen insects. The danger is their larvae, that is, worms. They constantly start in vegetables and fruits, have an unpleasant tendency to appear out of nowhere. What kind of insects can be found at home. There are rare species, while flies are frequent guests of almost any apartment or house outside the city.

What can motivate these pests to settle in your home?
Being in a small confined space of people, pets, various foodstuffs, a variety of all kinds of furniture, fabric and things from it. All this has a very good effect on the population of the insects listed above.


Humidity - as a rule, this problem concerns the residents of the lower floors. This is the best breeding condition for cockroaches and wood lice.

Heated rooms cannot be excluded. Heat-loving mosquitoes and fleas are not averse to breeding and living near your heating devices.

What is the conclusion from this? It is worth observing the normal (average) temperature balance in the room, ventilating heated rooms and heating wet and cold ones.

What is the main difficulty
Why is it so difficult to get rid of through various chemical insecticides. It's very simple - insects of all kinds quickly develop immunity to the means intended to eliminate them.




See also the expiration date on the label, this is no less important. Try to buy recently appeared products, those that the ancestors of certain insects have not yet become accustomed to.







Here you have purchased 5 different in composition, relatively new products on the market. Next, you should decide in which places to spray, glue or apply products and which ones to use against certain insects.
Various kinds of traps made on the basis of pheromones and insect smells.

Physical. Ventilate the room, because, for example, cockroaches cannot stand temperatures below -8, or vice versa, steam treatment of furniture from moths and bedbugs.

If the room is cool enough, the insects will leave your shelter and will not return to you. This also includes light traps - against moths and mosquitoes, shaking out clothes and using a vacuum cleaner, electric traps from cockroaches.

Chemical. Here we boldly include all sprayers and other types produced in factories. Today, such a method as microencapsulated is famous - it is he who is used by professional exterminators.

Folk remedies. We can recommend different methods - from bright lamps for flying insects to boric acid solutions.

What steps you need to follow to get rid of forever - instructions on how to properly deal with insects.
- Room preparation. Good cleaning, clearing corners, maybe you will find a cluster of insects or their nest.
- Cover dishes, buy masks or other personal protective equipment.
- Use of several chemicals at the same time exactly according to the instructions. It is advisable to do this all in the morning and leave the room for the day.
- When you return, you should ventilate the room.


We wish you success! We are sure that everything will work out! Effective ways to deal with insects most often appear when you yourself fight these creatures in practice.

