The Logosol DH410 reversible planer has much in common with the PH260. The machine is based on the same principles and most of its components are identical to the PH260, ie. it is a very stable machine with a cast iron worktable and separate motors for each cutter and feed. Both machines also have the same knives and cutting heads.
The difference is that the DH410 works with two cutters instead of four. Four-sided planing is performed by passing the board twice through the machine, with the initial roughing of the board and subsequent refinement to dimensions of 310 mm in width and 100 mm in height.
The DH410 is primarily bought by those who need a machine with the performance of a four-sided planer, but accepting that production will take a little longer. The main advantage of the DH410 over the PH260 is that you get a reliable 410mm wide planer. Some of our customers have modified the DH410 to plan tapered boards for decking or panels. The machine can also be used as a vertical feeder machine. If you will not plan the sides of the boards, replace the steel rollers with rubber ones.
Peculiarities
- Easy installation with a clear scale in 0.1 mm increments.
- Euro connector 16 A.
- Possibility of separate start of each of three engines.
- 6000 rpm guarantees a smooth surface.
- The maximum dimensions of the processed surface: 410x260 mm.
- Stainless steel for outdoor use.
- A low friction insert in the machine table guarantees smooth feeding.
- Maintenance minimum.
The Logosol DH410 planer is primarily bought by those who need a machine with the same processing quality as a four-sided planer, but accepting that the production of products will take a little longer. The main advantage of the DH-410 over the PH-260 is that you get an inexpensive, reliable planer with a 410mm spindle width.
PH-260 / DH-410 operation demonstration:
The DH-410 can also be used as a vertical feeder. If you do not need to plan the sides of the boards, replace the steel rollers with rubber ones.
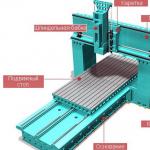
Double-sided machine Logosol DH410 is capable of processing workpieces with a width of 410 mm and a thickness of 260 mm. This is sufficient for most products. For profile planing, profiling and planing are possible at the same time. On the left side of the bed is a side cutter that plans or mills the sides of the workpieces. To achieve a four-sided profiling or thicknessing, the workpiece is planed twice. The maximum dimensions for four-sided profiling are 310 mm wide and 100 mm thick. Everything can be made on the machine: from timber for log cabins to profiled thin laths. By increasing the width of the cast bed, you can produce thin workpieces such as lining and floor lath. The difference in gripping depth between the cutter blades is only a thousandth of a millimeter, due to which the surface of the final product is extremely smooth and even.
The machine offers a wide range of profile knives for moldings. If necessary, it is possible to manufacture knives of a special configuration. The machine can plan deep, beautiful shapes. The machine has the ability to correct cutting errors. The upper horizontal cutter can cut to a depth of 8 mm per pass, and the side cutter cuts even deeper.
As standard, the planer is equipped with flat thicknessing knives HSS for the upper horizontal cutter and 50 mm. for the side cutter. All knives are made from standard steel. The spindle diameter of the side cutters is 30 mm, which allows you to choose cutters from existing ones.
| Workpiece size for one-sided planing, mm | 410 x 260 |
| Workpiece size for double-sided planing, mm | 410 x 260 |
| Horizontal cutter size, mm | D=72, L=410 |
| Max. horizontal cutter diameter, mm | D=72, L=410 |
| Power e / d, kW | 2x3 kw. |
| Number of revolutions, rpm. | 6000 |
| Depth of planing with a horizontal cutter, mm | up to 8 |
| Depth of profiling with a horizontal cutter, mm | to 10 |
| Vertical cutter size, mm | D=90, H=40 |
| Depth of profiling with a vertical cutter, mm | up to 30 |
| Max. Diameter, mm | 140 |
| Landing diameter of cutters, mm | Dox=30 |
| Horizontal knives, mm | 2 x 410 |
| Side knives, mm | 2 x 50 |
| Power e / d supply, kW. | 0,18 |
| Standard feed rate, m/min. | 6 |
| Additional feed rate, m/min. (Option 1) | 2-12 |
| Additional feed rate, m/min. (Option 2) | 4-24 |
Positive features of the machine:
Cast bed

Possibility of separate start of each of three engines.

6000 rpm guarantees a smooth surface.


The maximum dimensions of the processed surface: 410x260 mm.

