Article outline
For various pathological changes in the uterus or before the IVF procedure, a pipell biopsy of the endometrium is prescribed, that is, a specific study of the mucous membrane. What is a biopsy? This is a procedure in the form of curettage or tissue collection by other methods for further research, as a result of which pathological factors and causes of many diseases can be accurately determined.
Several methods are used for the procedure; their differences are associated with the characteristics of sample collection. But in any case, microsurgery is usually performed under local anesthesia; it has virtually no complications. Aspiration biopsy, performed on an outpatient basis, is considered the most gentle.
What is the biopsy procedure?
Most often, a pipel biopsy is prescribed for diagnosis - a safe and painless procedure, as a result of which no harm is caused to the body. During the examination, a thin plastic tube is inserted into the uterine cavity, through which a piece of mucous is taken for examination. Tissues are sucked into the cavity of the tube, that is, scraping or other traumatic actions are not performed. The difference between this method and the aspiration method is that the tissue is collected using a tube rather than a vacuum instrument or syringe.
Indications for use
Indications for a biopsy include:
- presence of uterine bleeding;
- suspicions of the appearance of neoplasms, adenomyosis;
- scanty acyclic discharge, amenorrhea, menstrual irregularities, menometrorrhagia;
- infertility;
- presence of miscarriages;
- as part of general control during hormonal therapy.
What does a biopsy show?
Let's look at what this procedure shows? Examination of tissues after surgery makes it possible to determine whether there are diagnostic signs of sample polymorphism or structural disturbances. The procedure can show whether there is hyperplasia of the endometrial layer, the presence of local proliferation of mucosal tissue, malignant tissue overgrowth, discrepancy between the thickness of the mucous membrane and the norm, atrophy of the uterine lining, atypical hyperplasia or hypoplasia.
How to prepare for the procedure
Preparation for the procedure begins with determining the time, usually these are the days before menstruation. If there is a suspicion of mucosal rejection, then it would be optimal to schedule a biopsy on the 5th day of the cycle, and with hormonal therapy it will be 17-24 days. If the examination is carried out under general anesthesia (for example, during a comprehensive diagnosis or in the form of a scraping), you must prepare for anesthesia - do not drink or eat anything for eight hours, and it is also prohibited to take medications. Tests are usually ordered as with any other surgical procedure.
Otherwise, there are no restrictions or special requirements; the study is carried out in an outpatient setting (with the exception of the classical method).
Research methods
Various techniques may be used for a biopsy, including:
- classic with complete scraping of the mucous membrane, the most traumatic;
- aspiration biopsy of the endometrium with sampling of materials using a vacuum instrument;
- pipel, which is the safest and completely painless.
Scraping
This method is also called classical; it is usually carried out under general anesthesia and involves complete curettage of the cavity of the cervical canal and uterus with special instruments. The procedure is painful, it requires the patient to stay in the hospital, before the manipulation you should prepare and undergo tests.
Pipelle endometrial biopsy - what is it?
Preparation for a pipel biopsy is very simple:
- the patient should undress, as during a routine examination by a gynecologist;
- the vagina is expanded using a special instrument;
- the cervix is treated with a solution, after which it is treated with an anesthetic;
- Next, a tissue sample is taken.
How exactly the procedure takes place depends on the chosen method, but usually it does not require much time and takes a couple of minutes. The scraping may take approximately 10-15 minutes, after which the patient can go home. A hospital stay is not required unless a biopsy is performed as part of general treatment or there is an indication for it.
On what day of the cycle is it done?
A biopsy sample is usually taken on days 21-23 of the cycle, so it is recommended to maintain a personal menstrual schedule. Some types of studies are best done immediately before menstruation, about 5-7 days, but for long cycles this period may be different. If the patient does not know the length of her cycle, the time for the study is approximately scheduled, focusing on the usual duration, that is, between 21-23 days, counting from the date of completion of the last menstruation.
What is the price
The price of a pipell endometrial biopsy depends on the clinic where the procedure is performed. On average, the cost of this diagnostic procedure ranges from 1,600 to 8,000 rubles. Research is recommended to be carried out only in specialized clinics with appropriate conditions and equipment.
Reviews about pipel endometrial biopsy
Anastasia N.:
“I had miscarriages several times, and for a long time they could not determine the cause. One of the clinics offered to perform a pipel biopsy. The procedure itself did not take much time, it went well, although it was painful. As a result, hyperplasia was discovered, which was the reason for the impossibility of a normal pregnancy. I completed a course of treatment, now everything is fine, we are expecting our second baby.”
“An IVF procedure was prescribed, and before it it was recommended to undergo a biopsy to rule out any problems. Everything went quickly in an outpatient clinic, there were no particularly unpleasant sensations, fertilization was scheduled within a month.”
Svetlana D.:
“The observing gynecologist ordered a biopsy because endometriosis was suspected. I was terribly afraid, but in vain - everything took literally five minutes, there were practically no painful sensations. The first couple of days I was bothered by a pulling sensation in the abdomen and light discharge, but everything went away without any consequences.”
Decoding the results
Decryption usually takes 10 days, this is done only by a qualified specialist. The results of the study reveal:
- discrepancy between the thickness of the mucous layer and the norm;
- the presence of endometritis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- atypical hyperplasia;
- precancerous condition;
- the presence of fibroids and other growths;
- presence of endometriosis.
Endometrial aspiration biopsy
Vacuum aspiration of the endometrium is a minimally invasive micro-surgery, almost painless. The operation is performed in an outpatient setting; it does not require a long stay in the clinic or restrictions after a vacuum examination.
The procedure involves taking an aspirate from the uterine cavity using a specially designed syringe. In this case, a long tip or needle is inserted into the uterine cavity, through which the tissue sample is literally sucked inside. This histological examination does not require general anesthesia or serious preparation; it is practically painless and does not cause bleeding.
Price
The price of endometrial aspiration biopsy usually depends on the status of the clinic. The average cost for aspiration research is 1900-8000 rubles.
CUG biopsy
A CG biopsy is a type of examination during which tissue is removed using line-shaped scrapings. This method is considered the safest; it is not accompanied by bleeding or mucosal rejection. The use of bar biopsy is allowed up to three times during one cycle, without causing injury to the body, and the hormonal levels do not change. This type of study is usually indicated when studying a precancerous condition, in the presence of tumor processes.
Hysteroscopy with biopsy
Diagnostic hysteroscopy with biopsy is used to accurately identify pathologies, the presence of fibroids, tumor processes, polyposis, and hyperplasia. The material is collected under anesthesia; intravenous anesthesia is usually used for this. The biopsy is taken using a special hysteroscope, after which tissue samples are sent for research.
Possible complications and consequences
Endometrial biopsy is a safe and virtually non-traumatic procedure, but there are a number of consequences, including:
- nagging pain may be observed in the lower abdomen, but this usually goes away after a couple of days;
- spotting also lasts only a couple of days, after which it goes away, the next menstruation will be normal;
- General weakness, nausea, and a feeling of dizziness may occur;
- there is a slight rise in temperature, fever is possible.
Severe bleeding is not observed; such a situation is possible only if the procedure was performed incorrectly. But even with a competently performed biopsy, a shift in the menstrual cycle may be observed; the first menstruation usually goes a little differently than always.
What to do after the procedure?
Usually a biopsy proceeds quickly and without any special consequences, but it is not prescribed in the following cases:
- pregnancy;
- blood clotting disorders;
- the presence of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- severe anemia;
- taking medications such as Trental, NSAIDs, Clexane and others;
- intolerance to drugs used for anesthesia.
