In connection with the popularization of energy-saving lamps, there is an increasing need to debunk myths about this device. Some sources say that this device is harmless and economical, while others say that it is harmful to health and about the inefficiency of energy saving. In this article, we will try to figure out how energy-saving lamps work and the advisability of buying the so-called "housekeepers".
The device and principle of operation of energy-saving lamps
The principle of operation of a conventional energy-saving lamp resembles a fluorescent lamp. The main components of an energy-saving lamp:
- ballast;
- luminescent bulb.
An ordinary energy-saving lamp differs from a fluorescent lamp in the presence of an electric ballast.

Fluorescent bulbs come in U-shaped or spiral shapes. The inner walls of the flask have a phosphor coating and consist of two spirals, which are sealed at the end of the tube. When the ESL is heated, electrons exit to the surface of the spiral. A large voltage arises between the spirals and ultraviolet radiation is released in mercury vapor, which provides the illumination process. The amount of mercury in the composition of the phosphor depends on the color of the glow of the lamp. The service life of the ESL ranges from 6000 to 15000 hours.
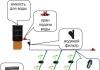
Scheme of an energy-saving lamp with a power of 11 W:
- anti-interference choke;
- fuse;
- diode bridge;
- filter capacitor.
Varieties of energy-saving lamps
Some sources call energy-saving lamps, only fluorescent lamps, but this is incorrect. After all, any device that has good light output, but at the same time consumes a small amount of electricity, has the right to be called an energy-saving lamp.

Therefore, energy-saving lamps include:
- compact fluorescent lamps;
- linear fluorescent lamps;
- some types of LED lamps.
The latter option has more advantages than conventional fluorescent lamps. LED lamps do not contain mercury and other substances hazardous to human life. The level of light output of LED lamps is much higher, and the mechanical strength ensures long and trouble-free operation of such a device.
The composition determines the temperature of energy-saving lamps, and, accordingly, the color that a conventional ESL emits. To obtain a soft white color, a 2700 K lamp (measured on the Kelvin scale) is chosen, a 4200 K lamp has a soft white color, and a 6400 K lamp emits a cool white tint.
Types of fluorescent energy-saving lamps
According to the type of device, fluorescent lamps are distinguished:
- with electromagnetic throttle;
- with electric throttle.

The second option is quieter and has better performance.
According to the size of the plinth, there are:
- E14 has a 1.4 cm threaded hole and is installed in reduced household cartridges;
- E27 - 2.7 cm is suitable for installation in standard cartridges;
- E40 - 4.0 cm are distinguished by a built-in electronic ballast.
Energy-saving lamps have an international marking that characterizes the brightness of the light emitted by the lamp. To find out the color rendering index, multiply the first digit of the marking by 10. The indicator interval is from 60 to 100.

The second and third digits of the marking are the temperature on the Kelvin scale, divided by 100. For example, when buying a lamp with a marking index of 827, you need 8 * 10, and 27 * 100. It turns out the color rendering index is 80, and the temperature and color are 2700.
To illuminate the subway, shops, public spaces, energy-saving lamps marked from 2700 to 3500 K are used.
The best option for lighting a residential area is provided by ESL marked 830, 840.
To increase the service life of energy-saving lamps, you must follow some rules:
- avoid voltage fluctuations, if possible, install voltage stabilizers;
- limit the number of times the lamp is turned on and off.
Troubleshooting basic energy-saving lamps
Causes of malfunctions in the operation of an energy-saving lamp:
- the use of low-quality components in the manufacture or repair of the lamp;
- use of parts that do not fit the existing voltage;
- constant operation of the lamp leads to overheating of the housing and failure of the lamp, since there is no ventilation in the bulb, all parts heat up quickly.

When the energy-saving lamp stops working, first check the integrity of the lamp filaments. Darkening of the glass of an energy-saving lamp is the main sign that the filament has broken. To restore such a lamp, use a 10 Ohm 0.25 W resistor, remove the diode that shunts this spiral. After this procedure, when the lamp is started, flickering will be observed for 10 seconds.
As a result of violations of the thermal regime, transistors fail. To replace transistors, first unsolder these elements, and then install new ones. When choosing transistors, be guided by the 13003 series.
Name of transistors depending on the power of energy-saving lamps:
- from 1 to 9 W - 13001 TO-92;
- 9 W - 13002 TO-92;
- from 15 W to 20 W - 13003 TO-126;
- from 25 W to 40 W - 13005 TO-220;
- from 40 W to 65 W - 13007 TO-200;
- 85 W - 13009 TO-220;
To eliminate the flickering of an energy-saving lamp, you need to check the capacitor. As a result of the increased voltage, a breakdown occurs. In this case, replace the capacitor.
If energy-saving lamps burn out quickly, then there is no ventilation, for example, in spotlights or there are sudden power surges. To do this, install a stabilizer.

