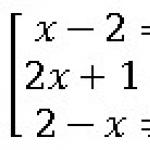This month marks
100th birthday
Alexander Leonidovich CHIZHEVSKY
(1897-1964)

SOLAR PULSE IN THE RHYTHMS OF THE PLANET
In the 20s, an interesting experiment was carried out, the results of which were then reported in the Operations Department of the People's Commissariat of Posts and Telegraphs and in the Electrical Engineering Department of the People's Commissariat of Railways: spontaneous disruptions in the operation of electrical communication devices were observed for a long time, the resulting statistical data were compared with astrophysical and geophysical observations. It turned out that the reliability of the functioning of telegraph communications and other electrical devices directly depends on the state of the surrounding environment, systematically disturbed by cosmic factors.The author of these studies was a young, twenty-eight-year-old scientist Alexander Chizhevsky. For some reason, they did not want to extend his work contract with him at the Biophysical Institute of the Academy of Sciences, but they attracted him to active scientific cooperation in the Practical Animal Psychological Laboratory of the Main Science of the People's Commissariat for Education, headed by the famous trainer Vladimir Durov...
The whole life of A.L. Chizhevsky is full of contrasts and contradictions. Either by the will of fate he was elevated to the crest of glory, or thrown into the abyss of misfortune, and in the central press the scientist was defamed as an “enemy of the people.” What to do - apparently, the ambiguity of the life line is characteristic of many extraordinary natures, and especially in the field of science. This logic was accurately noted by the Danish storyteller Hans Christian Andersen: from the “ugly duckling” a magnificent swan grows. From Chizhevsky, who at first seemed to some an eccentric, or even an adventurer, grew into a genius, whose memory is now applauded by the whole world.
A.L. Chizhevsky made an important discovery: everything living - from the simplest microorganisms to the biosphere as a whole - is born, develops and lives in the rhythm (or rather rhythms) of sun activity (or, as they also say, solar activity). He completed the great work begun by Nicolaus Copernicus - the breaking of geocentrism in its last refuge - in the sciences of the biological and social forms of the movement of matter. In the major monograph by A.L. Chizhevsky, “The Cosmic Pulse of Life,” just published by the Mysl publishing house, this is described in the most complete form.
But this is not the only thing the remarkable scientist is famous for. When Alexander Leonidovich was asked what he mainly does, the answer was: “Electricity of life!” In this direction he made fundamental discoveries. Any one of them would be enough for his name to remain forever inscribed in the history of natural science. It was he who discovered the biological effect of ionized and deionized air. Aeroions of negative polarity are the “vitamins” of the elixir of life we inhale; without them, the normal functioning of metabolic processes in biosystems is impossible. He was responsible for the establishment of the electrically determined structural-systemic ordering of living blood and the creation of the theory of electrogeodynamics. In the history of hematology, this scientist’s discovery is equivalent to the discovery of blood circulation itself. Based on his work, Chizhevsky proposed a method for early diagnosis of cancer, ahead of all known biochemical tests.
Based on his innovative scientific ideas and discoveries, Alexander Leonidovich laid the foundations of electro-aerosol therapy and electron-ion technology, which is used today everywhere in industrial production (from electro-painting to electro-separation of dispersed substances, from electro-cleaning and electric improvement of environmentally unfavorable environments to electric intensification of physico-chemical processes and management of the latter).
A.L. Chizhevsky was decades ahead of his contemporary science and technology, stepped into the 21st century, and his very significant contribution to the knowledge of the universe will also be appreciated by future generations.
Leonid GOLOVANOV, member of the Presidium of the K. E. Tsiolkovsky Academy of Cosmonautics.
As is known, the aeroionizer (“Chizhevsky Chandelier”) consists of a high-voltage DC source of negative polarity and the “chandelier” itself - the “emitter” of aeroions. Let's first get acquainted with the voltage source, the diagram of which is shown in Fig. 1. 
This is how the source works. The positive half-wave of the mains voltage charges capacitors C1 and C2 through diodes VD2, VD3 and resistors R5, R6. Transistor VT1 is open and saturated, and VT2 is closed. When the positive half-wave ends, transistor VT1 closes and VT2 opens. Capacitor C1 is discharged through resistor R4 and the control junction of thyristor VS1. The thyristor turns on, and capacitor C2 is discharged onto the primary winding of transformer T1. In the oscillatory circuit, consisting of capacitor C2 and the transformer winding, damped oscillations arise.
High voltage pulses arising on the secondary winding are fed to a multiplier made on diode columns VD6-VD11 and capacitors SZ-S8. A negative voltage of about 25...35 kV from the output of the multiplier is supplied through current-limiting resistors R7-R9 to the “chandelier”.
The source mainly uses resistors MLT, R7-R9 - C2-29 (MLT with the same total resistance is also suitable), R6 -SPOE-1 or any other power of at least 1 W. Capacitors - K42U-2 for voltage 630 V (C1) and 160 V (C2) and KVI-3 for voltage 10 kV (SZ-S8). In place of C1 and C2, you can use paper, metal-paper or metal-film capacitors for voltages of at least 400 and 160 V, respectively. Capacitors SZ-S8 - any others with a voltage of at least 10 kV and a capacity of at least 300 pF.
Diode VD1 - any low-power silicon diode, VD2 and VD3 - any for an operating voltage of at least 400 V, VD4 - 300 V, VD5 - any of the KD202 series for a voltage of at least 200 V or another similar one. High-voltage poles can be KTs110A, KTs105D, KTs117A, KTs118V or others with a voltage of at least 10 kV. SCR - KU201 or KU202 series for a voltage of at least 200 V.
Transistor VT1 can be replaced by almost any n-p-n structure of low or medium power, for example, the KT312, KT315, KT3102, KT603, KT608 series; VT2 - any of the same medium or high power structure with a permissible collector-emitter voltage of at least 300 V, for example, KT850B, KT854A, KT854B, KT858A, KT859A, KT882A, KT882B, KT884A, KT940A.
A B-115 automotive ignition coil was used as the T1 transformer, but any other automobile or motorcycle coil will do.
The source is assembled in a housing measuring 115 x 210 x 300 mm, made of dry plywood 10 mm thick, the walls of the housing are connected with screws and glue (Fig. 2). All elements of the source, except for the transformer, are mounted on a printed circuit board measuring 140 x 250 mm made of single-sided foil fiberglass, a fragment of which is shown in Fig. 3 in scale 1:1.5. For capacitors SZ - C8, windows measuring 55 x 20 mm are cut into the board. The capacitors are secured with petals screwed to them, which, in turn, are soldered to the contact pads of the printed circuit board. 

