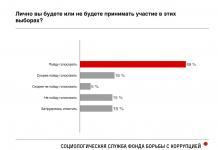
Talking about what value added tax (VAT) is is not the most difficult task, unless you go into details. Basic knowledge on this issue will not be superfluous not only for future accountants and economists, but also for people far from such specific areas of activity.
Economic content of VAT
VAT is one of the taxes in Russia that has a significant impact on the formation of the state budget. The essence of the tax is fully reflected by its name. That is, it is from the added value by which the manufacturer increased the value of the original product (raw materials or semi-finished product) that it is accrued.
For “dummies”: VAT is a tax that is assessed and paid by manufacturing enterprises, wholesale and retail trade organizations, as well as individual entrepreneurs. In practice, its size is determined as the product of the rate by the difference between the revenue received from the sale of one’s own products (goods, services) and the amount of costs that were used for its production. Simply put, that part of the product that the manufacturer or seller “increased” to the original product (in fact, this is the newly created value) is the taxable base. This type of tax is indirect, as it is included in the price of the product. Ultimately, it is paid by the buyer, and formally (and practically) its payment is made by the owners and producers of the goods.
Objects of taxation
Objects for calculating VAT are revenue from the sale of created products, works and services performed, as well as:
The cost of ownership of goods (work, services) when they are transferred free of charge;
The cost of construction and installation work carried out for one’s own needs;
The cost of imported goods, as well as goods (work, services), the transfer of which was carried out on the territory of the Russian Federation (it is not included in the taxable income tax base).
VAT payers
Article 143 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that VAT payers are legal entities (Russian and foreign), as well as individual entrepreneurs registered with the tax authorities. In addition, payers of this tax include persons moving goods and services across the borders of the Customs Union, but only if customs legislation establishes the obligation to pay it.
In Russia, VAT is provided in 3 options:
- 10 %.
- 18 %.
The amount of accrued tax is determined by the product of the interest rate divided by 100 by the taxable base.

Non-operating turnovers (deposit transactions for the formation of the authorized capital, transfer of fixed assets and property of the enterprise to the legal successor, and others), transactions for the sale of land plots and many others enshrined in law are not recognized as objects for the calculation of this tax.
18% VAT rate
Until 2009, the VAT rate of 20% was applied to the largest number of transactions. The current rate is 18%. To calculate VAT, you need to calculate the product of the tax base and the interest rate divided by 100. Even simpler: when determining (for dummies) VAT, the tax base is multiplied by the tax rate coefficient - 0.18 (18% / 100 = 0.18). Thus, the amount of VAT is included in the price of goods, works and services, falling on the shoulders of consumers.

For example, if the price of a product without VAT is 1000 rubles, the rate corresponding to this type of product is 18%, then the calculation is simple:
VAT = PRICE X 18/ 100 = PRICE X 0.18.
That is, VAT = 1000 X 0.18 = 180 (rubles).
As a result, the selling price of goods is the calculated cost of the product including VAT.
Reduced VAT rate
A 10% VAT rate applies to a certain group of food products considered socially significant for the population of the state. Such products include milk and their derivatives, many cereals, sugar, salt, seafood, fish and meat products, as well as some types of products for children and diabetics.
Zero VAT rate, features of its application
A rate of 0% applies to goods (work and services) related to space activities, sales, mining and production of precious metals. In addition, a significant volume of transactions consists of transactions for the movement of goods across the border, the registration of which must comply with the Zero VAT rate requires documentary evidence of export, which is provided to the tax authorities. The package of documents includes:
- An agreement (or contract) of a taxpayer for the sale of goods to a foreign person outside the Russian Federation or the Customs Union.
- for the export of products with a mandatory mark from Russian customs about the place and date of departure of the goods. You can submit documents on transportation and support, as well as other confirmation of the export of any products outside the borders of the Russian Federation.
If, within 180 days from the moment of movement of goods across the border, a complete package of necessary documents is not completed and submitted to the tax office, then the payer is obliged to accrue and pay VAT at an 18% (or 10%) rate. After the final collection of customs confirmation, it will be possible to refund or offset the tax paid.
Using Estimated Rate
The estimated rate is used for prepayment and in some other cases. For “dummies”, VAT at this rate is calculated when it is necessary to separate out the tax “sitting” in it from the total cost of the goods. This action is carried out according to the simplest formulas, depending on the type of VAT rate applied.
At a 10% rate, VAT calculated is 10% / 110%.
At an 18% rate - 18% / 118%.

Filling out a VAT return and deadlines for submitting it
At the initial stage of preparation for filing tax reports, the accountant’s work is focused on determining the base on which the tax amount is subsequently calculated. Filling out a VAT return begins with the design of the title page. In this case, it is very important to carefully and carefully enter all the required details (names, codes, types, etc.). All pages contain the date and signature of the manager (or individual entrepreneur), which must be stamped on the title page. The declaration must be submitted to the tax office at the place of registration, but no later than the 20th day of the month following the reporting quarter. Its payment is also established within the same deadlines (if the deadline is quarterly). Thus, payment and accrual of tax for the 1st quarter of 2014 had to be made before April 20 of the current year.
