Arabic is the official language of all Arab countries, as well as countries such as Chad, Eritrea, Somalia, Comoros, etc.
This is the official language of the UN.
The total number of carriers is 240 million. For another 50 million it is a second foreign language. Modern Arabic includes 5 dialects. They are not similar to each other in many ways, so speakers of different dialects do not understand each other.
However, only the literary dialect is used in newspapers, films and television.
Arabic is the language in which ancient literary works were written and translated. It is also one of the first languages into which the Bible was translated.
Therefore, connoisseurs of history and historical artifacts strive to master this language. In addition, every year thousands of tourists visit the UAE, Israel, Jordan, where the population mainly speaks Arabic. To travel freely in such countries, tourists usually learn the basics of the language - basic grammar and vocabulary.
However, Arabic is completely different from our related Slavic languages and even from such world languages as English, French and German. This is one big linguistic world with its own specific writing and pronunciation. Therefore, before choosing a form of training, it is necessary to consider the features of this language.
- Businessmen;
- Engineers;
- For tourists;
- Philologists and literary scholars;
- Who studies the Koran and Islam.
In classes at the Master Class center, the literary norm of the Arabic language, dialects, phonetics, vocabulary, and grammatical structures are studied.
The goal is to teach students to communicate fluently in Arabic within 48 hours.
6 options for studying Arabic in Moscow:
- Mastering basic skills;
- Learning Arabic from scratch;
- Intensive classes;
- Speaking workshop;
- Language for business;
- In-depth study.
The grammatical structure of the Arabic language is memorized with the help of visual materials and lively dialogue. At the end of any stage of intensive courses, a final test is carried out.
It allows the student to consolidate acquired skills, and teachers to evaluate the success of their work.
The difficulty of learning Arabic on your own from scratch
The principle of learning Arabic is to first memorize the alphabet and grammar. At the very beginning of training it can be difficult, because... Arabic words have no associations with the Russian language; they have a double meaning; they have to be memorized only mechanically.
There are 28 letters in the Arabic alphabet. Arabs write the alphabet and words from right to left, without capital letters.
- Take care of purchasing the necessary educational literature. First of all, you should purchase a printed dictionary and its electronic version.
- Electronic textbooks for learning Arabic must be accompanied by an audio recording in order to hone your pronunciation.
- It is best to choose teaching materials that contain practical tasks that should be completed for each lesson, and answers to them, which are located at the end of such a training course.
- A simple phrasebook will not ensure successful language acquisition.
- You should not purchase tourist materials.
- It is useful to listen to songs and watch films and TV series in Arabic.
The technique of writing Arabic words is performed in three stages
Basic letters are written without a single break. Additional parts of letters, which include dots, slanted and plumb lines, are written subsequently. At the end, additional icons are placed. It is necessary to write down each letter, practice writing daily, while pronouncing it out loud.
Features of Arabic dialects
The Arabic alphabet consists of 28 letters.
Each letter represents a consonant sound. The exception is the letter amef. It usually denotes either a long vowel or is used as an auxiliary spelling sign.
In order to indicate a vowel sound, harakat is used - superscript and subscript marks. Arabs write from right to left, but punctuation marks are written from right to left. The language lacks capital letters. It is unacceptable to move a word to another line - usually the empty space is filled with stretched letters. The vocabulary consists of native Arabic words. And only 1 percent are borrowed European words.
The Arabic language is characterized by polysemy of words, so the vocabulary is very rich. However, English words are used to represent modern terms. The three most commonly used words are three particles: al (the definite article), wa (the conjunction “and”) and bi (the preposition “through”). In the grammatical sense, language relies on word formation.
The root of the word is three-consonant - the percentage of three-consonant roots is 82%. This makes the task easier when learning new words and reading texts without a dictionary. As for the parts of speech, it is worth paying attention to the two main ones - the noun and the verb. The noun has three numbers - singular, plural and dual (rarely used in dialects).
Arabic has only two genders - masculine and feminine - and three cases (nominative, genitive and accusative). The verb is characterized by various grammatical categories. There are only 6 times (three simple and three difficult). In addition to the three moods characteristic of us (indicative, conditional and imperative), there is also a subjunctive and reinforced mood.
Another interesting feature is that Arabs do not use Arabic numbers, but numbers from the Hindi language. As you can see, Arabic is a difficult language to learn. First of all, this concerns writing and reading. Therefore, in order to avoid mistakes at the very beginning of learning, adults enroll in special language courses, where they are taught by professional teachers and tutors, as well as native speakers themselves.
Arabic lessons online
Online learning via Skype, which provides individual lessons with a tutor, has a number of advantages. One of them is that you don’t need to go anywhere, you just need to turn on the computer. These lessons are useful and rich, exciting and interestingly structured. In them, the listener will learn to write, read and speak Arabic correctly from scratch.
In individual lessons, the tutor pays full attention to only one student, honing his skills and abilities and repeating material already covered. With this approach, the number of recognizable Arabic words increases and overall efficiency increases. The acquired knowledge is consolidated with written test assignments. The course program is completely focused on the student’s personal achievements.