In addition, a number of restrictions apply to intimate relationships, the use of sanitary tampons, pregnancy can only be planned for the next cycle, especially for the IVF procedure.
What should you not do after a biopsy?
After a pipel endometrial biopsy, the following actions cannot be performed:
- have sex until the bleeding goes away;
- lift weights, engage in work involving heavy loads;
- take a bath, especially a hot one;
- visit a sauna, bathhouse;
- do douching;
- use tampons.
Such actions are prohibited in order to prevent some complications, including inflammatory diseases and heavy bleeding. Such restrictions are in effect for days, after which they are lifted. But, if the bleeding continues or purulent discharge from the vagina is observed, it is necessary to contact a supervising specialist.
Sex life after
It is better to postpone intimate relationships after a biopsy until the bleeding has completely passed. Further, sex no longer has restrictions, but if pregnancy is not planned, at first it is better to use barrier contraception, which will also protect the mucous membrane from infectious and bacterial lesions.
How do menstruation behave?
Immediately after the procedure, menstrual flow comes on time, there may be slight delays, but no more than 10 days, most often there are no delays at all. The discharge itself will be more scanty than usual, the presence of an unpleasant smell of discharge, the appearance of clots, the presence of pus, and fever are not allowed.
Biopsy and pregnancy
After a biopsy, some conditions are contraindicated, but pregnancy can be planned for the next cycle, when the endometrium has recovered. There is usually no delay in menstruation, although the discharge may be scanty immediately after the procedure. But over the full cycle, the functionality of the mucous membrane is completely restored, no problems arise with the arrival of menstruation, and the uterus itself will be fully prepared to receive the egg.
How long to expect results?
Results from an endometrial biopsy, as a rule, have to wait from 7 to 14 days, it all depends on the clinic where the research is carried out and the overall workload of the laboratory. It usually takes no more than 10 days to decipher the results, after which you can contact the supervising doctor to prescribe a therapy regimen or other treatment methods.
Endometrial biopsy before IVF
Preparation for IVF often requires a biopsy procedure, which allows you to solve the following problems:
- identifying the cause of infertility;
- identifying the causes of excessive menstruation and uterine bleeding;
- exclusion of cancerous tumors if ultrasound results are poor or there is suspicion of a tumor process.
Before in vitro fertilization, careful preparation of the endometrium is necessary. If the results of the study show that the thickness of the mucosa is insufficient, appropriate therapy will be prescribed to quickly bring the endometrium back to normal.
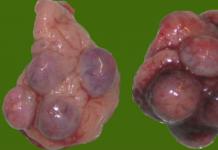
Pipelle endometrial biopsy– a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure aimed at obtaining tissue samples from the uterine mucosa for cytological, histological or microbiological analysis. The manipulation is performed to identify hyperplastic and chronic inflammatory processes of the endometrium, in case of menstrual irregularities, infertility, as well as in the process of dynamic monitoring to assess the effectiveness of hormone therapy. The procedure includes the following stages: fixation of the cervix, probing the uterus, insertion of an aspiration catheter into the uterine cavity, aspiration of the biopsy material. Complications of pipell endometrial biopsy are extremely rare.
Preparation for pipel biopsy
This technique is a minor outpatient procedure, so there is no need to prescribe a wide range of special instrumental and laboratory tests. Before the procedure, the patient undergoes general blood and urine tests, and swabs are taken from the vagina for flora. It is necessary to have the results of an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. 7-10 days before performing a pipell biopsy of the endometrium, it is recommended to stop using hygienic tampons. To prevent ascending infection, you can sanitize the vagina with antiseptic suppositories.
On the eve of the biopsy, you should stop taking gas-forming products or empty your bowels with a cleansing enema. For hygienic purposes, you need to shave the hair in the area of the external genitalia and perineum. To prevent spasm of the cervical canal, before performing a pipell biopsy of the endometrium, the patient is given an injection of an antispasmodic drug. For pain relief, paracervical anesthesia or irrigation of the cervix with an anesthetic solution is used.
Methodology
To perform a pipell biopsy of the endometrium, the patient is placed on a gynecological chair. The size and position of the uterus are assessed during a bimanual vaginal examination. The cervix is exposed under aseptic conditions using double-leaf speculum, treated with alcohol and fixed with bullet forceps by the anterior lip. The length and direction of the uterine cavity are determined using a probe. The assembled aspiration catheter is inserted through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity to the bottom of the organ. A centimeter scale is applied to the side surface of the catheter, which allows you to control the depth of insertion of the instrument.
After installing the catheter, a pipel biopsy of the endometrium is performed by pulling the piston. When the piston is pulled back, a “suction” effect is created on the walls of the uterus; as a result, the biomaterial in the form of strips enters the cavity of the aspiration probe through the perforation hole. To obtain more tissue volume, make 3-4 scraping movements in different directions. The instrument is removed from the uterine cavity. The resulting biopsy is squeezed out of the probe using a piston into a bottle with formaldehyde. Thin, uniform smears are applied to glass slides for cytological examination. The duration of the pipell endometrial biopsy procedure is from 3 to 5 minutes.
After pipel biopsy
After the manipulation is completed, the woman is sent home. It is recommended to take antibacterial drugs to prevent inflammatory processes in the genitals. Sexual rest is necessary for 10 days; until the next menstruation, you need to protect yourself from pregnancy. After a pipel biopsy of the endometrium, minor bleeding from the genital tract is normally observed for several days. You may experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which can be relieved with painkillers. Complications when performing pipell biopsy of the endometrium are extremely rare. The development of acute endometritis due to infection in the uterine cavity is possible if the conditions of the manipulation are not observed. External bleeding can occur when the bullet forceps slips and damages the cervix.
Pipelle biopsy of the endometrium has been an effective method for the primary diagnosis of the functional state of the uterus for many years. The sensitivity of the technique in detecting various intrauterine pathologies is 60-90%.
Cost of pipell biopsy of the endometrium in Moscow
Fluctuations in the cost of the study are determined by the form of ownership and reputation of the clinic, the order of the manipulation (in the order of priority, as soon as possible after treatment), the type of anesthesia (irrigation of the cervix with an anesthetic or paracervical anesthesia), the type of antispasmodic administered and the qualifications of the gynecologist performing this procedure. Pipelle endometrial biopsy does not require special preparation, the number of studies is standard and does not affect pricing. The price of pipell endometrial biopsy in Moscow may increase if additional services are available.
Surely the first reaction of a woman to whom a gynecologist prescribes a referral for a pipell biopsy of the endometrium will be fear of the name itself, and not just of the test procedure. We suggest you understand all the nuances of this diagnostic method and understand whether you should be wary of it. From our article you will learn about the purpose and indications for the procedure, features of its implementation and contraindications.
Why is it carried out?
First, we want to reassure those who panicked when advised to undergo this procedure. This is a standard diagnosis that is prescribed to many women in order to determine the condition of the internal mucous membranes of the uterus - the endometrium. It consists in the fact that using a special tube (pipel), the doctor penetrates the uterine cavity and takes a small amount of tissue for further histological analysis in the laboratory.

Previously, this analysis was carried out by biopsy, but this procedure requires dilation of the cervical canal, which is very painful, so anesthesia was required. The main advantage of pipel biopsy is painlessness. A thin catheter with a diameter of 3 mm passes well through the neck without expanding it; tissue or liquid is taken using a piston similar to the one located in a syringe. In this case, the patient may feel minor, quite tolerable, discomfort.