Stainless steel for outdoor use.
A low friction insert in the machine table guarantees smooth feeding.
Requires a minimum of maintenance.
PH-260 Four Sided Machine Brochure download (*pdf, 0.85 Mb)
PH-260 Quadruple Machine Instruction Manual download (*pdf, 1.03 Mb)
Planer knife catalog download (*.pdf, 3.96 Mb)
In the catalog of planer knives, you can see examples for the profiles of molded products that can be obtained by using them. Planer knives can be used both as leveling knives and as profiling knives. Swedish knives are made of high quality steel and one knife sharpening is enough for 300-600 m.p. material. The number of sharpenings - 5-10 times.
Various equipment can be used for wood processing. The type of equipment used depends on what kind of impact will be carried out: cutting, grinding or planing. Wood planing machines are used for planing wood. It is important to note that there are three almost identical types of cutting: jointing, thicknessing and planing. In recent years, thicknessing machines have become increasingly popular. This is due to what result can be achieved when using them.
Features of the planing process
For the home, various equipment is produced that can be used when working with wood. In order to understand what features a thicknessing machine has, it is necessary to consider the planing process in more detail.
Wood planing is a kind of cutting, which is carried out by reciprocating motion of the cutting tool or the workpiece itself. Such processing involves reducing the thickness of the workpiece in the longitudinal direction. It can be carried out at home in small-scale production or on an industrial scale. Previously, a jointer was used, which performed a reciprocating motion.
The thicknessing machine is made according to the principle of jointer operation: the workpiece or cutting element performs a reciprocating movement to remove a certain layer in one pass.
Thickness planing is a type of planing that allows you to obtain blanks with a given surface finish and the same thickness. The difference from the use of a jointer and the jointing process itself lies in the high accuracy of the obtained dimensions and the degree of roughness.
Classic design
For the home, you can choose a mini thicknessing machine, for industrial scale production - a more powerful model. Both for the home and the industrial version, they have approximately the same design, the key features of which include:
- a wide shaft with knives is used as a cutting tool. The number of knives may vary. They are made using tool steel that can withstand long-term impact. At the same time, sharpening of knives will be needed only after passing a large amount of material through a thicknessing machine;

The quality of processing, compared with the use of a jointer, is much higher, as is the speed of the operation. Due to the similarity of the process of thicknessing and jointing, many manufacturers are creating jointer-thickness machines, which significantly speeds up the process of obtaining the desired result.
Classification
It is possible to divide the thicknessing machines under consideration into two main categories:
- unilateral. In this case, the thicknessing is carried out only on top of the workpiece. The design has only one block with knives.
- double-sided thicknessing machine has an additional you with knives, which is located directly along the plane of the table. Double-sided models have a wide-purpose purpose.
The efficiency of the double-sided version is higher; it is rarely used at home.
Main technical characteristics
The machine has certain technical characteristics, among which we note:
- The maximum width of the processed workpiece. If it has a large width, then you will have to use a jointer. However, when jointing, it is difficult to maintain the desired thickness. The maximum width indicator practically corresponds to the width of the machine itself.
- The maximum thickness of the workpiece to be fed. A mini machine, often household, can have a maximum thickness of the supplied wood of about 10 millimeters, industrial versions up to 160 millimeters. As a rule, the blades are located on top. The design has two racks that rise above the table along with a drum and knives, as well as an electric motor with a drive. The drum is movable and moves in the vertical direction. It also rotates, having one centering axis. Many models have the ability to adjust the depth of cut through the control unit.
- Shaft rotation speed - up to 10,000 rpm. Changing the speed of rotation can be carried out when installing a V-belt drive.
- The power of the electric motor, which is needed to set in motion all structural elements, can be from 1 to 44 kW and more. For domestic use, thicknessing machines with low power are chosen. This is due to the fact that reducing the power leads to a decrease in energy consumption. Higher power allows faster processing of the fed tree, as the maximum penetration per pass is higher. Powerful electric motors require a three-phase power supply. Connecting to a high voltage and running under load causes the motor to heat up. Therefore, powerful models have their own separate cooling system.
- Chip removal is carried out using a special mechanism or manually after stopping the operation of the equipment. Chips must be removed from the cutting zone, as they can affect the accuracy of removing the wood layer.
- The amount of clamping force. Wood blocks of a certain length, width and thickness are pressed close to the cutting zone. This is necessary in order to improve the accuracy of removing a certain layer of wood.
- Some models have a control panel with keys, others have pedals. The control unit, as a rule, has a standard set of functions.
Similar qualities are characterized by a double-sided and one-sided version of the machine type under consideration.
Model selection
After we have decided what a thickness gauge is and what it is for, we have considered the main characteristics and purpose of the structural elements, we can proceed to the question of choice. When considering models for the home, many people think that it will be cheaper and easier to purchase a jointer. However, you should not compare a thicknessing machine and a hand tool.
The machine has the following advantages:
- high performance. Without extra effort, if you abandon a hand tool in favor of a mechanized one, you can process a large amount of material. For one volume, when using a manual jointer, planing takes almost the whole day, with a mini electric planer it will take an hour or more, the thicknesser will do it in a few minutes;
- simplicity and safety of the device. When using a jointer, you can get injured, rub blisters, and get physically exhausted. At the same time, only professionals with extensive experience can achieve the desired result;
- it is practically impossible to achieve the most even surface when using a jointer or an electric planer, since a person cannot determine and accurately control the force of his impact. It is possible to use a thicknessing machine to obtain a surface with high-precision dimensions and a degree of roughness.
There are quite a few reasons why they buy a thicknessing machine for home and industrial production.
There are several main criteria by which the choice of thickness gauge is carried out:
- Budget. The magnitude of the upcoming costs excites almost everyone. You should not choose cheap options if you plan to run more than 5 cubes of wood through the equipment per year. Cheap models are not designed for a large amount of work, they can fail when a high load is applied. Also, when creating them, non-energy-saving elements are used, since they have a high cost. The cost of hardy models is about 20 thousand rubles. For a one-time repair or construction of a house, a model is suitable, the cost of which does not reach 17 thousand rubles.
- The place of use and installation also plays an important role. The machine often has to be installed indoors, as it has an electrical supply that is not protected from exposure to high humidity. When considering the machine, its dimensions should be taken into account: after installation, free access must be provided on each side, which will allow convenient work.
- The main characteristics that are taken into account when choosing are the power of the electric motor, the depth of cut, the width of the workpiece, the shaft speed and the weight of the machine itself. All parameters, with the exception of weight, determine what material can be obtained after processing the workpiece. The weight of the structure determines the possibility of its installation at home. If the weight is very large, then you need a special plate that can withstand the load.
In addition to the above points, the popularity of the brand under which the machine model is produced is taken into account. How to choose a thicknessing machine for home? Low cost, but also insignificant performance is typical for Hitachi P13F, Caliber RR-1900/330 or STURM TH14203. To establish production, you should choose the Makita 2012 NB, Metabo DH 330 0200033000 and DeWalt DW 733 models. They have high reliability and performance.
With the help of a planer, perpendicular surfaces are planed, chamfers are formed at the ends of the workpiece at a given slope. Devices with similar functionality are produced by Jet, Zauber, Dewalt, Makita, Felisatti and some others.
The units are quite easy to use, allow you to produce wooden parts of the desired size.
Types
Depending on the number of cutting elements, jointers are single-sided and double-sided. Equipment may differ in other characteristics:
- planing surface width (400 mm, 500-520 mm, 600-630 mm);
- tabletop length (up to 2500 mm, 2500–3000 mm);
- knife shaft speed (4700–4800 rpm, 5000 rpm).
Home tools are compact, the processing width is less than that of industrial designs. Long worktops allow you to plan large-sized workpieces, while the quality increases. An engine installed on an industrial machine can demonstrate a high speed of rotation, reaching 12,000 revolutions per minute. The motor that completes the household instance has lower performance.
Work principles
Single-sided planers designed for small private workshops can be operated by one operator. The lumber is laid with the convex side up on the front half of the countertop. In this case, the workpiece is held with two hands, fed to the cutting element. The processed part of the board is pressed with the left hand against the back of the desktop. Planing of each side is performed 1-2 times, depending on the initial state of the wood.
When processing perpendicular sides with a one-sided machine, a large plane is first fed to the planer cutter. The two - sided unit allows cutting two planes at the same time . The fact that the knife is blunt, requires sharpening or replacement, is evidenced by defects in the form of moss, arson on the surface of the board. Parts with a length of less than 400 mm, a width of not more than 30 mm, when fed to the jointer, are held by pushers. If the workpiece has a complex configuration, it is held by templates.

