Covering with soft roofing is now chosen by an increasing number of people. This is easy enough to explain. The material is inexpensive and installation is not difficult. However, in order for the roof to last for many years, its crate must be properly created. If we take into account that the material has its own characteristics, then a number of rules must be observed during the arrangement. All operations are important and require a responsible attitude to yourself. It is about what should be the roof lathing for a soft roof that we will talk about further.
What is a crate and requirements for it
The crate is a set of boards and slats that are laid in a perpendicular plane to the rafter legs. It is she who acts as the basis for fixing the roofing. It also enhances the spatial structure of the roof.
Lathing under a soft roof must meet the following requirements:
- Have sufficient strength, which corresponds to the mass of the material being laid;
- Be reliable in operation;
- To sustainably perceive various kinds of influences. This mainly concerns atmospheric influences (precipitation, wind);
- There should be no protruding nails, cracks of more than 6 mm, sags and bumps;
- Must be installed according to accepted standards.
There are several types of crates. For soft materials, solid is recommended. Its feature is that when laying it, the step should be more than 1 cm.
Features of working with a soft roof
During the installation of soft tiles, certain conditions must be observed:
- It is allowed to cover a soft roof at an ambient temperature of +10°С. The lower layers capable of gluing when heated by the sun's rays will spontaneously stick to the base.
- When operating during lower temperatures, this layer will not melt. You will have to make additional efforts to warm up the lower layers. In addition, an additional tool is required.
- Also, do not start work in wet weather. You can install the cover. However, the crate will quickly begin to rot.
In general, the best period for working with a soft roof is summer. In winter, it is better to prepare for work. It is quite possible to build a rafter system and calculate the step of the crate for a soft roof.
You can buy all the necessary material in advance. It will not become superfluous, especially in the face of constant price increases. However, it needs to create optimal conditions for storage. So, direct sunlight should not be affected. Otherwise, the adhesive layer may start to melt. The temperature is not lower than 0°С.

What materials are suitable for the crate?
The following materials are suitable for preparing crates for soft materials:
- Calibrated board - width 140 millimeters. Be sure to choose a quality one. Preparation is recommended in advance.
- Wooden beam. Dimensions will vary depending on the pitch of the rafter system and the crate.
- Diffusion or roofing film. Improves waterproofing heat-shielding properties.
- Roof runs. Strengthen the entire structure, making it more stable and reliable.
- Moisture resistant plywood or OSB. It is used for arranging the most even surface. The plane is obtained without cracks and dips.
Pay attention! When choosing a material, it is necessary to focus only on the maximum quality. They must meet all quality standards. Otherwise, the durability of the roof remains in doubt.
What crate is suitable?
Dealt with the materials. Now consider the types of crates. They are solid and sparse.
When a sparse one is created, then the boards on the rafter legs are placed not with a continuous coating, but with a fixed step. Averaged 20-50 cm. Such a design cannot be used in conjunction with bituminous coatings. They are soft and will sag.
For high-quality installation of soft blood, it is necessary to make a continuous crate. It looks like solid flooring. Calibrated boards, plywood or OSB are used. It is allowed to leave a minimum gap, up to 10 mm.

Types of solid battens
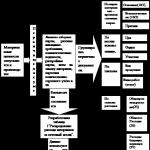
Under modern soft roofing materials, it is imperative to equip a solid base. This is clear. However, the crate for a soft roof can be made of several layers. There are two types of solid bases:
1. Single layer- all elements are mounted in a parallel plane to the ridge. Laid immediately on the rafters. Material - boards, plywood, OSB. This design is not often used, most often for the installation of roofing material.

2. Double- combine two layers. Even different materials are periodically used. The first layer is the working part, a lathing of a sparse type. Made up of boards. After it, the second layer is laid. It is already complete. Plywood, boards or OSB are used. This design makes it possible to create ventilation between the flooring and place insulation material between the rafter legs. The preferred choice for today's soft materials.

Manufacturing technology of a single-layer continuous crate
It is mounted directly on the rafters, without the use of additional elements. Suitable for low-cost construction, for example, for laying roofing material. Thermal insulation is not provided.
Board use
A grooved board will do. Unedged will not fit. This is due to the resulting surface drops. affects the final result.
The variant is the simplest. It is made by attaching boards perpendicular to the rafter legs.
However, there are certain requirements for boards:
- No knots. Maximum equal.
- Width from 100 to 140 millimeters. Thickness of 20-37 millimeters. Everything will depend on the step of the truss system used.
- Humidity should not exceed 20%. This is explained by the fact that wet wood will dry out. This will cause the fasteners to fall out. In addition, when in contact with a wet surface, bituminous materials reduce their service life.
- Must be treated with an antiseptic. The appearance of rot and various insects should be prevented.