Energy-saving lamps - impact on human health
Before we analyze the issue of the effect of energy-saving lamps on human health, consider the main advantages and disadvantages of this device.
ESL advantages:
- long period of use;
- using a small amount of electricity;
- a guarantee that allows you to replace the lamp;
- the presence of a stable light flux;
- use at high temperature limits;
- Possibility to choose the type of lighting.
Disadvantages of ESL:
- high cost compared to conventional light bulbs;
- in case of mechanical damage, mercury can enter the environment;
- a rather large basement that does not fit into all fixtures;
- scientifically proven harm of energy-saving lamps on human health.

When conducting research on energy-saving lamps, it was found that these devices have a high level of electromagnetic and ultraviolet radiation, so it is recommended to install energy-saving lamps at a distance of 300 cm from a person. It is not recommended to install such lamps in lamps or devices near which a person is constantly located. Effects of electromagnetic radiation:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- influence on the nervous and cardiovascular system;
- acceleration of the consumption of the body's resource forces.
A large number of switched on energy-saving lamps not only harms human health, but also negatively affects electrical safety.
The content of mercury in one light bulb can easily poison a large number of people, so it is recommended to hand over these devices for recycling to special institutions. Prolonged exposure to minimal mercury vapor also negatively affects human health and leads to micromercialism - mercury poisoning, accompanied by increased fatigue, drowsiness, apathy and other symptoms.
For people who are sensitive to ultraviolet radiation, such lamps pose a great danger. After all, a small amount of ultraviolet light comes out through the flask, which causes skin mutations. The ultraviolet light of energy-saving lamps is the most dangerous for the eyes, so do not use energy-saving lamps at a distance that exceeds 200-300 cm.
Energy-saving lamps characteristics and overview of manufacturers
Energy-saving lamps can be bought at any electronics store or on the construction market. Among the variety of brands that manufacture ESL, it's hard not to get confused, so let's look at the main manufacturers of energy-saving lamps:
1. OSRAM (Germany) - energy-saving lamps that have various shapes: spirals, balls, circles, candles, caps and more complex combinations.

Varieties of OSRAM energy-saving lamps:
- integrated type;
- non-integrated type.
The first option starts automatically, and the second one requires a special starting device in the lamp holder.
This manufacturer of energy-saving lamps has only positive reviews. Lamps do not burn out and perform functions for a long time.
Price from 2 to 6 $.
2. UNIEL (Russia) - presents three series of energy-saving lamps:
- Premium - ESL have improved performance and long service life;
- Promo - have a high luminous flux and first class energy consumption;
- Standard - lamps are in the form of an open spiral, save 80% of electricity.
A variety of shapes: spiral, pear, semi-spiral, spot lamps, reflectors, candles, linear lamps, modular, projector and ultraviolet lamps.
Price: from 3 to 5 $.
3. Philips (Holland) - represents a large selection of energy-saving lamps, which are distinguished by a variety of shapes, colors and applications.
Peculiarities:
- high energy efficiency;
- variety of color temperatures;
- no heating of the flask.
The price is from 4 to 7 $.

4. Camelion (Hong Kong) - energy-saving lamps that have a number of advantages:
- the service life is eight times longer than that of a conventional light bulb;
- use in both open and closed fixtures;
- when the lamp is turned on, there is no flicker;
- emitting soft light that does not dazzle the eyes;
- heat resistance from -25 to +50 degrees;
- a wide choice of capacities and models of lamps;
- three series: Classic, PRO and Eco.
Price from 2 to 5 $.
5. Cosmos (Russia) - represents energy-saving lamps that emit maximum light with minimum dimensions.
Usage:
- bedroom or living room to create a romantic atmosphere;
- lamps made in an unusual decorative form, which allows them to be used without a lamp;
- residential or industrial premises;
- illumination of decorative ceilings or exhibition centers.
Price from 2 to 4 $.
6. Wolta (Germany) - used to illuminate workplaces or residential premises.
Peculiarities:
- compact models;
- a wide range of applications;
- profitability;
- high reliability and durability.
Price from 4 to 9 $.
7. Vito (Turkey) - energy-saving lamps, which are represented by the Spiral and Vito T8 series.
Characteristic:
- operation within 8000 hours;
- spiral shape of lamps;
- colors: from warm white to cold blue;
- strong case, to prevent mechanical damage.
The price is from 5 to 7 $.
8. General Electric (USA) - presents a variety of ESL models.
Peculiarities:
- the line of energy-saving lamps Link - is a "smart lamp" that is controlled using a smartphone. The cost of such devices ranges from $25 to $60;
- the company created incandescent vacuum lamps that have been relevant for more than 30 years.
The price is from 5 to 9 $.
Content:
"Energy-saving lamps" (housekeepers, energy savings), designed to replace incandescent lamps, appeared on the market more than ten years ago and immediately attracted the attention of consumers. Manufacturers of energy-saving lamps promised a five-fold reduction in electricity consumption spent on lighting and a service life exceeding the life of an incandescent lamp by 10 times or more. It must be said that these promises were generally justified. The long experience of using housekeepers has confirmed the high energy and performance characteristics of new light sources.
It should be noted that the term "energy-saving lamps" is not entirely accurate. With the same success, energy-saving can be called any light source that consumes less electricity than incandescent lamps with equal luminous flux. There are many such light sources. These are the usual linear fluorescent lamps and DRL lamps. Energy-saving lamps also include halogen and LED lamps. So the accustomed term can be considered a successful marketing move, which made it possible to obtain a high level of sales of lamps of this type. A more correct name for an energy-saving lamp should be considered the name used by specialists - a compact fluorescent lamp.
In this material, we will try to tell in detail about the principle of operation and design of compact fluorescent lamps, discuss their advantages and disadvantages, and consider the most acceptable areas of application.
The device and principle of operation of energy-saving lamps
Energy-saving lamps are a modification of fluorescent lamps adapted for installation in lamps and chandeliers with Edison E14, E27 or E40 screw cartridges. A standard screw base allows you to replace conventional incandescent lamps with energy-saving ones without altering the lamps. Discharge tubes of energy-saving lamps can be U-shaped or spiral. The number of tubes and their size depends on the power of the lamp. Two filaments are placed inside the gas discharge tube, which are simultaneously cathodes. To increase the emissivity of the cathodes, they are coated with ceramics based on alkali metals. Discharge tubes are filled with an inert gas containing mercury vapor. The inner surface of the tubes is covered with a layer of phosphor, which determines the spectrum and color temperature of the lamp. Inside the lamp base there is a voltage converter (driver) that performs the function of an electronic ballast.