Many people are afraid to start learning Arabic, considering it extremely difficult. However, teachers insist that if you study it persistently for 3 months, you can learn to speak Arabic and confidently conduct dialogues with native speakers.
To learn the language more effectively, you should enroll in Arabic courses under the guidance of an experienced teacher.
Price for individual and group Arabic language training
The cost is calculated for eight lessons (16 academic hours), which take place over the course of a month. The duration of each meeting is 90 minutes. Classes are held 2 times a week. Their price includes a teacher visiting your home.
Corporate training price
You can determine the time, place and frequency of meetings with the teacher yourself.
Intensive Arabic course
Gives you the opportunity to get acquainted and learn one of the ancient and most widespread languages of the world - Arabic.
Arabic is considered the official language in the following countries of the world: Algeria, Bahrain, Djibouti, Egypt, Western Sahara, Jordan, Iraq, Yemen, Qatar, Comoros, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, United Arab Emirates, Oman, Palestinian Authority, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Somalia, Sudan, Tunisia, Chad, Eritrea. Arabic is spoken by about 290 million people (240 as a mother tongue and 50 as a second language).
The Arabic language played a big role in the history of world culture: in the Middle Ages, extensive fiction and scientific literature was created in it. A huge number of Arabic words have entered the languages of many Asian and African peoples. Even in European languages, including Russian, there are words borrowed from Arabic (algebra, azimuth, zenith, alcohol, genie, store, treasury, coffee, safari, tariff, etc.).
Currently, the Arabic language exists in two significantly different forms: on the one hand, there is the Arabic literary language - a common language for all Arab countries in education, the press, radio, science, literature, oratory; on the other hand, there are Arabic colloquial languages or dialects used by the population in everyday communication. The spoken language of each Arab country differs both from the common Arabic literary language and from the spoken languages of other Arab countries.
Like all language learners from scratch, we will talk about literary Arabic. The online lessons on the site are based on the tutorial by V. S. Segal (). Its peculiarity is that it allows you to get acquainted with the language gradually, without immediately bombarding you with a stream of incomprehensible and complex Arabic letters. Errors were also corrected, letter animation was added, and answers were added that can be viewed by moving the mouse over the key: . Plus, audio has been added! You will not only learn to read and write Arabic, but also begin to understand the language by ear. Lessons free.
Go to -› list of lessons ‹- (Click)
If the opportunity to communicate with 290 million people is not your big motivation for learning Arabic, then it might be, for example, the desire to stand out from the crowd. Few people know Arabic. And if now you just seem very smart, then in the future you will be able to build a successful career. The Middle East has a very large economic potential, so knowledge of the language and culture is beneficial and promising.
In today's climate of growing hostility between the Arab world and the West, understanding the Islamic religion is key information to overcome the crisis. People who know Arabic can bridge cultural and linguistic barriers between countries, help resolve or avoid international conflict, and help businesses successfully conduct international trade. In addition, knowledge of Arabic opens the door to other languages. For example, 50% of Farsi words are made up of Arabic words. The situation is similar with Urdu and Turkish. Hebrew is also linguistically related to Arabic, making it easier to understand grammatical and semantic concepts in the languages.
Arabs are hospitable. Once you speak a few words of Arabic in front of a native speaker, they will be delighted and want to help you in any way possible. But try to do the same thing, for example, in German in front of the Germans - it is unlikely that it will greatly surprise them. Arabs are proud of their language and will be happy to see someone making an effort to learn it.
Arabic is the 5th most widely spoken language in the world, and migration processes in recent years have only increased its spread. More recently, Arabic has become the second most common language in Sweden, but Finnish has always been so. And before Arabic takes over the whole world, you still have time to study it!
Surely you found something interesting on this page. Recommend it to a friend! Better yet, place a link to this page on the Internet, VKontakte, blog, forum, etc. For example:
Learning Arabic
Whether you want to devote your life to studying Muslim customs, conduct business in the United Arab Emirates, or want to visit Jerusalem for tourism purposes - in any case, knowledge of the Arabic language will be useful to you.
Arabic alphabet. Video lessons
Arabic for beginners and intermediate. Visitors will find grammar lessons, stress and conjugation rules on the channel. There is an online dictionary and video lessons with the Arabic alphabet, tips for learning the language. The founders of the page did not disdain entertaining methods of learning the language, so on the channel you can find videos with poems with subtitles and the like. A lot of educational information: among the videos you can even find translations of Russian names into Arabic.
On the pages of the YouTube channel, the student will find materials for conquering the Egyptian dialect of Arabic, and online tests. It’s convenient that the presenters’ comments are in Russian - a Russian-speaking user does not need to know another foreign language to learn Arabic. The channel will help you learn Arabic for business and teach you competent business communication.
Arabic at Shams School Irada Mersalskaya
A huge variety of videos for mastering the initial level of the Arabic language - much attention is paid to the alphabet on the channel. Vocabulary and grammar are taught, and carefully compiled video dictionaries will help you expand your vocabulary. The learning process is made easier by dividing the videos into topics.