Tax calculation
For dummies: VAT payable is calculated in several stages.
- Determination of the tax base.
- VAT accrual.
- Determination of the amount of tax deductions.
- The difference between the accrued and paid tax (deduction) is the amount of VAT payable.
If deductions exceed accrued amounts, the taxpayer has the right to compensation for this difference upon written application and after a decision is made, but more on that later.
Tax deductions
Particular attention should be paid to deductions, that is, the amount of VAT that is presented by suppliers and also paid at customs when exporting goods. It is very important that the tax accepted for deduction is directly related to the accrued turnover. Simply put, if VAT is charged on turnover on the sale of product “A”, then all purchases related to this product are taken into account. Confirmation of the right to deduct is certified by invoices received from suppliers, as well as documents for payment of tax amounts when crossing the border. VAT is included in them as a separate line. Such invoices are filed in a separate folder, and turnover for each product is recorded in the purchase book according to the approved form.

During tax audits, questions often arise regarding the improper completion of required fields, the indication of incorrect details, and the absence of signatures of authorized persons. As a rule, in such a situation, employees of the Federal Tax Service cancel the corresponding amounts of deductions, which leads to additional VAT charges and penalties.
Electronic submission of declarations
Since 2014, VAT returns must be submitted only electronically. There are only a few exceptions related to special tax regimes.
Conditions for VAT refund
Satisfaction of the rights of payers to reimbursement of the amount of tax paid is carried out on the basis of a desk audit carried out by the tax authorities. The declarative procedure for VAT refund occurs in relation to a few payers who meet the following conditions:
The total amount of taxes paid (VAT, excise taxes, income taxes and production taxes) must be at least 10 billion rubles. for the 3 calendar years preceding the year in which the application for compensation was submitted;
The payer received a bank guarantee.

The application of this procedure provides for one more condition: the payer must be registered with the tax authorities of the Russian Federation for at least 3 years before filing a tax return for
Refund procedure
To receive a VAT refund, the taxpayer must submit a written application to the tax authority for the refund of tax amounts. These amounts can be returned to the current account indicated in the application or offset against other tax payments (if there are debts on them). The inspectorate will make a decision within 5 working days. VAT refunds are made within the same period in the amount specified in the decision. If funds are not received into the current account on time, the taxpayer has the right to receive interest for the use of this money from the tax authorities (from the budget).
Desk inspection
To verify the validity of the returned amounts, the tax inspectorate conducts a desk audit within 3 months. If facts of violations are not established, then within 7 days after completion of the inspection, the person being inspected is informed in writing about the legality of the offset.

If violations of the current Russian legislation are detected, the inspectorate draws up an inspection report, based on the results of which a decision is made against the taxpayer (either to refuse to attract, or to hold accountable). In addition, the violator is required to return the excess amounts of VAT and interest for the use of these funds. If the specified amount is not returned, the obligation to return it to the budget of the Russian Federation rests with the bank that issued the guarantee. Otherwise, the tax authorities write off the necessary funds in an indisputable manner.
Some provisions relating to the calculation and payment of VAT are quite complex for immediate understanding, but thoughtful understanding gives results. Particular difficulty in understanding this tax is created by specific terms and regular changes in the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Among the variety of taxes and fees intended for mandatory calculation by business entities, VAT occupies a special place. The specificity of this tax lies in the complexity of its correct calculation, and in the ambiguity of the interpretation of the provisions of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code, which is subject to regular changes.
Over the 25 years that have passed since the introduction of the Law on Value Added Tax, many legal provisions relating to VAT have been subject to serious revision.
But over the past 10 years, the current tax rates listed in Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation have remained stable.
When and who is required to pay VAT?
The definitions given by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation fix the indispensable participation in the formation of the budget at the expense of VAT in specific situations:
- provision of services, sale/transfer of goods or the right to use assets under any form of agreement;
- performing construction, installation or equivalent work;
- the above-mentioned works, services or transfer of valuables for personal use;
- importation of goods or products from abroad.
Subjects for mandatory VAT payment are:
- organizations or individual entrepreneurs engaged in commerce or production using OSNO;
- non-profit companies – in case of realization of rights to property;
- banking and insurance structures;
- separate divisions and branches of organizations that sell services or products;
- customs intermediaries.
Why is VAT needed?
The very name of the tax implies that a share of the added value arising at all stages of the sale of one’s own products, goods purchased for resale, or services provided is withdrawn from the budget. This is how the main function of VAT is implemented - fiscal.
If you trace the chain from the manufacturer of a product to its final buyer, it turns out that the process of shifting the tax will end only at the moment the product is purchased by the consumer who is the last in this scheme. The regulatory function of VAT is manifested in the formation of the consumer market, since the real payer of the tax is not an LLC or individual entrepreneur, but a living buyer.
VAT, as a regulator of the consumption market, cannot be too high, since in this case, due to extremely high prices, the demand for goods and services will fall. This factor will invariably lead to a weakening of the economic position of both individual business entities and industries as a whole.