When voltage is applied to an energy-saving lamp, the driver generates a high voltage that can cause a breakdown of the gas gap between the electrodes. At the same time, the coils are heated, increasing the emissivity of the electrodes and facilitating the evaporation of mercury. After some time, a stable gas discharge appears in the tube. At this time, the driver enters the electronic ballast mode. Current and voltage are maintained at the optimum operating level. During a gas discharge, mercury vapor actively emits ultraviolet light. Ultraviolet radiation is absorbed by the phosphor, which in turn begins to emit light from the visible part of the spectrum.
Energy-saving lamps are usually powered by 220 V AC. However, 12 volt and 24 volt energy-saving lamps can be found on sale, which can be powered by car batteries or the on-board network of cars.
Lighting characteristics of compact fluorescent lamps
The lighting characteristics of energy-saving lamps do not differ from those of linear fluorescent lamps. For most manufacturers, the color rendering index of compact lamps is 80 - 98, which is included in the visual comfort zone. As for the color temperature, it can vary from 2700 K (warm) to 6000 K (cool white), which allows you to choose lamps with the right color temperature for various applications and rooms.
In principle, the use of an electronic ballast in energy-saving lamps should exclude light flicker (pulsation), since it operates at a frequency of several tens of kilohertz. However, some manufacturers save on high-voltage electrolytic capacitors installed in the rectifier filters of the drivers. This can lead to noticeable pulsations in the luminous flux of a lamp with twice the mains frequency. You can make sure that there are no pulsations of light by shooting a video using a phone or video camera.
Energy and performance characteristics of energy-saving lamps
The luminous efficacy of compact fluorescent lamps is four to five times higher than that of incandescent lamps. This means that with the same luminous flux, energy-saving lamps consume four to five times less electricity. For example, an energy-saving lamp 20w e27 shines, just like an incandescent lamp, with a power of 100 watts. Below is a table of correspondence between the power consumption of incandescent lamps and compact fluorescent lamps.
The service life of energy-saving lamps significantly exceeds the service life of incandescent lamps. While incandescent lamps last an average of about 1,000 hours, compact fluorescent lamps can last more than 10,000 hours.
Energy-saving lamps are much more expensive than incandescent lamps. However, given their high energy efficiency and long service life, there is no doubt that replacing incandescent lamps with energy-saving ones will quickly pay off.
Features of the operation of energy-saving lamps
Energy-saving lamps do not immediately enter the operating mode after switching on. It may take several minutes for them to reach maximum light output. The luminous flux of lamps gradually decreases as they are used. This is due to degradation of cathodes and phosphor. All these factors must be taken into account when choosing compact fluorescent lamps as light sources.
Compact fluorescent lamps do not perform well at low temperatures. This is due to the physics of a gas discharge. Therefore, energy-saving lamps should not be installed in street lamps or used in unheated rooms.
To illuminate the workplaces of specialists working with color, it is necessary to pay attention to the color rendering index of the lamps. For professions such as artists, printers or designers, a color rendering index of 80 may not be acceptable.
Not all types of energy-saving lamps can work with dimmers (dimmers). If you have already installed such devices or are planning to use such devices in the future, then you should carefully read the inscriptions on the packaging of the lamps or consult with the seller.
Also, energy-saving lamps may not work correctly with illuminated switches. The fact is that the backlight itself consumes a small current when the switch is off. This current will charge the driver capacitors and, as they charge, the lamp will periodically flash.
Energy saving lamps contain mercury. Therefore, used or failed lamps are subject to mandatory disposal at special enterprises. Unfortunately, the issue of collection and disposal of mercury-containing lamps has not yet been fully resolved, especially among the population.

