Mansard roof rafter system
More and more architectural, original houses are appearing, decorated with bay windows, superstructures, and mezzanines. Attics are becoming fashionable, expanding the usable area of the house. But attic roofs, unlike a simple gable roof, require complex rafter systems. Correctly calculating them and carrying out installation is not at all easy. Below we will try to briefly highlight this issue and provide useful recommendations from experts.
Types of rafter systems
At the design stage of a house, the roof structure must be calculated. Calculations using complex formulas should give a value for the load per meter of a square rafter system. For residential buildings, the standard load is 50 kg/m2.
In accordance with the calculations, the type of attic truss structure is selected. The main varieties include:
- hanging rafter system;
- sloping roof rafter system;
- layered gable roof system;
- combined.
The most common are combined rafter systems for pitched roofs. It is recommended to entrust the calculation of complex rafter systems to professional designers.

Advice!
To increase the usable area of the building, you should choose a multi-slope mansard roof design.
Rafter roof elements
Experienced specialists will perfectly understand what is being discussed in the article, since they know all the terms and names of structures. To make it clear to everyone, here are the common names of the structural elements of a mansard roof:
- Mauerlat - a beam attached to the upper crown or wall of the house on which the rafter system rests;
- Floor beams are a wooden structure that plays the role of an attic floor and, at the same time, the ceiling of the room below;
- Posts are vertically mounted posts on which rafters and beams are attached.
- Purlins - beams (boards) located horizontally serve as support for the rafters;
- Crossbars are horizontal beams in a U-shaped truss. They serve as a support and tighten the pitched rafters; they are also called “tightenings”;
- Rafters - timber or boards that form the basis of the roof structure;
- Suspension - a rack whose task is to support the crossbar, facilitating its operation, is also installed horizontally;
- Sheathing - a board or plywood base on which the roofing material is laid;
- The filly is a board that serves as the basis for installing the overhang and is installed at the bottom of the rafter system.
 Elements of the rafter system
Elements of the rafter system Rafter system calculations
The choice of truss structure largely depends on the size of the building, according to which the span length is determined, i.e. distance between main posts. For small houses, preference can be given to a gable structure.

 Gable roof rafter system with attic
Gable roof rafter system with attic Structural calculations are carried out to determine the load, in accordance with standards and building regulations. The basic rule for an attic roof is to limit its height, which should not be less than 2.5 meters indoors. Thus, the roof must have a minimum height of 2.80 m, since it requires laying an insulating layer and finishing inside the attic itself.
 Gable mansard roof design
Gable mansard roof design You should definitely make a design drawing, on which you should put all the dimensions and display the frame elements as much as possible. The drawing should show the dimensions of the house, the angle of the rafters, and the height of the roof.

Advice!
To make accurate calculations for all loads on the roof and its elements, it is recommended to use a calculator located on many sites dedicated to the construction of roofs.
It is enough to enter the type of roofing, the material of the attic roof frame and dimensions. The program will calculate the section angles and pitch of the rafters and give recommendations on the design of the sheathing.
Calculation of the rafter system
Attic roof installation technology
You should start with the installation of the Mauerlat, which is laid along the perimeter of the upper edge of the walls, if the house is brick or block. In houses made of timber or chopped with mauerlat, the upper crown can serve. The timber from which the Mauerlat is made must have cross-sectional dimensions of 100x100 mm or 150x150. Coniferous wood for timber must be well dried. The Mauerlat beams are fixed with anchors or studs to the walls in increments of approximately two meters. Waterproofing is placed under the Mauerlat, usually of a roll type (roofing felt).


Next, you should begin installing the ceiling. Beams 150x200 mm, placed on the Mauerlat, should protrude beyond the walls of the house by about 0.3-0.5 m. The beams are fastened with corners and screws (wood screws), starting from the outer ones, then intermediate ones.
Important!
When laying, use a cord to control the horizontal level so that the beams lie in the same plane.
The distance between them is, as a rule, 0.5-1.0 meters; if you plan to lay insulation, the standard sheet width of which is 0.6 m, then it will be more convenient to withstand the same spacing of the beams.
Installation of roof truss system
Installation of support posts and purlins
The next stage is the installation of racks. For them, a 100x150 mm beam is used, which is fastened to the front floor beams. It is necessary, using a plumb line, to check the verticality of each support and fix it with jibs. Intermediate supports are also installed strictly vertically on the beams, forming two parallel rows.
 Intermediate supports of the roof truss system
Intermediate supports of the roof truss system Next comes the installation of purlins, which can be made from boards 100-150 mm wide and 40-50 mm thick. The purlins are fixed using nails and corners with screws. Then, on top of the purlins, plank crossbars are laid, for rigidity, installed at the end.
 The purlin beam forms a cantilever to support the diagonal roof rafters
The purlin beam forms a cantilever to support the diagonal roof rafters Advice!
As a result, the outline of the future attic space is formed. To provide additional strength, the supports should be strengthened with struts and braces.
 Roof truss system
Roof truss system Installation of rafter elements
Installation of rafters starts from the bottom. A board 40-50 mm thick and 150 mm wide is suitable for them. We rest one end on the mauerlat close to the floor beams, and the other is attached to the purlins using angles, screws and nails. To install rafters at the top of the roof, mark the center line of the roof. All rafters must be the same length. To do this, you should make a template board, making cuts on it at both ends. Then you can saw off the rest of the rafters using the template.
 Rafter legs
Rafter legs The rafters are mounted on purlins, fixed at the top with metal plates. On the purlins, the beams are secured with edge-to-edge cuts and secured with corners on self-tapping screws.
 Fastening the rafter system
Fastening the rafter system For strength, the lower rafters should be strengthened with struts (board 50x150 mm). After securing the struts, the temporary stops can be removed.
 Often elements are connected not only with carpentry units, but also with fasteners
Often elements are connected not only with carpentry units, but also with fasteners Installation of rafters
In cases where floor beams are laid in wall pockets, fillets should be secured to the lower rafters to provide a roof overhang. If the floors lie on the mauerlat, then fillers are not needed, since the beams should protrude beyond the walls to form an overhang.
 Lathing is an important part of the roof structure
Lathing is an important part of the roof structure The sheathing is installed depending on the intended covering of the attic roof. Either the sheathing will be solid or with gaps. A waterproofing layer should be laid on top of the sheathing, after which you can begin sewing up the gables and laying the roofing material - metal tiles, corrugated sheets or slate.
Roof sheathing under metal tiles
If the attic roof has a broken structure, then, as a rule, it is not insulated, since the air layer under the rafters protects the premises while ventilating the space under the roof. To do this, when sewing up the gables, you should leave ventilation windows (holes) above the attic floor. Thermal insulation should be done only inside the attic room.
 Insulation of the attic roof
Insulation of the attic roof Thermal insulation of the attic has its own characteristics, since the rooms have triangular or trapezoidal ceilings. Builders consider insulation one of the complex technological tasks in the construction of attic spaces. The main thing is to lay the thermal insulation so that on the sloping ceiling and on the fences it does not shrink during operation.
Ksenia Skvortsova. Editor-in-Chief. Author.
Planning and distribution of responsibilities in the content production team, working with texts.
Education: Kharkov State Academy of Culture, specialty “Culturologist.” Teacher of history and cultural theory." Experience in copywriting: From 2010 to present. Editor: since 2016.
An attic in a house is always interesting, beautiful and profitable. However, not every master will undertake to do all the work independently. Reasons: ignorance of technological subtleties and the complex rafter system of the attic roof. But you can build an attic yourself, the main thing is a good design and a sober assessment of your own strengths and financial capabilities. And we will advise and tell you what types of rafters there are, and we will analyze the structure of the rafter system of the attic roof of various types.
The drafting must take into account all the nuances. If miscalculations are made, the developer runs the risk of ending up with something different from what was planned. The simpler the roof, the more convenient it is to make it yourself. Types of roofs are:
- Gable, where the slopes descend on both sides;
- A broken line, consisting of two or more slopes of different angles of inclination;
- Hip with a triangular shape of slopes;
- Semi-hip - end-type slopes are located approximately half the height distance;
- Dome for polygonal or round buildings;
- Vaulted - in cross-section, such a roof has the shape of an arc.
The attic roof is distinguished as ventilated and non-ventilated. The type is selected depending on the climatic characteristics of the region, for example, in areas with high rainfall it is better to build ventilated facilities.
Types of rafter systems