When working, the boards are fixed to the rafters across, in a parallel plane to the ridge. Laying is done from the bottom up. It all starts with the roof overhang. Docking points are placed on the rafters. Boards are fastened closer to the edge, the caps are recessed. Between adjacent boards in height, you need to leave a small gap, in the region of 3 millimeters. It will be required for thermal expansion. Resizing will occur within this gap.
Panel assembly
Boards can be replaced with one of the sheet materials - plywood or OSB. They are distinguished by a significant level of moisture resistance and flexibility. Long service life.
Such materials speed up the entire process of building the crate. The result is a smooth surface for laying soft materials.
However, they have their own requirements:
- Increased level of moisture resistance. Not all representatives have this quality. For roofing, OSB-3 or FSF plywood is the most suitable.
- Thickness from 9 to 27 millimeters. Everything is again repelled by the step of the truss system.
- Antiseptic treatment. Processing from rotting and fungus is required.
Sheets are placed immediately on the rafters in length parallel to the ridge. The joints must not match. That is, they fit into the run.
A gap of 2 mm should be provided. When laying on cool days, the gap increases to 3 mm.
For fastening, self-tapping screws or special solved nails are used. In increments of 30 cm, in the area of \u200b\u200bthe ends 15 cm. Edges - 10 cm.

Technology of installation of a double continuous crate
It can be represented as a two-tier structure. The first is boards fixed in a run. The second is a solid platform made of plywood, OSB or boards. It is the most effective when compared with a single layer. Therefore, it is most often used during the laying of modern soft roofing materials.
Assembling a double crate from boards
The basis for laying a soft roof is allowed to use only a board. They are used to fasten both layers.
- In the first row, use boards with a thickness of 25 mm and a width of 100 to 150 mm. It is allowed to replace it with a bar 50x50 and 30x70.
- The second layer is formed from boards 20-25 mm thick and 50 to 70 mm wide.
- Be sure to use an antiseptic.
The installation process takes place in the following order:
1. In a parallel plane to the ridge, boards are fixed with an interval of 200 to 300 mm. The main thing is to exclude the possibility of deflection of boards from level 2.
2. A board of 2 rows is punched over them at an angle of 45 degrees. A gap of 2-3 mm is also left. Work comes from the ridge to the eaves.
This design is usually prepared for roofing material. In the case of modern materials, a combined method is desirable.

Making a combined double crate
In this design, a combination of materials is used. In the first layer, a board or timber, the second - plywood or OSB.
According to tradition, it is collected in this way. A board or beam is laid perpendicular to the rafters, in a run. Top plywood or OSB. This method is usually used when creating a cold attic. There is no insulation or waterproofing.
If it is necessary to conduct insulation, then another option must be used. It is somewhat more difficult. Parallel to the rafters, the beam of the counter-lattice is laid. Above, already perpendicular to them, the boards of the first level. The roofing pie ends with sheet material. The method differs from the past by the presence of a counter-lattice. Due to it, a gap for ventilation is provided between the shield flooring and the vapor barrier.
The following requirements apply to materials:
- A beam for creating a counter-lattice - 25x30 or 50x50 mm.
- Board 2 layers - 25 millimeters thick, and width from 100 to 140 millimeters.
- Sheet material - 9-12 mm.
- Antiseptic treatment.

Sequence of work:
1. If there is a layer of thermal insulation and waterproofing, a row of counter battens is formed. The section is shown above. They are fixed over the rafters, along. This row is necessary not only to create a gap for ventilation, but also to fix the vapor barrier film laid on the insulation. If you break everything down into steps, it will look like this. First, thermal insulation material is laid between the rafters. A vapor barrier film is covered from above, nailed to the beam of the counter-lattice. In the absence of thermal insulation, you can immediately begin to arrange the crate in a run.
2. The boards are laid on the beam of the counter-lattice or immediately on the rafters. Across. Laying step from 200 to 300 millimeters.
3. Sheet material is placed in parallel. Long side across the rafters. An expansion joint up to 3 mm is required. Fastening is carried out to each rafter leg with an interval of 30 cm. Joints should be placed on supports. Joints are fastened with a gap of 15 cm.
Summing up, we can say that it is not advisable to build a crate for a soft roof on your own. It is better to turn to specialists who know all the subtleties. Otherwise, you can get a lot of problems with the roof.
The term "soft roof" combines a whole group of materials. This is roofing material, and roll-on built-up coatings, and soft tiles. Despite external differences, all these materials are made on the basis of modified bitumen, which makes the final roofing products soft and flexible. And also one important feature: they are not able by themselves to maintain a rigid shape and withstand external loads.
Bituminous materials perform their function only when laid on a rigid and durable frame. Such a frame when creating a soft roof is a crate in the form of an even continuous flooring.
When constructing a sparse structure, its elements (boards) are located on the rafters not all-over, but with a certain step. On average, this step is 20-50 cm. This design is not suitable for soft bituminous materials, as they will sag between the elements.
Soft roofing requires a continuous sheathing, which is a flooring made of boards, OSB, plywood. A small gap between the elements is allowed, but it should not exceed 1 cm.
Types of solid crates
So, under a soft roof, there must be a solid flooring. With this we have decided. But the crate for a soft roof can consist not only of this layer. There are 2 types of solid crates:
- Single layer decking- the elements of the crate are laid parallel to the ridge, directly on the rafters. Boards (tes), plywood or OSB are used as elements. A single crate is rarely used, mainly for laying roofing material.
- double flooring- a combination of two layers, sometimes made up of different materials. The first layer, the working layer, is, in fact, a sparse crate. It consists of boards (beams), which are mounted in acceleration. Then a second, already continuous layer is laid on it - flooring from boards, OSB or plywood. The double crate makes it possible to form a ventilation gap under the flooring and accommodate a thermal insulation pie between the rafters. Therefore, this design is preferred for all modern bituminous materials (also for shingles).
Let's consider the technologies for the device of continuous crates of all available types.
Installation of a single-layer continuous crate
A single-layer crate is laid directly on the rafters, without any additional elements. Suitable for budget construction with the use of roofing material, without the formation of an insulation pie under the roof.
Option # 1 - lathing from boards
For continuous single decking, tongue-and-groove boards or boards can be used. Unedged boards are not suitable, as all their irregularities will be reflected on the surface of the soft roof. And this will negatively affect the decorative and moisture-proof properties of the roof.
Such a crate is the simplest and consists of boards stuffed across the rafters.