Photo of insect control methods



WAYS TO CONTROL PESTS AND PLANT DISEASES
Ways to control pests and diseases
1. Agrotechnical
2. Physical and mechanical
3. Biological
4. Chemical
5.Integrated plant protection system
Literature
Ways to control pests and plant diseases
Among the measures that ensure the preservation and increase in the yield of agricultural crops, an important place is occupied by the fight against pests and diseases.
The success of this work depends on the timely implementation of protective measures in combination with preventive and agrotechnical methods of plant care.
Recommendations for the protection of crops from pests and diseases are combined under the general name of a system of measures, including various control methods - agrotechnical, mechanical, biophysical, chemical and biological.
The effectiveness of these measures, in turn, depends on the timely detection of plant diseases and foci of the most dangerous pests.
The plant protection service renders great assistance to collective farms and state farms in carrying out work to combat pests and diseases. Plant protection stations are located in all agricultural regions of our country.
When planning and carrying out measures to combat pests and diseases, it is necessary to take into account the biology of pests and pathogens, as well as climatic and weather conditions, on which the success of plant protection measures largely depends.
1. Agricultural method
The development of pests and microorganisms that cause plant diseases, as well as the development of the plants themselves, depends on environmental conditions.
Timely sowing provides the most favorable conditions for seed germination and plant development, which makes them more resistant to damage.
The use of crop rotation with the necessary spatial isolation for crops in a number of cases excludes the possibility of damage to them, since insects and many pathogens adapted to feeding on certain plants die from a lack of food when changing crops.
Fertilizers and top dressings improve the nutritional conditions of plants, which increases their resistance to damage.
The right choice of site, especially when laying perennial fruit and berry plantations, contributes to better development of plants, increases their resistance to pests and diseases. It is known that gooseberries and currants planted nearby are more damaged by gooseberry moth; in the neighborhood of potatoes and tomatoes, the latter are affected by phytophthora (potato rot).
Proper planting of crops (observance of optimal distances between plants) contributes to better ventilation of the site and prevents the spread of diseases such as apple and pear scab, currant anthracnose and many others.
Destruction of weeds, which are a food base for many pests, and fallen leaves on which microorganisms overwinter - pathogens of plant diseases, removal of dried branches, cleaning of dead bark on fruit trees, timely watering to a large extent prevent the mass accumulation of pests and harmful microorganisms.
However, it should not be forgotten that the effectiveness of the listed agricultural practices to a large extent depends on the timing of their implementation and the characteristics of the development of each pest or plant disease.
For example, the use of potash or phosphorus-potassium fertilizers increases the resistance of many crops to damage by diseases and pests. Top dressing carried out before pests resettlement (aphids, cabbage whites on cabbage) reduces the number of plants inhabited by them.
Of great importance is the quality of seed and planting material and the selection of varieties resistant to diseases and pests.
Thus, by changing the environmental conditions with various agrotechnical methods, it is possible to increase the yield of plants, their resistance to damage, and also contribute to the destruction of the wintering stock of pests and pathogens.
2. Physical and mechanical method
The physical and mechanical method of control consists in the direct destruction of pests and pathogens by hand picking and catching them with various traps and other devices.
This method is very time consuming, however, in some cases it is necessary. For example, if wintering nests of hawthorn and golden tail hanging on trees are not collected in winter or early spring, then caterpillars that emerge from nests in spring can destroy a significant part of the leaves. The same can be said about scraping onto the litter with the subsequent destruction of the ovipositions of the gypsy moth and about the cutting of young shoots with ringlets of the eggs of the ringed silk moth.
To catch the caterpillars of the apple codling moth, trapping belts are placed on the fruit-bearing trees, under which the caterpillars willingly climb to pupate. For the same purpose, in autumn, trapping heaps of fallen leaves are arranged in the garden, where various weevils go for wintering. In late autumn, such heaps are burned.
In small gardens, they practice the early spring shaking of weevil beetles on banners spread out under the trees.
Mechanical methods of struggle also include the use of traps and traps against mouse-like rodents.
Various light traps and electric traps are used to catch codling moth butterflies and some other pests. In the fight against strawberry mites, strawberry seedlings are treated in hot water.
In large vegetable farms, thermal disinfection of the soil with water vapor is widely practiced.
To do this, in the cultivation room in the middle of the prepared area, a steam distribution tube is laid in the longitudinal direction, connected by a rubber hose to the steam conduit. The soil intended for steaming is well loosened, and then covered with a heat-resistant film. The edges of the film are fixed with sandbags (size 1m x 12 cm).
Steam (10-110 0 C) is fed under the film until the soil temperature at the edges of the site rises to 70 0 C. At a pressure of 5 atm, the treatment lasts 10 hours, and at a pressure of 8 atm - 5 hours.
For steaming, you can also use perforated plastic pipes with a diameter of up to 5 cm, which are laid in the soil to a depth of 25-30 cm every 25 cm. The area is covered with a film from above. In this case, steaming continues for 6 hours and steam is used more economically. Then the pipes from the cooled soil are transferred to a new section. The soil mixture intended for the preparation of nutrient pots is also steamed.
The action of high temperature is also used to disinfect seed material. Cucumber seeds against viral diseases are dried and heated for three days at 50-52 0 C, and then for a day at 78-80 0 C. They are moistened before sowing. Cabbage seeds are kept for 20 minutes. in water at 48-50 0 C, after which they are immediately placed for 2-3 minutes. into cold water.
In the field of biophysics, work is underway on the use of radiation sterilization of insects that lead to infertility.
3. Biological method
From early spring to late autumn, predatory ground beetles are found in the fields, which destroy eggs, larvae (caterpillars), pupae and adults of many harmful insects. One ground beetle per day can destroy three to five caterpillars of the gooseberry moth, up to ten caterpillars of the rapeseed sawfly, up to 100 larvae of gall midges. No less useful are the larvae and adults of ladybugs. They actively exterminate aphids, mites, scale insects and other pests. A seven-spot ladybug destroys up to 200 aphids per day, and a small stetorus beetle - up to 210 spider mite eggs. The predatory larvae of lacewings and syrphid flies intensively destroy aphids and their larvae.
In our country, Trichogramma is widely used to combat many types of harmful butterflies, and the predatory mite Phytoseiulus is used to destroy spider mites that damage cucumbers in greenhouses.
Phytoseiulus is a warm and moisture-loving predatory mite. the most favorable temperature for its development is 25-30 0 С and the relative air humidity is above 70%. Under such conditions, one generation lasts 5-6 days. The fertility of the female is 50-80 eggs. per day, adults destroy up to 30 eggs or 24 spider mites in different phases of development. When foci of spider mites are found in greenhouses, phytoseiulus is released at the rate of 15-60 individuals per plant.
Phytoseulus is propagated on soybean plants previously infected with spider mites.
Many harmful insects are destroyed by birds (starlings, tits, rooks), as well as moles, shrews and some other animals.
4. Chemical method
Many years of agricultural practice has shown that for the successful implementation of plant protection measures, it is necessary to use all methods of control, especially agrotechnical. However, in some cases, the success of pest and disease control is decided by the chemical method. The advantage of the chemical method is the speed of action, the possibility of simultaneous destruction of several pests or pathogens, as well as its high payback.
However, we should not forget that the chemical method has its drawbacks and, with the inept use of chemicals, can give negative results. So, some drugs, destroying pests, simultaneously kill beneficial insects. Strong-smelling substances leave an unpleasant odor on processed fruits. Incorrectly formulated solutions can cause plant burns, etc. Therefore, when using chemicals to control pests and diseases, one should strictly adhere to the established regulations and rules for their use, apply them on certain crops within the established time limits in compliance with concentrations and consumption rates.
In the chemical method, toxic substances - pesticides are used to combat pests and plant diseases ("pestis" - infection, destruction; "cido" - I kill).
Depending on the organisms against which pesticides are used, they are divided into the following groups:
insecticides(fozalon, karbofos, dilor) - to combat harmful insects;
acaricides(acres, keltan) - herbivorous mites;
rodenticides(zinc phosphide) - with rodents;
molluscicides(metaldehyde) - with shellfish (slugs);
nematicides(carbation, thiazon) - with nematodes;
fungicides(copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture, captan, cineb, TMTD. copper oxychloride, formalin) - with plant diseases;
herbicides- for weed control.
Some chemicals have a complex effect. They can simultaneously be both insecticides and acaricides (phosphamide, antio. metaphos). Preparations nitrafen and DNOC have the properties of insecticides, acaricides and fungicides.
Depending on the effect on harmful organisms, pesticides are conditionally divided into groups: contact action (acrex. keltan. karbofos), intestinal (zinc phosphide), systemic (phosphamide, antio), fumigants and protectants (formalin, TMTD).
Fumigants poison the air and enter the pest through the respiratory system. Treaters destroy pathogens that are on the surface of the seeds, or protect the seeds from infection with bacteria, fungi that are in the soil.
Depending on the physical and chemical properties and weather conditions, pesticides are used by spraying, dusting, fumigation. in the form of aerosols, poison baits or dressings.
spraying - application of pesticides to plants or insects in the form of solutions, suspensions and emulsions.
Solution- a liquid in which chemicals dissolve completely (copper sulfate, iron sulfate, soda ash).
Suspension- a liquid in which solid particles of an insoluble drug are in suspension (wettable powders of colloidal sulfur, entobacterin).
Emulsion- a liquid mixture in which small drops of a liquid (for example, oil) are suspended in another liquid (in water) - an emulsion of karbofos. preparation No. 30. To increase the stability of emulsions, soap, clay, OP-7, etc. are added to them.
The fight against pests and diseases of agricultural crops is carried out mainly by the method of large-drop multi-displacement or low-volume small-drop spraying.