The rafter system of the attic roof is selected depending on the layout of the building and differs as follows:
- Layered rafter system attics are installed when the load-bearing partition runs through the middle of the building. The design redistributes the weight load and is suitable for buildings where the distance between the external wall panels and the internal support system does not exceed 7 m.
- Hanging rafter systems applicable in the absence of internal partitions and walls. Supported by a mauerlat and a ridge girder, they are suitable for buildings where the distance between the external walls and the structure does not exceed 14 m.
- Combined rafters Attics are most often needed in buildings where columns are installed instead of partitions. It turns out that part of the rafter structure rests on columns, and part is made in a hanging version. The absence of auxiliary elements, reduced load on the foundation and no cluttering elements are the main advantages of the system, which is why this option is used most often.
Important! Types of rafter systems are selected at the design stage in order to correctly calculate the required strength of the foundation. In the case when the decision to build an attic arises at the final stage of construction, an accurate diagram of the truss system of the attic roof and a complete recalculation of the weight of the house taking into account new data will be required. The process cannot be neglected, especially in areas with weak soil. Otherwise, the end result will be that the house will quickly subside, and groundwater will render the foundation unusable in a short time.
Structural features of the rafter system

The main components are little different from a conventional gable roof:
- Mauerlat is the base of the roof that bears the weight.
- Rafters are elements of the system that form the slope of the slopes. The top is fixed to the ridge, the bottom - to the mauerlat or stand.
- Post - an element that supports the ridge or back of the rafter leg.
- Struts are needed to strengthen and support the rafter legs. The strut has an oblique cut and serves to prevent the rafters from bending under the weight of the mass.
- Ties - a horizontal tie of a pair of rafters, placed in the upper or lower part.
Important! Rafter elements are often made from the highest grade wood. A timber with a moisture content of no more than 15-18% is purchased and pre-treated with anti-rotting compounds and antiprenes.
Assembly diagram of the rafter system for the attic

An attic rafter system is quite a troublesome task, so it is better to entrust the assembly to a specialist. But if this is not the case, tips and videos will help you complete the simplest design yourself.
- The mauerlat beam is laid on the top frame of the walls. If the house is log, you can get by with upper crowns reinforced with brackets.
- Install floor beams. Mounting on the mauerlat or protrusions of wall panels. The simplest fastening is without extension, supported on the walls, but with extension is when the beam is carried outside the perimeter of the house to create an overhang. In this case, the distance between the end of the beam and the wall panel should be at least 0.5-1.0 m.
- Vertical racks are installed. To do this, determine the middle of the floor beam, then equal intervals are set aside from it - the distance should be equal to the width of the attic room.
- The puffs are secured to the racks, and it turns out that each pair of racks looks like the letter “P”.
- Installation of the lower rafter elements is carried out with fastening to the rack. Fasteners - self-tapping screws or nails, fasteners on the mauerlat in the form of a movable fastening slider, compensating for the shrinkage effects of the timber.
- Installation of rafters for the upper part of the attic roof is carried out by connecting each pair with a metal plate or bar.
- Final processing includes laying a waterproofing membrane and sheathing. The lathing for soft roofing material is solid, for corrugated sheets and other hard materials it is sparse.
The proposed installation of the rafter system is the simplest. It is quite possible to equip such a structure with your own hands, you just need to make the correct calculations, the rafter system, drawings of the attic roof, and diagrams will help you complete the work without errors.
Rafters with extension behind the wall panel

This option is used when there is a small amount of internal space. You will have to rest the rafter leg on the upper floor beam. Mauerlat is not needed here, but reinforcing struts are required. To strengthen the base, you can fill in a reinforced concrete belt. Attaching the floor beams to the monolithic belt is done with anchors, into which support posts are inserted to the maximum thickness of the beam.
Important! The external structure forms a cornice: for wooden houses the width is from 0.5 m, for those made of concrete and stone - from 0.4 m.
Scheme of work:
- Install the outermost floor beams that form the outline of the overhangs. The cross section of the beams is 150*200 mm.
- The remaining beams are mounted along a cord stretched between the outer beams: the distance between them is equal to the pitch of the rafter legs. Insulated roofs require a rafter pitch of 0.6 m; if rafters are installed with the specified pitch, they can be made from timber with a section of 50*150 mm.
- Having cut out the tenons, prepare the supports.
- Install the corner posts and secure them with temporary supports.
- Use a plumb line to determine the location of the support points of the beams and select holes for them.
- Install row posts and a pair of load-bearing supports in the centers of the attic gable.
- Lay purlins from 50*150 mm boards. Secure the purlins with corners.
- Connect the supports with bars, also securing them with corners to the purlins.
- Fasten the crossbars using temporary fasteners with an inch. The deviation from the edge of the frame is 300-350 mm.
- Make a template for the bottom row of rafters: attach the blank board to the end of the purlin and beam, determine where to cut off the excess, try it on and trim it.
- Install the end rafter posts.
- Make a template for the top of the rafter legs.
- Try on the template and build a tier, how the rafter system will be, photos of the attic roof will clearly show the entire structure.
- If the templates fit perfectly, make the required number of rafter legs, mount them in place, strengthen the headstock of the crossbars to avoid their sagging and firmly sew them to the ridge area. The lower part does not require rigid hemming, it should be free.
The final completion is the installation of the gable frame, sheathing and roofing material. If it is not entirely clear how to complete this project, watch a video from professionals; the material will help you understand the intricacies of construction.
Attic from frame modules