Requirements for boards for solid lathing:
- Boards should be smooth, without knots.
- Their width is 100-140 mm, thickness - 20-37 mm (depending on the pitch of the rafters: up to 900 mm - thickness 20 mm, 900 mm - 23 mm, 1200 mm - 30 mm, 1500 mm - 37 mm).
- Humidity - no more than 20%. This is due to the fact that raw wood will sooner or later begin to dry out, and the fasteners will fall out of it. In addition, on a wet base, the life of bituminous materials is reduced.
- Boards must be antiseptic to prevent putrefactive processes, the appearance of woodworms and fungal plaque.
During the installation of such a crate, the boards are fixed over the rafters, perpendicular to them, along the ridge. Since the boards tend to warp, forming a concave tray on one side, and a bulge on the other, the crate must be laid with trays up. Then the water that has seeped through the roofing material will fall into the tray, follow the gorge to the cornice and flow down it to the outside, without getting into the attic.
Installation is carried out from the bottom up, starting from the overhang. The joints of the boards along the length are laid on supports (on the rafters). Nails (self-tapping screws) are hammered closer to the edges, while trying to drown the hats a little into the wood. A barely noticeable gap is left between adjacent boards (in height) - about 3 mm. It serves to level the temperature deformations of wood that occur during changes in humidity and temperature. As the conditions change, the boards will shrink and expand, so if you fasten them too tightly, bumps are likely to appear.
Option # 2 - crate made of panel materials
Instead of boards on the rafters, you can fix panel materials - plywood or OSB. They have the high moisture resistance and flexibility required for long-term roofing service.
The use of panel materials allows you to speed up the process of mounting the crate and get a perfectly flat base surface for the subsequent layout of rolled materials or shingles.

Requirements for shield materials:
- High moisture resistance. Not all panel materials have the parameters necessary to work in wet conditions on the roof. Among those suitable for roofing, OSB-3 (moisture-resistant brand of oriented strand board) and FSF (moisture-resistant plywood) can be noted.
- Thickness - 9-27 mm (depending on the pitch of the rafters: if this distance is up to 600 mm, then the thickness of the sheet should be at least 9 mm, if 600 mm - 12 mm, if 900 mm - 18 mm, if 1200 mm - 21 mm , if 1500 mm - 27 mm).
- Shields must be impregnated with an antiseptic - to protect against fungal infections. This is necessary because OSB-3 and FSF are only resistant to short-term exposure to moisture and require coating with waterproofing materials on the roof. Therefore, additional protection should not be neglected.
Sheets of plywood or OSB are laid on the rafters with the long side parallel to the ridge. In this case, the connecting seams of adjacent rows should not coincide. Sheets are mounted in a checkerboard pattern, apart.
A gap of 2 mm is left between adjacent sheets, so that when moisture is collected, they do not swell. If installation is carried out during a cold period, the gap is increased to 3 mm to compensate for the expansion of heated sheets in summer.
The shields are fixed with fastening elements (self-tapping screws or ruff nails) on each rafter - in increments of 30 cm, at the junction of the ends - in increments of 15 cm, along the edges - in increments of 10 cm.

Installation of a double solid crate
The double crate is a two-tier structure, the first layer of which is boards laid in a row, the second continuous layer is flooring from boards, OSB, plywood. A double crate is considered more efficient and reliable than a single-layer one, which is why it is recommended for the installation of modern soft roofs.
The structure can be assembled only from boards (sometimes - bars) or from their combination with OSB and plywood.
Option # 1 - double crate of boards
For the base for a soft roof, you can use only one type of material - boards. Both layers of the crate are constructed from them.

Requirements for materials:
- Boards of the first (sparse) layer: thickness - at least 25 mm, width - 100-140 mm. Boards can be replaced with bars 50x50 mm or 30x70 mm.
- Boards of the second (solid) layer: thickness 20-25 mm, width - 50-70 mm.
- Lumber is pre-coated with antiseptic compounds.
The installation of the crate is simple and is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- First, boards or bars are nailed parallel to the ridge (perpendicular to the rafter legs) with a step that excludes bending of the boards of the second layer, on average, 200-300 mm.
- From above, on a sparse crate, at an angle of 45 ° (diagonally), boards of the second layer are nailed. Not close, but with a gap of up to 3 mm, which can extinguish the thermal deformation of wood. Sheathing is carried out in the direction from the ridge to the eaves.
A similar base, as a rule, is used when laying roofing material. For flexible tiles, it is recommended to build a combined version.
Option # 2 - combined double crate
In the combined design, several materials are combined. The first layer is boards or bars, the second layer is plywood or OSB.
Traditionally, the combined crate is assembled as follows: boards or beams are fixed perpendicular to the rafters, and sheets of plywood or OSB are placed on top of them. This technology is used, as a rule, in the construction of a cold attic (without insulation pie and waterproofing film on the roof).
If insulation takes place, then use another version of the crate, more complex. Along the rafters, the bars of the counter-lattice are stuffed, on top of them, perpendicularly, the boards of the first layer of the crate. The whole structure is completed by plywood or OSB boards. This option differs from the previous one by the presence of a counter-lattice, which forms a ventilation gap between the large-panel flooring and waterproofing.