If after sawing the surface of the board has become curved, has taken the form of an impeller, it is necessary to adjust the planer, re-align the level of the plates, the knife shaft.
Wood dust can be removed with an industrial vacuum cleaner pre-installed on the equipment.
Customization Rules
It is best to place parts 1–1.5 m long on the machine for further processing. If the workpiece is shorter, it can slip out from under the knife and injure the operator. Too long sawn timber is inconvenient in planing. Getting started, you need to determine the thickness of the removed layer of wood. In the case of equipment equipped with autofeed, you must set the speed.
The thickness of the layer to be removed is determined by eye or after a test planing. If untouched areas are visible after the completed sawing cycle, the table should be lowered slightly. With an error of more than 2.5 mm, two cutting cycles are performed. After setting the height, the distance between the edges of the knives and the plates is measured. The optimal gap is 2–3 mm. If the parameters are exceeded, the wood will be torn in pieces, with a gap of up to 2 mm, the cutter will be deformed.
It is also necessary to determine the location of the guide rail. The distance between it and the left edge of the knife shaft must exceed the width of the bar. If the knife becomes dull, the ruler will move to the right, engaging all segments of the cutter. To perform a corner chamfer on the edge, the guide is mounted using a square.

The correctness of the adjustment of devices and mechanisms is determined empirically. In this case, the maximum permissible errors are taken into account (plane - 0.15 mm per 1 m, perpendicular - 0.1 mm per 10 cm).
Models
When choosing equipment, you need to take into account the size of the workpiece, the amount of work performed. If you plan to process small bars, you can purchase a compact model with a power of 4 kW. For large lumber, you will need a larger unit with a high-performance engine.
- Jointing machines "Kraton"
Model Kraton WMPT-260 (39,300 rubles) performs jointing and thicknessing, has a power of 1500 W, is compact, equipped with automatic feeding of workpieces.
- Jointer JET
Combined machines JET JPT-10B (34,000 rubles) with a power of 1.5 kW are distinguished by small dimensions, the ability to lengthen the working surface.

