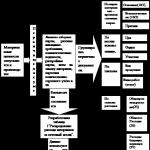
Automation of a warehouse for finished products of an industrial enterprise
Upon receipt of finished products at the warehouse, it is assumed:
1. The presence of an interface with automatic control systems (APCS) for production for automatic input of data on the type and quantity of products entering the warehouse. The input of such information is usually based on the use of stationary barcode scanners. It is also possible semi-automatic manual data entry from radio terminals at the stage of acceptance and QCD in production by employees of these services.
2. Use of means of applying labels with bar codes or means of radio frequency identification (radio tags).
3. The warehouse management system, based on the data coming from the automated process control system or the QCD radio terminals, must issue commands to print labels with data on the received products and control the means for marking.
4. The procedure for the receipt of finished products at the warehouse can be either fully automated (in the presence of conveyor lines) or require the intervention of warehouse personnel (acceptance by storekeepers of labeled products coming from production).
5. Automatic transfer of data on products received to the warehouse to the ERP system.
6. Existence of a developed quality control process that provides control over the sampling process.
When placing products in a warehouse, you must:
1. Mandatory support for the operation of radio terminal equipment.
2. Dynamic management of the placement of products in the warehouse with its serial and batch accounting (if such accounting is used).
3. The ability of the system to work with storage locations of various product capacities.
4. Placement of products, taking into account the need for its accelerated shipment to the buyer.
When collecting orders for products, you need to ensure:
1. The ability to automatically accept orders for shipment to work (the control system must independently calculate the time for the selection of a specific order and issue a task for the beginning of this collection in a timely manner).
2. "Ability" of the control system to work with cells of various types and places for floor storage of products on the principles of selection FIFO or LIFO; a selection of orders, both in terms of product expiration dates, and in batches and series, depending on the scheduled time of its removal from the warehouse.
3. Support for work with various means of automating the collection of orders (conveyors, carousels, elevators, etc.).
4. When exporting products from the warehouse, it is advisable to support the possibility of their direct shipment directly from the finishing production lines without temporary placement in the warehouse.
5. The possibility of repacking products and assembling kits (for example, furniture production)
Integration with the corporate enterprise management system is achieved through:
1. The presence of an interface for communication with other information systems based on various protocols (base-base, XML text files).
2. An advanced system for creating and transmitting reports.
Thus, the finished goods warehouse management system is characterized by a high degree of integration with the corporate enterprise management system, the ability to support a wide range of additional equipment, as well as significant autonomy for the possibility of warehouse personnel intervening in the operation of the management system.
In this regard, such systems are close in their parameters to industrial automated systems, which, in other respects, is not surprising, since in many enterprises the warehouse is called the finished product workshop and is considered as part of the production.
So, for the complex automation of the warehouse of finished products based on barcoding technology, online control over warehouse operations and address storage of goods, the company BS proposes a project consisting of:
1.
2. to support automatic identification: radio data collection terminals, wireless networks, label printers, consumables in the form of self-adhesive labels or hang tags
3. Implementation services: inspection, development of technical specifications, consulting, system installation, personnel training, equipment installation, commissioning.
Our forte is the use of the optimal implementation methodology and work experience. Thanks to this, we achieve results in a short time and with minimal project risks, which will allow the company to recoup the invested funds as quickly as possible.
RFID system for automation of warehouse processes
How to effectively control all warehouse processes, eliminating the human factor?
How to achieve order in the warehouse? Confusion in names, quantities and locations leads to confusion and regrading, loss of goods and incorrect inventory planning. As a result, the company incurs losses.
To prevent this from happening, you need to control all the processes and events that occur in the warehouse. It is necessary to monitor the shipment and receipt of goods, security, the correct registration of goods according to the invoice - and dozens of other operations. But how to automate warehouse processes and eliminate the human factor?
![]() Use the RFID system for automating warehouse processes, developed by ITProject,based on a ready-made universal solution.
Use the RFID system for automating warehouse processes, developed by ITProject,based on a ready-made universal solution.
Benefits of an RFID system?
Facilitate warehouse processes. Acceptance, shipment, movement and inventory of goods are carried out several times faster and with a greater degree of accuracy. |
|
Quick inventory. The reading speed of RFID tags is up to 100 in a few seconds, which allows you to carry out an inventory many times faster than manually or using a barcode. |
|
No mistakes. The human factor will no longer be a problem in all warehouse processes. All information is read automatically and immediately enters the system. |
|
Complete security. RFID tags cannot be faked, and portable readers will immediately send a signal to the system if the goods leave the area assigned to it. |
System Capabilities