Material requirements:
- Bars of the counter-lattice: even bars with a section of 25x30 mm or 50x50 mm.
- Sparse layer boards: thickness - 25 mm, width - 100-140 mm.
- Plywood or OSB-3: thickness 9-12 mm.
- Materials must be pre-antiseptic.
In order to build a combined continuous crate, perform the following steps:
- In the presence of a heat-insulating cake with a waterproofing film, counter-lattice bars are installed. Their cross section can be in the range of 20-50 mm, most often 25x30 mm. The bars are fixed over the rafter legs, along them. The counter-lattice serves not only to form a ventilation gap, but also to fix the waterproofing film, which is laid on the insulating material. If we consider the installation work in stages, then first heat-insulating mats are laid between the rafters, a waterproofing film is stretched over the rafters and mats, which is nailed on top with counter-battens bars. If a heat-insulating cake is not foreseen in the roof, this item is skipped and immediately proceed to fastening a sparse crate.
- Lathing boards (width - 100-140 mm, thickness - 25 mm) are fixed to the bars of the counter-lattice (if any) or to the rafters perpendicularly. Fastening step with nails (self-tapping screws) - 200-300 mm.
- Sheets of OSB-3 or plywood are placed along the ridge, with the long side across the rafters. Installation is carried out with a breakdown of the seams, that is, in a checkerboard pattern. A compensation gap of 2-3 mm is left between the shields. Fastening is performed on each rafter, using self-tapping screws or ruffed nails for fixing. The fastening step on the rafters is 30 cm. The plates are laid so that their edges must fall on the supports, they are also docked there and also fixed with fastening elements, but with a more frequent step - 15 cm.
To make it clearer, see how it looks during the construction process:

The technology is simple, to understand all its nuances, just watch a short video:
Checking the design for errors
When the crate is ready, you should look at it with a critical eye. Were fatal errors made that could have a negative impact on the operation of the roof?
A high-quality finished crate has the following properties:
- It does not bend under the weight of a person, otherwise it will be problematic to work on it and repair the roof in the future.
- Has no gaps (greater than allowed expansion gaps). If it was not possible to avoid cracks, then the gaps are covered with strips of roofing tin.
- It does not have protruding knots and non-recessed nails on the surface, which can break through the bituminous materials of the soft roof.
- The ends of the lumber, through which the bitumen products will subsequently be bent, are not sharp, rounded off with a planer to prevent tears and rubbing.
- All materials for the crate are dry, covered with antiseptic agents.
It is important that the solid crate does not have the above flaws. Only in this case, the roll coating or shingles will successfully perform their functions.
The category of materials referred to as soft roofing includes several commonly used coatings. This is roofing material, and soft bituminous tiles, and several varieties of welded roll materials. All of them differ from each other in appearance and characteristics, but their production is based on one component - modified bitumen. It is he who gives the roofing that very flexibility and softness. The material itself does not have a rigid shape, so under it you need a strong and rigid crate, which will withstand external loads. In this case, a soft roof will perform only protective and decorative properties.
Types of lathing for a soft roof
If we talk about the crate as a whole, then it can be of two types: sparse and solid. The first is assembled from boards or bars, between which gaps are left or, as they are also called, the installation step. The second is a continuous flooring without gaps. For a soft roof, it is the second option that is used, because when laid on a discharged crate, soft roofing materials will sag between its elements.
A continuous crate is made under a soft roof, otherwise the material will sag in the cracks between the boards
Sheets of moisture-resistant plywood, OSB boards and boards are used as flooring for continuous lathing. The latter must be either edged or grooved from softwood. As for moisture-resistant plywood, it must be chosen correctly by brand, because there are two positions on the market with this name:
- FC, which is recommended to be used only for interior decoration.
- FSF, which is used for both indoor and outdoor installation.
For a continuous crate, it is the FSF that is suitable. This material is made from several layers of veneer (from 3 to 21), which are glued together with a special compound based on phenol-formaldehyde resins. It should be added that during the production of FSF plywood, each layer is first treated with bakelite varnish, so the material has high strength and water resistance.
As for the OSB, it is also necessary to choose a waterproof modification for the crate, i.e., the OSB-3 and OSB-4 brands. The latter is intended for structures that are subjected to maximum loads at high humidity, so it is quite expensive. For roofing, you can use OSB-3 plywood, which is not inferior to the fourth model in terms of moisture resistance.
When assembling the flooring between the elements, you can leave a small gap, the size of which should not exceed 1 cm. It is called compensatory because it will compensate for the expansion of wooden products due to changes in humidity and temperature.
Types of solid lathing
Lathing under a soft roof can be single or double. In the first case, boards or panels are laid directly on the rafters. In the second, a sparse crate is first mounted, and a solid one is mounted on top of it. The second option is preferable because there is space between the two layers, which is used for roof ventilation. And this makes it possible to remove moist air vapor that rises from the interior of the house. It is they who, on uninsulated roofs, cause the formation of ice and condensation on the truss system.
But this is not the only criterion for choosing double decking. Much will depend on the angle of the roof slopes.
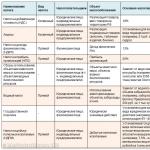
- With a slope of 5–10°, a single-layer flooring can be used.
- In the range from 10 to 15 °, a double crate is laid with a step between the lower elements of 45–50 cm. For the lower crate, it is better to use bars with a section of 50x50 mm.
- If the slope angle exceeds 15°, then the installation step can be increased to 60 cm.
In principle, it is possible to increase the step of the lower crate up to 100 cm, depending on the size of the lumber used for it. For example, if a board 40 mm thick and 120 mm wide was used for this. The smaller the cross section, the smaller the step, and vice versa. For each material, its own step is selected relative to its thickness.
Table: the ratio of the step of a sparse crate to the thickness of the solid decking elements
How to calculate the amount of material for lathing under a soft roof
Taking into account the above indicated ratios of the spacing of the elements of the crate and their thickness, it is possible to make a fairly accurate calculation of this design. To do this, you will first have to take the dimensions of the roof itself, which are indicated in the drawing of the building. And if the roof is a complex multi-level and multi-slope structure, then it needs to be divided into simple geometric shapes. It is on their basis that the total area of \u200b\u200bthe roof is calculated.
In this case, you will have to take into account the angle of inclination of each slope, because the smaller the angle, the greater the load on the crate system. This means that you will either have to reduce the spacing of the boards or bars, or increase the thickness of the slab and sheet flooring. Therefore, to simplify calculations, when determining the total area of \u200b\u200bthe roof, correction factors are used. For example, with a slope of 35°, a multiplier of 1.221 is used.
Calculation of a solid structure
With the calculation of a continuous crate, the situation is simpler, because it covers the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe slopes. That is, its area will be equal to the area of \u200b\u200bthe roof. Consider an example of calculating the number of plywood sheets for a slope with an area of 50 m².