The advantages of the described diagnostic method also include:- no need for inpatient conditions;
- no need to expand the cervical canal;
- minimal risk of spreading infections, since the collection is carried out with a disposable instrument;
- the ability to take analysis from any area of the endometrium;
- full preservation of the woman’s ability to work;
- increasing the chances of successful embryo implantation when carried out before IVF.
Pipelle endometrial biopsy is the most accurate diagnostic method, which allows you to correctly diagnose and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. 
Did you know? For decades, cervical cancer has been the second most common cancer in women after breast cancer. If detected early, the mortality rate from this disease is 9%. When oncology spreads to other organs - 83%.
Indications for use
Pipelle biopsy is prescribed in the following cases:
- uterine bleeding during menstruation or at the beginning of menopause, after abortion, childbirth, during hormonal treatment;
- long absence of pregnancy in the presence of normal tests;
- multiple miscarriages;
- absence of menstruation, menstrual irregularities, in particular in the luteal phase;
- the presence of fibroids, another tumor to determine its malignancy, suspicion of cancer;
- the presence of inflammation or suspicion of it;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- after hormonal treatment to evaluate its effectiveness.

Depending on the specific case, the test is prescribed on a specific day of the menstrual cycle. It can also be prescribed for vague symptoms and an unclear picture of the causes of women’s health problems, in order to confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis. If the presence of carcinoma is suspected, material can be collected on any day of the cycle.
Did you know? The uterus is the only organ of the human body that may not fulfill its function during a person’s life. This happens if the woman has never become pregnant. It is also the only organ that can increase its size tens of times and then return to its previous parameters.

Preparation for the procedure
There is no need to prepare specially for the procedure. When prescribing it, the doctor will tell you that the accuracy of the analysis can be achieved only if some simple rules are followed:
- do not have sexual intercourse the day before the biopsy;
- do not insert tampons and suppositories into the vaginal cavity, do not smear the vagina with ointments, do not use lubricants, do not douche - it is necessary to preserve the natural environment of the vagina.

The gynecologist will also prescribe additional tests, which will need to be completed in advance in order to accurately determine the location from which the tissue will be taken. Typically a woman goes through:
- blood test for HIV, hepatitis, Rh factor;
- general blood analysis;
- vaginal smear for microflora and cytology;
- Ultrasound of the uterus.

Important! You should not prescribe the procedure yourself. It should be done only with the direction of a doctor. Self-medication can lead to undesirable consequences and worsening of the condition.
Most often, for women of reproductive age, the procedure is prescribed on the 21st-23rd day of the menstrual cycle. However, if a specific disease is suspected, the day of collection will be determined individually for each patient.
From the eighth to the 11th day, the procedure is performed before IVF to accurately determine the condition of the endometrium.
Women who have reached menopause are given a referral for any day. 
When scheduling a procedure, the patient must inform the gynecologist about the medications she is currently taking. This is especially true for blood thinners.
Contraindications
Pipelle biopsy is contraindicated for women who have:
- inflammation of the vagina, cervix, pelvic organs;
- disturbances in hemostasis;
- anemia;
- purulent cervicitis.

If a woman has a reduced pain threshold, anesthesia is used before diagnosis. In this case, the patient feels absolutely nothing when the tissue is taken.
How is it carried out?
Due to the fact that the pipel biopsy procedure is quite simple, it is performed in an outpatient setting on a gynecological chair.
Before the procedure, the doctor lubricates the cervix with an anesthetic or injects it with a syringe. The gynecologist then inserts a tube with a plunger into the cervix. When it is lowered down, the required amount of tissue is sucked into the cylinder, which is located at the end of the pipe. After the tube is removed, the material is sent for histology. 
The collection procedure takes about half a minute. The entire process from manual examination of the uterus to removal of the pipel takes about 10 minutes.
After the procedure, it is rare, but undesirable consequences may occur in the form of painful spasms and minor bleeding. This is a reaction to interference in the uterine cavity. Usually the discomfort goes away after a day. If pain is observed, it can be relieved with antispasmodics.
Important! Unusual situations after the procedure include too much menstruation, brown spotting with an unpleasant odor that lasts for a long time (longer than a week), severe pain in the lower abdomen. Such conditions require immediate medical attention.

Despite the fact that a pipel biopsy does not affect a woman’s performance, on the day of aspiration you should still refrain from sports, heavy physical activity, and heavy lifting. It is also necessary to refrain from taking a bath if spotting occurs until it disappears completely. The washing procedure is best done in the shower. Until the discharge ends, you should refrain from sexual intercourse.
Result
The analysis results will be ready after 7-10 days. They are deciphered by the gynecologist who wrote out the referral.
Thus, pipel biopsy is an improved method of aspiration biopsy, the advantages of which are painlessness, rather rare observation of consequences and complications, and reliability of the results. Typically, such aspiration is performed without anesthesia or with the use of local anesthesia. To obtain a reliable result, two or three samplings will be required.
Video: indications for endometrial aspiration biopsy
Women, due to the structure of their bodies, often have to undergo various tests. A representative of the fairer sex should visit a gynecologist regularly. Doctors talk about annual visits to the doctor in the absence of any complaints. If symptoms of pathology occur, then you need to contact a specialist as soon as possible.
Gynecologists often prescribe tests for patients such as hysteroscopy, colposcopy, ultrasound diagnostics, and so on. Pipe endometrial biopsy has gained great popularity in recent years. The consequences and reviews of the diagnostic manipulation will be presented to your attention in the article. You will learn the specifics of the procedure. You can also find out why pipel endometrial biopsy is done.
What it is
Pipelle endometrial biopsy is a diagnostic operation that allows you to examine the inner lining of the uterus without the need to dilate the cervical canal. The patient feels virtually no discomfort at the time of material collection. This allows you to avoid the use of anesthetics and narcotic drugs.
Pipelle endometrial aspiration biopsy is named after the man who discovered it. It is carried out using the thinnest tube, which has a diameter of 2.3 or 4 millimeters. This tool is hollow inside, which allows you to collect material.
When is diagnostics necessary?
In recent years, patients are increasingly being prescribed this type of diagnosis. The main indications of such a study include:
- infertility of unknown nature;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- bleeding due to the use of hormonal drugs;
- suspicion of acute or chronic endometritis;
- lack of menstruation at the scheduled time;
- menopause period;
- polyps and fibroids in the cavity of the reproductive organ;
- preparation for surgical interventions and so on.
Sometimes a pipell biopsy of the endometrium is prescribed before IVF. This type of study eliminates possible difficulties during implantation of the fertilized egg and increases the likelihood of a positive result.

Contraindications for surgery
Like any intervention in the patient’s body, pipel endometrial biopsy has its limitations and contraindications. These include:
- the presence of pregnancy, including development outside the uterine cavity;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- vaginal infection;
- low pain threshold (pain relief required);
- defects in the development of the uterus (septum, adhesions, etc.).
In each individual case there may be additional contraindications. Before the manipulation, the patient is always examined by specialists and makes their opinion.

Preparing for the study
The collection of material is always carried out within the walls of the hospital. Before the procedure, the patient is asked to take an anesthetic and sedative. However, in most cases this is not necessary. Anesthesia is required only when the pain threshold is low and a pipel with a diameter of more than four millimeters is used.
Are there any special conditions for the procedure called endometrial tube biopsy? On what day of the cycle should the material be collected? It all depends on the purpose of the research being conducted. If a woman is of reproductive age and has a relatively stable cycle, then the procedure is performed between 20 and 25 days from the beginning of menstruation. Representatives of the fairer sex during menopause can be prescribed a study at absolutely any time.