With RFID - system you can:
full control of warehouse processes: everything from the receipt to the shipment of goods will now be under constant automatic control.
track the movement of goods or pallets : using the RFID gate, you can track which goods or pallets are taken out of the warehouse or moved to another location.
promptly inventory : due to the high speed of reading tags, inventory can be carried out at least every day.
carry out address storage : Each cell where goods are stored is affixed with an RFID tag, which contains all the information about the objects inside, so that you can determine the location of the cell and its contents at any time.
return goods on time : If any product has an expiration date, you will immediately know about it and can return it.
pick orders efficiently : you will see how many units of the product are in the lot: this will help you avoid shortages or surpluses.
quickly find a specific object : the location of any product can now be tracked instantly.
How and where to apply RFID system ?
On objects of any size and orientation, where access control or statistics collection is required:
at enterprises: for automation of warehouse processes
in logistics centers: for example, to account for transported goods
Completed projects:
Economic efficiency from the implementation of the RFID system
Why choose RFID technology to replace barcoding?
Barcodes are cheaper than RFID tags, but they often tear, get dirty, and cannot be rewritten. The speed of warehouse operations is not high enough.
RFID technology is much more reliable. It is based on RFID, so RFID tags can be read automatically from a long distance (up to 5 -7 meters) up to 200 pcs. at the same time, excluding the human factor. RFID tags cannot be counterfeited, they are not afraid of damage and exposure to heat and light. You can also add a barcode to the RFID tag.
RFID System Features
 |
Use of ultra-high UFH frequency
It is at this frequency that an ideal reading of an object at a distance of 1.5 to 5 meters is achieved. With the help of a mobile reader, one person can easily take inventory of goods that lie even on the highest shelves, without any extra effort and devices. Also, the peculiarity of this frequency is that it does not interfere with the use of any other devices. |
| Using the "ITProject RFID Server" platform + client and server modules
A convenient boxed solution from ITProject allows you to use any stationary and mobile RFID readers (even different manufacturers are allowed) and solve a wide range of tasks related to the use of RFID technology to optimize all warehouse processes. |
|
|
Easy integration with various accounting systems Integration with various customer accounting systems (at the database level, or using the library API): 1C, SAP, Microsoft Navision, etc. |
|

RFID system for automation of warehouse processes
How to control effectively all warehouse processes, eliminating the human factor?
How to achieve the order in stock? Confusion in the names, quantity and location leads to confusion and resorting loss of goods and improper planning of stocks. As a result, the company is losing money.
To prevent this you need to control all the processes and events that happen in the warehouse. You need to control shipping and receiving of goods, security, correctness goods processing in the bill of lading — and more for dozens of operations. How to automate all warehouse processes, eliminate the human factor?
| ANSWER IS: |
ITProject invites you to use the RFID system to automate the control of warehouse processes, based onplatform |
 |
The goods are marked by special RFID tags, which you can then read at the distance from 1.5 up to 5 meters with RFID-readers (hand-held or fixed). All information is sent to the data accounting system and can be checked at any time. |
What benefits brings the usage of RFID system?
Facilitation of warehouse processes. Receiving, shipping, moving and inventory of goods is carried out in several times faster and with greater accuracy. |
|
fast inventory. Speed of reading of RFID tags is up to 100 for a few seconds, it allows you to take inventory of many times faster than manually or using barcode. |
|
No errors. The human factor will no longer be a problem in all warehouse processes. All information is read automatically and comes immediately into the system. |
|
complete security. RFID tags cannot be forged, and portable readers will send immediately a signal to the system if the product leaves its assigned area. |
The System Capabilities

Using the RFID-system enables:
to control the warehouse processes in full: everything from receipt and to shipment of goods will now be under constant automatic control.
to track the movement of goods or pallets: using the RFID gate you will be able to track goods or pallets exported from a warehouse or moved to another location.
to perform inventory quickly: thanks to the high speed of reading tags inventory can be performed every day.
to implement address storage: for each cell that contains product RFID-label is fixed, which records all information about objects inside, so that at any time you can determine the location of the cell and its contents.
to return items on time: if a product will expire on the expiration date you will know it and will return it.
to complete effectively orders: you will see how many units of the item is in the lot: this will avoid shortages or surpluses.
to find quickly a particular item: now you can track the location of each product immediately.
How and where to apply RFID system?
in enterprises: to automate warehouse processes
logistics centers: for example, to account for the transported goods
Completed RIFD projects:
| "Elinar" - a multi-Holding, one of the main directions of which is the production of insulating materials. Partners" Elinar "in this field - the industrial giants of energy and electrical engineering, transport industry and the cable industry. |
Cost-effectiveness of the implementation of RFID Systems in your business
Reduction of personnel costs. Inventory and other processes now require no extra costs for additional staff, even at very large areas. |
|
Reduction of the duration of all processes. Receiving and shipping of the items as well as their movements and inventory occur much faster. |
Why should you choose RFID technology for the replacement of bar-coding?
Bar-codes are cheaper than RFID tags, but they often break, polluted and they also cannot recapture information. Speed of inventory transactions is not high.
RFID technology is much more reliable. It is based on radio frequency identification therefore RFID tags can be read automatically from a distance (up to 5-7 meters) up to 200 pcs at the same time, eliminating the human factor. RFID tags cannot be forged, they are not afraid of damage and exposure to heat and light. Also you can optionally record the bar-code on the RFID-tag.
RFID System Features
 |
Use of Ultra-High Frequency (UFH)
On this frequency the perfect reading of the object at a distance of from 1.5 to 5 meters is achieved. Using a mobile reader one person can easily carry out inventory of goods, which lie even on the highest shelves without superfluous efforts and devices. One more feature of this frequency is that it does not interfere with any other devices. |
| Use of "ITProject RFID Server" platform + server and client modules
Convenient box solution from the company "ITProject" allows you to use any fixed and mobile RFID reader (they may have even different manufacturers) and solve a wide range of tasks associated with the use of RFID technology to optimize all warehouse processes. |
|
|
Simple Integration with Different Accounting Systems Integration with different customer’s accounting systems (at the DB level or using the API library): 1С, SAP, Microsoft Navision etc. |
|