In this material, we tried to talk in detail about compact fluorescent lamps, their design and principles of operation, technical characteristics and features of their operation. We hope that the material was useful to you.
In the face of constantly rising electricity prices, we strive to save money and at the same time use normal lighting that does not hurt the eyes, is bright enough and does not cause irritation. That is why energy-efficient devices are the best solution for those who want to use high-quality light economically. From this material, you will find out which lamps are the most energy-saving, what varieties currently exist, the better one or another type, and whether their cost really pays off.
Energy-saving lamps: which ones are better
To understand which lamps are the most energy-saving, let's compare them with the usual incandescent bulbs already familiar to us all, or, as they were also called, “Ilyich's bulbs”. By purchasing one such device, in just a month you will understand how profitable it is, pleasing to the eye and more economical. Compared to a conventional incandescent lamp, they:
- Consume less energy, but give the same light output. That is, the efficiency of this device is much higher. Unlike an incandescent light bulb, which gives an efficiency of no more than 18–20%, such a product reaches a maximum efficiency of at least 70–80%. In simpler terms, out of every hundred watts, an ordinary lamp, working at full power and heating the coil, gives out only eighteen to twenty percent of the light.
- They last longer and have a longer warranty period. Any store that sells energy-saving light bulbs will give you a lifetime warranty. In some varieties, it can be about twenty years. Considering how often ordinary lamps burn out, this is very beneficial, because you can always change a burned-out energy-saving device under warranty.
- Pretty safe. All energy-saving lamps (except for the halogen type) do not have a direct connection of contacts, while Ilyich's light bulb has all contacts connected by a spiral. Therefore, in this case, a short circuit is almost impossible.
- They do not carry such a load on the general apartment network as usual. This is also one of the safety indicators, due to the non-congestion of the network, other household appliances will not suffer.

If we consider all these devices regarding their impact on human vision, energy-saving lamps, incandescent, daylight, then they all flicker with a certain frequency during their work. This is due to the way in which an electronic impulse passes through them. This is not noticeable to the naked eye, but upon closer examination, scientists found that:
- The cold spectrum affects vision more than normal and because of this, the retina is destroyed.
- Brightness and more frequent flickering in fluorescent lamps affect the brain and the stability of nerve nodes. People working in an office with such lighting are 30 times more likely to seek help from psychoanalysts.
- According to the latest data from ophthalmologists, the optimal brightness is 2700–3100 K. This is good both for the living room and for the children's room. Therefore, when choosing a light bulb, consider this.
- If the lamp is opposite the mirror, it affects vision by an order of magnitude higher. It is best to install energy-saving light bulbs near mirrored surfaces and glass doors. Paying attention to your appearance, putting yourself in order before going to the store or for a walk, your eyes and brain will not be so tired.
If we talk in more detail about what it is and what they are, then let's move on to the next paragraph of our material.
What are energy saving lamps?

By definition, an energy efficient lamp is a special device for uniform light distribution, powered by the mains. In comparison with its counterparts, such a product has an increased level of light output and significantly saves electricity.
Such economical devices are linear (LL) and compact (CFL). They all contain mercury and LED substances. A common feature of linear and compact fluorescent lamps can be considered a tangible savings in electrical energy consumption. And at the same time, they fill the space with much more light than the usual incandescent lamps. The latter are gradually falling out of use, as many countries around the world have recently set the course for the operation of energy-efficient devices due to their overall safety and economy.
What lamps are energy saving?

Energy-saving fluorescent lamps include compact and linear lamps, which differ from each other in terms of technical indicators and functions. Let's consider them in more detail to understand which energy-saving lamps are best for the home:
- CFL (compact fluorescent lamps) characterized by an arcuate shape, which allows it to be placed in small lamps. They are almost always used at home, being the optimal replacement for conventional incandescent lamps. Often they are included in the package of non-standard lighting fixtures. The composition of such a light bulb contains inert gases (known to many as argon and neon), as well as mercury vapor. The outer case is finished with a phosphor. Due to the collision of electrons with mercury components, an externally imperceptible UV radiation is released, which turns into scattered light (this is facilitated by the phosphor coating). Compact lamps consist of three parts: a base for connecting to the mains, an electronic control device for lighting and keeping the light bulb burning. It performs the transition from the 220W power supply to that which is required for stable operation of the lamp without flickering. The third component of the device is the flasks, which are the outer shell of the lamp. Due to the difference in these elements, the type of CFL is also determined: for example, by the color of the radiation, the features of the base (there are 2D categories, often installed in showers, E27 - for a regular cartridge, E14 - for a reduced cartridge, E40 - for a large cartridge).
- Linear fluorescent lamps (LLL) are ring, straight, or a specific U-variation. Rectilinear devices are in the form of long glass tubes, at the ends of which there are glass legs, where, in turn, electrodes are fixed. On the inner surface of the lamp there is a phosphor coating, and the tube cavity itself is filled with inert gases and mercury. The safety of people from the destructive evaporation of mercury is guaranteed by hermetic soldering of the lamp. Linear lamps differ in terms of the diameter and length of the tube, the width of the base element. As a rule, the larger the dimensions of the LL, the greater the consumption of electricity. Often, such LLs are used in manufacturing plants and enterprises, in offices and public places. The most popular among consumers are compact fluorescent lamps, and their linear alternative is slowly leaving production.
Proven benefits of energy efficient lamps