JET JPT-310 machines (80,000 rubles) have a power of 5 kW and are distinguished by double motor insulation. It is possible to connect a vacuum cleaner.
Jointer JET Jointer 6 '' (193,000 rubles) with a capacity of 3.5 kW is equipped with a shaft with 48 knives. This is equipment for planing and thicknessing.
- Machine tools SF-4
The single-sided jointer SF-4 (179,000 rubles) has a two-knife round shaft that rotates at 5,000 rpm. The machine is equipped with a three-phase squirrel-cage asynchronous electric motor.
- Machine Holzstar ADH 305
Planer-thickness unit of desktop type, with a power of 1.8 kW, equipped with two knives, rubber-coated output shaft. The average price is 44,900 rubles.

- Trademark Corvette
Series 106 (29,960 rubles) with a power of 1.5 kW is equipped with special pushers, a shaft with three knives.
The Encore Corvette-24 sample (18,130 rubles) has a power of 1.25 kW, which allows you to quickly switch planing from thicknessing to planer.
- Machine tools MB5026
One-sided model MB5026 (54,900 rubles) made in China is equipped with a shaft with three cutters, has a power of 3 kW.
- Trademark: Scheppach
Planing and thicknessing machines Scheppach HT-1050 (23,000 rubles) with a power of 1.5 kW, a capacity of 9000 rpm demonstrate reliable operation, clean processing of lumber.
A sample Scheppach HT-850 (17,000 rubles) of combined action with a 1.25 kW motor is compact and allows you to get a smooth surface of the workpiece.
The jointer HT-650 (18,020 rubles) is equipped with a 1.28 kW engine, has a mobile design, and provides for manual feeding of lumber.
| Manufacturer | Model | Power, W | Average price, rub |
| Kraton | WMPT-260 | 1500 | 39 300 |
| JET | JPT-10B | 1500 | 34 000 |
| JPT-310 | 5000 | 80 000 | |
| Jointer 6'' | 3500 | 193 000 | |
| Kurgan plant of woodworking machines | SF-4 | 2800 | 179 000 |
| Holzstar | ADH 305 | 1800 | 44 900 |
| Corvette | 106 | 1500 | 29 960 |
| Anchor Corvette-24 | 1250 | 18 130 | |
| — | MB5026 | 3000 | 54 900 |
| Scheppach | HT-1050 | 1500 | 23 000 |
| HT-850 | 1250 | 17 000 | |
| HT-650 | 1280 | 18 020 | |
| Makita | 2012NB | 1650 | 41 000 |
| DeWalt | D27300 | 1600 | 78 900 |
The price of Makita and DeWalt machines depends on the type of device and its configuration. Planer-thickness machine Makita 2012NB has a power of 1.65 kW, the price is about 41,000 rubles. The DeWalt D27300 machine with a power of 1600 W costs 78,900 rubles.
Video with a review of the jointer Enkor Corvette-24.
Jointers
TO category:
Woodworking machinery
Jointers
Design
On one-sided jointing machines, one of the planes of the workpiece (usually a face) is aligned or sequentially, in two transitions, two planes of the workpiece. The working body is a horizontal knife shaft, on which two, less often four legs are installed. The machines are designed for processing blanks and panels up to 600 mm wide.
The scheme of a single-sided planer is shown in fig. 130 The machine bed is cast, box-type. The machine has a front and rear tables, a guide line. The guide ruler is cast, with well-crafted support and vertical planes. They are mounted on the machine with a bracket.
A knife shaft is installed horizontally on the frame in ball bearings. The shaft is closed by a fan-shaped guard hinged to the machine. Thanks to the spiral spring, the guard is pressed against the guide rail, completely covering the knife shaft.
Each table is mounted on two eccentric rollers movably fixed in a slide separate for each table. The slides are bolted to the frame. Eccentric rollers allow you to move the tables in height, the sled to bring the tables closer or further away from the knife shaft.

Rice. 1. Schematic diagram of a one-sided planer: 1 - rear table, 2, 15 - eccentric rollers, 3 - thrust. 4 - bracket, 6 - nut, 6 - knife shaft, 7 - fan guard, 8 - bracket for fastening the guide ruler, 9, 11 - screws, 10 - bar, 12 - guide ruler, 13 - front table, 14 - mechanism handle raising and lowering the front table, 16 - slide, 17 - installation location of the push-button station, 18 - hand brake levers, 19 - knife shaft lock, 20 - frame, 21 - electric motor, 22 - hand brake cover
The horizontal position of the tables during lifting and lowering is maintained due to the pairwise connection of the eccentric rollers in the rods-screws 3. Lower and raise the front table by moving the handle in the plane of the sector with divisions; the position of the rear table in height is adjusted by changing the position of the screw rod with nuts.
The starting equipment of the electric drive is mounted in the frame. For sharpening and planing knives directly on the knife shaft, a special device can be provided.
Double-sided jointing machines have a second working body - a vertical spindle, which allows you to simultaneously process two surfaces of workpieces (face and edge) on them with the formation of a right angle between them.
In addition, they differ from single-sided planers by the presence of a composite guide bar. The machines are equipped with automatic feeders, depending on the design of which, for a change in height, adjust the handwheel.