|
Do you hesitate to order because you think the system is too complicated to use? Are you afraid that the staff would have a long time to understand and get used to the new work scheme? Throw a doubt! Our workers are always ready to help you at the first stage of the installation and implementation of the system, as well as to carry out the warranty service. |

|
Want to get an extra year of warranty service? In a conversation with our managers do not forget to mention that you have learned about RFID-system on our website. |
|
Implementation of RFID - systems for automation of production and warehouse processes . |
ERFID presents a new integrated solution for warehouse accounting automation based on RFID technology. This solution allows you to significantly reduce the time of cargo handling, ensure full transparency of the warehouse and minimize the number of errors caused by the human factor.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology for the unique identification of physical objects using radio tags. The introduction of an RFID system in a warehouse makes it possible to identify up to 100 objects per second. At the same time, each of them is recognized by the system “under its own name” - the unique identifier is the EPC code recorded on the microchip of the RFID tag. Reading information from the tags is carried out remotely, and the marked objects do not even need to be removed from the packaging. The system is able to carry out group accounting of goods directly in boxes or pallets.
RFID technology allows:
- take inventory every day;
- form large orders in a few minutes;
- to quickly search and sort goods;
- supervise loading and unloading operations;
- automatically prepare all accompanying documents at the time of order formation;
- minimize the number of errors;
- reduce personnel costs;
- promptly identify "bottlenecks" in the work of the warehouse;
- fight theft.
The key advantages of the RFID solution from ERFID are ease of implementation, scalability and wide functionality.
The solution includes RFID tags for marking goods, reading equipment and special software. It is fully integrated with any customer's accounting system, which makes it possible to avoid errors associated with an unusual interface or changes in the database when switching to new technologies. The system created by ERFID specialists does not require special skills and is available for warehouse employees who do not have technical training.
At the first stage, goods subject to accounting must be marked with RFID tags. They are applied to products like regular stickers. Recording information on labels and linking it to the accounting system is done by simply pressing a button.
The further process of work looks even simpler: the goods placed in the reading zone are automatically recalculated by the system. All information about products is displayed on a computer monitor - the operator has the ability to track the current list of products available. When placing orders, the system compares this list with the picking list and gives a signal about what exactly needs to be added or removed, and after all the necessary actions have been completed, it will automatically prepare a complete set of documents - they will only need to be printed.
In order to ensure the most complete and high-quality warehouse accounting, ERFID specialists used several types of readers in this solution. To control the movement of goods, stationary portal readers were developed that are installed at the entrance to the warehouse. To account for objects in the warehouse, desktop stationary readers are used. These devices can be used to record RFID tags, form orders, receive and sort goods. With the help of a mobile inventory complex from the ERFID company, it is possible to carry out an inventory in a warehouse without removing goods from the shelves, quickly and without errors.
Additional features of the solution can be implemented using virtual readers. These readers are perceived by the customer's accounting system as separate independent devices, and allow using one "physical" reader to simultaneously solve several different tasks. For example, if the reader is installed in the aisle, it can not only record the movement of goods, but also keep track of working hours and work as an anti-theft system. Thanks to the use of virtual readers, several people can work with one "physical" reader. Each of the employees can use one of the 4 antennas connected to the reader for their own task: receiving goods in 1C, placing an order, marking labels, etc.
You can learn more about the ERFID solution at http://www.erfid.ru/warehouse.html
ERFID is a system integrator specializing in the development and implementation of integrated solutions based on RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology. All work performed by ERFID is carried out in accordance with state standards and requirements of regulatory authorities, our specialists have extensive experience in creating, integrating and supporting complex distributed IT systems. ERFID is an active member of the EPC Global and GS1 RUS associations that set global and Russian standards for working with RFID technologies, as well as a member of the technical committee for standardization TK355 "Technologies for automatic identification and data collection and biometrics" of the Russian Federation.
The solutions developed by ERFID can be found on the website www.erfid.ru
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology is still quite expensive for the domestic market and works only in large warehouses. But the heads of companies that have already implemented the technique have managed to appreciate the advantages of radio-frequency identification of goods. The technology allowed to solve a number of problems related to the storage and accounting of products.
How does RFID work?
System RFID Reader pretty easy to use. A special label is applied to each unit of goods, in which all data is encrypted: weight, volume, date of loading or unloading, basic storage parameters. At the exit from the warehouse, a metal frame with sensitive RFID sensors is mounted. They scan the labels on every package they pass through the gate and send the information to a shared database.
The program can be configured to identify employee personal cards or combined with a video surveillance system. This will not only simplify the accounting and tracking of the movement of goods, but also reduce the number of violations in warehouses.
Examples of using
In the world there is a practice of using systems based on RFID technology. Radio tags are used in various areas:
At one of the Toyota factories , located in the US, RFID helps to control the fullness of trailers during loading. Similar technologies have been introduced at Chevrolet enterprises and major Asian ports. Tags are applied to large-capacity containers, and loading equipment is equipped with readers. This made it possible to increase the turnover, since there was no need to recalculate and verify large volumes of goods manually. With such a tracking system, the number of human errors is reduced.
At Sony Electronics factories use rewritable RFID tags. They are applied to kinescopes on production lines of the final stages of production. By scanning the tag, the system transmits data to the central database, and the operator receives information about testing and the location of a particular product unit.