Summing up all of the above, I would like to emphasize that the use of energy-saving lighting devices in everyday life or at work has many advantages, among which the following are especially noticeable:
- According to manufacturers of lighting devices, the use of energy-saving lamps can reduce up to 80% of electricity costs. The luminous flux of these devices is much higher than that of conventional incandescent lamps.
- Energy efficient lamps have a long service life. This is more than 10 times longer than ordinary light bulbs. Such a long operating time is also a big plus for placing economical lamps in places where frequent changes of light bulbs are very difficult (on high ceilings, between flights of stairs, etc.).
- They produce less heat than conventional lamps. Due to this, it is advisable to install small CFLs with a high power rating, especially in complex structures: sconces, chandeliers and swirling lamp shapes. Economic lamps will not melt the wires and plastic elements of the cartridge, which sometimes happens when using ordinary lamps.
- The light of energy-saving lamps is much more beneficial for vision, as it is distributed evenly. Uniform radiance is obtained due to the design of the lamp: the area of \u200b\u200btheir body is larger than that of a spiral of ordinary light bulbs.
- You can choose from different color temperatures. 2700K lamps give white color, 6400K - cold white, 4200K - daylight. The specified data are measured on the Kelvin scale.
For more information on choosing energy-saving lamps, see the video:
Modern manufacturers offer energy-efficient lamps of different sizes, capacities, equipped with various socles. Also, lighting devices have a different structure, from which their schemes differ. Depending on the manufacturer, you can choose products with more complex mechanisms that will have high-quality elements of an electronic ballast (electronic ballast).
Features of schemes
There are inexpensive models on the market, but they often lack important components that affect the life of products. The most popular in Russia are such manufacturers:
- Navigator (domestic manufacturer);
- MAXUS (international British-English corporation);
- DeLux (Chinese manufacturer);
- Camelion (umbrella brand originated in Hong Kong and successfully integrated today in Europe, Asia and America).
The circuit of an energy-saving lamp is its so-called heart, with the help of which the entire lighting device functions. The composition of the electronic board may include parts of various quality and size, depending on the conscientiousness of the manufacturer. It is worth noting that high-power devices, equivalent to incandescent lamps of 105 watts or more, cannot have small elements, since the electrical circuit must be equipped with massive parts to ensure normal operation.
If we compare the bulbs "Maxus" and "Navigator", you can make sure that their components will be different. This means that companies collaborate with different manufacturers of electrical components or use different approaches to create these elements themselves.
In general, all lamp circuits for 20, 30, 60 W and above will be very similar to each other, which helps to repair them if some mechanisms fail.
The principle of operation of the housekeeper
 An energy-saving lamp works on almost the same principle as linear fluorescent lamps. Its glow is provided by the passage of voltage through the electrodes located along the edges of the glass bulb. The tube is filled with an inert gas and mercury vapor or its compounds. When the medium inside the lamp is heated, ionized electrons are formed, which collide with gas atoms at high speed. All this leads to the formation of a low-temperature plasma that emits ultraviolet radiation.
An energy-saving lamp works on almost the same principle as linear fluorescent lamps. Its glow is provided by the passage of voltage through the electrodes located along the edges of the glass bulb. The tube is filled with an inert gas and mercury vapor or its compounds. When the medium inside the lamp is heated, ionized electrons are formed, which collide with gas atoms at high speed. All this leads to the formation of a low-temperature plasma that emits ultraviolet radiation.
However, a person cannot perceive either ultraviolet or infrared radiation. To convert it into light visible to our eyes, a special coating is used - a phosphor. Passing through it, the ultraviolet rays turn into a uniform, bright, saturated illumination.
Due to its low power, a 20W housekeeper is more efficient than a 100W incandescent lamp. Consider why light bulbs help save energy, and how they are arranged.
Components of the scheme
An energy-saving lighting device consists of the lamp itself and an electronic ballast, which is also called an electrical circuit. All electronic elements are designed to ensure uninterrupted and correct operation of the lamp. The biggest distinguishing feature of these devices from conventional incandescent lamps is that they operate on direct voltage, and not on the alternating voltage that the network produces. It is for this reason that the electronic ballast is built into the body of the light bulbs itself, it is used to transform, distribute and protect the mechanism. The switching circuit contains the following components:
- high-voltage low-power diodes;
- anti-interference choke;
- medium power transistors;
- high-voltage electrolyte (most often 400 V);
- capacitors of various capacities, but of the same voltage (250 V);
- high-frequency transformers (2 pieces);
- resistors.
How the lamp is ignited
When voltage hits the dinistor, a pulse is generated that goes to the transistor and provokes its opening. After the start is completed, this part of the circuit is blocked by a diode. After the transistor opens, the capacitor is discharged, which is necessary to prevent the re-opening of the dinistor. Transistors act on a transformer. It is made of a ferrite ring processed with three windings arranged in several rows. The voltage on the filament is given through a capacitor from a step-up resonant circuit.
 The glow in the tube begins at the resonant frequency, which is determined by a larger capacitor. At the time of ignition, its voltage is up to 600 watts. At start-up, it exceeds the average by 5 times, so it is important that the flask is whole and tight. Otherwise, the transistors may be damaged.
The glow in the tube begins at the resonant frequency, which is determined by a larger capacitor. At the time of ignition, its voltage is up to 600 watts. At start-up, it exceeds the average by 5 times, so it is important that the flask is whole and tight. Otherwise, the transistors may be damaged.
After complete ionization of the gas in the flask, the capacitor with the largest capacitance, which determined the frequency of the glow, is shunted. This leads to a decrease in frequency and the transfer of control of the generator to the second capacitor. The generated voltage is reduced, but remains within the limits necessary to keep the light bulb burning.
The fundamental point is that the cathode and anode alternately change their places, this helps to ensure the uninterrupted operation of the circuit and greatly simplifies repairs if it needs to be done.
Lamp device
In addition to the electronic ballast mounted in the base, an important element of an energy-saving lighting device is a lamp. It is she who is responsible for the uniformity of light distribution, its saturation, color reproduction and other properties of the device. It is possible to conditionally divide the sections of the flask into lower and upper. At the top, special holes are made for installing the tube. The lower part contains a board in which the parts are located, and from which the leads from the tube extend.