The MGShV-0.75 wire to the “chandelier” is led out of the housing through an insulator machined from fluoroplastic, but any thick-walled tube made of insulating material can be used.
In contrast, it is advisable to make a “chandelier” in the following order. First, you need to prepare the appropriate number of stationery pins with a ring as needles. Tin the rings by dipping them into molten solder, onto the surface of which solid zinc chloride is first poured (it melts). You can simply dip the rings into a solution of zinc chloride (soldering acid) before tinning.
Next, you need to make a ring with a diameter of 700...1000 mm by bending it from a metal tube with a diameter of 6...20 mm and connecting the ends of the tube end-to-end using a piece of metal rod of suitable diameter and rivets. Cut a circle from corrugated cardboard that fits freely into the ring. Mark the circle with a grid with a side of squares of 35...45 mm and insert needles into the nodes of the grid, then pull tinned copper wire through the rings of needles in two directions and solder the rings. Insert the circle into the ring and wind the ends of the wire around it, preferably soldering the turns. Carefully remove the cardboard circle, stretch the mesh a little to obtain the desired deflection - the “chandelier” is ready.
Install the “chandelier” at a distance of at least 800 mm from the ceiling, walls, lighting fixtures and 1200 mm from the location of people in the room. It is advisable to place it above the bed, securing it to two fishing lines with a diameter of 0.8...1 mm stretched tightly between the walls of the room. It is convenient to tighten the fishing line in a triangle - two hooks for attaching it are installed on the wall to which the “chandelier” is closer, one on the opposite wall. The “chandelier” itself is attached to the fishing line with small wire hooks.
It is advisable to install the voltage source at a height of about two meters, for example on a cabinet.
Before turning on the device for the first time, variable resistor R6 should be set to the lowest position according to the diagram. Having turned on the source with the “chandelier” connected to it, smoothly increase the voltage supplied to it by turning the axis of resistor R6. After the smell of ozone appears, reduce the voltage until it disappears.
If corona is observed in a high voltage source, determine its location in the dark and cover it with molten paraffin (of course, with the source de-energized).
It is useful to check the performance of the “chandelier”, as recommended in, and if you have a static voltmeter, measure the voltage on it. It should be about 30 kV.
It should be remembered that large metal objects in the room in which the air ionizer operates, for example, a chandelier or a bed, as well as people, can accumulate an electrical charge. The spark that occurs when you touch them can be quite painful.
In addition, after a lighting chandelier accumulates a charge, a breakdown of the insulation of its electrical wiring is possible, harmless, but accompanied by a fairly loud click.
Therefore, it is advisable to ground metal objects, preferably through resistors with a resistance of several megaohms. The metal frame of the lighting chandelier can be connected through the same resistor to one of the network wires.
The author turns on the aerial ionizer before going to bed for two hours, using for this purpose the timer described in.
LITERATURE:
1. Ivanov B. “Chizhevsky’s chandelier” - with your own hands. - Radio, 1997, No. 1, p. 36, 37.
2. Aleshin P. Simple timer. - Radio, 1986, No. 4, p. 27.
S. BIRYUKOV, Moscow
Radio magazine, No. 2, 1997
Laboratory analysis showed that the air in forests, fields and meadows contains from 700 to 1500 negatively charged air ions per cubic centimeter. The more of these particles there are in the air, the more beneficial it is for living organisms to breathe. In modern apartments, the number of air ions is reduced to 25 per cubic centimeter. This is almost on the verge of the minimum for the normal functioning of life processes. This indirectly manifests itself in rapid fatigue, constant ailments and constant painful conditions. You can increase the number of air ions in the apartment using a device - an air ionizer, or ionizer, or, quite simply, the Chizhevsky Chandelier.
The main element of Chizhevsky’s chandelier is a lightweight aluminum rim with a diameter of about a meter, on which bare copper wires with a diameter of no more than 1 mm are placed parallel to each other every 3-5 centimeters. This design is a mesh; needles with a maximum length of 5 centimeters and half a centimeter thick are soldered into the nodes of the mesh. It is advisable to even sharpen them; to increase the incoming current, you can use Soviet pins with a ring.