In a number of European countries, RFID tags have saved car owners from having to use the cash register every time they fill up their car. Electronic readers are mounted directly on the fuel pumps. The system starts the fuel supply after receiving the corresponding signal from the scanner.
Transport companies have also adopted the technology. . Tags are placed at the bottom of the windshield of trucks. RF scanners are located at each control point and end point. Not only the date and number of the vehicle are read, but also all information on the goods: waybills, waybills, etc. During the movement of the car, paperwork is completely excluded, data is transmitted through a central server.
RFID technologies appeared in our country about ten years ago and are mainly used in warehouses. But manufacturers of radio frequency equipment have already set up serial production, as they are confident in its active implementation.
Application of RFID in warehouses
The use of RFID technology for a warehouse is justified from an economic and practical point of view, especially when it comes to terminals with a large turnover. The purchase of equipment for large companies pays off pretty quickly.
Advantages of the RFID system:

Specialists who deal with the RFID device in the enterprise should pay special attention to the tasks that will be assigned to the system. It is necessary to determine the optimal reading range, adjust the antennas accordingly, and study the specifics of technological processes in the warehouse. It is important to understand the principle of moving commodity items. For example, a package passed through RFID-reader, does not have to leave the warehouse. It may be transported to another site, so the system does not have to mark it as shipped.
Perspectives on RFID
Similar chipping technologies are already used in Russia, for example, in new passports. But the system is not yet as active as in developed countries. Experts predict a great future for RFID, up to the complete replacement of modern computers. Of course, this will not happen soon. While technologies are being finalized in order to expand functionality and increase efficiency. One of the most promising areas of development is work in all kinds of online stores. Given the daily turnover, their warehouses need especially strict accounting of goods, tracking movements.
The positive experience of using RFID in this capacity was presented by Paxar. Its specialists created the Magicmirror program based on radio frequency technologies. This is some kind of electronic mirror. A visitor to the Paxar branded clothing store can choose any model from the collection with an RFID tag and bring it to the mirror. The display will show detailed information about the composition of the fabric, available colors and sizes. Based on the scanner data, the program will also suggest accessories suitable for this garment. With the RF reader, the buyer will be able to call the sales assistant while in the fitting room.