In the construction business, when calculating the amount of building materials, a small margin is made within 5–10%. Here you need to do the same, so the final result is 23–24 sheets.
In exactly the same way, the number of OSB boards is calculated. But with the boards a little more complicated. First of all, you need to calculate the area of \u200b\u200bone selected board. The length of edged boards varies in the range from 1 to 6.5 m in increments of 0.25 m. Width - in the range of 75–275 mm in increments of 25 mm.
Let's say a board 3 m long and 0.1 m wide is used for the crate:
- We calculate the area of one board: 3∙0.1=0.3 m².
- A slope of 50 m² will require 50: 0.3 = 166.66 boards.
- Round up to the nearest integer and add a margin of 10%: 167∙1.1 = 184 boards.
Calculation of a sparse crate
For this calculation, the slope area itself is not required. The length of the roof and its height, that is, the distance from the overhang to the ridge, are required.

Rules for installing lathing under a soft roof
Regardless of whether one- or two-layer lathing will be used on the roof, the main requirement for the design is a flat and durable surface without defects and flaws in the lumber. That is why when using boards, calibrated material is selected.
According to the building canons, the rafter system is set along the slopes in the same plane, so you need to be sure that the ends of the rafter legs are already set. So, we can assume that the stacked boards, plywood or OSB boards will lie in the same plane.
It is necessary to join the elements of the crate along the rafters. A board protruding beyond the rafter legs will not provide strength when installing roofing material
It is necessary to start the installation from the cornice, or rather, from the lower ends of the stop. The boards are selected in length so that two adjacent elements are joined on the same rafter log. If this was not possible, you will have to cut them, which will increase the amount of waste. The same goes for sheets and slabs.
The boards are laid with a small gap of 1 cm and attached to the rafters with nails or self-tapping screws. Fastening is best done from the end side. If self-tapping screws or nails are installed on the front side, then their hats must be driven into the body of the lumber to a depth of 0.5 mm. At the same time, on each rafter, two fasteners must be nailed to the board - one from each edge.
Plywood sheets or OSB boards on the roof as a continuous crate should be laid in a run-up with an offset of a third or half of the panel
As for flat materials for the crate, they are placed with an offset relative to each other by a third or half a sheet. This is done so that the loads acting on the continuous crate are evenly distributed over its entire surface. In this way, the panels are laid perpendicular to the rafters. Plywood with dimensions of 1.5x2.5 m can be installed along the rafters. In this case, it will be necessary to take into account that the sheet material itself cannot carry heavy loads, therefore at least three rafter legs must fall under it: one exactly in the middle and two along the edges. But even here you have to take into account that two adjacent plywood sheets must be joined on the same rafter. The gap between them (3–5 mm) is mandatory.
Plywood and OSB are fastened with galvanized self-tapping screws or ruff nails around the perimeter every 10–15 cm and along the entire plane along the rafters in a checkerboard pattern. It is these fasteners that must be used, because they can withstand the stresses that arise in OSB boards or plywood sheets during changes in humidity and temperature.
The order of laying flat panels on a discharged crate:
- A string is stretched along the edges of the rafters, defining the boundary of the roof overhang. It is tied to two self-tapping screws, which are screwed into the two extreme rafters located on different edges of the roof.
- The first sheet is laid along the outer edge of the first rafter leg, while its adjacent edge must exactly pass along the twine.
The first sheet of solid lathing is laid strictly along the edge of the rafter leg
- The first sheet is fastened with self-tapping screws 50 mm long along the rafters in increments of 20–30 cm.
- In this way, the bottom row is assembled.
The bottom row is laid with the joining of panels on the rafters
- The next row starts with half a sheet, so one panel must be cut in half.
- The half is attached to the rafters, like solid sheets, with the same self-tapping screws with the same pitch.
The second row of a solid crate starts from half of the slab so that the following elements are fastened apart from the first row