The top area of the board is equipped with wires that go to the base. The elements of the lamp can be attached to each other with the help of special latches. In cheaper models, parts are glued together. If you need to make repairs, you need to draw a screwdriver along the joint line or disconnect the latches.
How is the repair done
 In order to determine which elements of the circuit or the lamp itself are faulty, it must be disassembled. To do this, disconnect the upper part from the lower and turn off the flask. Using an ohmmeter, we check the filament spirals of the flask. If it is found that one spiral has burned out, the bulb is repaired. It can be closed with a resistor of 8-10 ohms. The resistor must be large. You will also need to remove the diode that shunts the burnt out spiral, if it is in the circuit.
In order to determine which elements of the circuit or the lamp itself are faulty, it must be disassembled. To do this, disconnect the upper part from the lower and turn off the flask. Using an ohmmeter, we check the filament spirals of the flask. If it is found that one spiral has burned out, the bulb is repaired. It can be closed with a resistor of 8-10 ohms. The resistor must be large. You will also need to remove the diode that shunts the burnt out spiral, if it is in the circuit.
If a resistor burns out in lamps of 30 watts or more, it is likely that the transistors are also out of order. This is due to the breakdown of the capacitor. You can correct the situation by installing a new fuse (resistor) and transistors.
In addition to replacing damaged circuit elements, you can upgrade the lamp. This is done by drilling ventilation holes in the plinth. Some models already have them, and if manufacturers have not taken care of proper cooling of electronics, you can do it yourself.
Attention! If you drilled ventilation holes in the base of a 30 W lamp or a lighting fixture of a different power, it cannot be used in rooms with high humidity. This can lead to a breakdown in the capacitor and failure of the lamp.
Expediency of intervention in schemes
 It is possible to repair lamps at 30 W or other power only if you are confident in your abilities and knowledge. When you don’t understand how the lamp circuit works, and what can break in it, it’s best not to try to fix the breakdown yourself.
It is possible to repair lamps at 30 W or other power only if you are confident in your abilities and knowledge. When you don’t understand how the lamp circuit works, and what can break in it, it’s best not to try to fix the breakdown yourself.
It is forbidden to perform any actions with housekeepers if the integrity of their flasks is violated. The tube contains mercury or its vapor, therefore, when it is depressurized, the device becomes dangerous to human health and life.
Let's summarize
The schemes are almost the same in all models. Differences may be in the presence of diodes, shunt coils and other elements. However, if you know the electronics of one device, then working with all the others will be quite simple.
Schemes are often interested in people who want to repair broken lighting fixtures on their own. This is not difficult to do if you have the necessary skills and are sure that the housekeeper can be brought into working condition.
In this article: the history of the compact fluorescent lamp; its structure and principle of operation; the spectrum of an energy-saving lamp depends on the composition of the phosphor; pros and cons of energy-saving fluorescent lamps; how to choose an energy-saving lamp.
The ban on the sale and production in Russia of incandescent lamps familiar to us has given rise to a number of persistent rumors around energy-saving lamps. For an ordinary consumer, which we are, the main task of lighting fixtures has been and remains the very quality of lighting. And, of course, I don’t want to incur extra expenses for the purchase of these “new-fangled” lamps, because they cost much more than “Ilyich's lamps”. Consider the characteristics of energy-saving lamps in this article.
History of creation
Officially, the first fluorescent or, as it is also called, fluorescent lamp was created at the beginning of the last century by an engineer-inventor from the USA, Peter Cooper Hewitt, who received a patent for it on September 17, 1901. Although some researchers dispute his primacy in the invention, calling the "father" of the fluorescent lamp the little-known German physicist Martin Arons, who experimented with mercury lamps at the end of the 19th century.
The fluorescent lamp invented and patented by Hewitt contained mercury, the vapors of which were heated by an electric current passed through it. The Hewitt lamp was spherical and slightly curved, it gave more light than the Lodygin-Edison lamps, but this light was bluish-green, unpleasant for the eye. For this reason, the first mercury lamps were used only by photographers and they were not widely used.