When preparing for the in vitro fertilization procedure, manipulation is prescribed one cycle before the use of hormonal drugs. It is worth noting that you need to stop all medications that can affect the condition of the endometrium. These include hormones, antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and so on. In exceptional cases, the study is carried out directly during treatment.
How is a pipell biopsy of the endometrium performed?
The material is collected by an experienced doctor in a gynecological chair. Before the procedure, the woman must perform hygiene procedures and undress. Next, the patient sits on the chair, and the doctor begins the manipulation.
A speculum with a speculum is inserted into the vagina of a representative of the fairer sex. With its help, the cervix is fixed in a stationary position. After this, the specialist needs to find out the size of the reproductive organ. For this, a special measuring device is used. It is carefully inserted into the cervical canal until it stops. After this, the doctor selects the appropriate size pipe and begins the procedure.
The doctor takes a suction tube and carefully inserts it into the cervical canal. It is worth noting that the device should not rest against the fundus of the uterus. Otherwise, it may be damaged. When the tube is inserted to the desired depth, the doctor pulls the piston from the outer end of the device. At this moment, negative pressure is created in the uterus. Some endometrial particles end up in the tube and remain there even after removal. The next step is for the doctor to carefully remove the pipette from the patient’s cervical canal. After this, the resulting material is applied to sterile glass and sent for examination.

Opinions of doctors and patients about manipulation
Pipelle endometrial biopsy has positive reviews. Patients say that the procedure is absolutely painless. It lasts no more than one minute. It takes much longer to prepare for it. Within a few minutes after collecting the material, the patient can go home. Only in some special cases do doctors leave a woman in the hospital for several hours.
Doctors say that pipell biopsy of the endometrium gives very accurate results. If a regular biopsy examines a specific area that was taken using curettage, then a pipel takes the endometrium from all the walls of the reproductive organ. Experts also report the safety of manipulation. Gynecologists do not have to expand the patient’s cervical canal. After all, this often leads to the development of complications.
Pipe endometrial biopsy is also a safe procedure due to the use of sterile materials. The straws are made of high quality plastic and can only be used once. During curettage, reusable metal devices are used. This often leads to infection and infection. That is why pipel biopsy is the more preferable way to study the condition of the internal cavity of the reproductive organ.
Patients talk about the relatively expensive cost of the procedure. The average price category for pipel biopsy ranges from two to five thousand rubles. However, in government institutions this research is performed absolutely free of charge, provided certain documents are available.
Duration of diagnostics and obtaining results
As you already know, the collection of material takes no longer than one minute. After this, the tissues are sent to the laboratory for testing. Diagnostics lasts no more than one week. The result is usually given within ten days.
Only a qualified specialist can decipher the received data. You shouldn't try to do this yourself. Your guesses may be wrong. If necessary, after a pipel biopsy of the endometrium, any medications are prescribed to correct the condition.

An endometrial biopsy is necessary to identify:
- causes of infertility and spontaneous abortion;
- hormonal abnormalities;
- causes of uterine bleeding not related to menstruation;
- endometrial hyperplasia - growth of the uterine mucosa;
- malignant changes - uterine cancer.
Types of uterine endometrial biopsy:
- Pipel biopsy - material is collected using a thin plastic tube with a side hole at the end. With the help of a piston, negative pressure is created in the tube, due to which the tissue of the uterine glands and endometrium is sucked into the cylinder. It is considered the least traumatic method of taking material.
- Aspiration biopsy - the principle of the procedure is the same as for Pipelle biopsy, but a syringe or an electric vacuum apparatus is used to create negative pressure.
- Diagnostic curettage of the uterus - sampling of material using a surgical spoon - curette. The gynecologist scrapes the top layer of mucosa from individual areas or from the entire surface of the uterus. The mucous membrane is scraped out completely or in the form of line scrapings - trains.
- Biopsy during hysteroscopy - samples of the uterine lining are obtained during an endoscopic examination using a hysteroscope - a probe equipped with a miniature video camera and a miniature surgical instrument.
Pain relief during endometrial biopsy. The choice of anesthesia depends on the method of biopsy. So the modern method - Pipelle biopsy is practically painless and does not require anesthesia. Diagnostic curettage is a minor surgical operation and is performed under local anesthesia or short-term general anesthesia.
Histologists and pathologists examine tissue samples using a light microscope. The whole process takes 7-10 days, after which a conclusion is issued that describes the structural features of the endometrium. A definitive diagnosis is made only in clear cases. For most patients, a clinical diagnosis is made by a gynecologist, taking into account the results of a biopsy and other examinations (subjective symptoms, examination results, hysteroscopy, colposcopy).
Structure of the uterus
The walls of the uterus consist of three layers:
- The outer layer or parametrium is the connective tissue that covers the outside of the organ. It also forms ligaments that provide attachment to the uterus.
- The inner layer or myometrium is smooth muscle. A thick layer of muscle tissue provides protection to the fetus and contractions of the uterus during childbirth.
- The inner layer or endometrium is a mucous membrane containing a large number of blood vessels. It contains the uterine glands, which secrete mucus that prevents the walls of the uterus from collapsing.
Structure and functions of the endometrium
The endometrium plays a key role in a woman's reproductive system. It monthly prepares the conditions for the fertilized egg: it ensures its attachment, and subsequently the formation of the umbilical cord and the creation of conditions for the development of the embryo. If pregnancy does not occur in a given cycle, the upper layer of the endometrium is shed, which manifests itself in the form of menstrual bleeding.
All changes that occur in the endometrium are controlled by female sex hormones, which are released in accordance with the maturation of the follicle in the ovary.
There are three phases in the development of the endometrium:
- The proliferation phase is the growth of the functional layer of the endometrium, its restoration after menstruation. Duration from the 5th to the 14th day of the cycle. The reproduction of endometrial cells, their proliferation, is stimulated by the hormone estrogen.
- The secretion phase is the active secretion of secretions by the uterine glands, which creates optimal conditions for the attachment and development of the embryo. Lasts approximately from the 15th to the 27th day of the cycle. The changes are stimulated by the corpus luteum hormone, progesterone.
- The bleeding phase is the period during which the functional layer of the endometrium peels off and is removed from the uterus during menstruation. Duration from the 28th to the 4th day of the cycle. Rejection of the functional layer is associated with progesterone deficiency. In its absence, the arteries supplying the upper layer of the endometrium are compressed, which is why the cells do not receive enough nutrients and die.
Histology of the uterine mucosa
The inner surface of the uterus is lined with columnar epithelium. Endometrial cells are low cylindrical in shape. They are smaller in size than the epithelium of the cervical canal. The cells contain one nucleus and well-defined cytoplasm. They may have cilia, which facilitate the movement of the egg to the site of attachment, or be unciliated.
- The basal layer is the lower layer adjacent to the muscular lining of the uterus. Its main function is to ensure restoration of the functional layer after menstruation or other damage. Thicknessmm. Poorly responds to hormonal fluctuations. The cell nuclei are oval and intensely stained. Depending on the phase of the cycle, the shape of the cells and the location of the nuclei in them change. Here there are large vesicle cells, which are immature cells of the ciliated epithelium.
- The functional layer is the superficial layer lining the uterine cavity. Its function is to ensure the adhesion of the fertilized egg and its subsequent implantation. It is most sensitive to the effects of female sex hormones. During menstruation, it is completely rejected. In the first days after menstruation, its thickness is minimal. By the end of the cycle it increases to 8 mm.
- The uterine glands are simple, unbranched tubular glands that secrete a mucous secretion that ensures the normal functioning of the uterus. The glands originate in the basal layer. During the cycle, with the growth of the functional layer, the glandular tube lengthens and acquires a tortuous shape, but does not branch.