VAT rates
Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determined the use of several percentage tax rates - 0%, 18% and 10%. The law clearly spelled out cases of possible application of one or another tax rate. In addition, tax legislation stipulates the circumstances when the amount of VAT is calculated by calculation.
When is VAT 0%?
Taxing at zero rate provided for LLCs or individual entrepreneurs engaged in clearly defined types of activities:
- transfer of energy resources outside Russia;
- international transportation of goods and passengers with luggage;
- transportation of gas and oil;
- transportation of passengers and cargo in railway cars that are on the balance sheet of the organization;
- services provided by water transport;
- work related to space activities;
- air transportation of people and luggage to Crimea and Sevastopol from March to December;
- movement of goods across the Russian border.
Important: To legally use the zero VAT rate, a transport expedition agreement must be drawn up instead of a standard agreement on the transportation of goods.
Tax authorities give the opportunity to entities that have indicated in their declarations revenue from preferential customs operations at a 0% rate, within six months confirm your right relevant documents. These include:
- photocopies of contracts with foreign partners;
- goods or shipping waybills;
- register of customs declarations or individual declarations.
The six-month period for collecting supporting documents begins from the moment the cargo crosses the border and the corresponding mark is placed on the accompanying papers.
If the taxpayer does not provide the established package of documents to the tax authority, then revenue from the provision of international transport services will be taxed at the standard rate of 18%.
Options for using a reduced rate of 10%
The 10% VAT tax rate is used in cases where sales are subject to strict certain product categories social orientation and only one type of service – air transportation throughout the country.
The Tax Code allows the use of a reduced VAT tax rate for sales transactions with the following products:
- food group of goods, excluding delicatessen products;
- subcategory of children's goods, except sports shoes;
- stationery for school purposes;
- periodicals, textbooks and scientific literature;
- goods related to medicine.
It is the question of eligibility for inclusion in a preferential group with a reduced VAT rate that raises the greatest number of questions among taxpayers and fiscal authorities.
How to check the legality of the 10% VAT rate
If a product is purchased for resale, then questions about the possibility of applying a reduced VAT rate, as a rule, do not arise. All products are supplied according to accompanying documents, including invoices, which indicate the applicable tax rate.
The situation is more complicated when an LLC or individual entrepreneur independently produces commercial products, which, according to formal criteria, are subject to preferential VAT taxation. In such situations, it is advisable to adhere to regulatory documentation - lists of product codes established by the relevant Government Decrees in the latest edition.
These registers indicate codes and names of product groups from the preferential tax list. The OKP code is selected in the All-Russian Classifier and is confirmed by a certificate or declaration of conformity.
You should know: If the manufacturer cannot find the product being sold in the list of codes, then it would be more reasonable to indicate the general VAT rate - 18%. Otherwise, there is a risk of additional tax assessment during an audit by the fiscal authorities.
When the tax office may refuse to apply a preferential VAT rate
When selling packages that contain groups of goods with different VAT rates, the use of a reduced percentage may lead to justified claims from the tax authority.
Example 1
To increase sales, trading organizations often use a sales scheme for self-assembled kits, where goods are subject to VAT at different rates. For example, on the eve of the New Year holidays, a huge number of children's gifts appear on sale, containing candy and toys. Confectionery products (sweets) are subject to VAT at the rate of 18%, and children's toys belong to a preferential group of goods.
The Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service considers the use of a 10% VAT rate on a New Year's gift set when setting the price to be an illegal action, since the list of codes of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 597 dated June 18, 2012 does not contain such a position.
A similar situation may arise, for example, when selling specialized magazines with the provision of an additional service - access to a web resource or electronic media. In this case, the 10% rate applied to printed products can only be applied directly to the magazine. The service of virtual news publication should be taxed at the standard rate of 18%.
Keep in mind! To avoid tax claims when selling sets with different VAT percentages, it is advisable to indicate in the documents and on the price tag the individual product items included in the set.
Example 2
Sales of bakery products are carried out using a reduced VAT rate of 10%. When updating the product range, you should be careful about the names of new products. For example, the term "pizza" not in the list of OKP, therefore, despite actual compliance with the letter of the law, for formal reasons the manufacturer must apply a rate of 18% when selling pizza.
Conclusion: It is advisable to choose a name for a new product for which it is planned to apply a preferential VAT rate, being as close as possible to the terms used in regulatory documents - lists of OKP approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Simple names will not give tax authorities grounds to refuse to use the reduced tax rate.
How to correctly apply the estimated VAT rate
The use of the estimated VAT rate - 18%/118% or 10%/110% - is stipulated in Article 164, paragraph 4 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is allowed in the following situations:
- when issuing an invoice for the received advance payment;
- when calculating VAT by a tax agent;
- when using an assignment agreement (assignment of monetary claims).
The calculation assumes that the amount of the advance received or the monetary claim accepted already includes the amount of tax, which should be calculated by simple arithmetic operations.
The most common option for isolating the VAT amount is to draw up an invoice for the advance received.
How not to overpay VAT on an advance payment
When issuing an invoice for prepayment received for the supply of goods taxed at different rates (10% and 18%), the tax department insists on applying the maximum rate - 18%/118%. However, an LLC or individual entrepreneur does not always know in advance the exact list of goods that will be shipped against the received advance payment.