Rice. 2. Double-sided planer S2F4-1: 1 - bed, 2 - rear table, 3 - handwheel of the mechanism for raising and lowering the car lift, 4 - automatic feeder, 5 - guide ruler, 6 - front table, 7 - handle of the mechanism for setting the table in height, 8 - control panel

Rice. Fig. 3. Scheme of the vertical spindle and the composite guide ruler of the double-sided planer: 1 - fixed part of the ruler, 2 - fixing screw, 3 - bracket, 4 - rack, 5 - V-belt transmission, 6 - electric motor, 7 - screw for belt tension, 8 - plate for fixing the electric motor, 9 - handle for mounting the bracket, 10 - eccentric for installing the movable part of the ruler, 11 - movable part of the ruler, 12 - cutter head, 13 - spindle
When changing the cutting tool, the automatic feeder is retracted to the side. To brake the knife shaft, an electromechanical brake is provided, interlocked with the “Stop” button of the machine.
The spindle (Fig. 3) is fixed with a bracket on a fixed stand. The electric motor is connected to the spindle through a V-belt transmission. The spindle rotates at a frequency of up to 7000 rpm, the diameter of the cutting circle is 104 mm. There is a cutter head on the spindle. The guide ruler is composite: its main part is fixed, the movable part is moved in a horizontal plane by turning the eccentric. When the eccentric is fully rotated, the movable part of the ruler moves relative to the fixed part by 2 mm.
Operating mode selection
First of all, it is necessary to determine the thickness of the removed layer of wood, and if the machine is equipped with an automatic feeder, then the feed rate.
The thickness of the removed layer depends on the warp of the workpieces, the magnitude of which is determined by trial processing of 3-5 workpieces.
If the processed workpieces have unplanned places, the front table is lowered by the desired amount. With a warp value of more than 2-3 mm, jointing is carried out in two passes.

Rice. 14. Surface machined by milling: a - general view, b - surface with the trajectory of the cutting edge of the cutter
Knowing the amount of feed per knife, the cutting radius, the number of knives and the frequency of rotation of the knife shaft, it is possible to calculate the numerical value of the size of the irregularities and thus the roughness class of processing and, conversely, determine the allowable feed rate from a given surface roughness class.
Machine setup
Adjustment of single-sided planers consists in setting the rear and front tables in height, as well as the guide line.
The working surface of the rear table must coincide with the horizontal tangent to the cylindrical cutting surface or be 0.02-0.03 mm lower than it. In this position, the kinematic irregularities do not rest against the sponge of the table. To set the table in the desired position, take a properly machined hardwood block, place it firmly on the table and turn the cutter shaft by hand. If at the same time the knives lightly touch the bar, then the table is set correctly, the bar lies on the knife - the table must be raised. Raise the table by moving the nut with a wrench along the rod screw connecting the eccentric rollers of the rear table. Adjust the back table after each change of knives and their regrinding and planing directly on the shaft.
The position of the front table relative to the back table depends on the thickness of the removed layer of wood, which should not exceed 2 mm. It is determined by the distance from the working plane of the front table to the horizontal tangent to the cylindrical cutting circle. The table is moved in height with a handle, setting it against the corresponding division marked on the sector. The design of the table movement mechanism allows you to quickly raise and lower the table by moving the handle, which is used for longitudinal milling of warped workpieces.
Having adjusted the tables in height, check the distance between the jaws of the tables and the cutting edges of the knives. It should be within 2-3 mm. Measure it with a calibrated plate of the appropriate thickness. The plate should easily, but without play, enter the gap between the sponge and the knife blade. At a distance of more than 3 mm, tears are obtained on the workpiece, less than 2 mm - the cutting edge of the knife is crumbled. Adjust the gap by turning the shaft until the knife is against the jaw. By unscrewing the screws, the slide with eccentric rollers is moved until a gap of 2-3 mm is obtained along the entire length of the knife shaft. After that, the slide is securely fixed.
When planing squared blanks, the distance between the guide ruler and the left end of the knife shaft should be slightly greater than the width of the workpiece being processed. As the knives become dull, the ruler is gradually moved to the right to ensure that the non-blunt sections of the knives participate in the work. Across the table, the guide ruler is moved by a rack and pinion mechanism driven by a handwheel. For longitudinal milling of the edge of the part at an angle to the face (usually 90 °), the guide ruler is set using a metal square or (at an angle other than a straight one) an appropriate template. To do this, the control square (template) is installed on the rear table of the machine. The gap between the flange of the template square and the surface of the guide ruler should not exceed 0.05 mm over a length of 1001 mm. The guide line, set at a certain angle, is fixed with a screw.
When setting up double-sided planers, the tables and the fixed part of the guide bar (above the back table) are adjusted in the same way as in single-sided planers. The plane of the movable part of the guide ruler (above the front table) must be separated from the plane of the fixed part of the guide ruler by the thickness of the layer of wood removed from the edge of the workpiece. It is set to the desired position by turning the eccentric handle, which moves along the hkoba, which has the shape of a semicircle.
If the handle is in the middle of the semicircle, will the ruler take a position in which the thickness of the cut wood layer will be 1 mm? if the handle is on 1/4 of a semicircle - 0.5 mm, etc. The tangent to the cylindrical cutting surface of the knives of the head mounted on a vertical spindle must coincide with the plane of the fixed part of the guide ruler or be 0.01-0 away from it .02 mm. To install the head, a bar with aligned planes is pressed against the fixed part of the ruler and the bracket carrying the head is rotated until the cutter head takes a position in which the cutting edges of the knives will lightly touch the bar. In this position, the head is fixed by tightening the locking screw of the bracket.
Both automatic feeders and conveyor feeders are set to feed workpieces of a certain thickness. Workpieces should be fed without “slippage” and with a slight pressure on them from spring-loaded rollers, chains or claws.
The supply of workpieces also depends on the location of the automatic feeders. When processing layers, it is better to install the automatic feeder behind the knife shaft (at a distance of 30-40 mm from it), when processing thick workpieces, the feeding organs can be located above the front table. The automatic feeder is installed at a slight angle to the guide rail, which ensures that the workpiece is pressed against it.
Automatic feeders are also used on one-sided planer machines. For planing the edges of the workpieces, they are installed parallel to the guide ruler; in this position, the automatic feeder presses the workpiece to the guide ruler and the machine table.
The setting is checked by trial jointing. The deviation from the plane should not exceed 0.15 mm over a length of 1000 mm and from perpendicularity - 0.1 mm over a length of 100 mm.
Work on machines
One worker works on a single-sided planer, two on a two-sided planer. The machine operator takes a workpiece from the stack, inspects it and lays it with a concave surface down on the front table. Pressing the workpiece with both hands to the guide ruler, feeds it onto the knives. In the future, when moving the workpiece with his left hand, he presses the processed part of the workpiece to the plane of the rear table. After the next pass, the machine operator again inspects the workpiece and either stacks it, or, in the case of a difficult horn, sends it back to the machine. Workpieces with a strongly warped surface should not be planed, since the chips have to be removed in several passes and the thickness of the workpieces as a result of such processing is reduced to the size at which they are transferred to marriage.