Peter Cooper Hewitt. 1861-1921
The fluorescent lamp in its almost modern form was created by a group of German inventors led by Edmund Germer, who patented their invention on December 10, 1926. It was Germer who came up with the idea to apply a fluorescent coating on the glass surface of the lamp from the inside, which converted the ultraviolet glow of a mercury lamp into a white light that did not hurt the eyes. Albert Hull, an engineer at General Electric, developed a fluorescent lamp with a similar coating by early 1927, but the company was forced to purchase a patent from Edmund Germer, who had issued it earlier.
Since the acquisition of the Germer patent, General Electric engineers have been actively engaged in improving fluorescent lamps, trying to bring them to mass production. To reduce the size of the bulb, round and U-shaped lamps were created, demonstrated at the GE booth at the New York World's Fair in 1939, lamps with a compact spiral bulb were developed by General Electric engineer Edward Hammer in 1976. However, helical fluorescent lamps were never put into production in the 1980s, as company executives considered the costs of building new factories excessive. In 1995, Chinese manufacturers took advantage of the slowness of General Electric by launching the production of energy-saving lamps with spiral bulbs.

Edward Hammer with his invention - a lamp with a compact spiral bulb
The magnetically ballasted (SL) screw-in lamp was introduced by Philips in 1980 and was the first fluorescent lamp of its kind to compete with incandescent lamps. An energy-saving lamp with an electronic ballast (CFL) in 1985 was first demonstrated by the German concern Osram.
The main structural elements of a fluorescent lamp are a bulb, an electronic ballast and a base. A base with a thread for screwing into the lamp socket and with contacts for powering it practically does not differ from the base of a conventional incandescent lamp.

The curved bulb of a fluorescent lamp is covered with layers of phosphor, filled with an inert gas and, in a small amount, mercury vapor - their ionization causes the lamp to glow when the power is connected. The content of mercury in fluorescent lamps ranges from 1 to 70 mg. Inside the flask are tungsten electrodes coated with a mixture of oxides of barium, calcium, zinc and strontium. The phosphor applied to the inner surface of the glass bulb in compact fluorescent lamps contains alkaline earth metals and is therefore 40% more expensive than phosphors used in oblong fluorescent lamps for ceiling fixtures. Alkaline earth metals in the composition of the phosphor of compact lamps provide operation at high radiation intensity, thanks to them it became possible to reduce the diameter of the lamp bulb. The bizarrely curved shape of the flask in fluorescent lamps makes it possible to reduce its length by dividing it into several short sections that communicate with each other.
The lamps themselves, coated with a phosphor and containing mercury vapor, will not work when the power is connected - a ballast starter is required, built into the lamp between the base and the bulb. Consuming high frequency current in the order of 50 kHz, the electronic ballast (CFL) eliminates the flickering effect of energy-saving lamps while increasing light output. The electronic ballast increases the high-frequency current for itself - it contains an inverter in its circuit. The tasks of the ballast also include heating the electrodes and maintaining the power of the fluorescent lamp at a nominal level, regardless of voltage drops in the network. The service life of an energy-saving lamp depends on how well the electronic ballast is made.

How does a fluorescent lamp work? Applying power causes a discharge between the electrodes, the current passes through a mixture of inert gas and mercury vapor, fast electrons collide with slow mercury atoms - the lamp lights up. However, 98% of the light emitted by an energy-saving lamp is ultraviolet, invisible to human vision. And the visible light coming from it is provided by phosphor layers that glow under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The color of the illumination produced by fluorescent lamps depends on the chemical composition of the phosphor applied to the glass bulb from the inside.
Dependence of the visible spectrum of a fluorescent lamp on the phosphor
The light generated by cheap energy-saving lamps is most often unpleasant for the eyes - blue and yellow colors predominate in its spectrum, as a result, the color of objects in the illuminated room is unnatural. The reasons lie in the type of phosphor containing inexpensive calcium halophosphate. Such lamps, having a high light output, are designed to illuminate non-residential premises (warehouses, etc.) - they externally produce white light, but its reflection from objects reveals an incomplete spectrum (lack of red and green colors).