With low-volume small-drop spraying, the size of the drops is 50-350 microns, the flow rate of the working fluid in the field is 100-200 liters, in the garden - 250-600 liters per 1 ha, and with large-drop multi-displacement spraying, respectively, 100-600 microns, 300-600 liters and 800-3000 liters per 1 ha. With small-drop spraying of the pesticide, the same amount is spent per 1 ha as with conventional large-drop treatment, but it is distributed in a smaller volume of water.
In this book, the concentration of drugs in the working fluid is indicated based on multi-liter large-drop spraying.
dusting - application of pesticides to a plant in the form of a powder (dust), in which a toxic substance is mixed with an inert filler, such as kaolin or talc.
Aerosol treatment - poisonous fog or smoke containing various pesticides (for example, the gamma isomer of hexachlorane and r.). the size of aerosol particles is 1-20 microns. Droplet aerosols - fogs are obtained using special aerosol generators.
Solid aerosols - smokes - are obtained by burning smoke bombs containing insecticides and acaricides. Currently, aerosols are used to treat greenhouses and other enclosed spaces.
Fumigation – processing of fruit and vegetable stores, greenhouses, etc. poisonous vapors or gases that have a detrimental effect on pests and pathogens. For disinfection of cultivation rooms, a mixture of the following pesticides is used: 2% formalin + 0.3% celtan + 0.5% karbofos (200 ml + 30 ml + 50 ml per 10 l of water) at a flow rate of 1 l of liquid per 1 m 2. Disinfection is carried out at a temperature not lower than 15 0 C.
With good tightness of greenhouses, the most effective is fumigation with sulfur dioxide, for which 100 g of sulfur or 50 g of sulfur blocks are burned per 1 m 2 of the room. After processing, the greenhouses are closed for 1-2 days, then they are well ventilated.
Soil disinfection . Carried out in film greenhouses, hotbeds, as well as in open ground. For this, carbation and other chemicals are used.
poisoned baits used mainly for the control of mouse-like rodents. For their manufacture, vegetable oil, a toxic substance (for example, zinc phosphide) are added to the feed product (grain, etc.) and mixed well. Baits are laid out in places of concentration of rodents.
Etching - disinfection of seed material with powdered or liquid fungicides from pathogens. TMTD, fentiuram, tigam and others are used as seed treaters for vegetable crops.
5. Integrated plant protection system
Experience in the fight against pests and diseases shows that reliable protection of cultivated plants is possible only with the integrated use of all methods. This requirement is currently met by an integrated plant protection system, which is the highest stage in the development of systems of measures, the theoretical foundations of which were developed by Russian scientists back in the 30s. The following elements form the basis of the integrated system: cultivation of zoned varieties resistant to diseases and pests; the use of a complex of agrotechnical practices that increase the resistance of plants; the use of biological means of control; rational use of chemicals, taking into account the number of pests that threaten a decrease in yield or deterioration in product quality.
This system is mobile and the value of the individual elements that make it up depends on the species composition of harmful organisms and their abundance. An integrated system involves the reasonable use of chemicals, and, above all, those that are the least dangerous for the person himself and the environment. Extermination measures are carried out if the number of harmful organisms exceeds a certain level, i.e. becomes threatening to crops. So, in the Crimea, it is recommended to spray apple trees (after flowering) against fruit mites, if their number is three to five individuals per leaf.
This approach to plant protection makes it possible to reduce the amount of chemical agents used, reduce material and labor costs for pest and disease control, and creates favorable conditions for the activation of beneficial fauna.
List of used literature
1. Bei-Bienko G.Ya. General entomology. 3rd ed. revised -M., Higher School, 1998, 485s.
2. Gar K.A. Chemical means of protection of agricultural crops. - 3rd ed. revised. and add.-M, Rosselkhozizdat, 1998, 147 p.
3. Gorlenko M.V. Agricultural phytopathology 3rd ed. and additional –M, Kolos, 1997, 441 p.
4. Dementieva M.I. Plant pathology. 3rd ed., revised. and additional - M, Kolos, 1997, 372 p.
5. Korchagin V.N. Garden protection from pests and diseases. - 3rd ed., revised. and additional - M, Kolos, 1998, 287 p.
6. Plotnikov V.V. Plant protection. 3rd ed. - M, Kolos, 1998, 138 p.
7. Pospelov S.M. Plant protection. 3rd ed. revised and additional - M, Kolos, 1998, 285 p.
8. List of chemical and biological pest and disease control agents approved for use in agriculture in 2004 - M, 2004, 148 p.
9. An agronomist's guide to plant protection (under the editorship of A.F. Chenkin). 3rd ed. rework and additional - M, Rosselkhozizdat, 1999, 352 p.
10. Chemical protection of plants (under the editorship of G.S. Gruzdev). –M, Kolos, 1997, 376 p.
11. Chemical and biological plant protection products (under the editorship of P.V. Sazonov) - M, Kolos, 1998, 209 p.
Tutoring
Need help learning a topic?
Our experts will advise or provide tutoring services on topics of interest to you.
Submit an application indicating the topic right now to find out about the possibility of obtaining a consultation.
Insect and pest control must be effective and as fast as possible. Whatever type of pests is wound up in the house or in the garden, you should immediately take action. The most unpleasant are those insects that can in any way harm a person, animal or plants. This type includes different types of ticks, mosquitoes, bedbugs and fleas. These insects can cause significant harm to the human body. It's not just about painful bites, because various fleas and ticks are carriers of a wide variety of infections. Obviously, with a bite, pathogenic bacteria enter the bloodstream.
It is no less unpleasant to coexist with insects that harm plants and also spoil food. We are talking about ants, midges and flies, cockroaches and Prussians, not to mention mice and rats in a house or apartment. There are other pests in the garden that can ruin the entire crop. For example, in the articles of this section we will tell you how to effectively and quickly drive away moles and mole rats from the garden, without harming the animals.
Useful tips and tricks will help you cope even with the eternal neighbors - spiders. Two-tails, scolopendras, centipedes, wasps, slugs and earwigs - all these pests cause a lot of inconvenience. In the articles, we will share the most effective folk remedies for insect control, as well as talk about how to safely and correctly use special household chemicals. If you can’t cope with pests on your own, there is always the opportunity to call specialists at home.
Methods and ways of dealing with insects and pests
The fight against various pests and insects both in a house or apartment, and in a summer cottage is not the easiest thing to do. It is very important to follow a number of rules, thanks to which you will not only effectively and reliably deal with the problem, but also protect yourself and the health of your loved ones. In this section, we will talk about the most effective methods and ways to deal with specific pests.
The main thing is to detect the problem in time. If you notice the appearance of a cockroach in the kitchen, you should not wait until there are more of them, solve the problem immediately and radically.
Before you figure out how to display a particular type of insect, you should consider the general rules and safety recommendations:
- The presence of insects in the apartment can be determined by the smell and unusual pollution. If insects are wound up in the kitchen, then this will be noticeable in bags of cereals and other products that you have access to. Some pests start directly in cereals or flour, so a preventive audit should be carried out every week..
- If you find traces of pests at home, you should first of all try to find out what kind of insects are wound up in the apartment. This will largely determine what means will be used to combat unwanted guests.
- Before resorting to the help of special aggressive chemicals, try to find out how else you can get rid of pests using folk remedies. First of all, it is important for your health and your loved ones.
- If you still decide to resort to using chemicals, take care of safety precautions. When working with harmful drugs, mucous membranes, respiratory tract, and skin should be protected. Thus, it is necessary to wear overalls, gloves, a respirator and goggles. It is very important to ventilate the room during the disinfection process.
- At the end of the work, it is necessary not only to take a very hot shower, but also to process the clothes. It is strictly forbidden to wash such things in the machine! Only manual cleaning is recommended.
- Do not think that if the problem is not visible, then it does not exist. Be sure to take the recommended preventive measures for a few more weeks after removing the insects.
These general rules will be relevant for the control of any insects or pests. We will consider special cases of breeding certain insects below.
The most dangerous insects are those that can harm a person or animal. That is why, first of all, we will figure out how to get rid of those insects whose vital activity is associated with living beings.
For convenience, we have prepared a small visual table that tells what to do if certain pests are wound up in a house or apartment.
Pests | Fighting methods |
Fleas and lice | |
Mosquitoes are seasonal pests that invariably appear in the apartment with the onset of heat. Even if you managed to install special protective nets on the windows in winter, you should not be surprised if the nasty buzzing is heard again with the onset of summer. The fact is that these insects hibernate and can live in the house all winter. Finding small insects is incredibly difficult, so you can only deal with them during the season of their activity. To combat mosquitoes, the most effective will be the use of purchased drugs. The abundance of factory products that deal with the problem of insects in the house eliminates the need for folk remedies. However, if you still prefer home remedies for insects, first of all, study information about what smells mosquitoes do not like. These include the aroma of anise, cedar, valerian, tobacco, eucalyptus and lemon. For more information on this topic, see the related article in the section. As for prevention measures, use special mosquito nets. |
|
Ticks and bedbugs | One of the biggest problems is ticks. These insects do not just bite, they penetrate the skin and can cause serious illness, and sometimes even death. Removing a tick is incredibly difficult, so it's best not to allow the insect to come into contact with the skin under any circumstances. At home, there are only two types of mites: dust and spider mites. Spider mites harm only plants, so we will talk about this species below in the appropriate section. As for dust mites, these small insects cannot be detected even under a microscope. Pests live in dust, so special tests are used to detect them. Symptoms of a sudden unseasonable cold, weakness, an allergic reaction - all this may indicate that dust mites have wound up at home. First of all, a special test should be carried out, and then it is necessary to start pest control. No matter how trite it may sound, but in order to get rid of this type of mites, you need to get rid of the dust in the house. It is also recommended to remove all textile items from the room if possible. It is very important to carry out wet cleaning as often as possible in order to prevent. Bedbugs are not as dangerous as ticks, but their presence in a house or apartment also causes a lot of inconvenience. To combat bedbugs, you can use various folk remedies, such as kerosene or turpentine with vinegar. More details on this topic can be found in the relevant article of the section. |