Three copper wires with a diameter of 1 mm are attached to the rim of Chizhevsky’s invention at 120 degrees, which are connected by soldering at one point, directly above the center of the rim. High voltage is supplied to this node. At the same place, the entire structure is attached to the ceiling bracket using plastic ties at a distance of at least 15 centimeters.

A voltage converter is used to create a high-voltage voltage of negative polarity with a rating of at least 25 kilovolts. Less is impossible, because air ions will quickly disintegrate and will not have time to get into the human lungs. If the room is large enough, then it is better to use a voltage converter designed for 40 - 50 kilovolts.
The circuit of a very simple to repeat high-voltage voltage converter is shown in the diagram below. Its main feature is that it is powered by standard AC power.

The operation of the circuit diagram is as follows: during the flow of the positive half-cycle of the mains voltage, capacitance C1 begins to charge through resistance R1, diode VD1 and the primary winding of the transformer. The thyristor is initially locked, because no current flows through its control electrode.
With a negative half-wave of alternating voltage, the diodes VD1 and VD2 are locked, but the thyristor, on the contrary, will open. Capacitance C1 will begin to discharge through the primary winding of the transformer. A high voltage pulse will be formed in the secondary winding of the transformer, since we have a step-up transformer.
Then these pulses are rectified by the rectifier of a voltage multiplier connected according to the classical circuit using diodes VD3-VD6, and from their output the high voltage goes to the ionizer.
Resistance R1 is 1 kOhm, and R3 is 10...20 MOhm. Diodes - any with a current of at least 300 mA and a reverse voltage of 400 V (VD1) and 100 V (VD2). SCR KU201K, KU201L, KU202K-KU202N. The transformer is a 6 V B2B ignition coil from a Soviet motorcycle, but a car one will also work.
The Chizhevsky aerial ionizer does not require adjustment and starts working as soon as it is plugged into the network. You can change the constant voltage at the output by selecting resistance R1 or capacitance C1.