Because of this, there is often an overpayment of VAT, the return of which is problematic.
The right to a deduction for the supply of goods at a rate of 10% will most often not be approved by the tax office, so it makes sense for the taxpayer to defend his truth in court in advance. It must be said that the Arbitration Courts, when considering such claims, side with the enterprise.
Important to know: When selling goods at different VAT rates, it is advisable to group goods with the same VAT rate in prepayment invoices (or specifications for the supply agreement).
Then the taxpayer can legally claim a tax deduction at the appropriate rate without resorting to court.
Incorrect application of the VAT rate is fraught for the taxpayer with additional tax assessment and the presentation of significant fines and penalties.
Since tax legislation is constantly changing, it is necessary to constantly monitor innovations regarding VAT.
- when implementing works and services (except for services for the transfer of breeding livestock and poultry under leasing agreements with the right to buy);
- when transferring goods (performing work, providing services) for one’s own needs, the costs of which are not taken into account when calculating income tax (except for the transfer of goods subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent);
- when performing construction and installation work for one’s own needs;
- when importing goods, the sale of which is not taxed at a rate of 10 percent (the import of which is not exempt from taxation).
This procedure is provided for in paragraphs 3 and 5 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Situation: At what rate should VAT be charged when selling printed products with a CD or electronic attachment - 10 or 18 percent? Printed products are not of an advertising (erotic) nature.
When selling printed products complete with CDs or electronic applications (for example, with a password to access a site with an archive of numbers), VAT is charged at a rate of 18 percent.
This is explained as follows. Only those types of printed products that are listed in the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 23, 2003 No. 41 are taxed at a rate of 10 percent. Sets of printed products with CDs or electronic applications are not listed in this list. Consequently, when selling such kits, the organization has no reason to apply a rate of 10 percent. Similar clarifications are contained in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 7, 2014 No. 03-07-11/56215, dated November 11, 2009 No. 03-07-11/297.
Advice: There are arguments that allow organizations to charge VAT at a rate of 10 percent when selling printed products complete with CDs or electronic applications. They are as follows.
If a CD or electronic supplement is an integral part of a magazine, its sale in conjunction with a printed publication may be subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent. Confirmation that the CD or electronic supplement is included as an integral part of the magazine is:
- mention of a CD or electronic supplement in the content of the magazine;
- linking the content of the CD or electronic application with the content of the magazine;
- sale of a CD or information for access to an electronic application in a single individual package with the magazine;
- no separate price for CD.
If these conditions are met, the supplement to the magazine in the form of a CD does not deprive the magazine of the characteristics of a periodical printed publication, the sale of which is subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent. In arbitration practice there are examples of court decisions that confirm the legitimacy of such a conclusion (see, for example, decisions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated December 10, 2012 No. A40-56031/12-91-312 and dated August 12, 2003 No. KA-A40 /4614-03).
When selling imported printed publications brought into Russia complete with CDs, organizations also have the right to apply a VAT rate of 10 percent. The fact is that when importing such kits into Russia, a single HS code is indicated in customs documents. If this code corresponds to the codes indicated in the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 23, 2003 No. 41, there are no grounds for applying a VAT rate of 18 percent when selling such kits (letter of the Federal Customs Service of Russia dated May 26, 2006 No. 05-11 /18275).
To avoid possible disputes with the tax office, it is more profitable for an organization to sell printed products with CDs or electronic applications separately, rather than as a set. To do this, state in the contract that not a single set is being sold, but two independent goods - a printed publication and a CD or electronic application. Set separate prices for them, and in the primary documents, highlight each product in a separate line with different VAT rates. At the same time, organize separate accounting for the sale of printed products and CDs, taxed at different rates (paragraph 4, paragraph 1, article 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If a CD included in a printed product is not related to its content and is of an advertising nature, the sale of such discs is not subject to VAT. But for this, the following condition must be met: the cost of purchasing (creating) each disk should not exceed 100 rubles. (subparagraph 25, paragraph 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated April 29, 2009 No. 16-15/042432). If this condition is met and printed products are included in the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 23, 2003 No. 41, then when they are sold together with advertising CDs, the VAT tax rate is 10 percent (subclause 3, clause 2, art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation: At what rate should VAT be charged when selling legal reference journals in electronic form (for example, via the Internet)? Magazines have a printed version. The organization is not a news agency.
When distributing reference and legal journals in electronic form, charge VAT at a rate of 18 percent (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This is explained as follows.
Goods, sales transactions of which are subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent, are defined in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. These, in particular, include periodicals (with the exception of periodicals of an advertising or erotic nature). Their specific types are indicated in the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 23, 2003 No. 41. At the same time, paragraph 5 of clause 1 of the notes to this list states that periodicals, the sale of which is subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent, do not include periodical printed publications in electronic form, distributed, in particular, on magnetic media, via the Internet, and via satellite communication channels. The exception is the distribution of such publications by news agencies.
