All materials on the site were prepared by specialists in the field of surgery, anatomy and specialized disciplines.
All recommendations are indicative in nature and are not applicable without consulting a doctor.
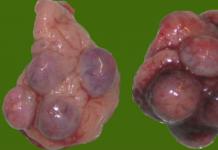
An endometrial biopsy is an operation in which the surgeon removes small sections of the lining of the uterus for pathohistological examination. The material is sent to the laboratory, and after microscopy the attending physician receives accurate information about the condition of the endometrium and its changes.
Histological examination of tissue fragments is an integral stage in the diagnosis of a wide variety of pathologies. In some cases, only microscopic analysis of tissue allows one to accurately determine the nature of the changes and their cause, which means that treatment prescribed taking into account the specific histological picture will be the most effective.
In gynecology, biopsy examination has been used very widely for many decades, during which tissue sampling techniques have been improved, which may differ depending on the diagnostic purpose. Each method has its own indications and contraindications, which the gynecologist takes into account based on the expected diagnosis.
If necessary, conventional microscopy can be supplemented with modern immunohistochemical techniques, which make it possible to detect malignant tumors and accurately differentiate their origin, determine the degree of differentiation and prognosis for the patient.

endometrial biopsy
Endometrial biopsy is an operation, albeit a minimally invasive one, so it requires careful preparation, assessment of possible risks, and a balanced approach to determining indications. Today, the operation is performed on a wide range of women due to its relative safety, ease of performance and the highest diagnostic value.
As a rule, biopsy sampling is performed routinely, as an independent study, but in some cases there may be a need for an urgent biopsy performed during surgery for pathology of the female genital organs. The main purpose of a biopsy is diagnosis, but sometimes it is also therapeutic, leading to an improvement in the patient’s well-being after removal of the pathological lesion.
Types of endometrial biopsy
The endometrium is the inner layer of the uterine body, its mucous membrane, which undergoes cyclic changes under the influence of female sex hormones. Its structure is different not only in different phases, but also on different days of the menstrual cycle. Pathology of the endocrine system, ovaries, and the uterus itself inevitably affects the structure of the mucous membrane, by the characteristics of which the doctor judges the nature of the pathology.
You can “extract” the endometrium only by penetrating the uterine cavity. In the first half of the last century, attempts to obtain a sample were accompanied by expansion of the cervical canal and curettage of the entire mucous membrane. Modern biopsy techniques mean that it is minimally invasive and has low morbidity, as well as a low risk of complications, which makes it possible to expand the indications for the study. The clinic uses several types of endometrial biopsy surgery:
- Classic curettage of the mucous membrane;
- Aspirate biopsy with vacuum or aspirator;
- Pipe endometrial biopsy is one of the least traumatic methods;
- CG biopsy;
- Targeted biopsy during hysteroscopy allows you to obtain tissue from the most altered areas of the endometrium, but has limited use due to the high cost of hysteroscopy itself and the lack of equipment in many hospitals.
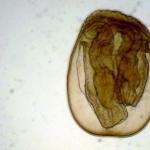
The operation of collecting endometrial fragments is only the initial stage of the diagnostic search, since without microscopy it is impossible to determine what structural changes occur in the uterine mucosa. The exact answer will be given by analyzing histological sections of the endometrium under a microscope.
Indications and contraindications for biopsy
Pathomorphological examination of the uterine mucosa is carried out for women of all ages, regardless of whether they have given birth to children or not. The reason for the procedure may be:
- Dysfunctional bleeding;
- Intense uterine bleeding or scanty menstruation;
- Amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) for an unknown reason (pregnancy must be excluded!);
- Possible tumor growth;
- Internal endometriosis;
- Suspicion of a chronic inflammatory process in the uterine mucosa;
- Infertility to clarify the cause;
- Planning an IVF procedure;
- Miscarriages, pathology of short term pregnancy (after medical abortion).
Contraindications to endometrial biopsy are:
- Pregnancy is an absolute contraindication to the study, since intervention in the uterus will provoke a miscarriage;
- Pathology of hemostasis due to the risk of bleeding;
- Treatment with anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents, anti-inflammatory drugs (require discontinuation in advance);
- Severe anemia;
- General infectious diseases (ARVI, intestinal infections, etc.);
- Acute or exacerbation of chronic genital tract infections;
- Allergy to anesthetics.
Since a biopsy is not performed for health reasons, in case of serious contraindications it can be abandoned in favor of other, safer diagnostic methods. If there are relative obstacles, the doctor will try to choose the most optimal method of tissue collection that eliminates complications.
Preparing for the study
Preparation for an endometrial biopsy includes general clinical tests (blood, urine), coagulation studies, determination of blood group and Rh factor, tests for HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis. During a gynecological examination, the doctor takes smears from the cervix for cytology and microflora from the vagina. If it is impossible to exclude pregnancy, a human chorionic gonadotropin test is performed.

After undergoing examinations and setting a date for the biopsy, the patient must abstain from sexual activity, douching, and vaginal tampons 2 days before the procedure, and stop taking blood thinners 7-10 days before. If curettage is planned under general anesthesia, then the day before from 6 pm, food and liquid intake is stopped.
On the morning of the study, the patient takes a shower, removes hair from the external genital tract; if there are varicose veins in the legs, the doctor may prescribe elastic bandaging to prevent thromboembolic complications.