- Further, whole sheets are used.
- The third row begins to be assembled from a solid plate.
Video: how to properly lay boards as batten elements
Solid crate on discharged
In principle, there are no serious differences from the above-described installation technology. Just a solid structure is laid on the boards, which are placed on the rafters with a certain distance between the rows. Boards are not used to create a continuous flooring. Plywood or OSB is being installed. At the same time, all the above requirements are preserved both in terms of the panel installation scheme and the method of their fastening.
Counter-lattice for soft roofing
To insulate the roof between the rafter legs, it is necessary to lay heat-insulating material. From the side of the attic, it is closed with a vapor barrier membrane, and from the side of the crate - with a waterproofing film. It is impossible to immediately lay the crate and make flooring from OSB boards or plywood sheets. It is necessary to create a ventilation duct that will remove moist air vapor from under the roof space. Therefore, bars with a section of 50x50 mm are laid along the rafters. This is the counter-lattice, and the space between the waterproofing and the solid flooring is the ventilation gap.
The process of assembling a roofing insulated structure consists of the following steps.
- From the inside of the future attic, insulation is laid between the rafters. The main requirement for laying is to tightly press the heat-insulating material to the planes of the rafter legs so that cold bridges do not form.
The insulation is placed in the space between the rafters so that even the smallest gaps do not remain.
- A vapor barrier film is laid on top of the insulation, which is attached to the rafters with metal staples using a stapler. The film is laid in rows with an overlap, the size of which is 10–12 cm. The joint must be closed with a self-adhesive tape.
The vapor barrier film is overlapped and fastened with staples
- Further, the work is transferred to the outer part of the truss system, where a waterproofing membrane is laid over the legs in the same way as the vapor barrier below. Laying should start from the bottom of the eaves.
- The elements of the counter-lattice are installed and fastened along the rafters, for which wood screws 70 mm long are used. Fastener pitch 40–60 cm.
To create a ventilation gap, bars are attached along the rafters, on which a horizontal crate is laid.
- Lathing elements - boards - are installed across the counter-lattice. They are fastened with self-tapping screws 50 cm long.
- On top of the crate, plywood sheets or OSB boards are installed and fastened in a checkerboard pattern. Fastener pitch 20–30 cm.
Typically, this design is used if there is no sparse crate on the roof, or it is assembled from boards 20–25 mm thick. Such a gap will not be sufficient for the effective removal of moist air.
Video: rules for laying a solid crate on the roof
Solid lathing for soft roofing material is the only way to guarantee the quality of the final result. The minimum gaps will not reduce it, but the fulfillment of the main requirement - the formation of a flat and durable surface - will create conditions under which the soft roof will last its warranty period.
Soft roofing is gaining more and more popularity among developers. However, not everyone knows how to properly mount the base under such a coating. The crate under the soft roof has significant differences. For example, you need to take into account the step between the wooden frame elements, as well as the methods of fastening sheet materials. This design is the main part of the roofing cake. It is designed to attach the cover to various roof elements. Technologically, such a crate is a series of boards nailed to the building system.
Selection of materials
Soft roofing can quickly deform. To prevent such situations, the crate should have the most even surface. It is better to exclude all depressions and irregularities. The following materials are ideal for formwork:
- solid board;
- plywood;
Roofing plywood is made from softwood veneer. It has good moisture resistance and sufficiently high strength. It is supplied to the market already treated with various impregnations, which exclude rotting and ignition of building elements. Due to the flat surface, these boards are ideal for shingles and roofing felt. Plywood is laid quite easily and quickly.
OSB boards are products made from large chips. Synthetic resin is placed in them as a binding element. The price of such material is lower than moisture resistant plywood.