The technology is good, especially when applied to warehouses. However, today system developers face some difficulties. Ways to solve problems over time should be found, but so far the technology inspires some concerns among users.
Difficulties in using RFID technology for a warehouse
So, what are the developers and end users of RF scanners afraid of:
- Price. The first RFID equipment was quite bulky and expensive. It is inconvenient to use and required financial investments that are unbearable for small firms. The engineers managed to gradually make the installations more compact. After all, small and light scanners are cheaper, and easier to use. The cost of the RFID tags themselves is not declining as fast as we would like. Not every company can afford to equip the entire warehouse with microchips worth 10 euro cents. Experts are confident that as soon as the cost of tags falls to 1 euro cent, the demand for them will increase significantly.
- Computer threats are viruses. The average amount of microchip memory is only 2 kb. Initially, it was believed that the label was simply impossible to infect with a virus, but Amsterdam scientists proved the opposite. They not only infected the microchip, but also analyzed the possible consequences of this situation. A faulty tag gives false information or stops working altogether. RF data transmission also infects the scanners through which the chip passes. This disrupts the central database and can completely stop the operation of the warehouse, which means huge losses for the company. Even more dangerous, the virus can spread via radio channels and other tags, causing havoc. When applied to hypermarkets and other large facilities, the consequences are completely unpredictable.
- Possibility of hacking . Actually, we are not talking about hacking, because the chips are not protected. The scanner is able to read information from a great distance, which gives a large field for the activities of criminals. Anyone who has received a product with a tag can use the reader and access the database. This includes customer credit card information and other sensitive information.
- Theft of data from electronic documents . For example, when reading passports, the scanner automatically sends the data to the central computer. In Germany, England and the USA, RFID technologies have long been used in the defense and healthcare sectors. But recent research has shown that data from chips can be copied from a distance of 100 meters, with a special scanner. That is, a criminal can gain access to the most important information, the dissemination of which is completely unacceptable.
All of these concerns apply to the use of RFID in warehouses. Experts are actively looking for methods to "break" the chip after the thing is transferred to the buyer, but so far all of them are ineffective. The tag deactivation programs only cause it to be put to sleep, not disabled.
Here are a few ways that consumers themselves have invented to keep their privacy private:
- cutting the antenna. In some cases this is not possible. For example, when removing a label from clothing, you will have to ruin the fabric;
- processing things in the microwave. The radiation causes an explosion of the chip, which also does not pass without a trace for the purchased goods.
German engineers have been working for many years to create a device that can permanently deactivate an RFID tag. The technology is based on the strong influence of an electromagnetic pulse. But while the device is being tested, it cannot be found in the public domain.
Data protection systems
 If it is impossible to disable the label, the scientists decided to develop ways to protect it. To date, there are several:
If it is impossible to disable the label, the scientists decided to develop ways to protect it. To date, there are several:
- Password protection. The chip sends the correct information to the scanner only after entering the secret code. Other code may trigger the chip's self-destruct program, for example, after purchasing an item. The technology turned out to be vulnerable to hackers, so it was not widely used.
- Hardware and network protection. The system blocks all tags in the warehouse and opens the required one only upon request. The program constantly scans the air, providing information about an unauthorized reading attempt. This technology is applicable to chips of any complexity and size. It is quite effective and protected from hacker attacks.
- Broken antenna. When buying a product, the buyer simply breaks off the tip of the antenna, which is responsible for transmitting data over a distance. When returning the goods, the seller can identify the item by bringing the scanner close to the label.
- Installation of "silencers". The device works on the principle of the RFID tags themselves, copying the algorithms of microcircuits. The difference is that the "jammer" gives false information to the scanner's requests - digital garbage. The creation of such an interfering chip is complicated by the fact that it must recognize various reading devices and issue a stream of unnecessary information to unregistered devices.
In the future, the use of RFID technologies in the organization of the warehouse should increase the speed of turnover and the efficiency of the entire warehouse system. If there is a serious data protection program, or the information on the chips is of little value to third parties, then RFID tags are a great solution for any business.
G. Frolova
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is gradually entering our lives. Chips are already actively used in logistics, the synthesis of RFID technologies and global positioning in Russia, they predict great prospects, but so far the market growth is still constrained by the price of the issue, or rather, radio tags
A radio tag, or transponder (tag), is the main component of this technology and a direct carrier of unique information and an identifier for objects and even people. The first radio tags were used during the Second World War: then the tags were used in military aviation and cost several thousand dollars, and information about them was classified. It wasn't until 1973 that Mario Cardullo et al. published US Patent No. 3,713,148 describing the first passive RFID transponder (radio tag). By the 1980s, tags had fallen in price to $1 and were used to pay for public transport. The development and widespread introduction of radio identification has long been held back by the lack of standards. But in the 1990s, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) adopted a number of fundamental standards in the field of RFID, which were widely supported by manufacturers of reading equipment and RFID tags. This fact, along with the reduction in the cost of transponders, undoubtedly pushed enterprises to actively implement RFID.
Further price “evolution” brought the technology to trade and warehouses: after the cost of tags reached $0.2, they began to be used to account for goods and control their movement. Even then, there were predictions that eventually tags would replace barcodes. Perhaps someday this will happen, but experts believe that for this only in Russia, tens of billions of tags worth no more than $0.05 will be needed annually. By the way, German scientists have recently taken another step towards reducing the cost of tags, and here's the one.
nanoink
A few years ago, bulky television receivers were common items in our apartments, and now the screens have become so light and flat that they can be easily fixed to the wall. A detailed examination of their device will reveal very thin conductive elements and transistors that regulate the electrical signals supplied to the pixels of the screens.
The architecture of electronic devices in question is created layer by layer, usually using the photolithography method. On a specially prepared surface (cleaned and leveled), materials are deposited - a substrate and a photoresist (polymeric light-sensitive material), which are then exposed to light in the presence of a mask-photomask with a pattern that allows only certain areas of the substrate to be illuminated. As a result of exposure, the “exposed” photoresist changes its properties, for example, becomes soluble, after which it is removed, and then the substrate is removed from open areas by etching, leaving only an unexposed pattern on the substrate.

However, the described process has a major drawback: most of the deposited materials, which are then removed by etching, are not used. The goal of any production is to reduce the cost and resources used in the technology, so the development of a method in which the material is applied only to areas that directly form the pattern has become an urgent task.
The technology of "printed electronics" has already been developed for the application of polymeric conductive materials. However, in terms of electrical properties, they are inferior to inorganic counterparts. In polymers, charge transfer occurs more slowly, which is why, for example, printed RFID chips have a shorter conduction band compared to classical electronic circuits. In addition, they are more sensitive to moisture and ultraviolet radiation.
Scientists from the Fraunhofer Institute of Integrated Systems and Device Technology (Fraunhofer Institute of Integrated Systems and Device Technology, Erlangen) have prepared for launch a production line that can print inorganic electronic components by feeding material for deposition in the same way as office printers work . “We developed a nanoparticulate ink with a stabilizer added to improve processing and prevent aggregation,” says research team leader Michael Jank.
The nanoink has already passed the first technological tests, and, according to Jenk, could appear in devices that perform simple functions within a year. “We expect products based on our design to be about half the cost of products that use silicon electronics for relatively simple purposes,” comments Jenk. Printable tags need to be cheap enough to be placed on the packaging of low-cost products such as yogurt, where they can help control temperature and other storage and shipping data.
Market