Timing and technique of performing a biopsy
Since the endometrium clearly reflects hormonal effects, the information content of the analysis depends on what day of the cycle it was received. For different pathologies, the timing of the biopsy may differ. Thus, when diagnosing the causes of infertility, anovulation, and disorders of the second phase of the cycle, young women are recommended to undergo a biopsy the day before their expected period or on the first day of their onset.
 In case of heavy menstruation, it is more advisable to carry out the operation from 5 to 10 days of the cycle. If the bleeding is not associated with menstruation, then a biopsy will be prescribed in the first 2 days from the moment of its occurrence. During one cycle, the procedure can be performed several times - in case of hormonal imbalance, for example.
In case of heavy menstruation, it is more advisable to carry out the operation from 5 to 10 days of the cycle. If the bleeding is not associated with menstruation, then a biopsy will be prescribed in the first 2 days from the moment of its occurrence. During one cycle, the procedure can be performed several times - in case of hormonal imbalance, for example.
In the second half of the cycle, from days 17 to 25, a biopsy is indicated to assess the effectiveness of conservative hormone therapy. If a malignant process is suspected, the study is carried out regardless of the day of the cycle and without delay.
The woman will be able to find out the result of the pathological examination 7-10 days after the operation, but if it is necessary to perform additional staining techniques, this period may increase. For detailed explanations, you should contact a gynecologist, who will either prescribe treatment for the pathology or refer you to an oncologist if a malignant neoplasm is detected.
The technique for collecting endometrium for microscopic examination differs with different methods of procedure. It may include the stage of expanding the cervical canal, after which sharp instruments are inserted into the organ cavity, cutting off areas or the entire mucosa. This route is the most traumatic, although it provides the largest amount of information, so it is preferred if cancer is suspected or diffuse hyperplasia diagnosed by ultrasound. In the second case, the procedure will become therapeutic.
A purely diagnostic biopsy is often performed using gentle methods that can be performed without dilating the cervical canal - the most painful stage of the entire operation, which improves the tolerability of the study by women and reduces the risk of complications.
Scraping

curettage
The most radical method of collecting endometrial tissue is curettage - a classic technique used for half a century. To penetrate into the organ cavity, it is necessary to expand the neck, for which special dilators are taken from the smallest to the maximum diameter, the neck is fixed with forceps, and then the surgeon removes the mucous membrane with a sharp curette. The method is traumatic and requires great care due to the risk of damage to the basal layer of the endometrium and the uterine wall.
Classic uterine curettage is quite painful and therefore requires anesthesia; general anesthesia - mask or intravenous - is considered optimal. Due to the need for anesthesia, the woman is advised to prepare similar to that for any other surgical intervention (examination, discontinuation of certain groups of drugs, refusal of food and water the evening before the operation).
Curettage of the uterine cavity is usually carried out in case of hyperplastic processes in the mucous membrane, non-developing pregnancy, prolonged and heavy bleeding, or suspected cancer. Removing the mucous membrane from all the walls of the organ and the area of the tubal angles in some cases allows not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also at the same time to remove the pathological process itself, that is, it is a therapeutic procedure.
Aspiration biopsy
Endometrial aspiration biopsy involves removing the mucosa using a vacuum. The method is not as traumatic as curettage, does not require expansion of the cervical canal, so the pain and risk of complications is much lower. In nulliparous patients, aspiration can cause subjective discomfort, so the surgeon may offer short-term general anesthesia to especially sensitive women.
When preparing for a study using vacuum aspiration, a woman should exclude sexual activity, douching and the use of tampons 3 days before the biopsy date, and an enema is indicated the day before to cleanse the intestines. Due to the risk of infection upon penetration into the uterine cavity, it is important at the preparation stage to exclude inflammatory and infectious processes in the genital tract.
Aspiration biopsy can be performed for any pathology in the uterus, and is also indicated for questionable ultrasound findings. Its disadvantage can be considered to be the smaller volume of aspirate compared to curettage, which can make diagnosing a malignant neoplasm difficult, so if cancer is suspected, it is better to do curettage.
Video: endometrial aspiration biopsy
Pipelle biopsy

pipel biopsy
Pipelle biopsy resembles aspiration, but has the advantage that tissue is collected using a thin tube, the diameter of which is about 3 mm. The method is low-traumatic, does not require cervical dilatation, and has virtually no complications.
Pipelle biopsy can be performed on an outpatient basis, in a antenatal clinic; you need to prepare for it in the same way as for aspiration. During the procedure, the doctor places a Pipel tip into the uterus and then pulls on a plunger, releasing a small piece of endometrium by creating negative pressure in the syringe.
Pipelle biopsy does not cause trauma to the mucous membrane, does not cause the formation of an open wound surface with the risk of infection, and is practically painless, therefore it is preferred for young patients who do not have children, with endometrial pathology, infertility, for tissue collection for immunohistochemical determination of hormone receptors.
CUG biopsy
A CUG biopsy is performed without dilating the cervical canal, using a special small curette, with which the surgeon scrapes off the narrow cavities of the mucous membrane, starting from the fundus to the internal os of the uterus. This type of biopsy is indicated mainly to determine the effectiveness of hormone therapy, the degree of endometrial maturation at the natural level of hormones in different phases of the cycle, so the study may include several procedures during one menstrual cycle.