The mansard roof rafter system involves a version of frame modules that is much simpler than the previous one. It is not groups of individual supports that are mounted on the ceiling, but ready-made block modules of the side walls of the future attic room. Such designs of mansard roofs and their rafter system allow you to work not at height, but below, calculating and measuring every step. The step-by-step process is as follows:
- Make the walls of the attic according to the design in advance, with the longitudinal beams acting as purlins and support elements. Together with the racks, lay out these elements on a flat area and mark the sockets for the support points of the side walls with squares - make cuts along them.
- Select a spike on the racks.
- Connect the longitudinal beam with the vertical posts and you get a frame module (double). These are the future walls of the attic.
- Lift the frames up and install them in place. Temporarily secure the installed frames with spacers and then fasten them with brackets.
- Select sockets at the edges of the beams for mounting the lower row of rafters; if necessary, modify the sockets with a chisel.
- The upper rafter tier is made on the ground, for which the blanks are first adjusted to the required elements.
- The base of the upper triangle of the attic structure is a stretcher, and its length is equal to the distance between the installed planes (vertical) of the already mounted frames.
- Select sockets along the edges of the stretch, and spikes on the lower heels.
- Assemble rafters for the attic of the upper tier, mount a crossbar for additional fastening, and reinforce the ridge assembly with a triangular-shaped wooden overlay.
- Pre-production of rafter legs for the attic will allow you to avoid working at height. You only need to cut the top bevel, which rests on the top post of the wall panel and on the tension of the upper trusses.
- Try on the lower rafter part to the end, mark the tenon shape area on the lower heel, cut out the tenons according to the drawing made.
Now all that remains is to move upstairs and raise all the rafters. First install the trusses, securing them to the upper frame of the walls, and then install the lower part, attaching them to the ceilings (beams) with brackets. It turns out to be a completely comfortable floor, the rafter system for which was assembled on the ground. To make it easier to understand the task of constructing an attic roof, a modular rafter system, watch the video. All other stages are carried out according to the standard scheme of a conventional gable structure; the attic and rafter system are shown above.
- This is not a very ordinary design.
Such a structure must not only complete the entire structure of the building and perform protection functions.
But also conducive to a comfortable life in the room located underneath it.
In order for the living space to be suitable for use, it is necessary to understand the essence of the design of such a structure and the nuances of its installation processes.
Such a design has a number of elements that make up a complete roof system.
The structure of the attic roof looks like this:
- Roof. Roofing is necessary for providing reliable protection from the influence of atmospheric conditions both the entire house and the entire roof system.
- . The supporting part of the attachment system is most often constructed from wooden boards.
- Ridge run. The very top of the entire system.
- Rafters. Supporting ribs that create rigidity for the structure. They have two varieties - hanging and layered.
- Mauerlat. The element is represented by beams that used for fastening the rafter system. The element repeats the location of the perimeter of the house and is fastened to each wall using fasteners.
- Diagonal piles. For that, so that the roof structure system has a high level of reliability, the rafters are connected to each other by beams located longitudinally and by vertical posts, which are connected together by diagonal braces or bevels.
- Internal supports. An element that is located under each rafter leg and provides it with stability.
- Insulation layer. This layer unites the entire roof system into a single whole, while creating reliable sealing, vapor and sound insulation. This layer has its own structure and is multi-layered. All materials that are used to equip this layer are necessary to provide all kinds of properties that ensure comfortable living in the attic.
What components and parts does the attic roof consist of, you will see in this drawing:
Mansard roof design drawing
Roofing pie
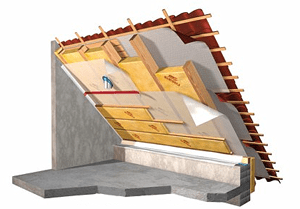 Each type of roof has its own individual structure.
Each type of roof has its own individual structure.
It is represented by several layers of different materials, which necessary to protect the attic space from cold air masses and high humidity levels.
The roofing pie of the attic roof includes:
- Lathing;
- Vapor barrier layer;
- Counter grille;
- Thermal insulation layer;
- Waterproofing;
- Ventilation systems;
- Roofing material.
Each layer is designed to perform specific functions that are necessary for the proper functioning of the entire roof system.
If you make mistakes during installation or neglect any of the layers, then this may lead to the need to redo the entire structure.
- . The simplest type of roof over an attic, but not very popular. Represents one inclined plane, which is supported on load-bearing walls of various heights.
- . This kind represented by two slopes, which are located opposite each other.
- Broken. This type of roof has other names - half-hip. This type of design allows you to make the attic space optimal. This design has four ramps. It is quite convenient to live in an attic with this type of roof.
- Conical. The most complex type of design, represented by a cone. Suitable for buildings which have round or polygonal outlines.

Types of roofs
If we talk about the types of rafter systems, they come in 3 types:
- The hanging type of rafters ensures the transfer of load in a horizontal position to load-bearing walls. Such rafters are the basis of the entire system. There is no need for intermediate supports; wooden or metal ties are used to connect the beams.
- The layered variety of rafters is used if the load-bearing wall is located in the center of the building or if there are intermediate supports. This type of rafters is installed on external walls, while their middle part is supported by internal walls. Such a structure can only be built if the distance from the load-bearing wall to another is up to 6.5 m.
- The hanging and layered version of the rafter system is represented by triangles having a right angle. Additionally, this design is equipped with contractions at the bottom and top of the system. To suspend the ceiling, use the tightening of hanging rafters.

Mansard roof: gable structure of a wooden house
Tilt angle
 A very important parameter in roof construction is determining the angle of inclination of the roof. This value is determined not only by the design of the building, the features of the facade, but also by the selected roofing material and local climatic conditions.
A very important parameter in roof construction is determining the angle of inclination of the roof. This value is determined not only by the design of the building, the features of the facade, but also by the selected roofing material and local climatic conditions.
If precipitation in the area where the house is located is of great importance, then The roof angle ranges from 45 to 60 degrees.
This slope value will ensure better snow removal from the surface, and, accordingly, a decrease in the load level. In addition to precipitation, this angle parameter protects the roof from icing.
If the house is located in an area where strong winds are a frequent occurrence, then the value of the slope angle should be minimal. Otherwise, the structure may be destroyed due to weather conditions. Under such conditions, variations in this parameter range from 9 to 20 degrees.
However, the most common and optimal roof angle is 20-35 degrees.. This value is suitable for arranging a roof with almost any type of material.
CAREFULLY!
The angle of inclination largely determines the durability and reliability of the structure.

Tilt angle
Installation process
In order to install an attic roof, you must follow a certain sequence of actions:
- Initially, the upper beam is attached, which has section parameters of 10x10 or 15x15 cm. Fastening is carried out using nails, metal staples or self-tapping screws. At the same time, the first beam provides the function of a rafter frame.
- The following is installation of the Mauerlat, which is necessary to take most of the load. To install it, you will need a board with a thickness of at least 5 cm and a beam with cross-sectional parameters of 5x10 cm. Before laying the board, lay a layer that is necessary to retain moisture and not destroy structural elements. The Mauerlat is attached with nails or staples and additionally tied to the walls using metal wire. The wire is installed at the stage of wall construction.
- Next, install the rafters, choosing for this step from 0.6 to 2 m.
- The gable rafters are installed first., after which they tighten the level and begin to mount the remaining elements.
- After the rafter legs are all installed, provide additional structural reinforcement, connecting the rafters to each other in their upper part.
- If the roof length exceeds 7 m, then installing ridge beams. Otherwise, equipping the rafter system with a similar element is not necessary.
- Once installed move on to equipping the layers of the roofing pie, having previously installed the sheathing.
- The last stage in roof construction is laying roofing.

Installation of sheathing

Installation of rafters

The construction of an attic makes it possible to increase the size of the usable area and arrange a living space directly under the roof. The choice of attic roof design depends on the architectural features of the house, the design load on the roofing system and building structures, and style preferences.
The rafter system of the mansard roof can be erected on the frame or box of the house instead of the old gable roof, if the walls and foundation are able to withstand the increased load.
Forms of mansard roofs
The usual option, familiar to everyone, is a “broken” pitched roof, in which the upper and lower parts of the slope are located with different slopes. This design of the rafter frame allows you to increase the height of the walls of the room under the roof, making it more spacious and more comfortable for living.
The attic roof may not have a break on the slopes, while its rafters are also two-part. This option is visually no different from a standard gable roof.
This means that the attic roof can be:
- pentagonal broken line;
- triangular.
The design feature of mansard roof frames is that they actually consist of two tiers. The lower trapezoidal tier is the useful space of the room, the longitudinal walls of which are formed from racks on which the rafters of the lower part of the slopes rest. The upper tier is the upper part of the roof, triangular in cross-section, which can be of any chosen height.
The rafters of the lower tier are only layered; for the installation of the upper tier, layered and hanging systems are used.

The overall shape of the roof depends on the angles of the rafters at the top and bottom. If these angles coincide, the attic roof will be triangular; if they are different, it will be pentagonal.
The room under the pentagonal roof has a rectangular cross-section - the frame of the walls in it is formed by racks on which the upper ends of the lower rafters and the base of the upper tier rest. The cross-section of the room under the triangular roof is a pentagon, since the rafter system uses short posts and the rafters form the inclined part of the ceiling.
Calculation of the attic roof
Calculation of the attic roof truss system includes the search for optimal sizes for all elements of the system. It is important to take into account the height of the ceilings in the room under the roof after installing the final finish.
The recommended ceiling height is 2-2.5 meters. If the room has sloping top corners, the height of the walls at the lowest point should be at least 80 cm - this will allow you to install furniture to make the most of the space along the walls. A wall height of 140-150 cm allows a person of average height to move freely half a meter from the walls if the roof slope is 45-60 degrees.