Therefore, if an organization that is not a news agency distributes legal reference journals in electronic form (for example, via the Internet), you pay VAT at a rate of 18 percent (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An example of how VAT calculation operations are reflected in the accounting records of a commercial organization when distributing reference and legal journals in electronic form (for example, via the Internet) on a paid basis. The publisher is not a news agency
Alpha LLC is engaged in publishing activities and publishes a reference and legal journal. Alpha has a certificate from Rospechat confirming that the magazine belongs to preferential types of printed materials.
Alpha distributes the publication as follows:
- printed version - through the direct mailing system (money from subscribers goes to Alpha's bank account);
- electronic version - on the Internet.
The monthly subscription price for both the printed and electronic versions of the publication is 100 rubles. The printed version of the publication is subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent, the electronic version - 18 percent.
Therefore, the amount of VAT that Alpha imposes on subscribers is:
- for the printed version - 10 rubles. (RUB 100 × 10%);
- for the electronic version - 18 rubles. (RUB 100 × 18%).
Thus, the subscription price (including VAT) is:
- for the printed version of the publication - 110 rubles. (100 rub. + 10 rub.);
- for the electronic version of the publication - 118 rubles. (100 rub. + 18 rub.).
In February, Alpha sold 1,000 subscriptions to the printed version of the publication and 100 to the electronic version. Alpha's accountant made the following entries in accounting:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
- 110,000 rub. (110 rubles/subscription × 1000 subscriptions) - revenue from the sale of subscriptions to the printed version of the publication is reflected;
- 10,000 rub. - (10 rubles/subscription × 1000 subscriptions) - VAT is charged on the proceeds from the sale of subscriptions to the printed version of the publication;
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
- 11,800 rub. (118 rubles/subscription × 100 subscriptions) - revenue from the sale of subscriptions to the electronic version of the publication is reflected;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
- 1800 rub. - (18 rubles/subscription × 100 subscriptions) - VAT is charged on the proceeds from the sale of subscriptions to the electronic version of the publication.
Situation: At what rate should VAT be charged on the sale of dry bread kvass - 10 or 18 percent?
When selling dry bread kvass, VAT is charged at a rate of 18 percent.
The list of food products subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2004 No. 908. Dry bread kvass, which has code 91 8536 according to the All-Russian Product Classifier, is not included in it. Therefore, when selling dry bread kvass, you pay VAT at a rate of 18 percent.
Situation: At what rate should VAT be charged on the sale of mushrooms (for example, champignons grown in a greenhouse) - 10 or 18 percent?
When selling mushrooms, charge VAT at a rate of 18 percent.
The list of food products subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2004 No. 908. Greenhouse champignon mushrooms, having code 97 3561 according to the All-Russian Product Classifier, are not included in it. Therefore, when selling them, you pay VAT at a rate of 18 percent.
An example of how transactions for calculating VAT on the sale of mushrooms are reflected in the accounting records of a commercial organization
Alpha LLC is engaged in the wholesale sale of agricultural products purchased from citizens who are not entrepreneurs. The organization purchases mushrooms (champignons grown by citizens in their own greenhouses) at a price of 50 rubles. for 1 kg.
On January 13, Alpha sold a batch of mushrooms to the retail chain - 100 kg. The selling price of 1 kg of mushrooms (excluding VAT) was 100 rubles/kg. Consequently, the total price of the lot without VAT is 10,000 rubles. (100 kg × 100 rub./kg).
Sales of mushrooms are subject to VAT at a rate of 18 percent. However, if an organization sells agricultural products or processed products purchased from the population, the VAT tax base is determined as the difference between the market price and the purchase price of these products (Clause 4 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Products for the sale of which this procedure is applied are indicated in the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 16, 2001 No. 383. Cultivated and wild (fresh) mushrooms are included in this list. Therefore, the accountant calculated the amount of VAT on their sale as follows:
Such rules are established in paragraph 4 of Article 154 and paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The amount of VAT that Alpha presented to the buyer was:
100 kg × (100 rub./kg - 50 rub./kg) × 18/118 = 763 rub.
Thus, the total cost of a batch of mushrooms (including VAT) is 10,763 rubles. (RUB 10,000 + RUB 763).
The money from the buyer for the sold batch of mushrooms was transferred to Alpha’s bank account on January 18.
Alpha's accountant made the following entries in the accounting.
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
- 10,763 rub. - revenue from the sale of a consignment of goods is reflected;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
- 763 rub. - VAT is charged on sales proceeds.
Debit 51 Credit 62
- 10,763 rub. - received money from the buyer in payment for the sold batch of goods.
Situation: At what rate should VAT be charged on the sale of roasted sunflower seeds - 10 or 18 percent?
When selling roasted sunflower seeds, charge VAT at a rate of 18 percent (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This is explained as follows.
The list of food products subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2004 No. 908. Oilseed processing products are not included in it. Therefore, when selling roasted sunflower seeds, VAT must be charged at a rate of 18 percent. This point of view is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 3, 2009 No. 03-07-07/11.