CUG biopsy is considered a safe and low-traumatic procedure, since only small areas of the mucous membrane are removed in the form of “stripes”. The information content of the study is increased by collecting several strips of mucous membrane from different parts of the organ.
Evaluation of biopsy results
To adequately assess the condition of the endometrium, the pathologist must know, if possible, the exact day of the patient’s menstrual cycle, therefore, the date of the last menstruation is always indicated in the referral for examination. It is also important to indicate the woman’s age, the nature of the treatment being taken (especially if it is hormonal drugs), the expected diagnosis based on the results of ultrasound and other examination methods.

Deciphering the results of an endometrial biopsy can show the norm, and then the pathologist in conclusion will indicate the specific phase of the cycle and its stage corresponding to the day of the menstrual cycle. These parameters are determined based on the structure of the glands, characteristics of the vessels and endometrial stroma.
The pathology most often detected by biopsy is:
- Hyperplastic processes - simple or complex non-atypical, as well as hyperplasia with atypia;
- Endometrial polyps with or without epithelial atypia;
- Malignant tumors;
- Atrophic processes (in older women - a variant of the age norm);
- Inflammation (acute or chronic).
Hyperplastic changes are more often diagnosed in patients whose age is approaching menopause, since during this period fluctuations in sex steroids occur, and many cycles are anovulatory in nature. Endometrial cancer occurs in both young and elderly women, and mucosal atrophy is a variant of the normal structure during the menopausal period.
One of the key points in assessing the morphological features of the endometrium is to identify or exclude cell atypia, which may indicate a high risk of malignant transformation. Atypia can be found in areas of overgrown endometrium with hyperplasia, in polyps.
The presence of a dysplastic process and a high risk of cancer is indicated by increased cell division with an increase in their number, polymorphism of the nuclei and epithelial cells of the endometrial glands themselves, and the appearance of pathological mitoses. In cancer, cells acquire malignant features (polymorphism, hyperchromic nuclei, many abnormal mitoses), characterized by foci of necrosis (death), hemorrhages, altered tissue grows into the underlying structures and vessels, which serves as the basis for metastasis.
The main question that a morphologist examining a biopsy often has to answer is whether there is cancer or whether it can be completely excluded. If there is a tumor, then the degree of its differentiation is indicated (well-differentiated adenocarcinoma, for example).
A biopsy for infertility is carried out not only to compare the morphological picture with the day of the cycle, established by the date of the last menstruation, but also for an immunohistochemical search for receptors for sex hormones, which may give a chance to determine the genesis of infertility and choose a way to combat it.
Consequences of endometrial biopsy and possible complications
Regardless of which way the mucous membrane was taken, the procedure inevitably injures the tissue, so there will be bleeding in any case. Their intensity and duration are determined by the method of manipulation.

After curettage, the bleeding is most profuse, often painful, but it is still lighter than during normal menstruation, since the mucous membrane is almost completely removed. The discharge should not contain large clots or pus-like fragments, it should not emit an unpleasant odor, otherwise the woman should contact the doctor again to exclude postoperative inflammation. E If the temperature rises, you need to go to the gynecologist immediately.
The first menstruation after the biopsy comes on time or a little later, it can be more abundant or more scanty. Most often, a delay occurs after a pipel biopsy, but to rule out pregnancy you should still do a test and go to the doctor.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, then she can count on it in the next cycle. The functional layer will have time to recover, the work of the ovaries is not disrupted, so the fertilized egg can be safely implanted in the uterus. However, experts advise abstaining from sexual intercourse until the discharge completely stops, and in the next cycle use barrier methods.
Further actions of the patient and the doctor will depend on the data of the morphological analysis. If cancer or atypical changes are diagnosed, a consultation with an oncologist is scheduled with the possibility of repeated surgical intervention, but this time radical. For inflammation, anti-inflammatory and antibiotic therapy is indicated; dishormonal processes may require the prescription of sex hormones.
Negative consequences after a biopsy are rare. Most often, patients complain of menstrual irregularities, painful menstruation, and discomfort during sexual intercourse. The most dangerous complication of the intervention is acute endometritis, which occurs with fever, abdominal pain, symptoms of intoxication, and foul-smelling pus-like discharge. This condition requires immediate treatment with repeated curettage of the uterine cavity.
In the presence of chronic inflammation in the genital tract, miscarriages or abortions for medical reasons, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed before surgery to prevent endometritis.
To prevent complications, a woman should maintain sexual rest until the discharge stops, carefully perform genital hygiene, and refrain from visiting the pool, sauna and bathhouse, as well as home hot baths.
Endometrial biopsy is usually performed free of charge, in antenatal clinics or inpatient clinics, but paid diagnostics are also possible. On average, the price of the procedure is 3-5.5 thousand rubles, depending on the qualifications of the personnel, the conditions of stay, the method used and additional treatment.
If a histological examination of the uterine mucosa is prescribed, then it is impossible to refuse it without compelling reasons. The risk of complications if you follow your doctor's recommendations is minimal, but the amount of information that can be obtained from a biopsy is not comparable to any other non-invasive methods. Only an accurate diagnosis will help you prescribe truly effective treatment, get pregnant, normalize your health, or avoid the consequences of a malignant tumor.
In the field of gynecology, one of the most popular methods for identifying histological problems is endometrial biopsy. The technique is aimed at examining a piece of uterine tissue under a microscope.