- In the basal layer, the uterine glands are narrow, densely located and separated by narrow strips of stroma. Their surface is lined in one row with columnar epithelium, similar to that covering the surface of the mucosa.
- The functional layer contains the main parts of the tubes and their excretory ducts. In the first week after menstruation, the gland tube has a straight shape and a narrow lumen. Then it lengthens and takes on a sinuous shape. At this stage, the gland cells begin to produce mucus, which initially accumulates in the duct and then is discharged into the uterine cavity, moisturizing its mucous membrane.
- The endometrial stroma is a connective tissue that provides strength to the mucous membrane and binds endometrial cells together.
- In the basal layer, the stroma is dense, consisting of connective cells and a large number of thin collagen fibers. The stromal cells are small, round, and smaller than the endometrial cells. They are located in loose groups between the uterine glands. They have a rounded nucleus surrounded by a thin rim of cytoplasm.
- In the functional layer after menstruation, the stroma is represented by delicate argyrophilic fibers, which become coarser towards the end of the cycle. The cells are spindle-shaped and contain large nuclei. The cells are located at a distance from one another, so the stroma is loose. During the secretion phase, the endometrium swells and water and nutrients accumulate between the stromal cells, increasing the gaps between them.
Indications for uterine endometrial biopsy
- Intermenstrual acyclic bleeding;
- Bleeding after menopause;
- Prolonged heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- Bleeding after spontaneous abortion or childbirth;
- Bleeding while taking hormonal contraceptives;
- Assessing the effectiveness of hormonal treatment;
- Lack of menstruation without pregnancy;
- Determining the causes of infertility;
- Endometrial polyps;
- During examination for uterine fibroids, endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia, ovarian cyst;
- Signs of atypia of the glandular epithelium identified in a cytology smear (Pap test);
- Changes determined by ultrasound of the uterus over 3 cycles;
- Endometrial tumors to determine malignancy;
- Preparation for artificial insemination.
Timing for endometrial biopsy:
- On any day of the cycle - if endometrial cancer is suspected;
- Immediately after menstrual bleeding with endometrial polyps;
- On the first day of bleeding or spotting to determine the cause of uterine bleeding not related to menstruation;
- On the 7-10th day of bleeding - with prolonged heavy menstruation;
- Day of the cycle to determine the sensitivity of the endometrium to hormones;
- 2-3 days before the expected menstruation in case of infertility, insufficiency of the corpus luteum, with a large number of anovular cycles.
Contraindications to any type of endometrial biopsy are:
- Pregnancy;
- Acute infections of the genitourinary organs;
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs - genital and urinary;
- Significant bleeding disorders.
How to prepare for a uterine endometrial biopsy?
- Sexual contacts;
- Douching;
- Using any vaginal medications without a doctor's prescription.
To exclude infections that can cause complications after a biopsy, it is necessary to undergo a number of tests:
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- Determination of blood clotting - coagulogram;
- Blood test for HIV, syphilis - RW, hepatitis B and C;
- Flora smear - bacteriological examination of the contents of the genital tract;
- A test for human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood or urine is a test to determine pregnancy.
On the morning of the biopsy, you will need to shower and remove hair from around your genitals. If the biopsy is performed under intravenous anesthesia, then you must refuse food 12 hours before.
Biopsy technique
- Treating the external genitalia with an antiseptic;
- Dilatation of the vagina with a gynecological speculum to gain access to the cervix;
- Treating the cervix with alcohol;
- Fixation of the cervix with bullet forceps.
The doctor's further actions depend on the biopsy method.
1. Diagnostic curettage of the uterus
- Using Hegar dilators (which are metal cylinders with a diameter of 4-13 mm), the cervical canal is dilated. Its width should correspond to the size of the curette - a surgical spoon.
- A curette of the required size is inserted into the uterine cavity.
- Pressing the curette to the anterior wall of the uterus, pass it from the fundus to the internal os, scraping out the functional layer of the mucosa.
- The spoon with the material is removed from the uterus and the material is collected in a container with formaldehyde.
- The action is repeated, sequentially scraping out all the mucous membrane from the anterior and then from the posterior wall of the uterus and the mouths of the fallopian tubes.
- When studying the reaction of the endometrium to hormones and establishing the cause of infertility, the doctor does not scrape the entire surface of the uterus, but limits himself to 3 separate scrapings - trains.
Advantages:
- With complete curettage, the risk of missing foci of atypia or endometrial cancer is eliminated;
- It is possible to immediately remove pathological lesions during the procedure.
Flaws:
- Performed in a hospital;
- Requires intravenous anesthesia;
- The procedure is quite traumatic;
- Long recovery period – up to 4 weeks;
- There is a risk of complications if the procedure is performed incorrectly.
2. Aspiration biopsy
Endometrial aspiration biopsy can be performed using a thin Brown syringe or a vacuum electric device.
- A catheter (thin hollow tube) with a diameter of 2-4 mm is inserted into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal. It is pressed tightly into the wall of the uterus.
- A syringe is attached to the outer edge of the catheter.
- By pulling the plunger of the syringe, a sample of the epithelium of the uterine mucosa is obtained.
- The resulting material is applied in a thin layer onto degreased glass slides.
Option II
- Using a thin catheter and syringe, 3 ml of saline solution with the addition of sodium nitrate is injected into the uterine cavity. The latter is necessary to prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Immediately after administration, the liquid is removed using a syringe.
- The resulting washing liquid is placed in a test tube and sent to a centrifuge for 8 minutes. After this, a sediment of cells forms at the bottom of the test tube. This method allows you to obtain information about the characteristics of individual cells, but not about the structure of the mucosa as a whole.
Option III
- 30 minutes before surgery, take medications to relax the cervix and reduce pain (baralgin, analgin, diphenhydramine) or inject an antispasmodic into the cervix with a 1-2% solution of lidocaine with adrenaline. A lidocaine solution is also injected into the periuterine tissue.
- A probe is inserted into the uterine cavity to determine its depth.
- After removing the probe, an aspiration tube connected to an electric vacuum aspirator is inserted into the uterine cavity.
- The doctor, moving the catheter through the uterine cavity, collects material from different parts of it.
- The collected material is placed in containers with formaldehyde solution.
- The procedure is performed blindly or under ultrasound guidance.
Advantages:
- Low invasiveness of procedure options I and II;
- Short recovery period after options I and II.
Flaws:
- It is impossible to determine the structure of the endometrium.
- The recovery period after vacuum aspiration takes 3-4 weeks.
3. Pipelle biopsy
To perform a pipel biopsy, a flexible aspiration probe is used. It is a plastic cylinder with a diameter of 3 mm with a side hole at the end. The inside of the cylinder is hollow and equipped with a piston.
- The gynecologist inserts a probe through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity.
- When the piston is pulled, negative pressure is created in the cylinder, and it sticks to the wall of the uterus.
- Through a hole at the end of the probe, material enters its cavity.
- The procedure is repeated 3 times on different areas of the mucosa.
- The probe is removed from the uterine cavity.
- The contents of the probe are placed in a container filled with a 10% formaldehyde solution.
Advantages:
- It is possible to conduct it in a gynecological office;
- No anesthesia required;
- Painless and non-traumatic;
- Rapid healing of the mucous membrane;
- Sensitivity 60-90%
- Does not cause complications if the procedure is performed correctly.
Flaws:
- Based on small fragments of the mucosa, it is difficult to establish the structure of the endometrium;
- Collection of material from limited areas of the uterus. There is a risk of missing pathological foci.