It is also supported by other regulatory agencies - the Federal Tax Service of Russia (letters dated August 6, 2009 No. ШС-21-3/824, dated December 17, 2007 No. ШТ-6-03/972) and Rostekhregulirovanie (letter dated August 4, 2008 No. EP-101-26/4432, which was brought to the attention of the tax inspectorates by letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 21, 2008 No. ШС-6-3/597). In their opinion, roasted sunflower seeds belong to group 91 4600 “Protein products, phosphatidic concentrates, oil kernels, oil seed processing products, natural glycerin, soap stocks” of the All-Russian Product Classifier. Assigning other OKP codes to these products (in particular, 91 4631 “Sunflower seed kernel” and 97 2111 “Sunflower for grain”) is unlawful. Since group OKP 91 4600 is not included in the List of food products subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent, VAT must be paid at a rate of 18 percent on the sale of roasted sunflower seeds.
Advice: There are arguments that allow paying VAT at a rate of 10 percent when selling roasted sunflower seeds. They are as follows.
Payment of VAT at a rate of 10 percent is provided, in particular, for the sale of oil seeds (subclause 1, clause 2, article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). A specific list of food products subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2004 No. 908. In particular, it includes groups of goods with code 97 2930 “Seeds and fruits of oilseeds and essential oils” (products with codes 97 2931 - 97 2933, 97 2936) and with code 97 2110 “Main oilseeds” (products with codes 97 2111 - 97 2115, 97 2117, 97 2118). In addition, roasted sunflower seeds can be assigned code 91 4631 “Sunflower seed oil kernel”. It is also included in the list. If any of the listed OKP codes are indicated in the technical documentation for the products sold, VAT can be charged at a rate of 10 percent.
In arbitration practice, there are examples of court decisions that recognize the legality of applying a 10 percent VAT rate on the sale of roasted sunflower seeds (see, for example, the rulings of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated April 23, 2009, No. VAS-5158/09, dated March 17, 2009 No. VAS-2690/09, dated April 28, 2007 No. 5052/07 and dated April 28, 2007 No. 5071/07, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District dated January 13, 2009 No. A14-3423/2008/40/33 , North Caucasus District dated December 9, 2008 No. F08-7451/2008, Volga-Vyatka District dated February 15, 2007 No. A39-2697/2006, dated February 8, 2007 No. A39-2699/2006, Moscow District dated May 18, 2010 No. KA-A41/4815-10, dated October 6, 2009 No. KA-A41/10434-09, Ural District dated March 3, 2009 No. F09-964/09-S2, dated February 25 2009 No. Ф09-686/09-С2, dated February 24, 2009 No. Ф09-565/09-С2, dated January 20, 2009 No. Ф09-10260/08-С2, dated September 15, 2008 No. Ф09 -6669/08-С2, dated September 2, 2008 No. Ф09-5676/08-С2, dated January 14, 2008 No. Ф09-11038/07-С2, West Siberian District dated November 10, 2008 No. Ф04- 6206/2008(13299-A03-34), dated August 1, 2005 No. F04-4975/2005(13526-A27-31)). The courts made such decisions if organizations had official documents (for example, certificates of conformity, catalog sheets, technical specifications for production), in which OKP codes were indicated for these products, allowing the application of a VAT rate of 10 percent.
Situation: At what rate should VAT be charged on the sale of canned sturgeon fish - 10 or 18 percent?
When selling canned sturgeon fish, VAT is charged at a rate of 18 percent.
Subclause 1 of clause 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that when selling seafood and fish products, including chilled, frozen and other types of processed fish, herring, canned food and preserves, you must pay VAT at a rate of 10 percent. The exception is delicious seafood and fish products, including sturgeon.
The same exception is contained in the section “Sea and fish products, including chilled, frozen and other types of processed fish, herring, canned food and preserves” of the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2004 No. 908, in which “ Other canned fish" (code 92 7160). Therefore, when selling canned sturgeon fish, you pay VAT at a rate of 18 percent (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Similar explanations are given by representatives of the tax service (see, for example, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated December 28, 2006 No. 19-11/115499).
Situation: At what rate should VAT be charged when selling a mixture of vegetable oils with food additives (for example, Soyuz 53) - 10 or 18 percent?
When selling mixtures of vegetable oils with food additives, charge VAT at a rate of 10 percent (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This is explained as follows.
The list of food products subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2004 No. 908. This list is compiled in accordance with the All-Russian Product Classification (OKP) and contains:
- codes of subgroups that include certain types of products;
- codes of specific types of products, the sale of which is subject to a VAT rate of 10 percent.
In the list of food products subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent, mixtures of vegetable oils are allocated to a separate subgroup with code 91 4190. In accordance with the OKP, this subgroup, in particular, includes the following types of products:
- 91 4195 - vegetable oil - mixture, unrefined;
- 91 4196 - vegetable oil - mixture, frozen;
- 91 4197 - vegetable oil - mixture, refined, deodorized;
- 91 4198 - vegetable oil - a mixture flavored with herbal additives.
Considering that the above classification covers all types of mixtures of vegetable oils, when selling such products, VAT should be charged at a rate of 10 percent.
Situation: At what rate should VAT be charged when selling a cheese brine product - 10 or 18 percent?
At a rate of 10 percent.
The list of food products subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2004 No. 908.