Thanks to this, it is possible to accurately determine the presence of morphological changes in the mucosa. To date, certain types of endometrial biopsy have been developed, which have different capabilities, purposes and contraindications.
Pipelle biopsy - what is it?
So, the diagnostic procedure involves taking a sample (during the patient’s lifetime) of mucosal tissue, so that chemical and histological studies can be subsequently carried out.
The event is an important component of minor surgical intervention, carried out as an independent intervention. But in severe cases, an endometrial biopsy is performed intraoperatively, urgently.
This is a procedure performed solely for diagnosis and histology determination. Although, it rarely happens that an endometrial biopsy is a therapeutic procedure.
Before the event, there must be appropriate preparation; this directly determines whether the patient will feel painful and uncomfortable sensations during the process.
Types of diagnostic tests in gynecology
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages;
- Avoid physical overexertion;
- Do not take hot baths or warm procedures.
Before the biopsy, the patient is asked to administer an anesthetic (this is optional, optional).
It is imperative to refrain from using medications that can affect the endometrium. If one of the rules is violated, you should not be shy - you need to tell the doctor everything.
Contraindications for surgery
 Despite the simplicity and ease of performing a biopsy, it is nevertheless a surgical intervention, and therefore has a number of contraindications:
Despite the simplicity and ease of performing a biopsy, it is nevertheless a surgical intervention, and therefore has a number of contraindications:
- Development of inflammation;
- The presence of pathologies of the uterine cavity;
- Incoagulability of blood;
- Infectious venereal diseases.
Also, the doctor may prohibit the procedure due to personal, individual illnesses that will be determined in advance.
The event is quite simple, so no consequences or side effects are observed. However, in specific, individual situations, slight short-term bleeding may occur, appearing on the day the biopsy is taken. It is worth knowing that in this case no inpatient examination or observation is required, so the woman can immediately go home.
The advantage of the procedure is a high level of accuracy and information content, compared to the fact that the intervention from a biopsy is minimal. In practice, this activity has not yet had negative reviews or any side effects or deterioration in well-being.
How is this procedure carried out?
The diagnostic event Pipelle biopsy is a modernized method of examining the endometrium and uterine cavity. The technique is based on the standard method of endometrial aspiration.
The procedure is carried out as follows:

 Previously, when standard curettage was performed, when a small amount of a diagnostic sample was taken, almost the entire endometrium disappeared, and a large wound appeared on the membrane.
Previously, when standard curettage was performed, when a small amount of a diagnostic sample was taken, almost the entire endometrium disappeared, and a large wound appeared on the membrane.
It is important that the modern diagnostic method is quite possible for use in cases of suspected formation of malignant or benign tumors in the uterine cavity or in case of metrorrhagia after a miscarriage.
The process of separating the endometrium for diagnosis and analysis is carried out by vacuum separation created in the uterine cavity.
If a more detailed examination and subsequent tests, laboratory tests are required, before performing a biopsy, the uterine cavity is sometimes irrigated with a special solution in order to subsequently perform washouts.
Professional experts recommend that before the procedure, as a preparation, ensure sexual rest and abstain from intimacy, do not do any douching, and do not use vaginal tampons for 2-3 days before the biopsy. To exclude STDs and all kinds of acute urogenital diseases, a qualified doctor must prescribe a preliminary examination.
After endometrial biopsy
Despite the fact that the procedure is minimally invasive and simple, it is nevertheless associated with a violation of the integrity of the mucous tissues of the uterine cavity. Therefore, it is not uncommon for slight bleeding that does not cause pain to appear during the first 24 hours after an event.
After a diagnostic curettage of Pipel, heavy, menstrual-like discharge may be observed for some time, accompanied by short-term pain in the lower abdomen.
It is worth immediately clarifying that the pain is not prolonged, and the rate of discharge after the procedure is much less than during the menstrual cycle and should not include blood clots, impurities of pus and any unpleasant putrefactive aroma. When any of the above symptoms appear, this is a signal to contact a specialized medical institution for advice.
Immediately after the study
When the diagnostic procedure is completed, the doctor recommends using a sanitary pad; discharge is possible. But, under no circumstances use tampons, they can irritate the mucous membrane, causing discomfort. Minor pain in the abdomen or lower back is considered normal; this fact is due to spasms in the uterus.
Important symptoms to worry about are the following:
- Heavy bleeding;
- Prolonged severe pain;
- Unpleasant odor of discharge;
- Increased body temperature.
If symptoms do not go away even after taking painkillers, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In order to prevent serious consequences and various complications, the following rules must be followed after a biopsy:

In addition, to prevent the development of infections and pathogens in the uterine cavity, it is recommended to take a course of antibiotics. If necessary, the leading doctor may prescribe hormonal medications.
The recovery period lasts no more than 3-4 days, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body.
Periods after biopsy
When using the gentle Pipel biopsy method to diagnose possible pathologies of the uterus, menstruation may begin with a slight delay of 8-10 days. The meager volume and period of menstruation also differs somewhat from standard indicators. This is not a reason to worry, there is nothing wrong with it.
If the delay continues for more than 10 days, you should take a pregnancy test and then consult a specialist.
 Planning to conceive a child is recommended only in the next menstrual cycle after the Pipel biopsy.
Planning to conceive a child is recommended only in the next menstrual cycle after the Pipel biopsy.
This is done so that the uterus rests and the mucous membrane undergoes a full course of restoration of functionality. It is worth knowing that the diagnostic procedure does not affect the functioning of the ovaries.