According to SNIP, the room under the roof is considered an attic, not an attic, if the distance from the ceiling to the ridge is at least 2.5-2.7 meters.
When calculating a roof with straight slopes, it is important to find the optimal ridge height, since the lower the roof, the smaller the size of the room, but an excessively high roof is more difficult and expensive to install and experiences increased wind loads.
Broken mansard roof
Attic rafter system with broken slopes:
- rests only on external walls (hanging type system);
- rests on the external frame of the house and internal walls or on columns (layer system).

The hanging system is used when the span between long walls is up to 8 meters. The support posts on which the rafters rest are mounted in two ways. In the first case, beams are laid on the floor beams, in the second, the supports are attached directly to the beams.
If the gap between the longitudinal walls is more than 8 meters, it is required at the design stage of the house to provide internal main walls or erect brick support pillars on the foundation.
Construction of the attic roof rafter system
The classic version of the attic roof is a pentagonal system with support posts that form the walls of the room. If you look at it in section, you can see a rectangle in the center, two symmetrical right triangles on its sides and an isosceles triangle on top.
The upper triangle of the attic roof is a rafter arch consisting of two legs and a tie. To prevent the tie (which also serves as a ceiling covering for the attic) from sagging, a suspension headstock is mounted in the center. This design option is used if the length of the horizontal element of the upper triangle exceeds 3 meters.

Mansard roof options
Since the headstock is a suspension and not a support, it cannot be attached to the truss arch using the cutting method, weakening the structure and forming a thrust. In addition to the vertical element, struts are installed.
In the standard version, the rafters of the lower part are supported by the lower part on the mauerlat, and the upper part is supported by a purlin, a beam, which is fixed to vertical posts and ensures the rigidity of the structure.
The racks rest on the floor or on the floor beams. The racks in the lower part and to the upper girder are attached using the cutting method, the connection is additionally strengthened with a metal plate or angle.
Please note: if the bench is laid on a concrete floor, column or main wall made of piece building material, it is necessary to lay a roll of bitumen waterproofing material under it.

If necessary, for structural rigidity, a strut is attached between the fifth support post and the layered rafters.
The rafters of the lower tier are installed at a relatively small angle to the vertical, so this part of the roof practically does not experience snow load. At the same time, the wind load is increased - sharp gusts of wind can tear off or move a poorly secured roof. For reliability, each rafter leg is additionally attached to the Mauerlat using twisted wire.
How to increase the area of the attic
The width of the room under the roof strictly depends on the width of the house if the rafters rest directly on the mauerlat. To increase the living space, the rafter legs are moved beyond the line of the walls. In this case, the rafter leg rests not on the Mauerlat, but on an elongated floor beam. This design requires the mandatory use of a reinforcing strut inside the side triangle formed by the post, beam and rafter leg.
If the house is built from brick, blocks or other materials, with the exception of wood, a Mauerlat is not required to be installed. But to make the system rigid, a monolithic reinforced concrete belt is poured around the perimeter of the house frame and on the internal main walls, which is then waterproofed.

Beams extending beyond the walls must form a cornice of a certain width. For houses made of brick, foam concrete, etc. The recommended minimum width of the eaves overhang is 0.4 m, for a house made of timber or logs - 0.5 m.
Installation of the rafter system
The construction of the rafter frame of the attic roof with the rafter legs moving beyond the wall line is carried out using the following technology:
- Using a beam with a cross-section of at least 150x200 mm, the outer beams of the future floor are laid. It is important that they lie in the same plane (if necessary, boards are placed for leveling) and form identical eaves overhangs. If the house box is not a perfect rectangle, we adjust the position of the beams and check the diagonals.
- We stretch control cords between the ends of the beams on each side. Based on them, we lay the remaining elements of the floor base with equal spacing, which should correspond to the spacing of the rafters.
- The distance at which the racks will be installed is set from the left and right edges of the outer beams. In the marked places, using a chisel, nests are made 1/3 of the height of the beam.
- At the lower ends of the corner supports, spikes are cut to fit the size of the sockets. The cross-section of the beam for corner posts is 100x150 mm, for ordinary posts - 50x100 mm. When cutting material to the designed length, you should add 10 cm for making a tenon and errors when cutting off excess wood.
- Corner posts are mounted, their verticality and relative position are checked. Control cords are pulled to install row racks.
- Using a plumb line from the control cord, the locations for the nests of ordinary supports are determined. The nests are selected with a chisel.
- Ordinary racks are attached, as well as load-bearing supports in the center of the gables.
- The verticality of the racks and the height of the upper ends are checked, and trimming is performed if necessary. The racks of each side are connected into a single system by purlins made of 50x150 mm boards. The boards are fastened using steel angles and nails.

Fastening the rack to the rafter system
- The supports, installed opposite each other, are connected by bars with a cross-section of 100x150 mm, which are also attached to the purlins using corners and work in tension, like crossbars. Under each crossbar it is necessary to install a temporary support from an inch board.
- On top of the crossbars, a temporary flooring is fixed from a couple of inch boards with a distance of 30 cm from the edges of the frame. It will simplify the installation of the upper segment of the rafter system.
- A template is made from an inch board, which is then used to make rafter legs. The blank is applied to the ends of the beam and purlin, and the places where the groove should be selected are marked on it. The excess is trimmed to fit the template exactly.
- The lower rafters are made on the ground using a template. If you are not sure that all dimensions of the structure are met exactly, only the upper groove is selected at the rafter legs, and the heel is cut at the place of installation on the beam.
- The outer rafters are installed on each side; they are connected with a control cord.
- All rafters of the lower tier are installed, struts are mounted in each triangle.
- A temporary gable board is attached to the top of the structure to create a template for the top rafter.
- On the ground, rafters for the upper arches are made from 50x150 mm boards (using a template and mirrored to them), then they are mounted on crossbars. The upper ends of the rafter legs rest against each other.
- To prevent sagging of the crossbars, a suspension headstock of the required size is installed in each upper truss. The headstock is rigidly attached only in the ridge part.
- If the house does not have gables made of wall material, the gable frame is mounted and sheathed.
- A sheathing is attached to the rafters for a sloping mansard roof, the pitch of which depends on the angle of inclination of the slopes and the characteristics of the selected roofing material. The attic roof must be well insulated.

There are other installation technologies, in particular, installation of ready-made frame modules assembled on the ground on the floors. This approach allows us to minimize work at height and ensure careful adjustment of all elements. The only difficulty is the need to lift heavy finished timber trusses to a height.
Before starting installation work, it is necessary to prepare a project by understanding which attic roof rafters are used and familiarizing yourself with the structure of the entire structure. The Marisrub company will help you in this matter, which will not only draw up a project, select and manufacture lumber, but also carry out the necessary roofing work http://marisrub.ru/uslugi/krovelnye-raboty.
We build an attic with our own hands
The installation of a mansard roof is very popular for residential buildings.

For layered rafters, you will need to install an internal frame of beams under each lower rafter.
In general, its installation is simple, but many novice builders find it difficult to work independently with the rafter system of mansard roofs.
Rafter structures
The popularity of these roofing types is understandable. A relatively small financial investment will help you get both a roof and a living space.
This type of roof will turn a small building into a homely and spacious hearth where both guests and home owners can gather. The construction of attics is possible both during the construction of a new home and an already built one. Moreover, without disturbing the main structure. But the old roof will need to be demolished and a new one erected.
Extreme attention should be paid to the thickness of the walls and foundation of the house, the soil on which the house is located, because, unlike ordinary roofs, attic structures are much more massive and heavier. This is taken into account when drawing up the project and will help to correctly calculate the loads that fall on the structure.