The listener will need knowledge of the English language, since the presenter’s explanations are in English.
Arabic at the Arabic Language School
The channel is aimed at those who are beginning to learn the Arabic language. Even those who have barely started learning will understand the materials, including the Arabic alphabet for children to master the Arabic language.
This is a simple yet high-quality video tutorial. Great emphasis is placed on mastering grammar, and if the student wishes, the channel will help in studying the Koran.
Arabic with "Brothers and Sisters"
Will be useful for beginners. Channel visitors will be able to watch video materials to learn the Arabic alphabet and reading rules. In addition to educational videos, the channel contains many videos for getting acquainted with the language and the Muslim way of life. There are videos and commentaries about Islam, interpretation of the Koran. Training in Russian.
Arabic by Daniyar Chormoshev
The author of the channel will help you master the initial level of Arabic. The teaching area included grammar, pronunciation, the Arabic alphabet and its features. Visitors to the page will be able to find valuable tips - for example, on memorizing Arabic words and phrases. Comments on the lessons are in Russian.
In addition to educational materials, the channel contains many educational videos about Muslim life, customs and rules. Comments in these videos are most often in Arabic.
Arabic with Ummanews
A lovely teacher named Zariyat will help everyone who wants to master the initial level of Arabic over the course of twelve lessons, in high quality, in detail and in Russian. Explanations are written on a white board with a black felt-tip pen, and the good quality of the image leaves no doubt about a particular symbol. Together with Zariyat, students will be able to master Arabic grammar, pronunciation, alphabet and features of some letters.
Arabic with Arablegko portal channel
The channel published unique materials from a course on teaching Arabic using the methods of Elena Klevtsova. Comments on the educational materials are in Russian, so knowledge of any intermediate language is not required. On the page you can find an online dictionary of the most frequently used Arabic words, grammar, and the teacher also pays special attention to a complex topic - the difference between similar sounds in Arabic words.
“Arabic no problem!”
The channel contains educational videos designed to introduce a novice user to the Arabic language and customs of the countries in which it is declared the official language. Visitors to the channel will become familiar with frequently used expressions in Arabic, will be able to learn how to behave in typical situations and communicate correctly with the local population.
Training and comments in Russian. The lessons are designed for beginners. The videos consist of clear and memorable presentations.
Arabic with Shammus Sunshine
On the channel, the visitor will find training videos for beginners who want to get acquainted with the language. Through videos in the form of easy-to-understand presentations, the student is introduced to basic Arabic words and expressions. The channel will help in learning the language for both beginners with level A knowledge and those who have reached level B. Lessons will teach you how to communicate about colors, vegetables, fruits, stationery, travel, antonyms, animals, the location of rooms and much more, as well as put it all into competent sentences . The videos consist of clear presentations that teach listening comprehension and introduce complex Arabic writing.
Arabic with Speakit (Prologmedia)
For those who are able to understand the language without Russian comments. Subtitles make it easier to understand. Temperamental presenters will help you master the most common standard phrases in Arabic.
The channel also contains many videos for practicing speaking in Chinese, German, English, Spanish, Italian, French, Portuguese and many other languages.
Arabic with Ahmed
On his page, a friendly Arab named Ahmed will introduce you better to the Arabic language. The videos will help beginners. The author of the channel will help everyone who wants to learn personal and demonstrative pronouns in Arabic, teach them how to use the masculine and feminine, singular and plural.
Visitors can expect lessons on politeness in Arab countries, pronunciation training and instructions on how to construct sentences. On his channel, Ahmed will tell you how to learn a foreign language as quickly as possible and share some other useful tips.
Arabic with Irada of Mersal
For the visitor's attention - useful collections designed to help learn Arabic. The author of the channel will talk about Arabic verbs of the past and present tense, personal pronouns, introduce sounds and letters, and the most commonly used words. Guests of the channel will be able to find tips on learning Arabic on their own. Comments in Russian.
Arabic grammar
Concise but clear lessons of the Arabic language for those who are starting to study it and want to consolidate the basics or lay them down. The author of the video will tell you about grammar in detail: prepositions, adverbials, predicates, idafa, parts of speech and members, and will teach you how to parse sentences.
Training is in Russian, visual information is conveyed through clear presentations. The author's method of quickly learning Arabic.
Tested on children.
If someone can read the Koran after this, the author is not to blame.
He had other goals, but - Good luck!
Different people have different ways of thinking, which is why, for example, physicists and lyricists need to be taught foreign languages in completely different ways. However, in all existing foreign language textbooks, one can feel the same and “shady” German approach: unnecessary thoroughness, an abundance of unnecessary, stupid, unstructured information at the start, tediousness that kills mood and motivation after 5 pages and puts you to sleep after ten.
That is, it is often not the student’s fault, but the teaching system that “fucks up.”
Roughly speaking, the teacher is to blame.
It’s as if someone put a filter on the “unworthy” foreign language.
And this is how the “cut-off” is carried out...
But why did they write a book for this, why was it called a “textbook”
and why were you sold “crap” that is of little use for learning??