Considering that the Peipel biopsy is a gentle method for diagnosing diseases of the female organs, the remaining layer of the endometrium is quite enough to undergo the IVF fertilization procedure in the next ovulation cycle.
Often, leading experts advise women not to resort to intimacy with their spouse during the period while spotting appears. In the subsequent menstrual cycle, it is recommended to use barrier method contraception.
Possible complications
Before the day for the procedure is set, specialists together with the patient will choose the most appropriate diagnostic method, based on the woman’s personal testimony, body characteristics, etc. Depending on this, preparation requirements and various risks after the event are regulated.
Despite the fact that bleeding and minor pain are possible after a pipel biopsy, you should not immediately say “No” to this event, because no other methodology will provide such an accurate histological analysis.
Possible complications:

How long should I wait for biopsy results?
As a standard, the diagnostic process and subsequent interpretation of the results takes at least 14 days. This should be performed exclusively by a pathologist or histologist. If the leading specialist has made an appropriate note in the referral for analysis, an additional immunohistochemical analysis is possible.
How long the results will be made depends on the capabilities of the laboratory and the experience of the specialist, as well as on the volume of research and additional analyzes performed.
Cost of the procedure
 Another important aspect today is the cost of the manipulation. Most clinics have already included this procedure in their list of services.
Another important aspect today is the cost of the manipulation. Most clinics have already included this procedure in their list of services.
The price will vary depending on the region, level of the clinic and other circumstances. In Moscow, the average price for this procedure is 3,000 rubles. In the regions, the price for Pipelle endometrial biopsy is lower.
When a Paypel endometrial biopsy is performed, the price includes payment for histological or cytological examination. On average it fluctuates from 4,000 to 5,000 rubles. So the final cost of the entire survey will be in the area 7,000-8,000 rubles.
Previously, for some gynecological diseases, only traumatic biopsy techniques of the uterine mucosa were used to collect endometrial samples, which involved curettage (i.e., a procedure similar to a classic surgical abortion). However, thanks to the advent of aspiration biopsy (or Pipelle biopsy), such a study has become more painless and safe.
This minimally invasive surgical technique for collecting endometrial tissue is carried out using a special plastic tube - pipel. The thickness of this device is 3 mm, and its operating principle is similar to the syringe mechanism. There is a piston inside the tube, and at one end there is a side hole for entry by aspiration of the endometrium into the tip of the pipel.
In this article we will introduce you to the indications, contraindications, how to prepare the patient for the procedure, the advantages and methods of performing endometrial aspiration biopsy. This information will help you understand the essence of this diagnostic technique, and you can ask your doctor any questions you have.
Unlike the classical surgical method of collecting endometrial tissue, aspiration biopsy does not require dilation of the cervical canal. The tip of a disposable tube is inserted into the uterine cavity without the use of additional devices. The doctor pulls the piston toward himself, creating negative pressure for the necessary aspiration of a small area of the endometrium. At the same time, extensive wound surfaces do not form on the inner layer of the uterus, the cervix does not suffer from mechanical stress, and the patient does not experience pronounced discomfort.
Indications
Indications for this study are pathological processes localized in the endometrium - the inner layer of the uterus.An aspiration biopsy is prescribed in cases where, after a gynecological examination and ultrasound, the doctor suspects that the patient has pathological changes in the condition of the inner layer of the uterus - the endometrium. The obtained tissue samples allow a histological analysis of the mucous layer of the uterus and make a correct diagnosis.
Endometrial aspiration biopsy is prescribed in the following clinical cases:
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- disorders (acyclic scanty bleeding, menometrorrhagia, scanty menstruation, of unknown origin);
- chronic endometritis;
- suspicion of infertility;
- heavy bleeding in women during their period;
- suspicion of the presence of a benign or malignant tumor (endometrial cancer).
Pipelle biopsy can be performed not only to diagnose endometrial pathologies, but also to evaluate the effectiveness of hormone therapy.
Contraindications
Endometrial aspiration biopsy cannot be performed in the following cases:
- in the acute phase;
- pregnancy.
Possible limitations for performing Pipelle biopsy include the following clinical cases:
- disorders of the blood coagulation system;
- severe forms;
- constant use (Clexane, Warfarin, Trental, etc.);
- individual intolerance to the drugs used.
If such conditions are detected, aspiration biopsy can be performed after special preparation of the patient or replaced with another study.
How to properly prepare for the procedure
Although aspiration biopsy of the endometrium is a minimally invasive procedure, during it, instruments are inserted into the uterine cavity and damage to the integrity of the inner layer of this organ occurs, albeit minor. That is why, in order to exclude possible complications of such a study, the patient needs to properly prepare for the collection of material.
To exclude possible contraindications to endometrial aspiration biopsy, the following diagnostic studies must be performed:
- gynecological examination;
- microflora smear;
- cytological smear from the cervix (PAP test);
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood test for hCG;
- blood test for hepatitis B and C, syphilis and HIV;
- (preferably).
When prescribing a Pipelle biopsy, the doctor must obtain from the patient all the information about the medications she is taking. Particular attention is paid to taking blood thinners (Clopidogrel, Aspirin, Warfarin, etc.). If necessary, the doctor can change the order in which they are taken a few days before the procedure.