Code 92 2600 in the list includes products and canned milk containing milk. These include products listed in the All-Russian Classifier of Products (OKP) under codes 92 2610-92 2697. Thus, brine cheese products, which have code 92 2697 according to the classifier, are taxed at a rate of 10 percent.
Situation: At what rate should VAT be charged on the sale of blood and its components by state health care institutions (blood transfusion stations) - 10 or 18 percent?
When selling blood and its components, charge VAT at a rate of 18 percent (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This is explained as follows.
The list of codes for types of medical goods subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 15, 2008 No. 688 (subclause 4, clause 2, article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For other medical goods subject to VAT, a rate of 18 percent applies.
Blood and blood products are not included in this list. Therefore, when selling this type of product by government health care institutions (blood transfusion stations), VAT must be charged at a rate of 18 percent.
This conclusion is confirmed by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter dated August 2, 2011 No. 03-07-07/44.
Application of settlement rate
Use the estimated tax rate of 18/118 in the cases provided for in paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. These include, in particular:
- receipt of funds for upcoming deliveries of goods (works, services), taxed at a rate of 18 percent;
- sale of property taxed at a rate of 18 percent, recorded at cost including input VAT, etc.
It must be borne in mind that the relevant products are subject to VAT at a rate of 10% only if certain categories of goods are contained in decrees of the Government of the Russian Federation, specifying certain product groups. For example: to apply a 10% rate on medicines, registration certificates for specific names are required. If the registration certificate is missing or has expired, the application of the reduced rate is unacceptable. The VAT calculation scheme when applying a tax rate of 10% will be similar to the calculation of tax at a rate of 18%. For example: a store that is engaged in the wholesale sale of children's clothing has entered into an agreement to sell products in the amount of 100,000 rubles. In this case, the tax amount will be: VAT amount = 100,000 rubles. * 10% = 10,000 rub.
List of goods subject to a VAT rate of 10 percent
Are there cases when applying a 10% value added tax rate is not possible? Such cases are possible, since in order to apply a 10% VAT rate on medical products, you must have a registration certificate, and an up-to-date one, since if such a certificate has expired, then a 10% VAT rate cannot be applied. This situation is commented on by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in letters dated June 27, 2016.
No. 03-07-07/37262, dated June 27, 2016 No. 03-07-07/37250 (and in earlier similar clarifications). However, according to the resolution of the Moscow District Court of September 5, 2014 No. F05-9677/2014, there is a chance to defend your right to a reduced rate in court - if you did everything you had to do to register on time, and the registration was renewed from - for the registration authority. Read also the article: → “Tax benefits for VAT”.
VAT 10 percent: list of goods and services
In order to receive a reduced VAT rate of 10 percent, the taxpayer is required to provide evidence to the authorities that the product meets all requirements. Therefore, a certificate and declaration are provided to the tax office.
It is very important to ensure that the manufacturer has a valid certificate. Otherwise, after checking by the tax service, it will identify a discrepancy and charge additional tax.
In the case where a product is not subject to either zero or ten percent tax, then 18 percent is applied. It is important to understand that when importing goods, they are subject to the same rate as when selling within the country.
VAT 10 percent: list of goods It is important to understand that an entrepreneur or company will not always be able to obtain a tax reduction, because the VAT rate of 10 applies to certain groups of goods, which are fully described in Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Let's look at the list.
List of goods subject to VAT at the rate of 10%
Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payment of VAT at a rate of 10 percent is established on the sale of food products, children's goods, printed materials, and goods related to medicine. 1. Sales of food products, as provided for in subparagraphs 1 paragraph.
2 tbsp. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The list of these goods was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 2004 No. 908 and includes:
- livestock and poultry (live weight);
- meat and (or) meat products. The exception is gourmet food products (veal, tongues, tenderloin, premium sausages, smoked meats, baked beef and pork, canned food);
- milk and dairy food products.
VAT 0%, 10%, 18%
Goods for children:
- knitwear for newborns and children of nursery, preschool, junior and senior school age groups: outer knitwear, underwear knitwear, hosiery, other knitwear: gloves, mittens, hats;
- sewing products, including products made from natural sheepskin and rabbit (including products made from natural sheepskin and rabbit with leather inserts) for newborns and children of nursery, preschool, junior and senior school age groups, outerwear (including dress and costume groups) , underwear, hats, clothing and products for newborns and nursery children.
In what cases is the VAT rate of 10 percent used - list of goods
If the products being sold are of Russian origin, then it is imperative to find out the code according to the All-Russian Classifier of Products by Type of Economic Activities (OK 034-2014). When it is known, it is necessary to check it with the codes specified in the Tax Code for VAT 10%.
If a company uses imported products for sales, then it should take time to search for the HS code and also make sure that it is present in the list. In this case, the product is charged at a rate of 10%.
The importance of checking codes is very high. If you do not check their availability in time, you will have to pay 18% VAT. This usually happens in two cases: when the product contains codes that are not included in the list of the 10% rate, or in the case of a complete absence of codes.
Tax rates VAT 18%, 10%, 0%.
Info
VAT is one of the most significant taxes in the Russian Federation. It replenishes the country's federal budget. VAT is considered an indirect tax.