Scheme of arrangement and fastening of hanging rafters for an attic roof.
The design of attics can be different:
- broken line;
- asymmetrical;
- symmetrical;
- triangular;
In addition to this, we can include the installation of not only single-level, but also two-level attics under the roof of the house, while the presence of geometric shapes of the room may differ. This is reflected in the external appearance of the houses.
For each roof, the inclined angle is important, which depends on both the covering material and the climate. But, despite this, the design of mansard roofs provides for inclined angles in the range of 30-60 degrees. Remember that the greater the angle of inclination, the smaller the usable area of the attics themselves.
If the roof angle is less than 30 degrees, this will make it difficult for precipitation to be discharged from the slopes and may lead to the destruction of the entire roof.
Tools and materials
When constructing an attic, you will need the following building materials:
- standard unedged board;
- wooden beams (10, 12 or 15 cm);
- slate nails (if you plan to cover with slate) or self-tapping screws (respectively, with metal tiles);
- nails;
- insulation (for example, mineral wool);
- hydrobarrier (ordinary water vapor barrier film);
- leg-split;
- annealed wire (3-4 mm);
- board 150x50 mm.

Attaching the rafter leg to the mauerlat.
As for tools, you don’t have to go to a construction hypermarket for professional equipment. Everything that is required for an attic roof is available in every house:
- axe;
- hammer;
- hacksaw or chainsaw;
- presence of a sharp knife and a construction stapler with staples;
- tape measure and plumb line.
In some cases, a screwdriver will come in handy if you decide to cover the roof with metal tiles. Believe me, fastening with self-tapping screws is much better than driving nails into metal.
Construction of the attic. Design
The installation of the roof of the house takes place in stages. The most difficult stage is the rafter system, where various components are present. It acts as the frame base of the entire roof.
Floor beams need to be laid. They are wooden beams with a cross-section of 100x100 mm, which are laid on waterproofing (roofing felt or roofing felt).
When installing the truss structure, use wood of a certain moisture content. Attic roof rafter systems are made from dried and sanded wood. The permissible humidity is no more than 18%. It is advisable to use coniferous species.

The attic frame can be made transversely and longitudinally. In both cases, assembly is carried out on the ceiling
If you use very wet building material, then as it dries it will begin to twist, which will affect the roof structure and can even lead to destruction. The attic roof will become unusable.
The next step is to install the posts on the laid beams. Wooden beams 100x100 mm are suitable.
- Markings are made for the racks so that the step between them does not exceed more than 2 m. It is necessary to ensure that the racks are in the same planes strictly vertically. You can use a plumb line or level.
- To avoid vibration of the racks and their shifting or tilting to the side, the presence of braces is required. To do this, take boards 100x50 mm, cut in the required quantity (2 for each rack) about 1 m long. Next, they are nailed to the racks on both sides.
The presence of vertical posts acts as a basis for the walls of the attic rooms. Therefore, it is necessary to cover them on both sides using sheathing material (plasterboard, plywood, chipboard, fiberboard), and insulation (mineral wool) must be laid between the sheathing board.
We lay the ridge beam. Bars 100x100 mm are suitable.
Fastening to the racks is carried out using nails or metal staples, i.e. the timber lies on the racks and is fastened together.
It is also possible to make a cut at the top of the posts in the form of an inverted letter “P” if the ridge will be a board (100x50 mm). Accordingly, the size of the recess must correspond to the size of the board for its free insertion. We also fasten it with nails.
Now the Mauerlat. It serves to perform important functions. Almost the entire attic roof structure is mounted to it.
With its help, the roof will not tip over in strong winds and a strong fastening will be created between the rafters and the load-bearing walls of the house.
How to install it?
For this, a board (at least 4 cm thick) or timber (100x150 mm) is used. This material is laid horizontally along the perimeter of the walls of attic roofs, and waterproofing (roofing felt in 2 or 3 layers) is first applied to prevent moisture. Fastened to the walls with bolts or staples.
Everything is clear about the staples: one end to the beam, the other into the wall and we hammer it in.