When prescribing endometrial aspiration biopsy, special attention is paid to choosing the date of the study. If a woman has not yet entered menopause, the timing of the procedure depends on the day of the menstrual cycle. If the patient is no longer menstruating, tissue sampling is performed depending on the onset of abnormal uterine bleeding.
Typically, endometrial aspiration biopsy is performed on the following days:
- 18-24 days - to establish the phase of the cycle;
- on the first day in case of pathological bleeding - to identify the cause of bleeding;
- on days 5-10 of the cycle - with excessively heavy periods (polymenorrhea);
- on the first day of the cycle or the day before menstruation - if infertility is suspected;
- once a week – if pregnancy does not occur and menstruation does not occur;
- on days 17-25 – to monitor the effectiveness of hormonal therapy;
- any day of the cycle – if the presence of a malignant neoplasm is suspected.
Direct preparation for Pipelle biopsy is carried out 3 days before the study. During these days, a woman must follow the following doctor’s recommendations:
- Refuse sexual intercourse.
- Do not douche, do not insert suppositories, ointments and creams into the vagina.
- Exclude from the menu products that contribute to increased gas formation.
- In the evening before the study, perform a cleansing enema.
The endometrial aspiration biopsy procedure can be performed in a specially equipped office in a clinic. As a rule, it does not require the use of local anesthesia, but sometimes this method of pain relief is performed for particularly sensitive patients. In such cases, before conducting the study, the doctor must make sure that there is no allergic reaction to the drug used (based on medical history or a test performed).
How is the procedure performed?
 During the procedure, the patient is on a gynecological chair.
During the procedure, the patient is on a gynecological chair. On the appointed day, the patient with a referral comes to the office for an aspiration biopsy. The procedure for collecting endometrial tissue is performed as follows:
- The woman lies down on the gynecological chair, and the doctor inserts a speculum into the vagina. If necessary, local anesthesia of the cervix is performed by irrigating it with a solution of local anesthetic.
- The pipel tip is inserted into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal.
- The gynecologist pulls back the piston, and negative pressure is created in the tube. As a result of this effect, part of the endometrium enters the pipel cavity. The doctor collects material from different areas.
- Once sufficient material has been obtained, tissue samples are sent to the laboratory for histological analysis.
- The pipel is removed from the uterine cavity. The duration of the procedure is 1-3 minutes.
The results of histological analysis of endometrial tissue are obtained 7-14 days after the biopsy. After assessing them, the gynecologist makes a diagnosis and draws up a plan for further examination and treatment.
After the procedure
After performing an aspiration biopsy of the endometrium, the patient feels satisfactory and can go home. Her performance is not impaired in any way, and there is no need for hospitalization.
In the next 1-2 days, the patient may feel minor painful pulling sensations in the lower abdomen. To eliminate spasmodic pain, which causes significant inconvenience, a woman can take antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine, Spazmalgon). As a rule, such discomfort does not last more than 1 day.
In the first few days after the aspiration biopsy procedure, women experience light, bloody discharge from the genital tract. Most experts recommend that their patients abstain from sexual intercourse during these days. After the bleeding stops, a woman can resume sexual activity and use barrier contraception to prevent pregnancy.
After the study, menstruation may occur on time or with some delay (up to 10 days). In such cases, the woman is advised to take a pregnancy test and visit a doctor.
After an aspiration biopsy, pregnancy can occur in the current or subsequent cycle. This method of endometrial sampling does not affect the functioning of the ovaries and the remaining area of the uterine mucosa is sufficient for implantation of the fertilized egg.
Possible complications
The endometrial aspiration biopsy procedure is minimally invasive and in rare cases leads to complications. After the examination, the gynecologist must familiarize the patient with the symptoms, when they appear, she should immediately consult a doctor:
- increased body temperature;
- bleeding from the vagina (thick, bright red discharge);
- incessant pain in the lower abdomen;
- dizziness or fainting;
- convulsions.
Benefits of endometrial aspiration biopsy
Pipelle biopsy has a number of significant advantages:
- low risk of injury to the walls of the uterus;
- there is no need to expand the cervical canal to insert instruments;
- the possibility of obtaining endometrial tissue from inaccessible areas of the uterine cavity;
- minimal risk of infection;
- minimal risk of complications;
- no pain during the procedure;
- rapid recovery of the patient after the biopsy;
- the ability to perform the study on an outpatient basis and there is no need for hospitalization of the patient;
- high information content;
- no negative impact on the body of a woman preparing for pregnancy (for example, before IVF);
- simple preparation for the procedure;
- low cost of research.
What will the result of histological analysis after aspiration biopsy show?
In the absence of pathological abnormalities in the structure of the mucous layer of the uterus, the analysis will indicate that the endometrium corresponds to the age norm and the phase of the menstrual cycle, and no signs of atypia were identified.
If deviations in the structure of the mucous layer of the uterus are detected, the following pathological changes may be indicated in the analysis results:
- adenomatosis (or complex endometrial hyperplasia);
- simple diffuse (or glandular, glandular-cystic) endometrial hyperplasia;
- local endometrial hyperplasia with or without atypia (or polyposis, single polyps);
- simple or complex atypical endometrial hyperplasia;
- endometrial hypoplasia or atrophy;
- endometritis;
- discrepancy between the thickness of the endometrium and the phase of the menstrual cycle;
- malignant degeneration of the endometrium.