On indoor flowers and plants
It is not recommended to try to remove pests with folk remedies, as they may not be effective enough. E If you delay even a little, you can simply lose your favorite flower or plant in a pot. Do not forget about the preventive measures that must be carried out after removing any insects.

In the kitchen and other rooms
The worst enemy of a person in an apartment, as well as the most frequent neighbor, are cockroaches and Prussians. These insects come in different sizes, most often brown or black in color. Habitat - kitchen. This is because these pests feed on leftover food. Very often, the reason for the appearance of cockroaches in the house is negligence in cleaning and a disregard for maintaining order, especially in the kitchen. If the Prussians appeared in an apartment building, they will inevitably hit all the living quarters. That is why it is so important to do this collectively in the fight against the Prussians and cockroaches. If one person starts pest control, cockroaches will move to another apartment through the ventilation system. Boric acid is very effective in the fight against Prussians. This tool must be scattered in all corners and baseboards, as well as on tables and behind the stove. Cleaning is also important for cockroach control.
Moth is the main enemy of textiles, as well as clothing and other things. However, it is very simple to deal with such a pest, even with folk remedies. It is enough to find out what smells the mole does not tolerate. Citrus fruits, tobacco, garlic, lavender, vinegar can all be used to permanently kill moths at home. An important preventive measure is the periodic ventilation of wardrobes with clothes.
Midges and flies will appear in the kitchen if you do not follow the cleaning schedule, and also leave dirty dishes with leftover food until the morning. Such insects prefer rot, as well as animal excrement. That is why very often flies start up in those houses where animals are incorrectly kept in cages. To combat such pests, it is enough to eliminate the source of the problem, as well as use a factory remedy in order to get rid of the existing midges and flies.
Rats and mice most often appear in private homes. These pests spoil food, and also carry a wide variety of infections. The most radical way to deal with rats is to use poison. However, if you do not feel like killing animals, you can use special sound repellers.
Woodlice, centipedes, spiders, centipedes and sciarids may also appear in the house. Read more about the fight against such pests in the relevant articles of the section.

In the country house or garden
Useful tips and recommendations from this material, as well as from the articles in the section, will help you in any situation to know how to deal with this or that pest both in an apartment or house, and in the garden, using popular household chemicals and effective folk remedies.


The season is coming! The season is not only gardening, but also mosquito, fly and gadfly ...))) Yes, soon in all gardens of the country we will endure the bites of mosquitoes, gadflies and annoying flies!
It is known that it is possible to fight all pests with chemistry, but
- firstly, it is harmful to our health,
- secondly, it is harmful to the environment,
- thirdly, in such a struggle we exterminate beneficial insects
So what to do? And there is a way out! Nature has thought of everything for us a long time ago! The main thing is to learn to read the Book of Nature!
We consider many plants to be weeds and as a result, the more well-groomed the site, the more pests. And Nature has long taken care of this and solved the problem. Green pharmacy, not only heals, but also has repellent properties.
Plants containing certain specific substances are called repellents.. Phytoncides, released into the environment, have a depressing or irritating effect on certain animals.
As a result, many pests "without a fight" leave the occupied territory and go in search of a better life.
The best way to expel pests is to plant the most suitable repellents next to the cultivated plants.
1:2647The role of plants - repellents!
1:64
First of all, these plants act as protectors! They protect our gardens and gardens, as soon as they are planted in certain areas of our gardens. Who are they protecting from?
2:907From the whitefly
2:946
Effective infusion of garlic. Chopped garlic cloves (150-170 g) pour 1 liter of water and insist in a tightly sealed container for five days.
For spraying, 6 g of concentrate diluted in 1 liter of water is enough. Keep in mind that folk remedies can help if there are not too many pests.
3:2001It is more effective to plant nearby repellent plants: nasturtium, peppermint, thyme, bitter wormwood.
3:201From white cabbage
3:253
10 g of white mustard powder is infused for two days in 1 liter of water, filtered and before spraying, bring 200 ml of the solution to a volume of 1 liter
Chamomile infusion and hellebore infusion give good results. For 10 liters of water, take either 1 kg of raw, or 500 g of semi-dry, or 100-250 g of dry hellebore.
This solution is infused for about two days or boiled for 30 minutes. A decoction or infusion is filtered and used for spraying.
It is more effective to plant nearby repellent plants: celery, tomatoes, peppermint, sage, bitter and medicinal wormwood.
4:1720From the cabbage caterpillar