Design of attic units: A - ridge unit; B - “rafter-screed-post” assembly; B - “rafter-ceiling beam” unit; G - “ceiling beam-post-strut” assembly; D - “post-strut” unit; 1 - attic screed; 2 - run; 3 - stand; 4 - main rafter; 5 - intermediate stand; 6 - strut; 7 - liner; 8 - ceiling beam; 9 - ridge rafter; 10 - crossbar; 11 - ridge overlay; 12 - nails; 13 - staples
What about the bolts?
- To do this, take a drill and drill solid holes in increments of 150 cm along the entire length of the beam, entering the wall about 15 cm, i.e. so that the bolts can be inserted and tightened. You can simply use pins that are driven through the wood into the wall.
- An additional fastening is annealed wire, mounted into the walls during laying. It is simply twisted along the Mauerlat. It is recommended to treat wood with antifungal agents, which are available in great abundance on the modern market.
- Next come the rafter legs. The rafters can be ordered, and then all that remains is assembly. But you can do it yourself according to the building design.
- The distance along which the rafters will be installed is marked. There is nothing complicated about it. Using a pencil, markings are applied on the mauerlat base and rafter structure. Those. First, we mark the location of the outer rafters (this will be the gable base), then every 1-1.2 meters.
- First, we install the outer rafters. To do this, take two boards (5x15 cm) and place one end on opposite sides of the walls. With their other ends they form an overlap along the top of the ridge beam.
- Then, using a square and a pencil, mark the cut of the lower base. The top is sawn down so that the ends meet closely. After this, the rafters are secured with nails.
- Along the top, between them, a piece of trimmed board (headstock) is nailed. Just below the stretchers (boards 50x100 cm) are attached between the middle of two rafters (this is also the base of the ceiling).
This option is also possible. The rafters of the attic roof are attached in a similar way (only not two, but three, and there is no overlap at the top). Those. the result is a slightly bent letter “P” (broken mansard roof).
- Then lacing (twine) is taken and secured between the outer rafters. Acts as a level for the devices of others. Installation is identical to the extreme ones.
- Installation of lathing, thermal insulation and vapor barrier.
- To do this, take a roll of film and roll it along the bottom of the rafter structure. Attached with staples using a stapler. The counter-lattice is being installed. Those. a 50x25 mm strip is taken and nailed along the top of the film to the rafters. In this case, you need to leave a gap for subsequent overlap (12-15 cm). In this way we go through the entire roof.
- Next we arrange the sheathing. We take a board 100x25 mm. We start nailing from the bottom. The step between the following depends on the type of roofing material (for metal tiles, slate, this is the distance between the waves - usually 20-25 cm; for rolled materials based on bitumen, a continuous sheathing is made).
Thus, the structure of the attic roof is ready. All that remains is to choose a covering, a material for the walls (maybe plastic, regular wallpaper or lining). It makes no sense to describe further installation, since any building material has its own subtleties in the work. It all depends on your choice.
- Secure the main components using construction staples and wire.
- There are tenon fastening units (for example, bolts and pins).
- A height of 2.2 m and a width of 3 m are the best options.
As you can see, the design of the attic roof is very simple. It all depends on your desire and skills.
Features of installing attic roof rafters
More and more architectural, original houses are appearing, decorated with bay windows, superstructures, and mezzanines. Attics are becoming fashionable, expanding the usable area of the house. But attic roofs, unlike a simple gable roof, require complex rafter systems. Correctly calculating them and carrying out installation is not at all easy. Below we will try to briefly highlight this issue and provide useful recommendations from experts.
Types of rafter systems
At the design stage of a house, the roof structure must be calculated. Calculations using complex formulas should give a value for the load per meter of a square rafter system. For residential buildings, the standard load is 50 kg/m2.
In accordance with the calculations, the type of attic truss structure is selected. The main varieties include:
- hanging rafter system;
- sloping roof rafter system;
- layered gable roof system;
- combined.
The most common are combined rafter systems for pitched roofs. It is recommended to entrust the calculation of complex rafter systems to professional designers.
To increase the usable area of the building, you should choose a multi-slope mansard roof design.
Rafter roof elements
Experienced specialists will perfectly understand what is being discussed in the article, since they know all the terms and names of structures. To make it clear to everyone, here are the common names of the structural elements of a mansard roof:
- Mauerlat - a beam attached to the upper crown or wall of the house on which the rafter system rests;
- Floor beams are a wooden structure that plays the role of an attic floor and, at the same time, the ceiling of the room below;
- Posts are vertically mounted posts on which rafters and beams are attached.
- Purlins - beams (boards) located horizontally serve as support for the rafters;
- Crossbars are horizontal beams in a U-shaped truss. They serve as a support and tighten the pitched rafters; they are also called “tightenings”;
- Rafters - timber or boards that form the basis of the roof structure;
- Suspension - a rack whose task is to support the crossbar, facilitating its operation, is also installed horizontally;
- Sheathing - a board or plywood base on which the roofing material is laid;
- The filly is a board that serves as the basis for installing the overhang and is installed at the bottom of the rafter system.
Rafter system calculations
The choice of truss structure largely depends on the size of the building, according to which the span length is determined, i.e. distance between main posts. For small houses, preference can be given to a gable structure.
Structural calculations are carried out to determine the load, in accordance with standards and building regulations. The basic rule for an attic roof is to limit its height, which should not be less than 2.5 meters indoors. Thus, the roof must have a minimum height of 2.80 m, since it requires laying an insulating layer and finishing inside the attic itself.
You should definitely make a design drawing, on which you should put all the dimensions and display the frame elements as much as possible. The drawing should show the dimensions of the house, the angle of the rafters, and the height of the roof.
To make accurate calculations for all loads on the roof and its elements, it is recommended to use a calculator located on many sites dedicated to the construction of roofs.
It is enough to enter the type of roofing, the material of the attic roof frame and dimensions. The program will calculate the section angles and pitch of the rafters and give recommendations on the design of the sheathing.
Calculation of the rafter system
Attic roof installation technology
You should start with the installation of the Mauerlat, which is laid along the perimeter of the upper edge of the walls, if the house is brick or block. In houses made of timber or chopped with mauerlat, the upper crown can serve. The timber from which the Mauerlat is made must have cross-sectional dimensions of 100x100 mm or 150x150. Coniferous wood for timber must be well dried. The Mauerlat beams are fixed with anchors or studs to the walls in increments of approximately two meters. Waterproofing is placed under the Mauerlat, usually of a roll type (roofing felt).
Next, you should begin installing the ceiling. Beams 150x200 mm, placed on the Mauerlat, should protrude beyond the walls of the house by about 0.3-0.5 m. The beams are fastened with corners and screws (wood screws), starting from the outer ones, then intermediate ones.
When laying, use a cord to control the horizontal level so that the beams lie in the same plane.
The distance between them is, as a rule, 0.5-1.0 meters; if you plan to lay insulation, the standard sheet width of which is 0.6 m, then it will be more convenient to withstand the same spacing of the beams.
Installation of roof truss system
Installation of support posts and purlins
The next stage is the installation of racks. For them, a 100x150 mm beam is used, which is fastened to the front floor beams. It is necessary, using a plumb line, to check the verticality of each support and fix it with jibs. Intermediate supports are also installed strictly vertically on the beams, forming two parallel rows.
Next comes the installation of purlins, which can be made from boards 100-150 mm wide and 40-50 mm thick. The purlins are fixed using nails and corners with screws. Then, on top of the purlins, plank crossbars are laid, for rigidity, installed at the end.
As a result, the outline of the future attic space is formed. To provide additional strength, the supports should be strengthened with struts and braces.
Installation of rafter elements
Installation of rafters starts from the bottom. A board 40-50 mm thick and 150 mm wide is suitable for them. We rest one end on the mauerlat close to the floor beams, and the other is attached to the purlins using angles, screws and nails. To install rafters at the top of the roof, mark the center line of the roof. All rafters must be the same length. To do this, you should make a template board, making cuts on it at both ends. Then you can saw off the rest of the rafters using the template.
The rafters are mounted on purlins, fixed at the top with metal plates. On the purlins, the beams are secured with edge-to-edge cuts and secured with corners on self-tapping screws.
For strength, the lower rafters should be strengthened with struts (board 50x150 mm). After securing the struts, the temporary stops can be removed.
Lathing
In cases where floor beams are laid in wall pockets, fillets should be secured to the lower rafters to provide a roof overhang. If the floors lie on the mauerlat, then fillers are not needed, since the beams should protrude beyond the walls to form an overhang.
The sheathing is installed depending on the intended covering of the attic roof. Either the sheathing will be solid or with gaps. A waterproofing layer should be laid on top of the sheathing, after which you can begin sewing up the gables and laying the roofing material - metal tiles, corrugated sheets or slate.
Roof sheathing for metal tiles
Attic insulation
If the attic roof has a broken structure, then, as a rule, it is not insulated, since the air layer under the rafters protects the premises while ventilating the space under the roof. To do this, when sewing up the gables, you should leave ventilation windows (holes) above the attic floor. Thermal insulation should be done only inside the attic room.
Thermal insulation of the attic has its own characteristics, since the rooms have triangular or trapezoidal ceilings. Builders consider insulation one of the complex technological tasks in the construction of attic spaces. The main thing is to lay the thermal insulation so that on the sloping ceiling and on the fences it does not shrink during operation.
Gable mansard roof designs: standard, pointed
Projects of gable mansard roofs are currently gaining increasing popularity. The reason lies in the opportunity to solve some of the problems of lack of living space, and without investing large amounts of money. And it depends only on the shape of the roof to what extent the attic floor can be used, and whether it will be suitable for use as a living space.
A gable mansard roof is an excellent option for obtaining a sufficiently large living space. Let us immediately make a reservation that this design is somewhat more complex in production than a standard roof. The use of modern construction technologies allows us to solve many of the problems associated with construction.
Advantages of the attic design

Typically, among the large number of advantages, the following are primarily noted:
- greater savings in building materials and labor resources,
- no need for heavy special equipment, which, naturally, is directly related to budget savings for building a house.
However, often while listing the advantages in technological terms, they forget about their visible aesthetic advantages.
- While maintaining the correct proportions, without any obstacles, you can realize the architecture of a house with a traditional shape.
- If you remove some overhangs, then in a matter of seconds you can witness the birth of a stylish, modern, spectacular home.
A gable roof can provide quite a large headroom for an attic space - you just need to increase its height.
Subtleties of assembling a gable mansard roof
Depending on the slope of the slopes, it happens:
- classic with a tilt angle of 45° for houses 6–8 m wide (very common in the middle zone of the country);
- pointed with a slope of 60° for houses with a width of 6 m - this is a rather expensive option;
- a broken line with two unequal slopes with different slopes (usually 30° and 60°) more often for houses up to 6 m.
Features of the rafter system