As tag companies struggle to lower their prices, the RFID market continues to grow. According to ABI Research, in 2009 its volume will reach $5.6 billion (forecasts for 2008 - $5.3 billion*) taking into account sales of RFID transponders, receivers, software and services. "There is no doubt that the crisis will affect the market," said Michael Liard, an analyst at ABI Research. “But despite this and some other factors, the dynamics of its development will be positive.” Analysts do not think that because of the crisis, revenue will decline. In any case, now it will continue to increase, although not at the same pace as previously expected. According to experts, RFID solution providers should focus on their cost-effectiveness, low cost of implementation and maintenance. This is especially important in the current economic environment.
Despite the unresolved technical problems that limit the use of RFID, talk about its potential and extraordinary possibilities does not subside. Recently, journalists from the PBS Nightly Business News program, along with [email protected] compiled a list of the top 30 innovations made in the last 30 years. PC World, in turn, chose from this list seven technologies that have changed the world the most. Among them was RFID, and in a very worthy environment of such already world-changing inventions as graphical interfaces, the Internet, online social networks and e-commerce, mobile phones, laptops and desktops.
*Cm. article "New steps in RFID technology", "C&T" No. 11 and 12, 2008

Unbelievable, but it is a fact
We have already written about the different areas in which RFID can be used. Recently, Wired magazine named ten of the most unexpected uses for this technology, some of which CIT has already covered in previous publications.
Arizona cacti. On the black market for landscape plants, these large cacti fetch over $1,000. Arizona's Saguaro National Park plans to use RFID tags to monitor the safety of these rare giants.
Elephants. The New Delhi Department of Forestry requires that all of these animals participating in national holidays be RFID tagged. So it will be easier to identify them and take them under control in case of sudden attacks of aggression. The proposal comes in response to police reports that there have been about 50 incidents over the past four months involving elephants in parades. The aggressive behavior of animals led to destruction and even human casualties. Chips are planned to mark about 1000 elephants. To accomplish this task, the authorities need the cooperation of their owners. A tag smaller than a grain of rice is placed under the elephant's ear, but it requires the animal to lie down to place it.

Surgical sponges. According to statistics, during surgical operations on the abdominal cavity, in one case out of a thousand, a surgical sponge remains in the patient's abdomen. Now, with the help of the SmartSponges system, the doctor can quickly detect the loss by swiping the reader along the body of the operated person.
Mexicans. Xega Company's security team has developed a chip the size of a grain of rice that is injected into a client's body. GPS can then be used to track his movements and locate him in the event of a kidnapping. The chip costs $4000, another $2200 is an annual subscription fee. But in a country where 6,500 people were abducted last year, such a measure may well be in demand.
Pirelli tyres. The chip in Pirelli's "cyber tires" transmits information about road conditions and the coefficient of friction to the on-board computer. This allows you to optimize the operation of the car's electronic systems: ESP, ABS, ASR.

Clubbers. The Barcelona club "Baja Beach" switched to a new system of work with VIP clients. They are injected with an RFID chip linked to their bank cards and thus allowing them to go to parties without a wallet. The radio tag gives the right to enter the VIP area, and is also used to pay for drinks at the bar. The owner of the establishment himself was the first to implant such a chip from VeriChip Corporation.
Tokyo. The Japanese capital seems to have set the task of covering all elements of the city's infrastructure with microchips - from bus stops to restaurants. It looks like tourists will soon be able to get maps, timetables and any other information just by waving their phones.
Police badges. Blackinton has come up with a security system for police badges. Now they will be embedded with identification chips, thus reducing the risk of fraud and counterfeiting. And the tricks from Terminator 2 will no longer work.
Prisoners. In Britain, prisons are overcrowded, so it was decided to release some of the prisoners. However, criminals will continue to be monitored, tracking their movements with the help of chips in order to intervene in a timely manner, if necessary.
Cat doors. The movements of pets can be better controlled and, if necessary, “lock” the cat door without letting the animal out of the house. And cats no longer need to wear a collar.

Perhaps another unexpected use of RFID will soon join this list. Recently, designer Ben Greene came up with an interesting idea about how two lonely hearts can find each other. He proposes to create electronic bracelets that will contain information about personal preferences, that is, about what a person likes and what he does not like. After all the necessary information is entered into the device, the bracelet can be activated in one of two ways - in the “finder” or “sought” mode. After activation, the bracelet begins to transmit radio signals to everyone who is currently in the dating club; on the wrists of the most compatible personalities, lights will flash in unison. When the two "halves" come closer, the lights on their bracelets begin to glow brighter.
But as curious as these exotic ways of using RFID are, let's get back to larger and more practical solutions that use this technology. Let's start with logistics.
RFID on packaging
Mondi Corrugated Packaging has started manufacturing corrugated boxes with RFID chips. The innovation will make the processes of scanning, tracking and receiving cargo much more efficient. Now smart containers will be equipped with RFID chips on a high-speed production line, and there will be no need for manual gluing of labels. Using RFID instead of traditional barcodes will allow whole pallets to be scanned, saving significant time. "Smart" packaging will provide round-the-clock access to information about the availability and location of goods. This will facilitate warehouse work and speed up the inventory process.

Rexam has introduced a new type of pharmaceutical packaging to the market - bottles, which are coated with RFID chips, which provides full control over the movement of the product from the moment of packaging. The chips, manufactured for Rexam by partner company Traxxec, read and write the necessary information. Their use is more cost-effective compared to existing analogues.