Endometrial aspiration biopsy is often used as a screening method for examining patients with questionable ultrasound results. However, this method of collecting tissue from the inner layer of the uterus does not always allow obtaining a sufficient amount of material to completely exclude the presence of malignant tumors. That is why, if a cancerous process is suspected, the examination of the patient is supplemented with a more informative diagnostic curettage.
What to do after endometrial aspiration biopsy
After performing a Pipelle biopsy, the doctor sets a date for the patient’s next visit. Typically, histological examination tests are ready 7-14 days after the procedure, and based on their results, the gynecologist can determine further tactics for diagnostic and therapeutic measures.
If signs of atypia or cancerous processes are detected, the doctor decides on the need for additional research and surgical treatment. If the results of histological analysis indicate the presence of inflammation, then the patient is prescribed antibiotic therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs.
When determining signs of hyperplasia or insufficient response of the endometrium to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle, the doctor conducts additional diagnostic tests to identify endocrine disorders. After this, the patient may be prescribed hormone therapy, which improves the condition of the endometrium and restores reproductive function, taking other medications and physiotherapeutic procedures.
“...I’m 26 years old and I haven’t been able to get pregnant for 2 years. I recently went to see a doctor and he advised me to undergo a pipel biopsy. What kind of procedure is this, is it really necessary in my case, and if so, will it help me get pregnant faster?..”
What is a pipel biopsy?
Pipelle biopsy, or aspiration biopsy of the endometrium, is a diagnostic procedure used in gynecology to clarify the diagnosis of infertility and suspected various diseases of the uterus.
This method gets its name from a doctor named Peipel, who invented an instrument for performing endometrial biopsies. The instrument itself also bears the name of its inventor.
A pipel is a long tube with a hole that is inserted into the uterine cavity. Thanks to the piston at the other end of the tube, the doctor creates negative pressure in it, as a result of which Pipel “sucks in” the endometrium of various parts of the uterine cavity (almost like a vacuum cleaner). The resulting material is then sent for histological examination under a microscope.
Why is a pipel biopsy necessary?
Pipel biopsy is currently widely used in reproductive gynecology to diagnose the causes of infertility, as well as before undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF).
With the help of aspiration biopsy, diseases such as (uterine endometriosis), endometrial hyperplasia, etc. can be detected. Pipelle biopsy may be recommended to clarify the diagnosis for uterine bleeding (including).
How to prepare for a pipel biopsy?
Since a pipel biopsy is contraindicated during pregnancy, you need to make sure that you are not pregnant (you can have or undergo it).
Another contraindication to endometrial aspiration biopsy is inflammation of the vagina or cervix. In order to make sure that there are no inflammatory processes, the doctor will check a few days before the procedure.
Pipel biopsy does not require special preparation. It is enough just to follow the basic rules, do not douche or have sex at least 2 days before the biopsy.
On what day of the menstrual cycle can a pipel biopsy be done?
Pipel biopsy can be performed on different days of the cycle, depending on the preliminary diagnosis and purpose of the procedure. Check with your doctor on which day of your cycle it is advisable to perform a biopsy in your case.
Pipel biopsy: does it hurt?
A pipel biopsy is performed in a clinic under local anesthesia. That is, during the procedure you will be conscious and may experience discomfort.
Some women find this procedure completely painless, while others report significant pain during the biopsy. Apparently, this is due to the pain threshold, individual for each woman. It is noted that for nulliparous women this procedure seems more painful than for those who have already given birth.
What happens after a pipel biopsy?
After the procedure, you may experience pain in your lower abdomen. This is completely normal. To relieve pain, take a Paracetamol or Ibuprofen tablet.
Bloody discharge of varying degrees of profuseness after a pipel biopsy is also completely normal. During these discharges (they can last several days), use, but not. Avoid sex until the bleeding stops.
You may take a shower or bath on the same day as your pipel biopsy.
Contact your doctor if:
After the pipel biopsy, heavy periods began (if more than two large pads filled within 3-4 hours).
If the brown discharge after a pipel biopsy continues for more than a week or if the discharge has a foul odor.
If the pain in the lower abdomen after a pipel biopsy is very strong and does not go away after taking painkillers.
If after the procedure the body temperature rises to 37.5C or higher.
How to interpret the results of a pipel biopsy?
The results of a pipel biopsy usually come in 5-7 days, but in some cases, analysis of the obtained material can take several weeks. Ask your doctor when you will be able to see the test results.
Only an experienced gynecologist can adequately decipher the results of a biopsy.
Is it true that pipel biopsy increases the chances of implantation?
Recently, pipel biopsy has begun to be used not only as a method for diagnosing the causes of infertility, but also to increase the chances of successful attachment (implantation) of a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.
Some studies have shown a higher success rate of in vitro fertilization (IVF) after endometrial pipel biopsy. Scientists have not yet found an explanation for this phenomenon.
The greatest chances of implantation after a pipel biopsy are observed if the biopsy was performed in the cycle preceding the embryo transfer.
Histological and other studies of endometrial tissue are very important, since the hormone-dependent nature of this tissue can lead to the formation of various tumors and tissue growths, including atypical ones. Therefore, for timely diagnosis and treatment of such processes, a biopsy is performed. It can be carried out using various methods, and one of these is pipel endometrial biopsy. What it is and how a sample is taken during this process is described in this article.