The rafter system of the attic roof of two slopes is constructed according to the principle of hanging rafters. It is they, since they do not have middle supports, that form a single space under the roof, without walls or supports - a void in the middle of the attic space. It is customary to call the system of hanging rafters non-running.
Hanging rafters rest solely on each other, forming a ridge, and on the outer walls. The rafters, trying to move apart, create a thrust on the walls, so the system must have tie rods that hold the rafter legs and the opposite slopes together. Tie-beams located at the base of the rafters simultaneously serve as floor beams. However, in the case of an attic room, the tie rod (crossbar) is installed higher, at a height sufficient for its installation.
If a system of hanging rafters is used for a span of more than 6 m, then the trusses are supported by racks or braces, which are installed on purlins located on the floor. In this case, the lower part of the rafter leg has a length of no more than 4.5 m.
To make it possible to use the attic space as a living space, it is necessary to make some changes to the structural and strength diagram of the rafter system of a gable attic roof, that is, to its supporting structure.
Options for reconstructing attics for living space
Option for standard roof
 Rafters and beams are reinforced with overlays, connecting the latter with racks. After this, tie rods are attached to the reinforced rafters and struts. Having strengthened the trusses, the struts, which previously played the role of load-bearing structures, are cut out. If the trusses are located in the attic with a fairly small pitch, about 600 mm, then the load from the roof is transferred to the floor beams in a dispersed manner. After making changes, the load will be redistributed. Thanks to this design, a space of about 3–4 m wide is freed up at the trusses.
Rafters and beams are reinforced with overlays, connecting the latter with racks. After this, tie rods are attached to the reinforced rafters and struts. Having strengthened the trusses, the struts, which previously played the role of load-bearing structures, are cut out. If the trusses are located in the attic with a fairly small pitch, about 600 mm, then the load from the roof is transferred to the floor beams in a dispersed manner. After making changes, the load will be redistributed. Thanks to this design, a space of about 3–4 m wide is freed up at the trusses.
 The frame trusses of such a roof use central posts and struts. When the rafter trusses are located in increments of 0.5–1 m, the rafters and ceiling beam are strengthened by doubling their cross-section. To redistribute the load of the roof onto the floor beams, tie rods and inclined beams are fixed to the rafters and the central post along the height of the ceiling. Then, by removing the supports and the lower parts of the racks, they free up space for the future room. The future room is insulated and windows are cut out.
The frame trusses of such a roof use central posts and struts. When the rafter trusses are located in increments of 0.5–1 m, the rafters and ceiling beam are strengthened by doubling their cross-section. To redistribute the load of the roof onto the floor beams, tie rods and inclined beams are fixed to the rafters and the central post along the height of the ceiling. Then, by removing the supports and the lower parts of the racks, they free up space for the future room. The future room is insulated and windows are cut out.
How to assemble an attic roof: main steps

Having prepared a project for an attic roof with precise calculations of the angle of inclination and rafter system, we begin its phased implementation. The assembly itself begins after the installation of the floors.
First of all, blocks for partitions are installed, external and front walls are erected, after which they begin to construct the rafter structure. As a rule, beams 50 x 150 mm are used for them. By assembling them into a single structure, a wooden frame is obtained for the future roof.
To strengthen the first and middle purlins, U-shaped blocks are laid and filled with cement mortar. This prevents cracking of the walls, which can be caused by the load from the rafter system.
The rafter structures are laid evenly and neatly - this must be monitored. The bevels of the gable are brought to an even state using a band saw.
Next, a sheathing is made from boards, on top of which waterproofing and insulation are laid, most often mineral wool or polystyrene foam. The insulation is fixed and covered with another layer of sheathing. On the inside, the insulation is reinforced with a vapor barrier.
The interior decoration of the attic is usually made of wood. After this, they begin to lay the roofing material, for example, tiles.
If the attic is being reconstructed for living space, then other issues have to be resolved: arranging a staircase, laying additional layers of sound and heat insulation, determining the location of the attic windows and installing them.
Mansard roof design
One of the most rational methods of acquiring the constantly lacking additional square meters for your home is to arrange an attic floor in it. The special design will make it possible to significantly increase the usable living space, making the attic comfortable for permanent living.
Types of mansard roofs
These roofs can be made in a variety of configurations, and, ultimately, their effectiveness in using the usable area of the attic can be very different.
There are such roofs:
- Symmetrical or asymmetrical.
- Single-level or two-level.
- Gable or broken.
The triangular shape of a roof with a rectangular outline is the simplest of all types of structures. In this embodiment, the floor of the attic is the lower chord of its truss. The main operational loads here fall on the parallel beams that make up this structure, so high strength requirements are placed on them. But horizontal fights with vertical posts can be made from thin bars and boards.

A sloping roof is constructed when the dimensions of the attic are not reduced to a triangular shape. At the same time, it becomes possible to significantly reduce the area of “dead zones” formed in the under-rafter space, and to organize the attic space in the most optimal way. It is more difficult to build such a roof, and the costs when choosing this option increase. But, if the attic is planned in the design drawing of the house, then this form of roof, in which the roof elements act as the walls of the attic, is used quite often, because a sloping roof with two slopes really allows you to use the space of the attic to the maximum.
Advantages
Despite the fact that this method of covering a house will be more expensive than a conventional gable roof, it has a number of advantages:
- This option allows you to increase living space, being much cheaper in cost than constructing an extension or additional building.
- For many owners of suburban areas, saving available land space is a significant advantage of this method of increasing the usable area of the house.
- Energy costs for heating a house with this option are reduced by approximately 30% due to the reduction of heat losses through the roof.
- If we consider the aesthetic side, then a house with an attic floor looks more interesting than ordinary buildings with triangular roofs.
Peculiarities
The design of the attic roof has its own characteristics:
- Such a roof is made with the obligatory installation of steam and waterproofing, being insulated, soundproof and aesthetically designed, because, as a rule, an attic floor is built to provide additional living quarters.
- The rafter system inside this attic room is made without braces and struts, since the design allows them to be moved beyond the ceiling.
- The attic floor must be built from lightweight materials, since the calculation requires taking into account the additional load on the existing structure, and reducing the weight of the structure being built to a minimum, and transporting materials upstairs will be much easier. As a rule, attic structures are built from wood or cold-formed thin-walled metal profiles, but materials made from stone or concrete are not recommended.

- When choosing the geometry of the roof, you must remember that its architecture must be combined not only with the functional purpose of the building, but also with the design of the interior space. The selected architectural and construction system determines the further arrangement of the supporting structure and fences.
- Such a roof is quite simple to implement, so you can build it yourself: without any serious financial costs or the involvement of construction companies. You just need to have the desire, the necessary materials, several assistants and some knowledge of the technology of work.
DIY installation
The main steps for constructing such a roof are almost always the same, although the nuances of this process may change due to the characteristics of each house, so it is better to entrust its calculation and design drawing to specialists.
Planning
For further comfortable living in the attic room, the walls of the attic before the beginning of the slope must have a minimum height of 1.5 meters. Rafters are most often erected at an angle of inclination from 30 to 60 degrees. When completing the drawing yourself or entrusting it to specialists, decide on the skylights (whether they will be inclined or vertical), and also remember that the architecture, design and roofing material must be combined with the entire structure.