Rice. 5. Device for feeding short workpieces to the cutting tool: 1 - workpiece, 2 - pusher
If the part needs to be aligned with two mutually perpendicular surfaces, then at first they align the wider one (for example, the face), and then the workpiece is pressed with this surface to the guide ruler and the second surface (edge) is milled. On a double-sided planer, this operation is performed in one pass.
On a planer, you cannot mill to size in thickness or obtain workpieces with parallel planes. This is done on other machines, such as thickness gauges. The optimal length of parts processed on planer machines is 1-1.5 m; shorter workpieces should be milled using a special tool (fig. 5); longer planing is inconvenient and difficult due to the large mass.
If the machined surface will have curvature or winging, it is necessary to align the position of the tables relative to the knife shaft. When “beating off” the workpiece with knives, the appearance of moss and arson on the treated surface, the knives should be sharpened; if two adjacent planes are not at right angles, you need to adjust the guide ruler.
Workpieces shorter than 400 mm, 50 mm and thinner than 30 mm, when manually fed, can be directed to the cutting tool only by pushers, and curved workpieces - by templates. It is forbidden to perform shaped longitudinal milling and quartering on jointers.
Machine construction. Jointing machines are distinguished by the largest width of the workpiece being processed: 250 mm (SFZ-Z, SFAZ-1, S2FZ-E), 400 mm (SF4-1, SFA4-1, S2F4-1) and 630 mm (SF6-1, SFC6- 1).
According to the number of cutting mechanisms, there are single-sided and double-sided machines. On double-sided machines (S2FZ-E, S2F4-1), two surfaces of the workpiece are milled simultaneously: face and edge.
According to the type of feed of the processed material, planers with manual and mechanized feed are distinguished. Mechanized feed is carried out by attached automatic feeders (SFAZ-1, SFA4-1) or a conveyor feed mechanism built into the machine (SFK6-1).
To collect and remove chips and dust, the machines are equipped with chip receivers connected to the factory exhauster network.
Single-spindle planer SF6 is shown in fig. 1. A cutter shaft, front and rear tables and a guide fence are mounted on a box-shaped bed. The knife shaft is mounted on ball bearings and is driven by an electric motor through a V-belt transmission. The electric motor is located on the under-engine plate inside the frame. For a quick stop of the knife shaft there is a brake acting from an electromagnet.