repellent plants: onion, sage, tansy, thyme, medicinal wormwood, nasturtium.
5:707From an earthen flea
5:756
when fleas appear, the plants are pollinated using sifted wood ash, tobacco dust (in equal proportions) by dew.
6:1495And one more recipe for an old, undeservedly forgotten means of dealing with a wide variety of insects:
6:1689In an enameled or metal vessel with a capacity of at least 5 liters, boil 1-2 liters of water, dissolve 200 grams of laundry or green soap in it and bring to a boil, after which 200 grams of kerosene are added.
The mixture is forced to boil two or three times, removing from heat when it rises in foam above the level of the dish. The resulting emulsion concentrate is diluted with warm (30-40°) water to 10 liters.
6:742But it is more effective: plant repellent plants nearby: catnip, peppermint, bitter and medicinal wormwood, tobacco, tansy, head and leaf lettuce.
6:1025From the five-point hawk
6:1088
7:4
good results are given by infusion of calendula and peppermint. For 10 liters of water, take either 1 kg of raw or 500 g of a semi-dry mixture of plants.
7:237But it is more effective to plant nearby repellent plants: dill, borage, basil.
7:387From the Colorado potato beetle
7:440
for the successful use of folk remedies and methods of dealing with the Colorado potato beetle, it is necessary to fulfill a number of simple requirements when using them.
1) It is recommended to process plantings in warm (at a temperature of 18-25 ° C), calm weather, in the morning after the dew has dried or in the evening before it appears. It is better to spray herbal preparations in the evening hours, since in the sun they lose their insecticidal properties faster.
8:17472) Working solutions must be prepared 1-3 hours before spraying. For better adhesion, green (potassium), laundry soap, liquid soap or washing powder is added to them. Usually 20-40 g per 10 liters of solution. Having previously cut and diluted the soap in a jar of water, pour it into the working solution.
8:5543) Treatment with infusions and decoctions is repeated after 5-10 days as needed. The last spraying is carried out 20 days before harvest.
8:816Folk ways to deal with the Colorado potato beetle:
8:913
A week or two before planting potatoes in the garden, dig several holes up to 10 cm deep. The earth around them is sprinkled with hot coal ash and slag taken from the furnace of a boiler or stove. Beetles crawl into these holes and die. In the same way, peat or wood ash has a detrimental effect on the pest.
9:1986In the spring, before the emergence of potato shoots, 3-4 pieces of tubers are placed in half-liter jars. Then the banks at 10-11 o'clock are placed on the site in the recesses previously dug in the ground. Beetles caught in jars are destroyed.
9:410It is recommended to soak tubers in the spring for 1 day in a solution of urea. Lay out on the site in cloudy weather or at night. The beetle dies by attacking poisoned baits. This method is repeated in the fall after harvest. (CHEMISTRY)
9:861An infusion of wormwood with ash is also used: a glass of wood ash is added to 150-200 g of crushed fresh wormwood, everything is poured with hot water, infused for 2-3 hours, stirred, filtered and potato bushes are sprayed with the resulting liquid.
9:1289Potato bushes can be pollinated with sifted ash (preferably birch). About 10 kg of ash per 1 hundred square meters of plantings. (1 kg per 10 sq.m). After a day or two, not only the larvae of the Colorado potato beetle die, but also most of the adults. Together with organic matter, pour wood ash into the furrows. The soil, flavored in this way, is disastrous for the beetle.
9:1884After hilling around each bush, sprinkle 1 tbsp. a spoonful of ash. When the stems rise by about 15-18 cm, the planting is sprayed with ash-soap infusion.
9:293Gives good results spraying potatoes with an infusion of fresh walnut leaves. Leaves, fruits and walnut shells are used to combat the Colorado potato beetle. From autumn, fallen leaves are harvested and stored in a dry, ventilated place. 3-4 weeks before the mass appearance of the beetle, the leaves are soaked in a bucket (2 kg per 10 liters of water). Before use, the infusion is filtered twice.
9:1013The Colorado beetle does not tolerate marigolds (this plant is also called calendula). Where potato beds are “circled” by a row of calendula, and additionally “stitched” diagonally by this flower, there is no pest, although neighboring plantings are affected by the Colorado potato beetle.
9:1502Repel the Colorado potato beetle and beans planted next to potatoes. In addition, potatoes are more productive from such a neighborhood, and beans are not superfluous on the farm.
9:288In the aisles of potatoes (or in the rows of bushes), plant sidun beans. These two cultures grow without interfering with one another. But bean beetles do not tolerate and leave the site.
9:602In a bucket of water (10 l) dilute 100 g of birch tar. Spray plantings with a solution 3 times a week.
9:782Good results are obtained by using a 4% solution of chicken manure (about 80 buckets per 1 hundred square meters). In the cases described, the beetle disappears for several years (up to 10 years). Processing should be carried out only after harvest.
9:1182But it is easier and more efficient to plant nearby repellent plants: catnip, coriander, nasturtium, onion, tansy, horseradish, vegetable beans, white yasnitka.
9:1442From moles
9:1474
10:4
Old grandfather's, truly natural way. You have to be like an animal. They (mainly males) mark their territory to scare and warn their own kind. And we mark - with urine (male), pouring it into molehills. The effectiveness of the method exceeds expectations.
Throughout the site, in a spread of 2 - 3 m, we drive thin metal rods into the ground, empty beer cans, put them upside down. Any breeze, rocking the banks, creates a very unpleasant noise for the moles.
10:861The surest way is to get a dog. People who have done so say they have forgotten what a mole is and how to deal with it. Apparently the dog also marks its territory with urine.
10:1186Any bottle is dug into the ground, into the mole's hole at an angle of 45 degrees. The howling of the wind in empty bottles scares away this animal
10:1435A good way is a piece of ordinary water pipe and a plastic bottle. Pieces of pipes are hammered into the ground so that their lower end is deeper than the level of the animal's moves. A pin with a diameter of 8-10 mm is hammered into the upper part of the pipe, reinforcing it in the center of the pipe with a wooden plug. A hot nail or metal pin is used to burn a hole in the bottom of the bottle with a diameter greater than the diameter of the pin. Cuts are made on the bottle along a solid line, and along a dotted line, the plastic is bent. There should be 4 such bends. At the slightest breath of wind, the bottle rotates, the hollow pipe resonates and creates noise that the animals are afraid of.
10:2539But it is more effective to plant nearby repellent plants: castor beans, daffodils.
10:141How to get rid of ants in the garden:
10:236
Loosen their nest and sprinkle with lime or tobacco dust;
11:868Ants do not tolerate strong odors. On the anthill, you can put the head of a smoked herring, sliced \u200b\u200bgarlic cloves into several parts, spread out tomato tops or parsley leaves;
11:1217A decoction of tomato tops helps well. The more concentrated the solution, the better;
11:1376Take corrugated cardboard about 20 cm wide, sprinkle it with a soot solution or powder it with cinnamon. Ants cannot stand the smell of soot and cinnamon;
11:1647Not a very pleasant way, but you can water the nests of ants with urine, this often helps;
11:162Make a solution: take ten liters of water, two glasses of vegetable oil, some cheap shampoo and vinegar. Poke a hole in the center of the anthill and pour this mixture into it. Close with foil for a few days;
11:576Bring large red ants from the forest and settle in the garden, and after that the black ants themselves will leave your territory