Some books should be called - not textbooks, but "turnstiles",
like, if you made it through, you move on, if you didn’t make it through, sit, smoke, and smoke bamboo...
Existing textbooks are poorly designed for the thinking of a normal Russian person.
modern, not "outdated" version. When you are told obvious platitudes that have clearly been rewritten over the last 100 years, you get the feeling that you have “gotten it”... thoughts that you turned out to be smarter than your teacher, and the teacher is “acting out” - really interfere with learning.
Perhaps philologists wrote textbooks - for people with a different background,
Perhaps the “background” of the average student has grown over 100 years
or the methods are outdated.
It may also be that people who don’t know anything useful except languages increase the value of their knowledge by making show-offs and meaningful snot - where everything can be explained more simply, on the fingers, faster and more interestingly.
Can a teacher be boring?
After all, language is a means of communication.
The author of the textbook, the teacher, already has a “credit” from the student who bought and picked up the textbook. And if a student quits studying, maybe also because the author doesn’t “pull it out” - maybe because he’s a bad teacher? It is not customary to criticize teachers, but here the criticism is not from a student, but from a “colleague.” And in this case, criticism is more than appropriate. Because there is no need for bad teachers to scare students away from all teachers.
Let's take Arabic.
Most fears about learning Arabic stem from its written form.
Which the textbook presents in such a way that... you begin to understand the Inquisition...
Often textbooks focus on layers of language - from Islam and the Koran.
if the textbook is Soviet, then it is based on the experience of building communism.
For what??
Why frighten a person by aggressively imposing archetypes of behavior that are alien (for a Russian). Orthodox Christians and atheists do not need to immediately give words meaning “namaz” and “Akbar”.
That is, these words must be present, but then, where their presence will be justified by the logic of teaching, and not just by the teacher’s desire to immediately “convert” the student to his Faith. The student came for another. And the market says that you should respect your consumer. In the end, the student came to the Arabic teacher, and not to the madrasah.
How to interest a student.
How to awaken motivation?
The Arabic language gives precisely the Russian and Orthodox Christian the opportunity to touch the Biblical texts - in a different coordinate system. And understand the hidden meanings that (alas) disappeared without a trace in Russian translations - from Greek translations.
Eg. King Herod turns out to be the "king of the Earth." Ard and Herod (land) are spelled the same.
Bethlehem - (beit lahm) - turns out to be a sheep house, a barn. Like in popular prints showing the stable where Jesus was born.
The English Queen "Bloody Mary" turns out to be the "Mother of the State".
The Pharisees turn out to be ordinary Persians or horsemen.
Saducees - friends, brothers, monks.
Pharaohs turn out to be simply the leaders of these horsemen.
Kagan - High Priest.
The possible meaning of the “new spelling” of the name Jesus (the appearance of the second letter “i”) during the Great Schism of the 17th century becomes clear - precisely as a result of the translation of Arabic texts into “Cyrillic”. the stroke under the consonant “and” is the second “and”, which is written but not necessarily read. And the main dispute of the split takes on a different logic and harmony. This is precisely from the translation of Semitic texts - through Greek - into Russian.
The best motivation.
There is such an “Old Belarusian language”. This is a language in which ordinary text in Old Russian is written in Arabic letters. Agree, it’s nice when, in the process of learning one modern language, you find yourself “in the load” as a speaker of another, and ancient one.
The laws of “Freebies” (sweets in Arabic) have not been repealed. And the learning process turns out to be more effective if you lead the student “from freebie to freebie.”))
An example of the text of the "Old Belarusian language" from the Internet. This is an Old Church Slavonic language written in Arabic script.
My teacher, a KGB officer, once gave advice that was very appropriate in that situation - not to try to translate your life into Arabic. University, cinema and clubs are images of another culture for which another language would be better suited.
It’s more useful to come up with an “image” of an Arab and tell it from him. It is the language of nomadic peasants and has 70 words for camel and 5 verbs for “to think.” No need to complicate things...
May I have 5 brothers and 6 sisters,
your father has three wives and three houses.
It’s easier to learn from an authentic map than to pull out of thin air, as if to delicately name the concepts “airborne troops”, “institute”, “potatoes”, “privatization” and “investment banking business” that are absent in Arab culture.
So, the first principle of memorizing letters is “Shemakha”.
As the hero of Pushkin’s fairy tale said: “Reign while lying on your side”...
There are many Arabic symbols - you can memorize them by tilting your head to the right or left.
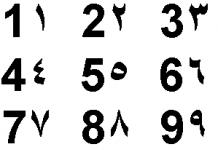
For example, the “European” numbers 2, 3, 4, 6, 7 are frankly of Arabic origin. It’s just that someone “messed up”, sat “drunk” and wrote down numbers, sitting “to the left” - from the source. Or poked him from behind his shoulder.

Second.
For some reason it is not customary to talk about this, but almost all Latin and Slavic letters were derived from Arabic script. Don't believe me? It’s simply not customary to talk about this. But calmly and without panic, take a closer look at the letters. If you can’t do it straight, try writing them not from right to left, as the Arabs themselves write. And reproduce them “our way”, as we write, from left to right.