Rice. 1. Single-spindle planer SF6: 1 - bed, 2.8 - tables, 3 - fence, 4 - guide ruler, 5 - knife shaft, 6 - clamps, guide ruler fastenings, 7 - bracket, 9 - scale, 10 - handle for adjusting the table height
To change the thickness of the layer to be removed, the front table can be moved in height relative to the knife shaft. The rear table is designed for precise basing of the machined surface of the part. It is made unregulated, i.e. rigidly attached to the frame, or adjustable in height. The presence of the adjustment mechanism makes it easier to set up the machine. The guide ruler is designed for precise lateral positioning of the workpiece. It is made in the form of a narrow plate and mounted on a bracket. It can be tilted to the working surface of the table and moved along the width of the machine. The working area of the knife shaft is closed by a fan guard.
Double-sided planer with horizontal and vertical spindles S2FZ-2 is designed for simultaneous milling of the face and edge of the workpiece. Unlike a one-sided planer, it is additionally equipped with a vertical edge jointing head, front and rear guide lines. The front ruler can be adjusted relative to the head for the thickness of the layer to be removed. The edge jointing head is driven by an individual electric motor mounted on a bracket at the back of the bed. The processed material moves the rotating rollers of an automatic feeder.
Planer with built-in conveyor SFC6-1 has a conveyor feed mechanism. It is made in the form of an endless chain, put on sprockets, one of which is a drive one. Spring-loaded pointed metal grips are attached to the chain links for a secure grip on the workpiece. The feed mechanism is mounted on two racks and can be moved in height from a separate electric motor through a screw and worm gear.
Setting up machines. Adjustment includes the installation of knives in the knife shaft, adjusting the position of the tables, the guide line and the feed mechanism. Properly prepared knives should be installed in the cutterbar. They must be sharpened, balanced and balanced. Before installing the knives in the knife shaft, you must:
turn off the input switch; turn the automatic feeder to the non-working position or raise the support of the conveyor feed mechanism; move the guide ruler to the extreme right position; lower the front table to the extreme position; fix the knife shaft with a locking device; loosen the blade fastening screws and remove the dull blades; clean the grooves in the body and the wedges from chips, dust and resin; install prepared knives.
The knife is installed in the knife shaft so that its cutting edge protrudes beyond the edge of the pressure wedge (chip breaker) by 1.5 ... 2 mm with a cut layer (chip) thickness of more than 0.2 mm and 0.5 ... 0.2 mm. The non-parallelism of the cutting edge of the installed knife of the working surface of the rear table should be no more than 0.1 mm over a length of 1000 mm.
To achieve the required installation accuracy, control and installation devices are used (Fig. 2). The installation accuracy is controlled by a ruler or a wooden bar with a section of 30 X 50 mm and a length of 400 mm. The bar is placed on the back table of the machine to the end of the knife shaft (Fig. 2, a). The shaft is turned manually and, having loosened the fixing screws, change the position of the knife so that the cutting edge touches the bar. The fastening screw closest to the bar is slightly tightened. Rebasing the bar, align the position of the other end of the knife. The position of the knife is adjusted so that its edge along the entire length is located equally relative to the bar. The following knives are also adjusted. The adjusted knives are finally fixed with screws. The gap between the knives and the jaws of the body is not allowed. The quality of the installation of knives is controlled by the force of turning the knife shaft manually and by the sound that occurs when the knife comes into contact with the working surface of the template.
In some cases, to achieve installation accuracy, a template is used, made in the form of a C-shaped bracket (Fig. 79.6). The bracket is equipped with base supports, with which it is installed on the body of the knife shaft. The template is preconfigured. Using a screw, adjust the base stop to ensure the optimal protrusion of the knife relative to the body. When setting up, the cutting edge of each knife is brought to touch with the base stop. By moving the bracket along the knife shaft, the knives are parallel to the shaft body.
The device with an indicator (Fig. 2, c) has a body with precisely ground plates, in which a dial indicator is fixed. The device is installed on the back table so that the stop touches the cutting edge of the knife. The position of the knife in the body is adjusted using the indicator scale. The device allows you to install knives on the same cutting circle with an error of up to 0.02 mm while ensuring parallelism and the necessary extension of the knives relative to the working surface of the rear table.
After the final tightening of the spacer bolts, the blades may move. Therefore, you should once again check the correctness of their installation, rotate the shaft idly and make sure that the knives are securely fastened.
The rear table is set so that its working surface is tangent to the circle described by the cutting edges of the knives, or 0.02 ... 0.03 mm below it (Fig. 3, a). If a verified template (control ruler) is used when setting up the knife shaft, then the knives will be installed tangentially. If a control and installation device is used during adjustment, basing it on the cylindrical surface of the knife shaft housing, it is necessary to adjust the position of the rear table in height. The table is adjusted by turning the eccentric rollers through the rod-screws 2 with the nut 3, and the accuracy of the installation is controlled by a verified template or indicator device.