Arrangement of the rafter system
For the installation of rafter beams, the basis will be beams installed on racks with a step between them not exceeding 2 meters. These racks, which will serve as a special “skeleton” holding the attic walls, are reinforced with temporary braces. Do not forget to carry out the simplest waterproofing of these beams using roofing material.
Then the upper beam is laid, the installation of the rafter frames is completed, the lower beam is installed and secured, which plays the role of supporting the rafter leg. Rafter legs are mounted, the distance between which is recommended to be from 100 to 120 cm.
Video review: Installation of the rafter system
Watch a video about how the rafter system of an attic roof is made:
For large roofs, it is also necessary to install a ridge beam due to the large weight of the roof. If the length of the rafters is shorter than 8 meters, you can only install guy wires under the ridge. To do this, first install the two outer fillies, after which the twine is pulled, and the remaining fillies are brought out, on which the hem board is secured.
In the places where the attic windows are installed, the rafters are secured with transverse bars. The window frame will subsequently be attached to them.
Lathing and waterproofing
The frame is done. The next step is to nail the sheathing battens to the rafters. A hydraulic barrier is secured to the sheathing with construction staples, and a layer of thermal insulation is laid on top of it.
Installation and strengthening of the roof
Then the attic roof structure is complemented by the construction of side attic walls.
And, in the end, the attic itself is directly arranged. Since it is often built for living, work is required to insulate and illuminate the additional floor.
Everyone decorates the room according to their own taste, but the most often used when decorating this room is plasterboard, lining or plywood. The choice of materials today is huge.
The housing problem, for many, has become the number one problem. And if it is not possible to increase the living space in width, then you have to look for other ways and arrange unexpected premises for housing. One of the possible solutions was a mansard roof, in the internal space of which premises suitable for living will be organized.
Today this solution is very popular. And this is understandable, because the rafter system of the mansard roof in its modern design allows you to find the most rational design option, which allows you to achieve comfortable room shapes under a reliable, and therefore durable, roof.
Mansard roof rafter system: photo of the design of the sloping roof load-bearing system
Rafter structures for mansard roofs
The attic roof, like any roof structure, consists of two systems:
- fencing, including roofing pie, hydro-, steam- and thermal insulation;
- power, which includes, firstly, the rafter system, and, secondly, the power plate.

Mauerlat distributes the loads experienced by the rafters of the attic roof onto the load-bearing walls
The rafter system of an attic roof is its power frame with many types and varieties. In addition, it is considered the most optimal due to its relative simplicity and low costs for increasing the internal space.
Note: for example, a square meter of usable area of an 8x10 attic roof costs about 70–75 dollars. That is, equipping an attic of 60–65 m2 is much cheaper than building the same area from scratch.
Classic attic - rafter system
Being the basis for the attic roof, the rafter system, in addition to its weight, must also withstand the design loads from wind and snow. If we also take into account that this is the link that connects together the roof slopes, floor beams, walls and ceiling, then it is obvious that the calculation of the rafter system of the attic roof must be carried out carefully and competently.

The relationship between the usable area of the attic and the angle of the roof
The design and dimensions of the attic depend on many parameters, in particular on the width of the house and the height of the room. Therefore, you first need to prepare the appropriate drawings and work out all the connections. The diagram of the attic roof rafter system must contain comprehensive information about
- interconnected height, pitch and cross-section of the racks;
- the length and slope of the rafters;
- location of roof windows;
- sheathing size
- material for gable cladding.
System calculations can be significantly simplified if you use tables that present ready-made design solutions for the supporting system units, indicating fastening methods and main dimensions.
The design of the attic roof truss system
There are two types of rafters for the attic.

Types of rafter systems
- Hanging ones have two supports, say, walls, columns, etc. They simultaneously work in bending and compression, thus transferring horizontal forces to the load-bearing walls. The simplest hanging trusses consist directly of rafters and a lower belt - a tie (crossbar), resting on the mauerlat. Such a system justifies itself if the supporting walls are no more than 6–6.5 m apart from each other.
- Layered rafters have additional support in the center, for example, an internal wall or column, so they only work in bending. This design reduces the loads that load-bearing walls are exposed to. The layered supporting system can cover a distance of up to 10 m, and when installing additional purlins and racks - up to 16 m.
- The load-bearing system of the attic floor often includes both of these types

The simplest attic rafter system
As can be seen from the top figure, the load-bearing system of the attic roof includes lower rafters (sloping), upper (hanging) rafters, vertical posts, a connecting horizontal crossbar and a ridge beam. For a small attic, the presence of ridge beams is not necessary. It can be completely replaced with a continuous sheathing, which creates a diaphragm of rigidity.
As you know, the most rigid figure in geometry is a triangle, therefore ridge and side trusses, made in a triangular shape, can provide rigidity to the system in two directions - lateral and vertical.

The design of the supporting system for the attic
As for volumetric rigidity, for this purpose struts are installed, which also form a triangle together with the vertical posts.
Materials in the construction of rafters for the attic
The most popular materials for attic rafter systems are wood and metal.
As a rule, the system is assembled from solid wood species such as pine and spruce. Beams and boards must be treated with antiseptics and fire retardants, which protect them from fungus, mold, insects and fire.
Glued laminated timber is often used for these purposes, which has certain advantages over regular timber:
- it is more durable and lightweight;
- allows you to increase the distance between the rafters of the attic roof without loss of rigidity;
- does not require additional impregnation.

Metal rafters for mansard roofs
To give special strength to the attic structure, thin-walled steel structures are used. They are distinguished by durability, endurance and ease of assembly, they are fire-resistant, but, unfortunately, they cost much more than wooden ones.
Note: Since LSTK is assembled using bolts and rivets, such structures can be disassembled and rebuilt if necessary, replacing any part or rebuilding the entire roof.Rafter system of a gable mansard roof
The attic roof, depending on the angle of inclination, is divided into three main types:
- classic: slope slope 45 degrees, house width 6–8 m;
- pointed: slope – 60 degrees, width – from 6 m:
- broken line: has two unequal slopes, usually with a slope of 30 and 60 degrees. This design is often found in houses up to 6 m wide.

Project of a country house with a gable attic floor
Features of rafters for an attic with two slopes
The gable roof uses the principle of hanging rafters. Relying only on the outer walls and on each other, they form a single under-roof space - a void without walls or supports in the middle of the attic space. Hanging type attic rafters are also called non-roof rafters.

Gable roof rafter system
The design of the rafter system of the attic roof in this case has some features, for example, a bolt tie, which, in contrast to the thrust created by the rafter legs, fastens them and the opposite slopes, is located not at the base of the attic rafters, but above. The height is chosen in such a way that it is enough to construct an attic space.
If a system of hanging rafters is used for an attic with a span of 6 m or more, then the trusses are supported by braces or racks. They are placed on purlins installed on the ceiling. The lower part of their legs has a limitation - the length should not exceed 4.5 m.
As you know, the pitch of the rafters varies from 0.6 to 1 m. How to calculate this distance for a specific roof?
Initially, in the calculations we will use the average pitch value - 0.8 m. We will carry out calculations for a roof with a slope length of 23 m. For its installation, on average, taking into account rounding up, 23/0.8 = 29 rafter legs will be required. Let's add 1 more - this is an element that must be installed along the edges of the frame. In total, there were 30 elements. It remains to adjust the step: 23/30=0.77. Thus, the rafters must be installed with a distance of 0.77 m between them.
Installation of attic roof rafters
Installation of rafters for the attic is schematically carried out in the following order.

Gable roof rafters
- The top beam is attached to the racks, and the first one will simultaneously serve as a rafter frame.
- Install the Mauerlat.
- The rafter legs are mounted in increments of 60–100 cm. First, the trusses that are outermost to the pediment are installed and a level is drawn in accordance with which the intermediate elements are installed.
- The rafters at the top of the frame are connected to each other.
- For roofs longer than 7 m, a ridge beam is installed.
Rules for fastening rafters
They are attached to the Mauerlat using a rigid or sliding method. In the first option, the possibility of interaction between fixed elements is almost completely excluded.

Attachment to the Mauerlat: sliding and rigid
For this
- use metal corners to fasten the lower part of the rafters with additional rigid support on the sheathing beam;
- They are attached to a notch made on the rafter leg and the connection is additionally secured using staples, nails, and wire.
The sliding coupling of the elements provides the rafters with freedom of movement within certain limits. It is more suitable for wooden houses, as it eliminates deformation of the supporting system when the house shrinks. It is carried out using a “sled”, a bracket, and nails.

Attachment to the ridge: butt and overlap
Attachment to the ridge is carried out:
- connecting the rafters end-to-end, cutting the upper edges at a certain angle.
- fastening per run one at a time
- overlap connection.