11:805Plant nearby repellent plants: Peppermint and spike, tansy, bitter wormwood, lavender, small valerian, peppermint and spike, tansy, bitter wormwood, lavender, small valerian.
11:1162From cabbage fly larvae
11:1224
12:4
Sprinkle the soil under the plants with ordinary wood ash, which has a double benefit for cabbage: it repels the cabbage fly, and it is a good fertilizer.
12:279Exclusion from the crop rotation of radish, which most attracts cabbage flies.
12:422To repel flies, sprinkle with naphthalene, after mixing it with sand in a ratio of 5-8 parts of sand and 1 part of naphthalene; instead of naphthalene, tobacco dust is used in a mixture with an equal amount of lime (300 g of the mixture per 10 m2).
12:842You can also soak peat chips (200 g per bucket of peat) with creolin and sprinkle around the plants.
12:1028In the fight against larvae, a tobacco solution is also used: 200 g of tobacco and 1 tbsp. a spoonful of soap in 10 liters of hot water. The drug is filtered and sprayed with plants and soil.
12:1330Plant nearby repellent plants: garlic, marigolds, radishes, sage, wormwood, hyssop.
12:1505From the carrot fly
12:46
You can prepare a spray solution from dry tomato plants. Pour 1 kg of dry mass into 10 liters of water, leave for 4-5 hours, then boil for 2-3 hours on low heat, dilute with water 2 times, add 30-40 g of soap per 10 liters of solution. The decoction retains toxicity to pests for a year when stored in a cool place.
13:1142Sowing carrots in early or late periods in dry, unshaded areas. Sowing is important to do immediately sparse: then you do not have to thin out the plants, during which a strong smell of carrots appears, and a large number of flies flock to it.
13:1605To scare away the carrot fly, the aisles are pollinated with ground hot pepper or ash.
13:166Spray the soil and plants with infusions of black or red pepper (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water), garlic, onion peel, marigolds, tomato tops, wild rosemary, spruce and pine needles and other odorous plants. But in order for the smell of these herbs to constantly stand over the carrot bed, it must be sprayed every three days.
13:731Pour boiling water over crushed bitter wormwood. Infusion to process the beds.
13:874Between the rows of carrots, especially in May and June, pest repellents are added: mustard, ground red or black pepper (1 teaspoon).
13:1149It’s great if onions, garlic or tomatoes grow next to a bed of carrots.
13:1291To protect crops from carrot flies, which cause a lot of trouble, on one side of the garden, place onions on a green feather, on the other - garlic;
13:1567Plant nearby repellent plants: lettuce, leek, onion, rosemary, sage, tobacco, wormwood.
13:187From wasps, hornets, gadflies, horseflies and bees
13:269
All of them are similar in many ways, and therefore the methods of struggle do not differ.
14:904If a wasp, a bee or a gadfly flies up to you, remain calm, stay still, do not wave your arms or make sudden movements - this can provoke aggression.
14:1246After bathing in the river, dry your body immediately, it attracts insects, as does sweat and various perfumes. They don't like strong odors.
14:1505Lubricate exposed areas of the body with any cologne that has a little mint oil or mint drops added (5 drops per tablespoon of cologne). The tool works for about an hour.
14:335You can make a trap for wasps. Take 250 ml of water, 4 teaspoons of honey and some vinegar. Heat water, dissolve honey, cool, add vinegar. Pour the solution into a dark glass bottle and place it near the place where the wasps roam.
14:784If you find a wasp nest in or near the house, wait until it gets dark and the wasps gather in the nest, soak a cloth in turpentine, wind it around the end of the pole and plug the entrance tightly with it. Leave it like this for a day (But in my opinion, this is not humane!)
14:1242If wild bees, wasps, hornets are trying to make their home near you, plant a bush of peppermint or plucked greens.
14:1477But given that the benefits of wasps are not commensurate with the inconvenience of their neighborhood, it is best to contact a beekeeper. They know how to deal with them. In the evening, they fumigate, put a bag on the nest, cutting the nest to disconnect it and take it away to the forest. The bag is left untied along with the nest, hastily moving away. All this time you should be in a mosquito net, tight clothing and gloves.
14:2241If this is a garden plot, plant repellent plants nearby: peppermint.
14:149From mice
14:179
It’s not bad to prepare baits from vegetable oil, flour and gypsum, which will harden in the stomach of a rodent and cause death (I AGAINST daring!) A similar remedy: spread a mixture of alabaster and sugar (or flour) near the holes and put a saucer with water next to it.
15:1149Rats and mice cannot stand the smell of mothballs and mint, which can also be used as a rodent control.
15:1381Finely chop the cork and fry it in pork fat. Then throw the bait to the mouse holes. After eating the cork, the mice immediately die from the swollen mass in the stomach.
15:1676Scatter hot peppers and dried chamomile flowers along the trajectory of the possible movement of rodents, scatter burdock thorns in the corners of rooms.
15:276Quicklime is mixed with sugar and scattered in places where rodents are most concentrated. Mice and rats willingly eat the bait and soon die. Quicklime in the stomach is heated by the action of water and gastric juice, causing the death of the animal.
15:746When using means of control such as mousetraps, it should be remembered that mice have an extremely acute sense of smell and will try to stay away from a mousetrap that their compatriot has landed in. Therefore, when re-installing the trap, you need to pour boiling water over it, and take the bait with gloves so as not to leave your smell on it.
15:1366In the garden, plant repellent plants nearby: at home, where we keep food, lay out dry branches: wormwood, garlic, rank, daffodils.
15:1619From apple honeydew
15:54
To destroy the larvae in the period from bud break to flowering, sprinkle the plants with infusion of yarrow, ash, tobacco, shag, soap solution.
16:847Fledged psyllids and those that have returned to lay eggs can be destroyed by tobacco smoke. Pour 1.5-2 kg of tobacco waste on pre-prepared heaps of straw and fumigate for two hours for two plants inhabited by adult suckers. Fooled by the smoke, copperheads fall to the ground. Now it is important to immediately collect them from the ground under the plants, otherwise many will come to their senses and rise into the crown.
16:1553Some gardeners use spraying with bitter pepper infusion (1 kg of fresh or 0.5 kg of dry red pepper per 10 liters of water). The infusion is boiled for 1 hour over low heat, then infused for 24 hours. The resulting concentrate can be bottled and stored in a dark, cool place. Before spraying, 125 g of concentrate and 40 g of laundry soap are added to 10 liters of water. Plants are sprayed with an interval of 10-15 days.
16:761Plant nearby repellent plants: black henbane, common harmala, creeping mustard, clematis vine, medicinal dandelion, bittersweet nightshade, real tobacco, garlic.
16:1099From nematodes
16:1132
17:4
Arranging quarantine for new plants. Disinfection of dishes, tools (the simplest measure is scalding with boiling water). Sterilization of the substrate in a water bath at a temperature of +50-55C for at least 10 minutes.
17:365After spraying the plants, allow them to dry quickly, at low temperatures, keep the plants in relatively dry conditions.
17:610Nematodes are very sensitive to heat and can be killed by a 30-minute water bath at 45°C.
17:831Among garden plants, everyone knows how hostile to nematodes are erect marigolds and asparagus. They can be planted in row-spacings or for the whole season they can occupy a plot intended for potatoes to destroy the pest.
17:1243An effective preparation is well-made ripe compost. Therefore, where the soil is fertilized with compost, the risk of mass spread of nematodes is minimized.
17:1560Plant nearby repellent plants: marigolds, calendula, erect marigolds, asparagus.
17:170From codling moth apple
17:229