You can check the operation of the air ionizer using a small piece of cotton wool, as it should be attracted to the “chandelier” from a distance of about half a meter. The photo above shows a possible version of a compact home-made ionizer, where ions spread from a metal plate. If you bring your hand ten centimeters close to the needles, you will feel the influence of the electric field. When the ionizer is operating, there should be no foreign odors, since all odors are an indirect sign of harmful gases, which should not be present in a properly functioning Chizhevsky chandelier. It is worth noting that this design is worse than a fully functional chandelier.

In the positive half-wave, the voltage from the secondary winding of the first step-down transformer through the diode VD1 and the primary winding of the second transformer charges capacitor C1. At this moment, the converter thyristor is closed, because no current flows through the second diode. In the negative half-wave, the thyristor opens through VD2, and capacitance C1 begins to discharge through it and the primary winding of the second transformer, and an increased voltage appears on its secondary winding, which can be supplied to the Chizhevsky chandelier through a high-voltage diode.
First transformer: PEL wire 0.2. Primary winding 2120 turns; secondary - 2120 turns; the third - 66 turns.
An ignition coil from Ural chainsaws was used as a step-up transformer.
A special feature of this air ionizer circuit is that it is powered by a constant voltage of 12 Volts, which makes it possible to use this ionizer inside a car, and it is precisely when driving along crowded city streets that a breath of fresh air is so necessary.

The timer microcircuit generates rectangular pulses that travel to the gate of a field-effect transistor, which opens or closes from them at a given frequency. Therefore, an alternating voltage is created on the primary and then on the winding of the pulse transformer.
The field-effect transistor must be high-voltage, if you cannot find the one in the diagram, then it can be replaced with an IRF740 or IRF840. We use a transformer from the line scan unit of a CRT TV. On the free side of the core we wind ten turns of copper wire with a diameter of 1 mm. And the secondary high-voltage winding is original from the lineman. The high from the secondary winding of the transformer is rectified and charges the capacitance. The high-voltage diode can be replaced with the domestic KTs106G or KTs123.

DIY Chizhevsky chandelier
Introduction
All human life is inextricably linked with atmospheric air. Moreover, for normal life activity it must satisfy many parameters. Temperature, humidity, pressure, percentage of carbon dioxide, degree of pollution and so on.
If they deviate from the norm, a person’s ability to work, well-being and overall health may deteriorate...
We all know that after a thunderstorm the air becomes very “fresh” - unusually clean and light.
The whole point here is that during thunderstorms the air is abundantly saturated negatively charged oxygen molecules - air ions.
For the first time, a Russian scientist began to study the influence of negative air ions on the human body Alexander Leonidovich Chizhevsky in the 20s of the last century (by the way, it was he who called them that...) and found out that they are the ones who have a positive effect on well-being and even more than that: they also have some healing properties.
Prototype of the first Chizhevsky chandeliers appeared back in the 20s of the XX century. It was something like an ordinary chandelier suspended from the ceiling, but emitting not light but negatively charged oxygen ions. The principle of operation of the device was based on the creation of a high-tension field using parallel conductors under high voltage (20...30 kV).
In this high-voltage field, the formation of negatively charged oxygen ions occurred.
This device looked something like this:

Well, in general, everyone has already guessed that we are talking about an ordinary ionizer, which we propose to repeat with our own hands.
By the way: it would be extremely interesting for all of us to look at the finished product and we would be very grateful if those who assembled Chizhevsky’s chandelier would share with us all
Ionizer for Chizhevsky chandelier
The efficiency of the air ionizer largely depends on the design of the “chandelier”. Therefore, special attention should be paid to its manufacture.
The basis of the “chandelier” is a light metal rim (for example, a standard gymnastic ring “hula hoop”) with a diameter of 750... 1000 mm, on which bare or tinned copper wires with a diameter of 0 are stretched along mutually perpendicular axes with a pitch of 35...45 mm ,6...1.0 mm. They form part of the sphere - a mesh that sags downwards. Needles no more than 50 mm long and 0.25...0.5 mm thick are soldered into the mesh nodes. It is desirable that they be sharpened as much as possible, since the current coming from the tip increases, and the possibility of the formation of a harmful by-product - ozone - decreases. It is convenient to use pins with a ring, which are usually sold in office supply stores.