Edged boards are less suitable for sheathing under a soft roof. The installation of a structure that is knocked together from such a material requires certain rules to be followed. This is due to the fact that during operation, the boards can be deformed under the influence of moisture. The fastening of such elements in comparison with plywood is also difficult.
Basic Rules
When making a frame for a soft roof, the following rules must be observed:
- with a roof slope angle of 5-10 degrees, it is necessary to make it a continuous flooring of boards or plywood;
- if the roof slope is 10-15 degrees, it is better to use 45x50 mm bars and plywood;
- with a slope of more than 15 degrees, the construction of the crate is made of bars 15x50 mm, in increments of 60 cm;
- in the places where the ridge and valley are attached, it is necessary to install an additional beam.
To make the formwork as smooth as possible, you should pay attention to calibrated boards. They allow you to create ideal conditions for the installation of soft tiles. If the thickness of the formwork elements is different, the coating may be damaged. Also, the frame can turn out to be stepped.
Advice! With this type of lathing, the service life of a soft roof is significantly reduced. For this reason, it is better to choose only high-quality materials for installation, and adjust the joints as carefully as possible.
Boards should be chosen from coniferous trees. Such products have low cost and excellent performance characteristics.
Formwork should be carried out with a step of no more than 100 mm. Elements stuffed with solid material must meet certain moisture levels - no more than 2%. The strength of the frame must be appropriate to the loads received from:
- roofing material;
- snow.
Depending on such factors, it is necessary to calculate the desired characteristics of the roof structure. For example, with a rafter pitch of 50 cm, it is better to choose boards of 20 mm for formwork. If the rafter pitch is 120 cm, it is worth using bars no thinner than 30 mm or plywood 20 mm thick.
Features of the construction of rafters
If the Mauerlat is installed correctly, the installation of rafters that are prepared according to the template, even in the case of figured roofs, will be quite simple. Under flexible tiles, it is better to perform a double crate. It is also worth taking care that there is a smooth base. Other features of the rafters:
- humidity of wooden elements - no more than 20%;
- when calculating the distance between the rafter legs, the thickness of the plywood should be taken into account;
- if the pitch is 100 cm, OSB must be at least 20 mm, and the bars must not be thinner than 25 mm.

It is also necessary to understand that the timber supports the boards or plywood in an optimal position. If you make too much step of the crate under the soft roof, the panels (OSB, plywood) will begin to bend. The roof can be made quickly enough, subject to the choice of installation technology in accordance with the coating material.
solid frame
How to make a crate for a soft roof of plywood or OSB? Fastening of sheet material is carried out on self-tapping screws. Spiral nails can also be used. OSB can be mounted on ring nails 4.5-7.5 cm long. The step between the fasteners should not be more than 30 cm. The nail heads must be sunk into the thickness of the material. Otherwise, they may damage the roofing.

When installing sheet material, it is worth remembering that gaps of 2 mm must be left between the panels. In the case of OSB boards, this figure rises to 3 mm. This measure is due to the ability of materials to swell with increasing humidity. If the sheets are folded close together, the coating may warp.
When plywood or OSB is laid, it is worth considering that the sheets must be mounted on at least 3 supports. They are joined only on wooden elements. The nailing step should be 30 cm.
Plywood is attached to the ridge with the long side. In this case, each element must be shifted by ½ length relative to the others.
plank frame
The plank frame for soft roofing should be characterized by maximum evenness. Such a requirement can be achieved only if the elements are carefully selected in thickness. The elements are attached to galvanized nails. They are hammered near each edge at the place where the rafters intersect. To prevent warping of the roof, you must follow these rules:
- The distance between the boards should be at least 3 mm.
- During the layout of the bars, it is worth looking at the annual rings on the cut. Installation is always carried out rounded up.
- The plank frame is carried out from the overhang to the ridge.

The device of the lathing under the soft roof is quite simple. To do this, you should decide on the materials, calculate the distance between the primary formwork boards, and also take into account the load on the roof. Only when taking into account such indicators, it is possible to carry out the correct installation of the roof.

Sergey Novozhilov is an expert in roofing materials with 9 years of practical experience in the field of engineering solutions in construction.

















Roofing material based on modified bitumen refers to soft roofing. If you chose it for the roof of your house, then it's time to find out what a crate for a soft roof is. The article will become a guide to questions about the types of battens for roofing felt, soft tiles, floor coverings in rolls, and the features of its installation. You will receive answers to basic questions about what thickness to choose consumables, what is the pitch of the crate.

What is the crate made of
The main problem of a soft roof lies in the name: it is flexible, it can sag if the attachment points are at a great distance from each other, the service life depends on the quality of the base.
The material is selected so that it meets the requirements for the crate:
strength sufficient to counteract all types of mechanical loads (from the weight of the roofing material, snow, wind action);
absence knots, cracks, gouges and any other defects in the lumber, the size of which exceeds 0.6 cm;
elements geometrically correct, rectilinear, without sagging;
the possibility of mounting in such a way that fasteners (nails, screws, brackets) did not rise above the surface;
life time comparable to the warranty period of operation of the roofing material.

The following materials meet the requests put forward:
Edged or tongue-and-groove board at least 14 cm wide high quality. The functionality of the crate largely depends on the humidity of the board: wet lumber will begin to dry out and warp, which will lead to a violation of the integrity of the roof, the appearance of bulges, breaks;
Wooden bars dried to a moisture content of not more than 20%. The size of the bars is selected according to the step of the crate;
Plywood- durable, environmentally friendly, easy to process, with a sufficient level of wear resistance, smooth and plastic. The light weight of the sheets will allow you to install the roof on different types of foundation. Plywood under a soft roof is taken only moisture resistant, which is indicated by the manufacturer when marking. The advantage is the budget price of the sheets;
OSB boards dense, durable, moisture resistant, resistant to deforming loads. From OSB they will get a flat surface under the roof, without height differences.
When choosing a material with wood at the base, pay attention to the presence of impregnation with antiseptics, fire retardants.