The largest Japanese packaging manufacturer Toyo Seikan Kaisha has developed the first metal can for drinks equipped with an RFID chip (we recall that in 2007 this company, together with NEC, produced a plastic lid with an integrated tag). As you know, conventional RFID tags do not function on a metal surface, due to the interference and diffraction of the radio signal. Specialists from Toyo Seikan Kaisha attached the antenna to the ring on the bank and connected it to the chip, and thus managed to establish communication. According to the manufacturer, the design of the jar itself and the lid has not changed, and traditional equipment can be used when filling and sealing it without any changes. New RFID chips will make it possible to contain information about storage conditions and package integrity.
RFID chips that will allow the use of this technology in any storage conditions, including on metal surfaces, were also presented by Ferroxcube. Products have a weight of 2.5 g, dimensions 25 x 12.5 x 5 mm, are attached to the package with glue, double-sided adhesive tape or bolts, operate at temperatures from -25 °C to +130 °C.
But a group of German researchers and Alcan Packaging recently presented the results of an RFID-based research and practice project to create a system for remote tracking and automatic identification of packaged food and medicine. The goal of the Smart Pack project, funded by the German Federal Ministry of Science and Education since 2005, was to create a technology to protect goods from counterfeiting, theft, individual recording of information, track its path in the logistics network. The originality of the technology lies primarily in the fact that passive sensors integrated into the packaging can not only serve as information carriers, but also report on the state of the product, signaling a violation of the temperature regime and humidity parameters. Thus, the consumer at the final stage of distribution will be able to determine whether the temperature regime of storage was observed, as well as to judge the integrity of the package.

new standard
Another problem limiting the large-scale implementation of RFID is the lack of necessary regulations and standards. To eliminate it, the International Organization for Standardization ISO has introduced a new radio frequency standard ISO / TS 10891:2009, which regulates the use of RFID tags used to identify cargo containers by sea, rail and road.
The ISO/TS 10891:2009 standard regulates the use of permanently attached chips that store data about the container and optimizes the efficiency of the use of control equipment. In particular, requirements are established for RFID tags when transmitting information from a chip to processing systems, requirements for container data codification systems, and the composition of recorded data. This standard also establishes requirements for the location of the RFID tag on the container and the protection of data on it from intentional or unintentional deletion.
“Containerization has reduced the time and cost of delivering goods to markets across the ocean, the number of their thefts in the process of delivery. In addition, it has led to improved transport safety. ISO/TS 10891 will help container manufacturers, shipping companies, consignees, terminal operators, rail operators benefit from the use of RFID to ensure the efficiency, speed, security of shipping and container handling,” said Frank Nechber, ISO Committee Chair, who developed this standard.
TV + RFID
Sony has announced the upcoming release in Japan of two new series of Bravia TVs with a refresh rate of 240Hz. The models have an RFID tag reader built into their remote controls that allows users to pay for various multimedia services (such as video-on-demand) using mobile phones. The W5 series is available in 40-, 46- and 52-inch versions, all with Full HD resolution and 240Hz. Devices from the F5 line are more modest in size (available in 32, 40 and 42 inches), but have the same panel parameters (with the exception of the younger model, which supports a resolution of 1366 x 768 at 120 Hz). New items are thin (only 85 mm) and good contrast (3800:1).

Mobile phone instead of a credit card
The Visa company announced the start of "field" tests of an innovative payment system in which an ordinary cell phone performs the function of a plastic card. A special chip is responsible for organizing secure interaction between the payment terminal and the mobile device, which provides the possibility of short-range wireless communication. At the moment, Nokia 6212 phones are equipped with such a chip.
In order to use the service, the user only needs to purchase a phone equipped with the necessary electronic component and “link” the device to their own bank account. After completing this simple procedure, he will be able to pay for goods or services by simply bringing the phone to the payment terminal at a distance of no more than 4 cm. As a result of these manipulations, the required amount will be automatically withdrawn from the account. If desired, the user will be able to enter a password that will prevent the leakage of funds from the bank account if the phone is stolen. However, if the owner of the device forgot about the precautions, the bank will independently disable the possibility of making payments from a mobile phone at the request of the client.


Currently, the service is provided only in Malaysia, but over the next few years, residents of other countries will also be able to appreciate the benefits of this service. For greater customer convenience, the new technology provides for the possibility of transferring funds from several accounts. For example, Malaysian users can set up separate accounts to pay for parking or public transport. In the near future, the phone will also be able to combine the functionality of credit or debit cards provided by different banks. To quickly switch to different accounts on your mobile phone, you need to install the appropriate software.
Similar solutions based on RFID technologies have already gained popularity in the United States. However, many users will like the ability to use the phone instead of a regular card, which must be removed from a special compartment in the wallet before use.
Intel: powered by radio waves
At the Rawcon conference in San Diego (USA), researchers from the Intel laboratory (Seattle) demonstrated WARP (Wireless Ambient Radio Power) technology, which allows you to power up to 60 mW over a radio channel at a distance of up to 4.1 km. During testing, the developers managed to ensure the operation of a temperature and humidity sensor with a liquid crystal screen from a radio signal from a television transmitter.