4. Biopsy during hysteroscopy
It is carried out using a hysteroscope - an endoscope designed to examine the uterine cavity. The device is a probe with equipment attached to the end that allows you to obtain an image of the lining of the uterus and take samples from suspicious areas.
- A sterile saline solution is injected into the uterine cavity to obtain high-quality images.
- A hysteroscope is inserted through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity.
- The mucous membrane is examined and the image is displayed on the monitor screen.
- Determine the areas from which material samples need to be taken.
- A curette or other surgical instrument is inserted through the hysteroscope port. It is used to remove endometrial particles by scraping or aspiration.
- Mucosal samples are placed in a container.
- The saline solution is removed from the uterine cavity, then the hysteroscope is removed.
Advantages:
- It is possible to remove identified pathologies - polyps, synechiae;
- Short recovery period;
- High diagnostic accuracy.
Flaws:
- The need for intravenous anesthesia;
- High cost of the procedure;
- Insufficient number of clinics equipped with appropriate equipment.
The resulting material is marked accordingly (indicate the date of the biopsy, the patient's last name and year of birth) and sent to the laboratory for histological examination. After the examination, the results of the endometrial biopsy are sent to the doctor who is seeing the woman. As a rule, it is necessary to wait days for the conclusion.
What can be the results of biopsy histology?
- Information content of the sample.
- Uninformative, inadequate sample. This phrase in the histological report indicates that the resulting material does not contain a sufficient number of endometrial cells. Blood cells, squamous stratified epithelium of the vagina, and columnar epithelium of the cervical canal may be present. This situation is possible if the sample is taken incorrectly.
- An informative, adequate sample – the biopsy contains a sufficient number of endometrial cells.
- Macroscopic description of the drug.
- Weight of submitted samples;
- Size of fragments (large, small);
- Color (from gray to bright red);
- Consistency (loose, dense);
- Blood clots, blood clots;
- Slime.
- Microscopic description of the drug.
- Type of epithelium (cylindrical, cubic, flat, indifferent), its size, number of layers;
- Stroma - its presence, density, homogeneity.
- Size and shape of stromal cells;
- Fibroplasticity of the stroma - the number of connective fibers;
- Deciduous stroma - accumulation of fluid and nutrients;
- The uterine glands, their shape, description of the epithelium lining them;
- The shape and size of the lumen of the glands, the presence of secretions inside the glands, branching;
- Lymphoid accumulations are signs of inflammation;
- Chorionic cells, the presence of edema or dystrophic changes in them - this option indicates that the woman had a frozen pregnancy or an incomplete spontaneous abortion.
- Diagnosis
- It is indicated which phase of the cycle the endometrium corresponds to;
- The presence of hyperplasia - growth of the endometrium;
- The presence of polyps and a description of the tissue from which they consist;
- The presence of endometrial atrophy – thinning of the uterine mucosa;
- Hypoplastic mixed endometrium is a borderline condition that is not a disease;
- Chorionic villi, which are particles of the fetal membrane, indicate an interrupted pregnancy.
- Degeneration of the epithelium or vessels of the chorionic villi - indicates that the fetus initially did not receive nutrients, which could cause its death
- The presence of atypia - cells with signs not characteristic of a given tissue, indicates a precancerous condition of the endometrium;
- The presence of malignant (cancerous) cells indicates endometrial cancer.
Often the conclusion contains only one phrase: “Normal endometrium in the proliferation/secretion/menstruation phase.” It means that the endometrium is normal, no signs of disease or changes in cell structure have been detected, there are no polyps or hyperplasia.
It is important that the condition of the endometrium corresponds to the phase of a woman’s menstrual cycle and the period of her life. Thus, the conclusion “Normal endometrium in the proliferation phase” 3 days before the planned menstruation indicates hormonal disorders in the body.
What diseases can be detected by this study?
The lumens (orifices) of the glands are enlarged, and mucous contents are visible in them.
The stromal cells are small, round, with signs of mitosis, when the nucleus breaks up into separate chromosomes.
A large number of cells of cylindrical, less often cubic epithelium.
Large epithelial cells with enlarged nuclei of irregular shape.
The cells have large nuclei that are intensely stained. The surrounding cytoplasm is stained with alkaline dyes.
There are no cells in a state of mitosis.
Thickening of the basal layer due to the proliferation of glands.
On the surface of the endometrium, the epithelium is tubular or villous.
Atypical epithelial cells, as a rule, are not detected.
On the surface are large columnar epithelial cells that contain enlarged nuclei with nucleoli. The ratio of cytoplasm and nucleus is not disturbed.
The epithelium of the glands is multinucleated. Individual nuclei are enlarged and polymorphic, irregular in shape.
Large cells are vesicles with an enlarged nucleus and wide cytoplasm.
Areas of squamous metaplasia in the form of scales are foci where columnar epithelium is replaced by squamous epithelium.
Light cells with inclusions of lipids (fats). A sign indicating a high risk of developing endometrial cancer.
The epithelium is single-layered with signs of atrophy - small cells with reduced nuclei.
Small glands, scraps of glands.
Uneven distribution of glands in different areas of the mucosa.
Small cells of the functional layer.
Signs of mitosis in the epithelium of glands.
Some uterine glands are lined with single-layer epithelium, while others have a multirow arrangement of cells.
Uneven stroma density and cell structure in different areas of the mucosa.
Microorganisms that cause inflammation of the endometrium.
Signs of mitosis in the epithelium.
Clusters of plasma cells.
Bacteria that cause inflammation.
Well-differentiated adenocarcinoma - endometrial cells are enlarged, but retain their regular shape. Polymorphism (diversity of forms) is weakly expressed.
- Increase in kernel length.
- The nuclei are hyperchromatic, excessively intensely stained.
- Vacuoles are often found in the cytoplasm.
- Cancer cells form glandular structures in the form of rosettes.
Moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma tumor, characterized by pronounced cell polymorphism. They can be of various sizes and shapes, but the similarity with columnar epithelium can still be established.
- The nuclei are increased in size and contain nucleoli.
- Most cells are in a state of mitosis - the nucleus breaks down into individual chromosomes.
- The cells do not form glandular structures.
Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma - the cells have clear signs of malignancy. They have completely lost their resemblance to the endometrial epithelium.
- The cells form small dense clusters.
- Cells of different sizes and irregular shapes. Small cells predominate.
- There are large cells, the cytoplasm of which contains vacuoles.
- The cells contain several irregularly shaped nuclei.
The nuclei are hyperchromatic and become brightly colored when stained.
Signs of mitosis in cells.
The cytoplasm contains inclusions (lipids, vacuoles).
Round or irregularly shaped clusters of cells.
Each cell contains several nuclei of different sizes and irregular shapes. They can be enlarged or reduced.
The nuclei contain nucleoli.
Signs of mitosis associated with impaired cell reproduction. The chromosomes are arranged in a star shape.
Cell fragments are present.
What to do after taking a biopsy
The following signs indicate the development of complications and the need to consult a doctor:
- Heavy bleeding - more than 3 pads in 2 hours;
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen and lower back that does not subside after taking painkillers;
- Prolonged bleeding: more than 5 days after pipel biopsy, more than 4 weeks after curettage;
- Discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- Temperature rise above 37.5 C.
To avoid the development of complications, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Take a shower instead of a bath;
- Carefully observe genital hygiene - water procedures at least 2 times a day;
- Refuse sexual intercourse;
- Avoid physical activity;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia;
- Take antibiotics after diagnostic curettage and vacuum aspiration to prevent infections;
- Taking hormonal contraceptives as prescribed by a doctor to restore hormonal levels;
- It is advisable to observe bed rest for 2-3 days after diagnostic curettage and vacuum aspiration.