Types of crates
Most often, the crate is divided into varieties according to two main installation methods:
Sparse framework. Parts of the structure are placed on the rafters with a certain step, there will be a gap between them. Without additional coverage, soft roofing will sag and deform. A solid roof is laid directly on a sparse crate.
solid flooring. The building material is laid end-to-end, with a distance of at least 2 mm to prevent swelling, jumps in height. On this basis, it is easy to place vapor and moisture insulation, insulation. Used for installation of a roof under a soft roof.
Depending on the purpose of the building, the climatic conditions of the area where it is located, sheets for continuous lathing are laid either directly on the rafters (single-layer flooring) or on a sparse frame (double flooring).
Flooring in one layer is used for buildings that do not require insulation, more often for household purposes. He performs quickly.
At double coating There are special benefits:
more sustainable, durable;
between the sparse frame and the solid part is formed ventilation gap;
between the rafters and the beams of the sparse crate is laid thermal insulation material.
The disadvantages include the additional weight of the frame elements, which must be taken into account when choosing the type of foundation.

Arrangement of a single-layer structure from boards
The board is taken hewn or tongue-and-groove. Its width depends on the distance between the lines.
Work order on the finished truss system:
boards are cut off to size;
mounting starts at the bottom;
elements are attached perpendicular to the rafters and on them, with orientation along the ridge;
protruding fasteners carefully recessed into the wood;
board joints should fall on the attachment points to the rafters.
Wood is subject to deformation when the temperature and humidity state of the external environment changes. So that the flooring from the boards does not warp from temperature fluctuations, a gap of up to 3 mm is left between the elements.

On our website you can find contacts of construction companies that offer services roof design and repair. You can directly communicate with representatives by visiting the exhibition of houses "Low-Rise Country".
Installation of a single-layer construction of shields
Sheets of plywood, OSB boards are cut to fit the size of the roof. Their thickness is taken from 9 mm. Any shield material is attached to the crate in a checkerboard pattern, so that the connecting seams of adjacent rows do not intersect.
The resistance to deflection of sheets is directly related to their thickness. Thinner shields should have more fastening lines, which means the rafter pitch is minimal. OSB thickness for roofing is shown in the table:
The step of attaching a sheet of panel material to the rafters along the sheet connection line is 15 cm, along the edges 10 cm, along individual slings - 30 cm. A gap of 2 to 3 mm is created between the sheets.

Algorithm for the formation of a two-layer crate from boards
The first layer is formed from a board with a thickness of 25 mm or more, the width of which varies from 10 cm to 14 cm. A beam can serve as a material for a sparse layer.
The second layer is laid from boards 2-2.5 cm thick, 5-7 cm wide.
Work order:
The bars are attached to the rafters parallel to the skate. The step of the crate under the soft roof of the first layer is 20-30 cm;
Top stacked second layer- diagonally, starting installation from the ridge. A gap is left between the boards.
Double-layer crate with shield materials
Double crate, which uses panel materials, is the most practical and functional option. It will provide a solid foundation for all types of soft roofing, but is usually used for soft tiles.
For high-quality arrangement of this type of double crate, the following materials are used:
Vapor barrier membrane. It performs a protective function against the "greenhouse" effect created by the internal heat of the building.
insulation. The most budgetary and common option is mineral wool. The thickness is selected depending on climatic conditions, general requirements for thermal insulation of the roof. The width of the pieces of insulation should not be less / more than the pitch of the rafters.
Bars / boards for the first sparse layer 5x5 in size.
Vapor diffusion membrane protects the insulating layers of the roof from moisture, dust, destruction.
Plywood, OSB boards.

The device of a roof under a soft tile consists of several stages:
Strengthening the vapor barrier to the rafters from the inside of the roof. Laying is done in strips overlapping each other and on the walls.
Covering the vapor barrier with insulation. Depending on the required level of insulation, one or more layers are laid. The seams of the second and subsequent layers are staggered relative to the first, each other. To prevent the insulation from slipping, it is fixed with support boards nailed from the side of the attic.
If necessary, on the first layer of insulation a crate of bars is stuffed. The resulting cells are filled with thermal insulation with a thickness equal to the height of the beam.
Vapor diffusion membrane coating. Strips of material are overlapped by 10 cm on top of each other, fastened with a stapler. The tightness of the joints can be strengthened with the help of special adhesive tape, sealant.
With the help of boards / bars a sparse crate is made, which is also necessary to create a ventilation duct. Mounting step - 30 cm.
Superimposed on top shield coating. Determining what thickness of OSB for a roof under a soft roof to take depends on the step of the first crate. But it should not be less than 9 mm. Sheets are fastened apart with gaps up to 10 mm.
The entire multi-layer system is reinforced with cornice strips.

Important Points
The thickness of the material for the lathing must be sufficient to withstand the weight of the roofing material and the mass of precipitation without critical deformation. At the same time, the weight of the crate itself should not significantly increase the foundation load. The parameters of consumables also depend on the design of the truss system.
This means that at the design stage it is necessary to take into account the parameters of not only soft tiles, but also the crates.
Video description
From the video you can learn how to properly make a roof crate
Conclusion
Competent installation of the crate under a soft roof requires not only knowledge of theory, but also some practical skills. To perform this work, the best option would be to turn to professionals who will do the job efficiently and with a guarantee.