If you don’t recognize them, try to relax, imagine how Cyril and Methodius “stole” the letters from the Arabs without indicating their sources. In order not to deduct copyright. Still, the Arabs have “close relatives” (perhaps even Cyril and Methodius themselves). Try writing the letters from left to right again. And look at the clues.

So, in order to convey information in the Old Belarusian language, you need to write Arabic letters - from right to left.
And these letters are modified Russian (Latin letters).
In Arabic, only consonants and long (stressed) vowels are written.
Short vowels are not written.
- there is no letter “p” in the Arabic alphabet, Arabs use the letter “b”
- the letter "g" is similar to the Russian one.
- the letter "i" twice. Once at the end of a word, the other in the middle. It can be seen by two points below it. The spelling is different, but these two dots “give it away”.
The letter "v" twice. Its writing anywhere (at the beginning in the middle, at the end - the same)

Vocalization rule
There are only 28 letters in the Arabic alphabet.
Strictly speaking, they are all consonants. Vowel sounds (and there are only three of them) are conveyed by special signs that are placed “above” or “below” the letter. The icons are called "vocals".
The vowels “a”, “i”, “u” are called “Fatha, kesra, damma”
A - stroke above the consonant
"and" is a stroke from below,
"y" - comma on top,
“without a vowel” - circle, “sukkun”,
ending "an" - two strokes above the consonant
shadda "w" - doubling of a consonant.
ending "in" - two strokes under the consonant
This is how the previous sentence “let’s talk” -
will look like “Old Belarusian” with vowels.

In most cases, you will not find texts with vowels in Arabic books and media. Why? Because Arabs read and understand these texts perfectly even without vowels. This is comparable to when in Russian we encounter the letter “Ё” without dots, but we understand that it is “Ё”. This is experience and skill. A couple of months of reading the exercises in their textbook - and anyone will have it.
Vocalizations were developed by medieval philologists. One of the theories of their origin is this: in those days, a large number of people accepted Islam - without knowing the language. And so that “fresh” Muslims could read the Koran without errors, a system of vowels was adopted. Now vowels can be found mainly in textbooks, in some Holy books (Koran, Bible), in reference books and dictionaries. But moving in this environment, anyone begins to read and understand texts without vowels at all.
Arabic writing allows us to better understand the speakers of Turkic, Iranian and Caucasian languages. And due to the fact that Moscow is already the largest Tajik, Tatar, Azerbaijani, Uzbek city - it is advisable to have this just in case, let it be... Because this writing allows you to better understand the grammar of the language. After all, doubling, transferring vowels - in these languages was historically justified by "Elm", and when written in Latin or Cyrillic - the logic turns out to be much more complicated.
The main thing is not to be afraid and to understand that the rejection of the Arabic language in the Russian cultural field may not have always been the case. One may discover that someone actually deliberately destroyed “Semitisms” (Arabisms) in Russian culture. You can see that many principles of Russian cursive writing/stenography amusingly repeat the laws of Arabic calligraphy (of course, in their mirror image).
Russian endings (for example, for adjectives) are written in Arabic not with 2-3 letters that do not carry information (-ogo, -ego, -ie, -aya), but are written in one short stroke. After all, the Slavic ancestors were not masochists when they left endings in their language that sometimes turned out to be longer than the word itself. In a word, the experience of the Arabic language is only an opportunity to regain what your ancestors had.
By the way, all European languages may have such an “Arabic” experience. It is known that the most ancient documents of the Afrikaans language (which, excuse me, is the language of the Dutch settlers of the 17th and 18th centuries in Africa) were written in Arabic script. It is known that in the 20th century there were translations of writing into Cyrillic and Latin, after which in Russia and Turkey ALL documents written in ligature were destroyed.
That is, perhaps it is necessary not so much to “teach” as to try to “awaken” the subconscious.
Arabic script is not at all complicated, but it amazingly helps to “reveal” different ways of thinking in a person: analogue, creative, composite...
True, there was such a story. Once, in a large Russian bank, I had to teach the basics of economics to local managers. I discovered with horror that the top management did not understand the diagrams at all and could not read pictures. And it can only read sequential text.
That is, the evolution of the banking business in the country has taken place - very strange. According to the principle of “washing out” people with abstract thinking. That is, those who do not know how to think abstractly have come together. Their entire advantage is the ability to “be shit”... With Arabic training, it will be more difficult to become a banker. But we learn a language - for a different development...
So if you are going to work in banks (or with such a category of people), stop learning Arabic (and forget what I already said). Otherwise, then you will have to stupidly hide a third of your brain in order to fit in with the “environment” and especially with your superiors.
But there is nothing wrong with abstract, creative thinking. In the end, when a crowd of Caucasian youth stops you in a dark alley, there is no need to panic. Really use your brains. As a rule, this does not mean anything bad, except that young people have nothing to occupy their time, and you have a reason to drink together. And you need to know how to see this reason. And how to develop it correctly.
Here in the picture below are two Arabic words of three letters.