The length of time it takes to recover depends on the method of biopsy. So, after a pipel biopsy, you can return to your normal lifestyle within 2-3 days. After more traumatic methods, restrictions are imposed for a month.
Login to profile
Registration
It will take you less than a minute
Login to profile
Endometrial (uterine) biopsy: indications, methods and implementation, results
An endometrial biopsy is an operation in which the surgeon removes small sections of the lining of the uterus for pathohistological examination. The material is sent to the laboratory, and after microscopy the attending physician receives accurate information about the condition of the endometrium and its changes.
Histological examination of tissue fragments is an integral stage in the diagnosis of a wide variety of pathologies. In some cases, only microscopic analysis of tissue allows one to accurately determine the nature of the changes and their cause, which means that treatment prescribed taking into account the specific histological picture will be the most effective.
In gynecology, biopsy examination has been used very widely for many decades, during which tissue sampling techniques have been improved, which may differ depending on the diagnostic purpose. Each method has its own indications and contraindications, which the gynecologist takes into account based on the expected diagnosis.
If necessary, conventional microscopy can be supplemented with modern immunohistochemical techniques, which make it possible to detect malignant tumors and accurately differentiate their origin, determine the degree of differentiation and prognosis for the patient.
Endometrial biopsy is an operation, albeit a minimally invasive one, so it requires careful preparation, assessment of possible risks, and a balanced approach to determining indications. Today, the operation is performed on a wide range of women due to its relative safety, ease of performance and the highest diagnostic value.
As a rule, biopsy sampling is performed routinely, as an independent study, but in some cases there may be a need for an urgent biopsy performed during surgery for pathology of the female genital organs. The main purpose of a biopsy is diagnosis, but sometimes it is also therapeutic in nature, leading to an improvement in the patient’s well-being after removal of the pathological focus.
Types of endometrial biopsy
The endometrium is the inner layer of the uterine body, its mucous membrane, which undergoes cyclic changes under the influence of female sex hormones. Its structure is different not only in different phases, but also on different days of the menstrual cycle. Pathology of the endocrine system, ovaries, and the uterus itself inevitably affects the structure of the mucous membrane, by the characteristics of which the doctor judges the nature of the pathology.
You can “extract” the endometrium only by penetrating the uterine cavity. In the first half of the last century, attempts to obtain a sample were accompanied by expansion of the cervical canal and curettage of the entire mucous membrane. Modern biopsy techniques mean that it is minimally invasive and has low morbidity, as well as a low risk of complications, which makes it possible to expand the indications for the study. The clinic uses several types of endometrial biopsy surgery:
- Classic curettage of the mucous membrane;
- Aspirate biopsy with vacuum or aspirator;
- Pipe endometrial biopsy is one of the least traumatic methods;
- CG biopsy;
- Targeted biopsy during hysteroscopy allows you to obtain tissue from the most altered areas of the endometrium, but has limited use due to the high cost of hysteroscopy itself and the lack of equipment in many hospitals.
The operation of collecting endometrial fragments is only the initial stage of the diagnostic search, since without microscopy it is impossible to determine what structural changes occur in the uterine mucosa. The exact answer will be given by analyzing histological sections of the endometrium under a microscope.
Indications and contraindications for biopsy
Pathomorphological examination of the uterine mucosa is carried out for women of all ages, regardless of whether they have given birth to children or not. The reason for the procedure may be:
- Dysfunctional bleeding;
- Intense uterine bleeding or scanty menstruation;
- Amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) for an unknown reason (pregnancy must be excluded!);
- Possible tumor growth;
- Internal endometriosis;
- Suspicion of a chronic inflammatory process in the uterine mucosa;
- Infertility to clarify the cause;
- Planning an IVF procedure;
- Miscarriages, pathology of short term pregnancy (after medical abortion).
Contraindications to endometrial biopsy are:
- Pregnancy is an absolute contraindication to the study, since intervention in the uterus will provoke a miscarriage;
- Pathology of hemostasis due to the risk of bleeding;
- Treatment with anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents, anti-inflammatory drugs (require discontinuation in advance);
- Severe anemia;
- General infectious diseases (ARVI, intestinal infections, etc.);
- Acute or exacerbation of chronic genital tract infections;
- Allergy to anesthetics.
Since a biopsy is not performed for health reasons, in case of serious contraindications it can be abandoned in favor of other, safer diagnostic methods. If there are relative obstacles, the doctor will try to choose the most optimal method of tissue collection that eliminates complications.
Preparing for the study
Preparation for an endometrial biopsy includes general clinical tests (blood, urine), coagulation studies, determination of blood group and Rh factor, tests for HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis. During a gynecological examination, the doctor takes smears from the cervix for cytology and microflora from the vagina. If it is impossible to exclude pregnancy, a human chorionic gonadotropin test is performed.
After undergoing examinations and setting a date for the biopsy, the patient must abstain from sexual activity, douching, and vaginal tampons 2 days before the procedure, and stop taking blood thinners 7-10 days before. If curettage is planned under general anesthesia, then the day before from 6 pm, food and liquid intake is stopped.
On the morning of the study, the patient takes a shower, removes hair from the external genital tract; if there are varicose veins in the legs, the doctor may prescribe elastic bandaging to prevent thromboembolic complications.
Timing and technique of performing a biopsy
Since the endometrium clearly reflects hormonal effects, the information content of the analysis depends on what day of the cycle it was received. For different pathologies, the timing of the biopsy may differ. Thus, when diagnosing the causes of infertility, anovulation, and disorders of the second phase of the cycle, young women are recommended to undergo a biopsy the day before their expected period or on the first day of their onset.
In case of heavy menstruation, it is more advisable to carry out the operation from 5 to 10 days of the cycle. If the bleeding is not associated with menstruation, then a biopsy will be prescribed in the first 2 days from the moment of its occurrence. During one cycle, the procedure can be performed several times - in case of hormonal imbalance, for example.
In the second half of the cycle, from days 17 to 25, a biopsy is indicated to assess the effectiveness of conservative hormone therapy. If a malignant process is suspected, the study is carried out regardless of the day of the cycle and without delay.
The woman will be able to find out the result of the pathological examination 7-10 days after the operation, but if it is necessary to perform additional staining techniques, this period may increase. For detailed explanations, you should contact a gynecologist, who will either prescribe treatment for the pathology or refer you to an oncologist if a malignant neoplasm is detected.
The technique for collecting endometrium for microscopic examination differs with different methods of procedure. It may include the stage of expanding the cervical canal, after which sharp instruments are inserted into the organ cavity, cutting off areas or the entire mucosa. This route is the most traumatic, although it provides the largest amount of information, so it is preferred if cancer is suspected or diffuse hyperplasia diagnosed by ultrasound. In the second case, the procedure will become therapeutic.
A purely diagnostic biopsy is often performed using gentle methods that can be performed without dilating the cervical canal - the most painful stage of the entire operation, which improves the tolerability of the study by women and reduces the risk of complications.
Scraping
The most radical method of collecting endometrial tissue is curettage - a classic technique used for half a century. To penetrate into the organ cavity, it is necessary to expand the neck, for which special dilators are taken from the smallest to the maximum diameter, the neck is fixed with forceps, and then the surgeon removes the mucous membrane with a sharp curette. The method is traumatic and requires great care due to the risk of damage to the basal layer of the endometrium and the uterine wall.