Collapse
Definition
What is a biopsy? A biopsy of the endometrium of the uterus is the process of collecting tissue from this layer for subsequent study of their histological (cellular) composition. The intervention is considered surgical and can be considered, to some extent, traumatic, therefore it is performed under anesthesia. The main purpose of a biopsy is to examine the material in a laboratory setting to determine the presence of atypical cells in it.
Material sampling tools
Tissues for such research can be collected in various ways. During curettage, the layer of mucous membrane is removed using a special loop. Sometimes sampling is performed during diagnostic hysteroscopy. But the simplest and least traumatic method is pipel biopsy. Sometimes it is also called endometrial aspiration biopsy, since these methods are very similar - only the sampling tool is slightly different, but the principle and actions are the same.
The endometrium is sampled using a thin plastic tube called a pipel, which has a hole in the side at the end. At the other end of the tube there is a piston, which creates negative pressure in the cylinder. Under the influence of negative pressure, some of the endometrial tissue is “pulled” into the tube and remains there. Endometrial aspiration is also performed using negative pressure, but instead of a pipette, equipment more similar to a syringe is used. The process is shown in detail in the video at the end of the article. 
Why is it carried out?
An intervention of this kind makes it possible to study the cellular composition of endometrial tissue. As a result, it is possible to install:
- The presence or absence of atypical cells in the mucosa, which helps prevent the development of the oncological process;
- The presence or absence of endometrial hyperplasia, which can cause a variety of unpleasant symptoms;
- The presence or absence of bacterial, viral, infectious, fungal agents that potentially pose a danger to health and reproductive function.
The study helps to establish the possibility of conception when planning a natural pregnancy or in vitro fertilization. It also helps to make a particular diagnosis in cases where other diagnostic methods are ineffective and uninformative.
It may also be prescribed in some other cases.
Indications
What does a pipel biopsy show? For what conditions and diagnoses is it prescribed?
- Pipel endometrial biopsy before IVF or natural pregnancy is performed in order to establish or deny the presence of obstacles to pregnancy;
- In case of infertility or frequent miscarriages, especially in the early stages, it is considered a necessary and informative diagnostic procedure;
- It is carried out for uterine bleeding of unknown origin, as it helps to establish their cause;
- Necessary if an oncological process is suspected;
- Quite often it is also carried out if hyperplasia or endometriosis is suspected;
- Sometimes it is carried out when viral, bacterial, or fungal infections are suspected;
- It is often carried out for hormonal abnormalities in order to establish their effect, nature, and sometimes the cause, for further effective treatment.
In some cases, such diagnostics are also carried out for other diagnoses and suspicions of them.
Contraindications
Despite the high efficiency, information content and low risk of injury of this procedure, it still has a number of contraindications. Most of them are associated with a complete ban on manipulations in the uterine cavity during certain periods. General contraindications are the following:
- Pregnancy of any stage, including unconfirmed or suspected pregnancy. Taking material from the uterine cavity during such a period can lead to miscarriage or injury to the fetus. After childbirth, manipulation can be performed if still required;
- Confirmed infectious, inflammatory, viral, fungal or other pathological processes occurring in the vagina, since additional infection from it into the uterus is possible;
- Low blood clotting is a contraindication because the technique of performing such an endometrial biopsy does not involve coagulation of damaged vessels, since, usually, bleeding (at least significant) does not occur during such manipulation. However, if there is a clotting disorder, they can occur;
- Presence of sexually transmitted infections.
Most of these restrictions impose only a temporary ban on manipulation. For example, it can be done after the disease has been cured. However, neglecting these contraindications may lead to unpleasant consequences.
Preparation
It is in order to exclude potential contraindications that a number of studies are carried out before prescribing this manipulation. You need to do the following:
- Perform an ultrasound examination to confirm or refute the presence of pregnancy;
- Take a vaginal smear to determine sterility in order to exclude the presence of infections, including sexually transmitted ones;
- A coagulogram is necessary for those who do not know exactly what their blood clotting ability is.
In addition to such research, a number of other measures need to be taken:
- Avoid sexual intercourse for 3 days before the intervention;
- Maintain good hygiene;
- Stop taking medications that thin the blood at least a week before the intervention, as they reduce blood clotting, which may result in bleeding (cancellation is possible only in consultation with the doctor);
- Stop taking hormonal medications (strictly in consultation with your doctor) at least a week before the procedure;
- Carry out the procedure strictly on the established day of the cycle, as this can have important diagnostic significance.
On what day of the cycle is a pipel biopsy performed? It depends on the purposes for which it is carried out. Usually, the most optimal day of the cycle is prescribed by a specialist. Proper preparation for pipell endometrial biopsy is very important, as it affects the information content of the procedure.
Carrying out
Anesthesia is not usually used for this procedure, as it may be more unpleasant than the procedure itself. The collection of the material is almost painless. The pipel is inserted into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal under ultrasound guidance or blindly, after which the tissue is taken for laboratory testing, which lasts from 7 to 10 days. The patient can leave the medical facility immediately after the intervention. 
results
The results of a pipell biopsy of the endometrium can only be correctly deciphered by a doctor, depending on what disease the study was conducted for (based on this, specialists pay special attention to certain characteristics of the endometrium). In this case, there will be no single norm, since much depends on the woman’s age and her hormonal balance. Decryption is possible only taking into account these indicators. 
The absolute norm is only the complete absence of atypical cells. But even their presence in minimal quantities is always considered a sign of a precancerous process.