Three copper wires with a diameter of 0.8...1 mm are attached to the rim of the “chandelier” at 120° intervals, which are soldered together above the center of the rim. High voltage is applied to this point. At the same point, the “chandelier” is attached using a fishing line with a diameter of 0.5...0.8 mm to the ceiling or bracket at a distance of at least 150 mm.
A voltage converter is needed to obtain a high voltage of negative polarity that powers the “chandelier”. The absolute value of the voltage must be at least 25 kV. Only at such a voltage is sufficient “survivability” of air ions ensured, allowing them to penetrate into the human lungs.
For a room such as a classroom or school gym, the optimal voltage is 40...50 kV. It is not difficult to obtain this or that voltage by increasing the number of multiplying cascades, but you should not get too carried away with high voltage, since there is a danger of a corona discharge, accompanied by the smell of ozone and a sharp decrease in the efficiency of the installation.
Chizhevsky chandelier diagram
The circuit of the simplest voltage converter is shown in Fig. 2, a. Its special feature is direct power supply from the network.

The principle of operation of the Chizhevsky chandelier circuit
This is how the device works. During the positive half-cycle of the mains voltage, capacitor C1 is charged through resistor R1, diode VD1 and the primary winding of transformer T1. The thyristor VS1 is closed in this case, since there is no current through its control electrode (the voltage drop across the diode VD2 in the forward direction is small compared to the voltage required to open the thyristor).
During a negative half-cycle, diodes VD1 and VD2 close. A voltage drop is formed at the cathode of the trinistor relative to the control electrode (minus - at the cathode, plus - at the control electrode), a current appears in the control electrode circuit and the trinistor opens. At this moment, capacitor C1 is discharged through the primary winding of the transformer. A high voltage pulse appears in the secondary winding (step-up transformer). And so - every period of mains voltage.
High voltage pulses (they are double-sided, since when the capacitor is discharged, damped oscillations occur in the primary winding circuit) are rectified by a rectifier assembled using diodes VD3-VD6. The constant voltage from the output of the rectifier is supplied (through limiting resistor R3) to the ionizer-“chandelier”.
Resistor R1 can be made up of three parallel-connected MLT-2 with a resistance of 3 kOhm, and R3 - from three or four series-connected MLT-2 with a total resistance of 10...20 MOhm. Resistor R2 - MLT-2. Diodes VD1 and VD2 - any others for a current of at least 300 mA and a reverse voltage of at least 400 V (VD1) and 100 V (VD2). Diodes VD3-VD6 can be, in addition to those indicated in the diagram, KTs201G-KTs201E. Capacitor C1 - MBM for a voltage not lower than 250 V, C2-C5 - POV for a voltage not lower than 10 kV (C2 - not lower than 15 kV). Of course, other high-voltage capacitors for voltages of 15 kV or more are also applicable. SCR VS1 - KU201K, KU201L, KU202K-KU202N. Transformer T1 is a B2B ignition coil (6 V) from a motorcycle, but you can use another one, for example from a car.
Install the “chandelier” at a distance of at least 800 mm from the ceiling, walls, lighting fixtures and 1200 mm from the location of people in the room.
There is no need to configure the device; if assembled correctly, it starts working immediately.
It is only advisable to pay attention to the following:
1. Volume of the room. If the size of the room exceeds 20 sq.m, then it is advisable to increase the voltage at the output of the multiplier by adding another bridge of a diode and a capacitor (picture “b” in Fig. 2).
2. It is not advisable to install the ionizer near electronic devices and metal structures. The ionizer can cause the accumulation of static electricity, which is fraught with consequences.
3. It is recommended to turn on the Chizhevsky chandelier for no more than 30 minutes (for residential premises).
Sources:
1. Ivanov B. “Chizhevsky’s chandelier” - with your own hands. - Radio, 1997, N 1, p. 36, 37.
2.Ivanov B. S. Electronics in homemade products. - M.: DOSAAF, 1975 (2nd ed. - DOSAAF, 1981).
Air is the most important natural resource that humans cannot do without. The state of health largely depends on its quality. To boost immunity and improve well-being, doctors advise spending more time in the “fresh air.” However, increased pollution in cities deprives people of this opportunity. Everyone gets out of this situation in their own way. One of the methods to solve the problem is to use a Chizhevsky chandelier in the apartment. What this device is, whether it brings benefit or harm to the body and how to do it yourself - these are the topics that will be covered in this article.
What is a Chizhevsky chandelier?
The Chizhevsky chandelier is a device designed to saturate the air with high polarity ions. The unit received its name from the name of the famous scientist. He was the first to develop an electroeffluent device, on the basis of which the chandelier itself was created. It is the world's first air ionizer. Thanks to Chizhevsky’s chandelier, a person can get that same “fresh air” in his apartment that benefits the body.
The benefits and harms of Chizhevsky's chandelier
There is no consensus among scientists about whether the device is beneficial or harmful to the body. On the one hand, experts do not deny the fact that the device purifies the air, neutralizing the effect of harmful bacteria. On the other hand, the oversaturation of oxygen with negatively charged ions in itself can cause harm to human health. Only the balance of all air elements will avoid such a result. However, achieving balance at home is almost impossible. Therefore, scientists were divided into supporters and opponents of the device.
Advantages
Experts who are positively disposed towards the unit have found that Chizhevsky’s chandelier benefits the body:
- accelerates the process of restoration of soft tissues after mechanical damage, which includes scratches, burns, cuts, etc.;
- improves the body’s condition in case of infectious pathologies, promoting a speedy recovery;
- increases endurance and performance;
- prevents the occurrence of cardiovascular pathologies, in particular heart attack and stroke;
- normalizes metabolic processes occurring in cells;
- increases the body's defenses;
- reduces the likelihood of the spread of infectious pathologies;
- generally improves a person’s well-being, relieving chronic fatigue and weakness;
- has a positive effect on the nervous system.
Experts advise using the Chizhevsky chandelier to purify the air for people suffering from pathologies of the respiratory system - bronchitis, asthma, whooping cough and tuberculosis (only at the initial stage of development). The use of the device is also relevant for allergies, high blood pressure and unstable emotional background.
Modern scientists have been able to establish that Chizhevsky’s chandelier has a positive effect not only on people, but also on animals, so the device can also be used in those homes where beloved pets live.
Flaws
Some scientists have concluded that using the device can cause harm to the body:
- worsens the functioning of the respiratory system and against this background wheezing and other pathologies occur;
- disrupts heart function;
- provokes frequent headaches;
- creates additional stress on the body, which makes overall health worse.
Description of the Chizhevsky chandelier
The Chizhevsky chandelier, the benefits and harms of which are still controversial among scientists, is an indoor device of a tabletop or pendant type. The unit runs on electricity. After turning it on, negatively charged ions begin to be produced, which results in air disinfection.
What does Chizhevsky's chandelier look like?
The device is a plastic cylindrical body, on top of which a wire spherical metal frame is fixed. It is the working part of the device. It is he who produces air ions. The device is equipped with a cord and plug that connects to the network. The device can be installed on any flat surface or hung on the wall.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of the device is to supply high voltage to the electrode. Due to this, negatively charged ions begin to be released into the environment. When a person inhales air saturated with these particles, they penetrate into the body and give their charge to red blood cells. These formed cells, in turn, deliver ions to all human organs and systems, which improves the metabolic processes occurring in the cells.
Instructions for use
To avoid negative consequences from the operation of the device, you must follow the instructions for its use. Before turning on the unit, the room needs to be well ventilated.
The duration of the first use should not exceed half an hour. Gradually the time can be increased. After several sessions, the operating time of the chandelier should be 3-4 hours a day.
When the chandelier is working, all windows and vents must be tightly closed, otherwise air masses may carry away the generated ions. If after the first sessions you experience any discomfort such as headaches or dizziness, there is no need to worry. These conditions are not a side reaction of the body or a manifestation of pathology. They often occur in metropolitan residents after prolonged exposure to the so-called fresh air. To avoid recurrence, it is recommended to shorten the next session. When dizziness and headaches do not bother you, you can increase the duration of operation of the device, bringing it to the desired value.
Contraindications
Skeptical specialists have established contraindications for using the device:
- exhaustion of the body;
- increased blood pressure in the kidneys;
- oncological pathologies;
- bronchial asthma and similar pathological conditions;
- pulmonary tuberculosis in late stages of development;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system, which include heart failure, atherosclerosis and vascular spasms;
- ozena.
To date, no reasonable evidence has been provided that the device cannot be used for these conditions, but a number of experts argue that contraindications are relevant.
How to make a Chizhevsky chandelier yourself?
Despite the fact that the device is not a scarce commodity and acquiring it in our time is not difficult, ordinary people are interested in the question of how to make a Chizhevsky chandelier on their own. To manufacture the unit, you will need a metal rim, the diameter of which should be 1 meter. Bare copper wires with a diameter of 1 mm are stretched onto it. They are fixed at a distance of 4 cm from each other. The wires should form a hemisphere with a slight sag at the bottom. Needles with a length of 5 cm and a diameter of 0.5 mm are soldered into the sides on four sides. It is important to ensure high-quality sharpening of such elements. This prevents the formation of ozone, which can cause severe harm to the body. For this reason, experts advise purchasing a professionally produced Chizhevsky chandelier rather than making the device yourself. Three copper wires with a diameter of 1 mm should also be soldered to the rim. At one end they are fixed on the made device, and the other ends are soldered together above it. The final stage is the creation and connection of the power supply, from which all the operation of the unit will be carried out.
To make a generator you will need:
- fuse;
- diode;
- voltage divider;
- a pair of dinistres;
- output to resistor winding;
- diode bridge;
- capacitor;
- timing chain.
A generator is assembled from such elements and fixed to the device. After this, you can start using it.
To check the functionality of the unit, you need to turn on the device and bring your hand to the needles at a distance of 10-15 cm. If you feel cold, it means the unit is functioning. There is another way to check. You need to take a small piece of cotton wool and bring it to the device at a distance of half a meter. If the fiber is attracted to the unit, then the chandelier is functioning normally.