Currently, three natural (free) sources of energy are used - vibration, sunlight and heat. WARP technology completes this list with the possibility of being powered by a television signal. According to Joshua Smith, one of the co-authors of WARP, their technology is not the result of large-scale discoveries in the field of chip design or radiophysics. In fact, the implementation of WARP technology became possible only thanks to the evolution of traditional electronics and is the development of the WISP (Wireless Identification and Sensing Platform) wireless information reading platform based on serial readers for RFID tags operating in the microwave range (in most TVs this range is indicated like UHF). Each WISP module contains a radio tag with an embedded microcontroller - currently the Texas Instruments MSP430 chip.
Each WISP module includes a log-periodic antenna, impedance matching components, a radio signal energy trap, a demodulator for information from the reader to the WISP module, and a modulator for transmitting data to the reader. The module also includes a voltage regulator, a programmable microcontroller (the notorious MSP430) and additional external sensors. The energy catcher is a 4-stage charge pump generator. The power consumption of a standard WISP module is on average 2 µW to 2 mW.
The authors of the WARP technology practically repeated the design of the WISP modules, they only changed the input circuit of the energy trap, tuning it to one of the television channels. As a result, the modified serial WISP module began to receive energy not from an RFID reader, but from a TV tower!

RFID in Russia
Recently, RFID technologies have been used in Russia as well. True, the first large-scale experience - the use of tags in tickets for passage to the Moscow metro - cannot be called very successful. Firstly, their buyers received absolutely no benefit, since they cost the same as old-style tickets, and they must be bought at the same box office. The time to buy or pass through the turnstiles has not been reduced. In addition, as it turned out, they are not so difficult to fake, which scammers were not slow to take advantage of. For a long time, they acted with complete impunity, openly selling fakes at metro stations, in particular VDNKh, where huge queues line up at the ticket office during rush hour. Only at the beginning of March, officers of the Moscow police department detained about 100 members of the criminal group.

The official supplier of tickets with chips based on RFID technologies is the Zelenograd Mikron plant. In 2008, Mikron supplied more than 250 million contactless cards to the metropolitan subway and other Russian enterprises. Despite the crisis phenomena, OJSC NIIME i Mikron still has grandiose development plans. So, Mikron has every chance this year, together with the state corporation Rosnano, to start financing a project to prepare for the development of technology for the production of microcircuits with a topological size of 90 nm. This was announced at a reception dedicated to the 45th anniversary of the enterprise, its general director Gennady Krasnikov. The technology partner for this project is the French company ST Microelectronics, which is ready to supply Mikron with new technology.
“In addition to the supply of transport cards, where we are already reaching the regions, other areas are opening up in terms of using RFID, primarily in retail, where billions of RFID tags are needed,” Krasnikov said. - Now the head of Rosnano, Anatoly Chubais, has taken personal control over the project of introducing RFID technologies in trade. This opens up a huge market for us.”
The banking sector decided to take advantage of the results of this implementation. Some banks already provide their customers with the opportunity to pay for travel in the subway using bank cards with an RFID chip embedded in them. Following the capital's Citibank, Bank of Moscow and Master Bank, the project was implemented in St. Petersburg. The State Unitary Enterprise "Saint-Petersburg Metropolitan" jointly with the Bank "Saint-Petersburg" issues for the passengers of the Saint-Petersburg Metro the "Unified" card, combined with the international bank card VISA Electron. The holder of the United-VISA Electron card can use it to pay for travel in the St. Petersburg Metro, to pay for goods and services in trade and service enterprises equipped with POS-terminals, to receive cash from ATMs and cash points.

Another large-scale RFID project was the exchange of old passports for new ones, the so-called biometric ones. Despite financial difficulties, Muscovites are going on holidays abroad, and by spring the number of issued international passports has doubled, and 80% of them are biometric. Note that the price difference between the old (400 rubles state duty) and new (1000 rubles) passports is quite significant, but the “expensive” passport does not give any special advantages. The new document differs from the old one with a special sign on the front side, which indicates that the passport contains biometric data, but neither fingerprints nor the retina of its owner is yet removed. The difference is that the photo page in the new passport is not at the end, but at the beginning, and the usual seal has been replaced by a hologram. However, passport office employees often strongly recommend Muscovites to issue biometric passports, arguing that old passports are produced much longer than biometric ones, although by law the procedure should not take more than 30 days, and in Moscow it was decided to reduce this period to 20 days.

The FMS claims that the document has an electronic filling: an RFID chip is embedded in one of the pages, on which the information reflected on the first page of the passport is recorded. It is believed that the chip cannot be faked, and its information can only be read using a special device. The information on the chip is also protected by an electronic signature.
Recently, a message appeared in the media about another large-scale and very promising project. The Supervisory Board of the Russian Corporation of Nanotechnologies approved the participation of the corporation in organizing a high-tech enterprise for the production of RFID tags, which will be the owner of production facilities in Russia, Italy and Serbia, as well as technologies and know-how. It will be created jointly with the Italian company Galileo Vacuum Systems S.p.a. The total cost of the project will be 43 million euros, of which 21 million will be invested by the Russian side.
According to the calculations of the largest Russian retailers (X5 Retail Group, Auchan), as a result of the introduction of RFID systems, there will be a reduction in warehouse costs, as well as a reduction in losses from theft by 40%. The project uses innovative nanotechnology from Galileo Vacuum Systems, which makes it possible to metallize any flexible surface, including selectively (according to a given pattern), with high productivity and low production costs. Another product of the new enterprise will be metallized packaging (film and paper). The production of such materials in the Russian Federation is very promising, since about 80% of the metallized film and almost 100% of paper are imported into the Russian Federation from other countries.