Energy-saving lamps for home lighting have a higher price. the phosphor in them creates 3-5 colored bands (for example, red, green and blue) from the spectrum visible to the human eye and imitates the effect of natural light, but at the same time reduces light output.
It is worth mentioning right away that the positive characteristics given below depend on the manufacturer of this lamp - his desire to save on raw materials and components seriously reduces the quality and life of fluorescent lamps.
pros energy saving lamps:
- significantly lower, compared to incandescent lamps, energy consumption with higher light output. If a 100 W incandescent lamp has a light output of 100-150 lumens, then the light output of a 20 W fluorescent lamp will be 1,100-2,000 lumens - the difference is obvious. The low power consumption of energy-saving lamps, among other things, significantly reduces the load on the wiring;
- significant service life, 8-10 times longer than the service life of incandescent lamps. When working an average of 2.5-3 hours a day, a fluorescent lamp will illuminate the room for 8,000-11,000 hours and will last for several years (depending on the model and manufacturer), about 6-8 times longer than the usual "Ilyich lamp";
- during the entire period of operation, the intensity of illumination by compact fluorescent lamps does not change;
- the highest temperature of an operating energy-saving lamp will not exceed 60 °C. 95% of the energy in incandescent lamps goes to heat, i.e. at a power of 100 W, an incandescent lamp will heat up to 95 ° C;
- lamps of several light shades of illumination are produced, the main ones are warm daylight (similar to the color of lighting from incandescent lamps), daylight and cold daylight;
- in the produced luminous flux, flicker is completely absent (stroboscopic effect), lighting stability is ensured by the electronic ballast of the lamp;
- factory warranty from the manufacturer for each energy-saving lamp. There were never any guarantees for "Ilyich's lamps".
Minuses energy saving lamps:
- high price. If incandescent lamps cost 10-25 rubles, then fluorescent lamps will cost 80-400 rubles. Chinese and domestic energy-saving lamps are cheaper, European ones are more expensive;
- the protrusion on the base, where the ballast of the lamp is located, sometimes prevents it from being installed. The lamp with electronic ballast does not look even when it is installed in a chandelier, because the plinth is too noticeable;
- to warm up to full brightness of light emission, these lamps require from 30 seconds to two minutes;
- The lifetime of compact fluorescent lamps depends on how often the power is turned on and off - the more often this happens, the faster the lamp will fail. Between switching off and on again, it is necessary to pause for at least 5 minutes;
- such lamps cannot be used by people with skin diseases and epilepsy, because. the intensity of illumination of energy-saving lamps is higher than conventional ones and can lead to negative consequences;
- do not break the glass bulb of the lamp, because mercury vapor will enter the premises and they will have to be ventilated for several hours at any time of the year, and residents will need to leave the premises of the house (apartment) for the entire period of ventilation - this is important. If several lamps are broken at once, you will need to call the specialists of the Ministry of Emergency Situations for demercurization. Do not break fluorescent lamps;
- it is not at all clear how to dispose of failed fluorescent lamps - it is forbidden to throw them away, and there are no specialized collection points in most settlements.
How to choose an energy saving lamp
First of all, make sure the integrity of the lamp offered by the seller, the reliable connection of the bulb with the base - lamps of small Chinese manufacturers, assembled by hand, usually sin with a loose connection.
The power of a new lamp is determined by the power of incandescent lamps previously used in a given room with a decrease of 4-5 times. Those. if “Ilyich lamps” of 100 W were used, you will need a fluorescent lamp of 20-25 W (it is better to take with a small margin of power).

The intensity of illumination of this lamp is determined in the temperature on the Kelvin scale indicated on its packaging: from 2,700 to 4,000 oK - warm light (similar to light from incandescent lamps), such lamps are suitable for lighting bedrooms and kitchens; from 4,000 to 5,000 oK - warm white light, suitable for living rooms and halls; from 6,000 to 6,500 oK - cold white light, used for classrooms and offices. Lamps of the latter type for lighting houses should not be purchased - the light is too saturated, it is difficult to tolerate.
Lamp size. The base of fluorescent lamps, as noted above, is longer than the base of incandescent lamps - for home lighting, the base of the E27 standard (length - 105 mm, diameter - 60 mm) will be optimal, the dimensions of which are similar to cartridges for "Ilyich lamps".
Warranty and operational life. They are indicated by manufacturers on the packaging: the optimal service life is in the range of 6,000-12,000 hours; warranty - from a year or more. Please note that the stated terms will not be valid for all brands of fluorescent lamps - Chinese manufacturers may indicate high terms, but in fact the lamps will fail much earlier.
Manufacturers and brands. European energy-saving lamps are represented on the Russian market - German "Osram" and "Wolta", Dutch "Philips", Danish "Comtech", Polish "Ikea", American "General Electric"; Russian - "Ecola", "Cosmos", "Aladin", "Lisma", "Uniel"; Chinese - "Camelion", "Navigator", etc. Of course, the products of the largest European manufacturers are of high quality and performance, but it is worth noting that compact fluorescent lamps of domestic production are also of good quality at a lower cost.
In custody
As you can see from this article, fluorescent lamps really save energy and work properly, provided that the requirements for their operation are met. High cost and some mercury vapor, of course, remain a problem for consumers, but manufacturers are trying to solve them - for example, in modern models of energy-saving lamps, mercury is bound by calcium amalgam and will not evaporate, as manufacturers claim, if the lamp is damaged.
Another way to save energy and ensure that mercury vapor does not enter living quarters is to use LED lamps, but this is a topic for a separate article.
Abdyuzhanov Rustam, rmnt.ru