Classic uterine curettage is quite painful and therefore requires anesthesia; general anesthesia - mask or intravenous - is considered optimal. Due to the need for anesthesia, the woman is advised to prepare similar to that for any other surgical intervention (examination, discontinuation of certain groups of drugs, refusal of food and water the evening before the operation).
Curettage of the uterine cavity is usually carried out in case of hyperplastic processes in the mucous membrane, non-developing pregnancy, prolonged and heavy bleeding, or suspected cancer. Removing the mucous membrane from all the walls of the organ and the area of the tubal angles in some cases allows not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also at the same time to remove the pathological process itself, that is, it is a therapeutic procedure.
Aspiration biopsy
When preparing for a study using vacuum aspiration, a woman should exclude sexual activity, douching and the use of tampons 3 days before the biopsy date, and an enema is indicated the day before to cleanse the intestines. Due to the risk of infection upon penetration into the uterine cavity, it is important at the preparation stage to exclude inflammatory and infectious processes in the genital tract.
Aspiration biopsy can be performed for any pathology in the uterus, and is also indicated for questionable ultrasound findings. Its disadvantage can be considered to be the smaller volume of aspirate compared to curettage, which can make diagnosing a malignant neoplasm difficult, so if cancer is suspected, it is better to do curettage.
Video: endometrial aspiration biopsy
Pipelle biopsy
Pipelle biopsy resembles aspiration, but has the advantage that tissue is collected using a thin tube, the diameter of which is about 3 mm. The method is low-traumatic, does not require cervical dilatation, and has virtually no complications.
Pipelle biopsy can be performed on an outpatient basis, in a antenatal clinic; you need to prepare for it in the same way as for aspiration. During the procedure, the doctor places a Pipel tip into the uterus and then pulls on a plunger, releasing a small piece of endometrium by creating negative pressure in the syringe.
Pipelle biopsy does not cause trauma to the mucous membrane, does not cause the formation of an open wound surface with the risk of infection, and is practically painless, therefore it is preferred for young patients who do not have children, with endometrial pathology, infertility, for tissue collection for immunohistochemical determination of hormone receptors.
CUG biopsy
A CUG biopsy is performed without dilating the cervical canal, using a special small curette, with which the surgeon scrapes off the narrow cavities of the mucous membrane, starting from the fundus to the internal os of the uterus. This type of biopsy is indicated mainly to determine the effectiveness of hormone therapy, the degree of endometrial maturation at the natural level of hormones in different phases of the cycle, so the study may include several procedures during one menstrual cycle.
CUG biopsy is considered a safe and low-traumatic procedure, since only small areas of the mucous membrane are removed in the form of “stripes”. The information content of the study is increased by collecting several strips of mucous membrane from different parts of the organ.
Evaluation of biopsy results
To adequately assess the condition of the endometrium, the pathologist must know, if possible, the exact day of the patient’s menstrual cycle, therefore, the date of the last menstruation is always indicated in the referral for examination. It is also important to indicate the woman’s age, the nature of the treatment being taken (especially if it is hormonal drugs), the expected diagnosis based on the results of ultrasound and other examination methods.
Deciphering the results of an endometrial biopsy can show the norm, and then the pathologist in conclusion will indicate the specific phase of the cycle and its stage corresponding to the day of the menstrual cycle. These parameters are determined based on the structure of the glands, characteristics of the vessels and endometrial stroma.
The pathology most often detected by biopsy is:
- Hyperplastic processes - simple or complex non-atypical, as well as hyperplasia with atypia;
- Endometrial polyps with or without epithelial atypia;
- Malignant tumors;
- Atrophic processes (in older women - a variant of the age norm);
- Inflammation (acute or chronic).
Hyperplastic changes are more often diagnosed in patients whose age is approaching menopause, since during this period fluctuations in sex steroids occur, and many cycles are anovulatory in nature. Endometrial cancer occurs in both young and elderly women, and mucosal atrophy is a variant of the normal structure during the menopausal period.
One of the key points in assessing the morphological features of the endometrium is to identify or exclude cell atypia, which may indicate a high risk of malignant transformation. Atypia can be found in areas of overgrown endometrium with hyperplasia, in polyps.
The presence of a dysplastic process and a high risk of cancer is indicated by increased cell division with an increase in their number, polymorphism of the nuclei and epithelial cells of the endometrial glands themselves, and the appearance of pathological mitoses. In cancer, cells acquire malignant features (polymorphism, hyperchromic nuclei, many abnormal mitoses), characterized by foci of necrosis (death), hemorrhages, altered tissue grows into the underlying structures and vessels, which serves as the basis for metastasis.
The main question that a morphologist examining a biopsy often has to answer is whether there is cancer or whether it can be completely excluded. If there is a tumor, then the degree of its differentiation is indicated (well-differentiated adenocarcinoma, for example).
A biopsy for infertility is carried out not only to compare the morphological picture with the day of the cycle, established by the date of the last menstruation, but also for an immunohistochemical search for receptors for sex hormones, which may give a chance to determine the genesis of infertility and choose a way to combat it.
Consequences of endometrial biopsy and possible complications
Regardless of which way the mucous membrane was taken, the procedure inevitably injures the tissue, so there will be bleeding in any case. Their intensity and duration are determined by the method of manipulation.
After curettage, the bleeding is most profuse, often painful, but it is still lighter than during normal menstruation, since the mucous membrane is almost completely removed. The discharge should not contain large clots or pus-like fragments, it should not emit an unpleasant odor, otherwise the woman should contact the doctor again to exclude postoperative inflammation. If your temperature rises, you should go to the gynecologist immediately.
The first menstruation after the biopsy comes on time or a little later, it can be more abundant or more scanty. Most often, a delay occurs after a pipel biopsy, but to rule out pregnancy you should still do a test and go to the doctor.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, then she can count on it in the next cycle. The functional layer will have time to recover, the work of the ovaries is not disrupted, so the fertilized egg can be safely implanted in the uterus. However, experts advise abstaining from sexual intercourse until the discharge completely stops, and in the next cycle use barrier methods.
Further actions of the patient and the doctor will depend on the data of the morphological analysis. If cancer or atypical changes are diagnosed, a consultation with an oncologist is scheduled with the possibility of repeated surgical intervention, but this time radical. For inflammation, anti-inflammatory and antibiotic therapy is indicated; dishormonal processes may require the prescription of sex hormones.
Negative consequences after a biopsy are rare. Most often, patients complain of menstrual irregularities, painful menstruation, and discomfort during sexual intercourse. The most dangerous complication of the intervention is acute endometritis, which occurs with fever, abdominal pain, symptoms of intoxication, and foul-smelling pus-like discharge. This condition requires immediate treatment with repeated curettage of the uterine cavity.
In the presence of chronic inflammation in the genital tract, miscarriages or abortions for medical reasons, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed before surgery to prevent endometritis.
To prevent complications, a woman should maintain sexual rest until the discharge stops, carefully perform genital hygiene, and refrain from visiting the pool, sauna and bathhouse, as well as home hot baths.
Endometrial biopsy is usually performed free of charge, in antenatal clinics or inpatient clinics, but paid diagnostics are also possible. On average, the price of the procedure is 3-5.5 thousand rubles, depending on the qualifications of the personnel, the conditions of stay, the method used and additional treatment.
If a histological examination of the uterine mucosa is prescribed, then it is impossible to refuse it without compelling reasons. The risk of complications if you follow your doctor's recommendations is minimal, but the amount of information that can be obtained from a biopsy is not comparable to any other non-invasive methods. Only an accurate diagnosis will help you prescribe truly effective treatment, get pregnant, normalize your health, or avoid the consequences of a malignant tumor.