After the end of the collection of fruits - collection and destruction of the remnants of the packaging material; cleaning dead bark from boles and branches on old trees.
18:1015Mulching between rows and minimal tillage in tree trunks.
18:1170Satisfactory results are achieved by hanging on trees special pheromone evaporators (polyethylene and rubber tubes, rings, cords, paper tapes with a consumption of 20-100 g/ha of pheromone) in order to disorient males.
18:1600To destroy the caterpillars of the first generation in the second decade of June, belts are placed on the boles of productive trees. They can be agile, requiring periodic review, and suicidal. For the manufacture of hunting belts, paper, gauze, burlap, matting and other materials are taken.
18:520Most of the codling moth caterpillars gather under belts made of burlap and old cloth. Belts are applied at a height of 30-40 cm from the ground, they are looked through weekly, crawled caterpillars are selected and destroyed.
18:898
Self-killing belts are imposed on trees no younger than 15 years old. For the preparation of belts, wrapping paper is used, cutting it 40-45 cm wide, and one of the longitudinal halves is impregnated on both sides with the composition of chlorophos - 1.5%, preparation No. 30 - 5%, earth - 50% and water - 43.5% . The belts, applied to the trees with the oiled side, ensure the death of the apple codling moth and other pests that have crawled under them throughout the season and do not require viewing.
19:2227The fight against apple codling moth can be successfully carried out with an infusion of wormwood. For this, wormwood is harvested from the moment of its flowering, dried and stored in the attic. To prepare the infusion, finely chopped plants are placed in a cauldron (half or 3/4 of the volume) and poured with water; after a day, boil for 30 minutes, cool, filter through gauze and dilute with the same amount of water. Spray trees with an interval of 10-12 days.
This method is effective, and in combination with light traps, it allows you to save the crop without the use of poisons.
19:987There is another way to deal with the apple codling moth. In the garden, immediately after flowering, hang jars of apple syrup seasoned with yeast. You can prepare it from apple juice of dry or green fruits, previously mashed together with the rotting part. Butterflies fly on such syrup and die in it.
19:1567Plant repellent plants nearby: garlic, wormwood.
19:118From slugs and snails
19:168
A good neighbor for strawberries is parsley, if you sow it with a border around strawberry beds, then they will not be afraid of snails and slugs.
20:934Spread wet rags or burdock leaves between the rows of plants on which snails have become accustomed, in the morning the mucus will hide under their shadow, and you will go and collect them in the morning.
20:1249Arrange saucers with dark beer for the night in the aisles of strawberries. Pour beer somewhere up to a height of 1.5 -2 cm so that the slugs drown.
20:1490Sand and sawdust. Snails cannot crawl on sand and sawdust, so a sawdust and sand circle around the plant can be very effective.
20:1770An ordinary cup of coffee will scare away pests and will not harm plants. USDA research staff in Hilo, Hawaii, tested caffeine sprays on houseplant-eating slugs. They noticed that a 1–2% solution of caffeine killed almost all snails and slugs in two days, while lower concentrations (about 0.01%) repelled them.
For comparison, a cup of instant coffee contains approximately 0.05% caffeine, coffee brewed from ground beans has even more. Coffee grounds can also be used as a snail repellent, but spraying with a caffeine solution is much more effective: slugs crawl away as soon as they come into contact with caffeinated soil.
20:1308Caffeine can kill small snails and slugs, and scare large ones away from the garden. It is best to use caffeine for small gardens and plots. Unfortunately, it can act not only on snails and slugs, but also on beneficial insects. High concentrations (from 2%) can damage foliage and cause yellowing of plants.
20:1921To kill snails (slugs), the surface of the soil should be sprinkled with freshly slaked lime powder, in the amount of 40 quarters per tithe. Sprinkling of the soil with lime is carried out in 2 steps in the interval of 10-15 minutes. At the first sprinkling, the snail is protected from lime by secreting mucus from itself, while at the second sprinkling, the snail is no longer able to excrete mucus, turns black and dies. Sprinkling the soil with lime in this way for two days in a row, in the morning, you can finally destroy all the snails.
20:888
Sprinkle the earth in the evening or in wet weather with finely crushed iron sulphate mixed with sand. None of these animals will pass where iron vitriol is poured, since they die from contact with this substance.
21:1828Hedgehogs, frogs and toads eat slugs and snails with great pleasure. True, in the conditions of our sites, quite often these natural enemies simply have nowhere to stumble, and therefore they bypass the gardens.
As for hedgehogs, there is definitely no place for them on 6 acres: it’s too crowded and noisy. And frogs and toads can be completely lured to your site by making some mini-shelters for them in the form of piles of leaves and branches, or even digging a small pond.
21:863Perhaps the simplest remedy is to sprinkle (or, rather, pollinate) the aisles with lime after rain or watering, when the slugs begin to move actively. Getting on strips of lime, they burn their abdomen and die. You can take not pure lime, but mixed with ash or tobacco dust (1: 1). In the absence of rain, the soil is treated in this way late in the evening or at night, when slugs are on the soil or on plants.
Soil treatment is periodically repeated (after 7-15 days), which leads to the gradual death of mollusks.
21:1829Plant nearby repellent plants: fennel, garlic, rosemary, parsley, oak bark.
21:160From the scoop
21:189
Butterflies can be caught using fermenting kvass (dilute it 3 times and add some yeast). Jars with bait are hung in plantings. Butterflies can also be caught on fermenting molasses (bred 3 times, poured into bowls).
22:1137To use an effective and harmless biological method for combating scoops - a Trichogramma predator that destroys pest eggs. During the laying period, carry out a three-time release of Trichogramma (30-40 thousand individuals per 1 ha with each release) with an interval of 5-6 days.
22:1629Against caterpillars of younger ages of each generation of scoops, apply biological preparations: concentrated lepidocide, BA (biological activity) - 2000 EA / mg - 40-50 g per 10 l of water (1.5-2 kg / ha); bitoxibacillin, BA - 1500 EA / mg - 50 g per 10 liters of water (2 kg / ha). If necessary, re-treatment should be carried out after -8 days. (The working solution must be prepared immediately before the treatment of plants.
22:725Caterpillars of younger ages can be destroyed with an infusion of wormwood. 1 kg of dried and crushed mass of wormwood is added to a small amount of water, boiled for 10-15 minutes, then the solution is cooled, filtered and diluted with water to 10 liters. Spraying of plants is carried out several times at intervals of 7-10 days.
22:1280Plant nearby repellent plants: amaranth, oak bark, geranium, marigolds, kosmeya.
22:1435From Medvedka
22:1471
The best way to deal with this insect is to invite a mole to the charged area :). Moreover, both have a similar habitat - both love light, soft soil, and a mole bear is a delicacy.
23:401In areas infected with a bear, it is impossible to feed plants with fresh mullein - it will attract a pest from all over the area. Diluted bird droppings, on the contrary, scare away the bear (you need to water the ground with infusion of chicken droppings in dry weather).
23:859Marigolds sown along the borders of the site block the access of the bear from neighboring territories - the bear does not tolerate the smell of marigolds.