Of course, since we are learning Old Belarusian, it might be worth writing an Old Belarusian word of three letters, but the one who needs it will write it himself by the end of the lesson...
three letters are three troughs. The dots above the letter indicate that the first word is “BIT”, the second is BNT.”

as already mentioned, even without vowels, a literate Arab will guess
that these are the words Bayt - house (hamsa and two sukkun - in vowels),
and Bint - a girl (kesra and two sukkun).
With vowels - two words will look like this.

I draw in Adobe with a mouse, if you don’t like it, draw it yourself.
Pencil, paper, sharpener - go ahead.
Beautiful handwriting for many is sufficient aesthetic satisfaction,
to practice Arabic. But we are talking about the harmony of language in general here,
and not about the beauty of his handwriting. Although - you will be pleased to think that after one day of training you will be able to write Arabic words - more beautifully than your teacher.
Lastly.
There is no need to feel complex about your lack of knowledge of the Arabic language in front of today's carriers of Arabic culture.
Firstly, all the Arabs you are interested in (for one reason or another) speak Russian or English. And English will be objectively more comfortable for them to explain the terms of European culture. The Arabic language is an opportunity to touch Arab culture in general, and not to a specific person in particular.
Secondly, we must understand that the Arab culture of the Middle East is, after all, rather a young culture. Its renaissance in the Middle East began only at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries. And when you get acquainted with the works of German and Russian Arabists (Krachkovsky’s four-volume work), you see and understand that at the end of the 19th century, the centers of study of the Arabic language and the Koran were Berlin, Kazan, St. Petersburg... And not Cairo and Damascus .
Jerusalem and Riyadh became centers of Arab culture only in the second half of the 20th century... and before that, an ordinary Arab in the desert in the morning washed himself with camel urine, jumped on a camel, and wandered to the neighboring oasis. And the harsh desert life then left no room or resources for higher manifestations of culture. This is neither good nor bad. Walk through museums in Arab countries to understand the meager and dreary life of nomads - even half a century ago.
To catch up.
Arabs consider "a" and "o" as one vowel,
they do not distinguish between these vowels.
they distinguish consonants as front ones.
They have different consonants with which the syllables “sa” and “so” begin.
That's why they have two consonants - where we have one.
And there are two different letters - “t”, “s”, “d”, “th”, “z”. One of them is “front” - after it you hear “a”,
and the other is the back one, after it you hear “o”.
The difference between them is colossal.
Kalb and Kalb are almost imperceptible to the Russian ear, but to the Arab they mean “heart” or “dog”. A gentle compliment - or an insult. They always call one famous Israeli politician “Kalb-va-ibn-al-kyalb” (The dog and the son of the dog).
And if you mess it up... it won’t turn out very nicely...
The letter, which simply means the short sound "o" - they convey it through the special letter "ain", means a guttural "semi-wheezing" and which in writing looks similar to the "non-Russian" letter "Ъ", as in the word "B-Ъ- Bulgaria"
Cyril and Methodius were stealing ideas - clearly not from the Greeks (or not only from the Greeks).
But for some reason it was forbidden to see Semitic roots in the Russian Empire.
That is, one could see the roots - from a certain “Greek” language 2 thousand years ago. But the “Arab” roots are relatively young - they didn’t notice.
Soviet Arabist Vashkevich. By the way, I found hundreds of parallels between the Russian and Arabic languages. You can find a lot about this on the Internet. Here are examples only starting with the letter "e".
BARELY, barely - the same as barely. ♦ From Arabic علة yillah "weakness".
EMELYA, Give up Emelya is not your week (proverb. Dahl) - Behind the name Emelya is the Arabic عمل amal “work”.
EREMEY, every Eremey understand to himself (proverb. Dahl) - on his own mind. ♦ Behind the name Eremey is the Arabic آمر "a:mara" to plot.
YERMIL, the hillbilly Yermil, is dear to the townswomen (proverb. Dahl). ♦ behind the name Ermil is the Arabic أرمل “armal “widow”.
Nonsense, talk nonsense - tell lies, talk nonsense. ♦ Behind the Russian nonsense lies the Arabic ده غير gerun da “not that,” i.e. wrong. For Russian, carry the Arabic نصت nassa(t) (feminine) “pronounce the text”, “read”. The grammatical term of Latin grammar comes from ar. جرد garrada "to form the original simplest grammatical form of a word."
To learn a language you need practice.
beautiful handwriting is in itself a reason to be proud.
After 10 conscious writings, a person automatically remembers everything.
Paper, pencil, sharpener - and as in childhood - through copybooks.
What frightens us in Arabic studies is the multiplicity of spellings for the same letter. initial, final, middle, separate. But these are just the principles of adding a letter.
As in the Georgian joke:
Vilka - bottle - written without a soft sign,
salt beans - with soft
This is impossible - we need to believe in it...
Here it is worth telling an anecdote that all Russians who have lived in Arab countries for a long time know about.