Manufacturers of Chizhevsky chandeliers
The Chizhevsky chandelier is produced by several manufacturers:
- EcoUnit - makes Chizhevsky chandeliers with a ceramic body. Thanks to its stylish design, the device will fit into any interior. Disadvantage: if not handled carelessly, it can break.
- Ecology-plus - devices from this manufacturer are easy to operate. They have a stylish modern design and do not require changing filters.
- Atmos - produces stylish modern units. They are easy to operate, do not require filter changes and consume little energy. The devices are equipped with backlighting, which distinguishes them from similar devices.
- Super-plus-ECO - units from this manufacturer do not just saturate the air with air ions. The devices also disinfect it from dust and harmful viruses and bacteria.
- Hippocrates - devices from this manufacturer are equipped with an air purification filter and ultraviolet disinfection. The units operate in two modes. They are easy to use and do not consume much electricity. Easily disassembled to change filters.
Where to buy a Chizhevsky chandelier?
You can buy a Chizhevsky chandelier in the online store. There is a large selection of units from various manufacturers available here. Prices range from 1,500 to 6,000 rubles. In specialized stores you can also purchase air ionizers made based on Chizhevsky’s developments. Cost from 1000 to 10000 rubles.
Chizhevsky's chandelier is a device thanks to which “fresh air” like in the forest can be obtained even in a city apartment. Despite the fact that scientists have not been able to prove that the device causes harm to the body, it is recommended to use it for various pathologies only after the approval of a doctor.