23:1109In autumn, when the soil temperature is not lower than +8 degrees, it is recommended to dig trapping pits 50-60 cm deep in the areas infected with the mole cricket (at least two pits are dug per 100 square meters of territory), covering the bottom and walls of the pits with an old film and filling the pits with semi-rotted manure - in them the bear climbs for the winter. With the onset of persistent frosts, manure with bears is scattered over the surface of the earth and the bears die from the cold. After the soil temperature drops to +5 degrees and below, the bears become inactive and mainly settle in a vertical course - this must be taken into account when making trapping pits, without postponing their digging until late autumn.
23:2345In the spring, after mid-May, on the eve of the egg-laying period of the bear, it is recommended to dig shallow holes on the site and fill them with fresh manure or chopped straw, or simply lay out heaps of manure on the surface of the earth. Medvedki crawl into manure for laying eggs; the larvae hatching from the eggs do not leave the nests in heaps at first and feed on manure. After 3-4 weeks, the manure, together with the larvae, is removed and burned, or placed in specially equipped pits.
23:844In the spring, before the emergence of seedlings of plants, baits are prepared for the bear from grains of corn, barley, rye, and wheat. It is important to prepare and lay out the bait just before the emergence of seedlings - otherwise the bears begin to feed on young plants and almost do not eat the bait.
23:1349The grain is steamed until swelling and dusted with aldrin powder (50 g of powder per 1 kg of dry grains). Up to 0.8 kg of seeds are consumed per 1000 square meters, evenly distributing them over the soil surface, covered with a rake and watered. Zinc phosphide is also used as a poison (for 1 kg of dry grain - 50 g of the drug, adding 3% sunflower oil); mix thoroughly and close up to a depth of 3-5 cm. Medvedki find bait by smell, eat it and die. Poisoned insects are regularly collected from the surface of the earth and destroyed so that they are not pecked and poisoned by birds. (AGAIN CHEMISTRY!)
23:2423In the summer, this method of dealing with the bear is also used: a few drops of sunflower oil are poured into the opening of the bear's stroke and 1-2 liters of water are immediately poured from the watering can. After a few minutes, the bear comes to the surface of the soil and dies.
23:446Plant nearby repellent plants: marigolds, garlic.
23:554From aphids
23:580
In addition to special preparations for combating aphids, which are sold in stores, various infusions are also used, which are prepared on the basis of available means. These methods of struggle are harmless, environmentally friendly.
24:1479Soap solution. Dissolve 25-30 g of laundry soap in 1 liter of water (soft).
24:1620Ash-soap solution. Pour 30 g of soft wood ash (or 15 g of hard wood) into 1 liter of hot water, bring to a boil, strain the solution and dissolve 25-30 g of laundry soap in it.
24:344Dry mustard. 60 g of powder is brewed with a liter of water and insisted for three days in a tightly closed container, dissolving the infusion in three liters of water, spray the plant.
24:643Infusion of wood ash: 3 kg of wood ash is poured into 10 liters of hot water, kept for two days, filtered and sprayed or washed with plants.
24:912Ash decoction: 2-3 kg of wood ash is poured into 10 liters of water, boiled for 30 minutes, settled and plants are treated with a cooled solution.
24:1147Infusion of garlic: 200-300 g of unpeeled garlic heads are finely chopped and poured with two liters of water. After a day, the mass is squeezed out, 8 liters of water and 20-30 g of laundry soap are added to the solution. For the treatment of plants, the prepared solution is diluted: 8 liters of water are added to two liters of the solution.
24:1657Infusion of onion or garlic. 100 g of onion peel or 75 g of finely chopped onions or garlic, insist under a lid in 5 liters of water during the day, strain. Spray 3 times at weekly intervals.
24:352Tobacco infusion: 400 g of tobacco or shag are infused in 10 liters of hot water for two days (you can insist for a day and then boil for 2 hours). Before spraying, the infusion is filtered, if boiled, it is diluted with water (1: 1), and 30-40 g of laundry soap is added.
24:807Infusion of potato tops: green, disease-free tops of 1-2 kg are infused for 3-4 hours in water (the tops are placed tightly in a container and poured with water to cover the tops). Use freshly prepared infusion.
24:1216Coniferous infusion: 200 g of pine or spruce needles are crushed, poured with 2 liters of warm water, insisted for 6 days in a tightly closed container, then squeezed and filtered. Before processing, dilute with water up to 20 liters. Plants are treated with an interval of 3-7 days.
24:1683Pepper infusion: 1 kg of raw or dried peppers are boiled for 1 hour in 10 liters of water in a sealed container. Insist for two days, filter. To treat plants, 0.5 l of infusion is diluted with 10 l of water and 40 g of laundry soap are added.
24:401Infusion of citrus peels: 100 g of dry tangerine, orange or lemon peels, pour 1 liter of warm water and insist under the lid for 3 days. How to use: Spray the plant as needed.
24:772Tar soap - 40 g of soap per 1 liter of water.
All infusions are designed for a large number of plants and a huge amount of water. But these proportions can always be converted to the amount you need.
24:1123Aphids are eaten by adults and ladybug larvae, hover flies, lacewings, and several species of wasps. To naturally attract these insects, as well as birds, to your garden, plant fragrant herbs, nettles, and green manure.
24:1573Plant plants that are attractive to aphids away from crops that you want to protect against these pests. Aphids especially love nasturtium, cosmea, sleeping pills, mallow, tuberous begonias.
24:367Kalina and linden are favorite aphid trees. Never plant valuable aphid-attacked crops in the vicinity of these trees.
24:623Some plants repel aphids. Among them are traditional onions and garlic, as well as Dalmatian chamomile.
24:817Plant nearby repellent plants: catnip, coriander, chives, fennel, garlic, marigolds, mustard, nasturtium, mint.
The opinion that at home plants cannot become infected with diseases or be attacked by insects is erroneous. In an isolated room, the risks are certainly less than in the open air, but they are still there.
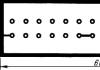
In order to identify such troubles in time, you need to regularly monitor the plants. You can, for example, hang Velcro tapes for insects near the hydroponic installation and from time to time study and record their “catch” ( Rice. 39).
If you find pests, take action against them immediately if you do not want to lose your crop.

Rice. 39 Velcro for detecting the presence of insects
The most common insect pests include: aphids, whiteflies, spider mites, miner moths, thrips. It is not easy to identify a pest and here one cannot do without special literature, but choosing the right way to deal with it is much more difficult.
In general, there are two ways:
- natural biochemicals;
- Beneficial insect predators;
Natural, and therefore safe, chemicals include extracts of some plants.
For example, finely crushed garlic helps a lot in the fight against whiteflies. Celandine collected during flowering helps against thrips. You can use an infusion of onion peel, garlic, tomato leaves in the fight against aphids. All of these are natural insecticides in pest control.
Also on sale you can find special ready-made solutions to combat various insects. They are sold as sprays or solutions. Some growers advise adding a little sugar to their composition as an additional bait for insects.
Biosubstances are sometimes used to treat plants for fungal and other diseases.

Rice. 40 There are 1500 live ladybugs in a bucket
Do not be afraid of all these pests. If you take proper care of your plants, you will, at worst, encounter only a few of them.
Regularly carry out wet cleaning of the room with disinfectants. Wash your hands before handling plants. Wipe down all the tools you work with. It is worth wiping the equipment located near the plants (lamps, fans, etc.).