When “another Arab” decides to learn Russian, he spends several days learning the Russian alphabet, in the process of learning which he annoys everyone around him. Who can hardly tolerate his senseless tediousness. we know that the Russian language must be taught differently. And those who change the way they study achieve success in it. But - Arabic really needs to be taught, starting with letters - and going from the roots of words - to more complex meanings.
And to the oral language - it is advisable to go through the written one.
sometimes you think that those who developed methods for teaching children English and French went through the “torture of Semitic languages.” Because you can see the “ears” of other methods that are poorly suited for European languages.
Why did I start telling all this?
exactly - not only to teach the basics of the Arabic language.
And certainly not so that you sit down with the Holy Books this evening. Although - I repeat - if anything happens, it’s not my fault. This is your subconscious. Arabs sincerely believe that Arabic is the language of angels. So perhaps there is something “in the subconscious”.
More to tell in detail that the connections between Russian, Slavic culture - and Semitic, Arabic languages - are much stronger than we were taught from childhood. We were even forced to read the Bible translated from Greek and German. Although Arabic is the closest of the world languages to the biblical one. When they take the long route to get acquainted with the Truths, this means that they want to deceive someone, to fool someone. And perhaps there is a reason for not revealing everything to us.
– there you can find a lot of useful materials on different languages and improve your Arabic on your own in 12 weeks.
Good textbooks on phonetics:
5) Kovalev A.A., Sharbatov G.Sh. “Textbook of the Arabic Language” In the introductory phonetic course, the position of the speech organs when pronouncing all sounds is described in detail and there are exercises for practicing.
6) Lebedev V.G., Tyureva L.S. “Practical course of Arabic literary language. Introductory course" The position of the speech organs when pronouncing all sounds is also described in detail and there are exercises for practicing.
Copybooks
7) Arabic language. Copybook. Alphabet, reading, writing (Dilya Publishing House). All Arabic letters in all positions in a word.
8) “Kharisova G.Kh. Arabic script” Also an excellent script.
9) Imran Alawiye Arabic without tears. The manual is beautifully designed, the most common font is given.
Resources for basic skills (reading, writing, speaking, listening):
Online resources:
11) CultureTalk on LangMedia – This site contains videos featuring speakers of different languages talking about interesting aspects of their cultures. All videos are supplied with a text file with a recording of the speaker's speech.
Good benefits:
- Lebedev V.G., Tyureva L.S. “Practical course of Arabic literary language. Normative course". Very comprehensive course, covers most everyday topics.
- Ibragimov I.D. "Intensive Arabic language course." A classic textbook, excellent grammar base plus basic conversation topics.
- Educational and methodological set in the Arabic language “Al-‘Arabiya baina yadaik” for non-Arabic-speaking students
Grammar
Online resources:
Good grammar books
- Bernikova O.A. Arabic grammar in tables and diagrams.
- Bolotov V.N. Arabic language. Grammar reference book.
- Sarbulatov I. Entertaining sarfology (Arabic morphology).
- Khaibullin I.N. Arabic grammar. Summary.
- Chernov P.V. A reference book on the grammar of the Arabic literary language.
- Yushmanov N.V. Grammar of literary Arabic.
- Yakovenko E.V. Irregular verbs in Arabic.
Manuals on dialects of the Arabic language (list, without links, probably found on the Internet):
16) Arabian group of dialects (Kuwait, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, UAE, Oman, Yemen):
- Accent on Iraq
- Alkalesi Y. Iraqi Phrasebook
- Alkalesi Y.M. Modern Iraqi Arabic
- Arabic Dialect of Sana'a (Advanced Dialogues)
- Blanc H. Communal Dialects in Baghdad
- Clarity B.E., Stowasser K., Wolfe R.G. Dictionary of Iraqi Arabic (English-Arabic)
- CRE – Iraqi Arabic from English
- De Jong Rudolf E. A Grammar of the Bedouin Dialects of Central and Southern Sinai
- Defense Language Institute. Arabic Basic Course. Iraqi Dialect
- FSI. Saudi Arabic Basic Course. Urban Hijazi Dialect
- Holes C. Colloquial Arabic of the Gulf and Saudi Arabia: A Complete Language Course
- Ingham Bruce. Najdi Arabic: Central Arabian
- Khoshaba M. Iraqi Dialect Versus Standard Arabic
- Mutahhar Abd al-Rahman, Watson J. Social Issues in Popular Yemeni Culture (book+audio)
- Qafisheh H.A. A Basic Gulf Arabic: Base on Colloquial Abu Dhabi Arabic (book+audio)
- Qafisheh H.A. Yemen Arabic 1
- Qafisheh H.A. Yemen Arabic 2
- Qafisheh Hamdi A. A Short Reference Grammar of Gulf Arabic
- Scenes from Yemeni life (Yemeni dialect)
- Van Wagoner M.Y., Satterthwait A., Rice F. Spoken Arabic (Saudi)
- Woodhead D.R. Dictionary of Iraqi Arabic (Arabic – English)
17) Egyptian-Sudanese Arabic:
- Abboud P., Lehn W. Beginning Cairo Arabic
- Abdel-Massih E.T. Egyptian Arabic: A Comprehensive Study, vol.I-IV
- Absi S.A., Sinaud A. Basic Chad Arabic. Spoken Chad Arabic
- Anwar Mohamed Sami. Be and Equational Sentences in Egyptian Colloquial Arabic
- CRE – Arabic from English
- Defense Language Institute. Arabic Basic Course. Egyptian Dialect
- Khalafallah A.A. A Descriptive Grammar of Saɛi: di Egyptian Colloquial Arabic
- Louis S. Kallimni ‘Arabi Aktar. An Upper Intermediate Course in Spoken Egyptian Arabic
- Louis S. Kallimni ‘Arabi Bishweesh: A Beginners’ Course in Spoken Egyptian Arabic
- McGuirk Russell. Colloquial Arabic of Egypt
- Mitchell T.F. Colloquial Arabic
- Pimsleur Egyptian Arabic: Level 1
- Smith I., Ama M.T. A Dictionary of Juba Arabic and English
- The Rough Guide to Egyptian Arabic Dictionary Phrasebook
- Wightwick J., Gaafar M. Colloquial Arabic of Egypt
- Wightwick J., Gaafar M. Michel Thomas Method: Arabic Advanced Course (Egyptian arabic)
- Wightwick J., Gaafar M. Michel Thomas Method: Arabic Vocabulary Course
- Wightwick J., Gaafar M. Teach Yourself Arabic Conversation
- Wightwick J., Gaafar M. Arabic Verbs & Essentials of Grammar
18) Maghreb group of dialects (Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya):
- Abdel-Massih E.T. Advanced Moroccan Arabic
- Abdel-Massih E.T. An Introduction to Moroccan Arabic
- Amor Taoufik Ben. A Beginner's Course in Tunisian Arabic
- Ben Abdelkader Rached and others. Tunisian Arabic
- Boudlal Abdelaziz. The Prosody and Morphology of a Moroccan Arabic dialect
- Cherif A.A., Boukbout M., Mahmoudi M., Ouhmouch A. Moroccan Arabic (Darija)
- Hours Abdessalem. Competency Based Language Education Curriculum Guide
- Heath J. Jewish and Muslim Dialects of Moroccan Arabic
- Talmoudi F. The Arabic Dialect of Susa (Tunisia)
19) Levantine dialects (Syria, Lebanon):
- Cowell M.W. A Reference Grammar of Syrian Arabic
- Crow F.E. Arabic Manual. A colloquial handbook in the Syrian dialect
- Defense Language Institute. Arabic Basic Course. Syrian Dialect.
- Feghali M.N. Spoken Lebanese
- Foreign Service Institute. Levantine Arabic Pronunciation
- Instant Immersion. Arabic Eastern. Colloquial Arabic.
Business Arabic
Online resource:
20) Basic Arabic for Business – a very cool online course: animated dialogues, subtitles, exercises, everything is bright and colorful
21) Business Arabic Tutorials:
1. Dubinina N.V., Kovyrshina N.A. Learn to write business letters.
Letters are given in Arabic with translation into English and Russian.
2. Bodnar S.N. Arabic language. Genre of commercial business papers and their linguistic specificity
This wonderful book explains the linguistic and cultural features of many Arabic documents (invoice, bill of lading, etc.), at the end of the textbook there are examples for all types of documents.
3. Yakovenko E.V. Practical translation course.
This is an ideal tool for developing a thesaurus in the field of news reports on socio-political topics.
4. Ibragimov I.D., Manuals on the topics “Economics”, “Politics”, “Social problems”.
Very good, high-quality manuals, vocabulary is thoroughly practiced, there are lesson dictionaries, texts for independent work.
5. Mayburov N.A., Mayburov N.K. Reading and translating an Arabic newspaper
The textbook can be used as a continuation of the previous one in the topic. A good lexical base, the lexical features of a newspaper text are analyzed in detail, there are a lot of examples and exercises for practicing new material.
Arabic Language Tests
Qualifying exams:
25) The European Language Certificates (TELC) - a language test of a German non-profit organization at level B1. The test includes tasks for selecting headings for passages of texts, reading the text and answering questions with answer options, inserting missing words from the proposed options into the text, listening, etc.
26) Arabic Language Proficiency Test - an online version of the test developed by the Oriental Institute at the University of Leipzig. The test is divided into three levels: A1/A2, B1/B2, C1/C2. You can choose the level you want to check. The test includes multiple-choice questions, listening and watching videos, and open-ended questions.
27) California Subject Examinations for Teachers Test Guide - a sample test taken by Canadian Arabic teachers. The test includes only open-ended questions on language and culture: describe the role of the family in Arab society, change sentences in accordance with given parameters, read a poem and give comments.
Level determination test:
28) ESL – Language Studies Abroad Arabic Test – an Arabic language test from an international company that organizes language courses around the world. The test includes 40 questions with 3 answer options. At the end you will be shown all the questions with the correct answers and your level will be determined from A1 to B2.
General language tests:
Youtube channels
36)https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCcJV52bXxFldKMRoTrBDgSQ– AppyKids Arabia children's channel with songs and educational videos, perfect for listening at an elementary level