Attention
It falls on the shoulders of the end customers. Those. The more intermediaries (more precisely, the intermediary price) there are between the producer and the consumer, the higher the state income. No one thought, maybe this is why the state is so actively eliminating “outbidders”? But that's a completely different topic.
We will talk in more detail about VAT 10 percent (the list of goods taxed at this rate). But first, let’s talk about how the tax came about. The history of the appearance of tax in Russia In our country, VAT has been in effect since 1992.
Before this, there was a sales tax. But such a measure legally exempted many subjects from payment. Then the government of Yegor Gaidar introduced VAT. It was then regulated by a separate Federal Law, which was called “On Value Added Tax.”
VAT 10 percent: list of goods, in which cases it applies
An exception is made for garments made of genuine leather and natural fur, with the exception of natural sheepskin and rabbit;
- shoes (except for sports): booties, husarikov, preschool, school; felted; rubber: small children's, children's, school;
- children's beds;
- children's mattresses;
- strollers;
- school notebooks and diaries;
- toys;
- plasticine;
- pencil cases;
- counting sticks;
- school abacus;
- notebooks and sketchbooks;
- albums for drawing;
- folders for notebooks;
- covers for textbooks, diaries, notebooks;
- cash registers of numbers and letters;
- diapers.
VAT 18 percent list
- garment industry products, including those made from natural rabbit or sheepskin, outerwear (including suit and dress groups), underwear, clothing, hats. An exception is products made from natural leather and fur, except for goods made from sheepskin and rabbit;
- shoes (other than sports shoes);
- cribs;
- children's mattresses;
- strollers;
- toys;
- diapers;
- school supplies (school notebooks and diaries, pencil cases, sketchbooks and notebooks, counting sticks, school abacus, folders for notebooks, sketchbooks, covers for diaries, notebooks and textbooks, boxes of letters and numbers, plasticine).
A specific list of children's goods subject to a ten percent tax rate is presented in subparagraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation 3.
List No. 688; For medicines that are manufactured by pharmacy companies, but are not registered by virtue of paragraph 1 of part 5 of article 13 of the Federal Law No. 61 of April 12, 2010, they may be taxed at a rate of 10% VAT only if there is a prescription for a medical product or a requirement of a medical organization ( according to Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated August 10, 2011 No. AS-4-3/13016). 5 Sales in agriculture Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 20, 2016 No. 1069; All-Russian classifier of products by type of economic activity OK 034-2014; Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity of the Customs Union Until October 1, 2016, there was a 10% rate on all agricultural products; Since October 20, 2016, 2 lists of breeding livestock have been approved Table “Definitions of basic terms” Below is a similar list of definitions used in this article with reference to the regulations that reveal their essence.
When calculating the tax payable, it is necessary to take into account the types of VAT. Depending on the object of sale, the tax percentage may vary. The tax rate is necessarily prescribed in the basis document to determine the payment required to be paid to the state budget. Such a document is an invoice. Its form is regulated by law. The tax rate is indicated in the documentation as a separate line. If an error was made on the invoice, a correction document must be issued.
There are three VAT rates in the Russian Federation: 0, 10 and 18%. Let's consider in what cases at what percentage the tax payment will be calculated.
When is 0% VAT used?
The most commonly used VAT is 0% when exporting and selling products intended for transit through Russia. This list includes:
- products intended for export outside the customs territory of Russia, as well as products moved under the customs regime (in a free zone);
- provision of services or performance of work related to the sale of products intended for export, as well as organizing the movement (escort, loading, etc.) of these products if they are imported into Russia or exported abroad;
- provision of services related to the transportation of passengers, as well as their luggage (the main condition is the location of the point of departure or destination outside the borders of the Russian Federation);
- carrying out work or performing services that are related to the transportation or movement of something through the territory of Russian customs, as well as products placed under the customs regime.
The listed services can be provided under foreign economic agreements with Russian counterparties, non-residents, as well as under intermediary agreements. It does not matter the type of vehicle or the method of organizing transportation.
In the reporting declaration for the quarter, financial and economic movements at a 0% rate are displayed on a separate page (section 4).
VAT 10 percent: list
Many products sold fall under the 10 percent VAT list. Thus, VAT of 10% is paid to the budget for operations regarding:
- food products (livestock, poultry, meat products, dairy products, butter, margarine, salt, sugar, grain, feed mixtures, seafood, vegetables, baby food and other goods);
- products intended for children (knitwear, clothing and footwear, bedding and beds, strollers, diapers and other goods for preschool children);
- products intended for school-age children (pencil cases, plasticine, stationery, diaries, notebooks, sketchbooks and other goods);
- periodicals (with the exception of publications that are advertising or erotic in nature);
- literature with a scientific focus or published for educational purposes;
- goods intended for medical purposes from domestic and foreign manufacturers;
- pharmacological agents, including drugs intended for clinical trials;
- breeding livestock and poultry.
VAT 18% is paid by the taxpayer to the budget if his activities do not fall into the above lists, where a reduced preferential rate applies.
Transactions at rates of 10% and 18% are displayed in the reporting declaration in section 3. The same section displays estimated rates.