Rice. 2. Alignment of knives in the knife shaft of the jointer: a - with a control ruler or a wooden block, b - with a template, c - with a device with an indicator; 1 - bar, 2 - table, 3 - knife shaft, 4 - stop, 5 - bracket, 6 - lock nut, 7 - screw, 8 - body, 9 - indicator
When processing bar parts, the guide ruler is positioned so that the distance to the left end of the knife shaft is slightly greater than the width of the workpiece being processed. As the knives become dull, the ruler is moved to the right and the parts are processed with that part of the knife shaft on which the knives have not yet become dull. When machining parts with non-perpendicular adjacent surfaces, the guide ruler is positioned so that the angle between its working surface and the knife shaft is obtuse.
The guide rails of the reversible planer perform the same functions as the front and rear tables. The rulers are adjusted relative to the edge jointing head with a handle, and the amount of the layer to be removed is set according to a scale mounted on the frame.
The automatic feeder or conveyor feed mechanism is adjusted in height (Fig. 3, b) with a handwheel depending on the thickness of the workpieces being processed. The distance from the working surface of the front table to the feed rollers (conveyor fingers) should be 2 ... 3 mm less than the thickness of the workpiece. The automatic feeder is placed above the knife shaft so that the first feed roller is above the front table at a distance of 50 ... 60 mm from the knife shaft, and the other rollers are above the rear table.
Relative to the guide line, the automatic feeder is oriented so that the rollers are not parallel to the axis of the knife shaft (angle 1 ... 30), for which the automatic feeder is turned relative to the vertical axis. This arrangement of the feed rollers allows you to press the workpiece to the guide ruler and improves the conditions for its basing.
The pressure of the feed elements on the workpiece must be sufficient to feed without slipping. Excessive pressure causes increased wear of the automatic feeder mechanisms and deformation of the part in the area of the knife shaft.

Rice. 3. Setting up the jointer: a - setting up the tables, b - installing the automatic feeder; 1 - rear table, 2 - rod-screws, 3 - nut, 4 - knife shaft, 5 - front table, 6 - adjustment knob for the thickness of the layer to be removed, 7 - scale, 8 - eccentric roller, 9 - rods
The front table is set so that its working surface is below the upper generatrix of the circle described by the cutting edges of the knives. The value of the protrusion of the knives relative to the front table determines the thickness of the layer to be removed. Since the thickness of the largest layer depends on the degree of warping of the workpiece, the table is adjusted in height before processing each workpiece. By rotating the eccentric rollers through the rods, the handle 6 raises or lowers the table. The amount of lift is controlled on a scale.
Work on machines. The hand-feed planer is operated by one worker for processing small workpieces. The machine operator takes a workpiece from the stack, visually evaluates the convex and concave edges of the workpiece and places it with its concave surface on the front table. Severely warped and defective workpieces should be discarded.
Pressing the workpiece to the side of the table and the guide ruler with the left hand, with the right hand it is fed onto the knife shaft. When moving, the front end of the workpiece pushes the fan guard and thus provides access to the rotating knives.
After processing the front end of the workpiece, with your left hand, firmly press the processed part against the plane of the rear table and continue feeding.
When feeding, carefully monitor the position of the hands relative to the knife shaft and keep them at a safe distance. When processing small parts, there is an increased risk of injury, so workpieces shorter than 400, narrower than 50 and thinner than 30 mm are fed into the machine only with a special pusher (Fig. 81). After each pass, the machine operator evaluates the quality of processing and, if the surface is not pierced, it is re-sanded.
If the part needs to align two surfaces, then first the face is milled, and then the edge, pressing the part with the previously machined surface to the guide ruler. On double-sided machines, these operations are performed in one pass.
When processing massive and large parts, the machine is operated by two workers. The machine operator bases and feeds the workpiece, and the second worker, being behind the machine, helps at the final stage of processing, receives the finished part and stacks it. If necessary, additional roller tables are installed in front and behind the machine.
The manual feed rate on the machine is selected individually for each workpiece, depending on the defects and the required milling depth. Reduce the speed for cross-cutting and milling against the grain. The depth of milling depends on the machining allowance and the size of the defects.

Rice. 4. Scheme for processing small parts using a pusher
Removal of the allowance in one pass usually does not allow obtaining the required quality of processing. The best effect is achieved in two or more passes at a small milling depth, since in this case the deformation of the part under the action of clamping forces and internal stresses in the workpiece material is reduced.
In machines with mechanized feed, the feed rate is selected according to the schedule from the condition of maximum loading of the cutting motor and ensuring a given surface roughness.
The received parts must be checked for accuracy of processing. By applying one part to another with processed surfaces, visually, the magnitude of the processing error is judged by the size of the gap between them. In addition, the flatness of the machined surface can be checked with a straight edge and feeler gauge. The deviation from the plane should not exceed 0.15 mm over a length of 1000 mm. Adjacent machined surfaces must be mutually perpendicular. The tolerance is 0.1 mm at a height of 100 mm. Perpendicularity is checked with a square and feeler gauge. The roughness of the treated surface should be 60 ... 100 microns. If the parts do not meet the specified requirements, the machine should be readjusted.
Jointing machine SF6-2 consists of a bed and a working table, which is two horizontal smooth cast-iron plates (rear and front), equipped with thin steel jaws on the side of the knife shaft. The purpose of the sponges is to protect the ends of the plates from abrasion, to reduce the gap between the knives and the plates, and to support the fibers when cutting chips. A knife shaft is placed between the plates. The cutter shaft is located so that the cutting edges of the knives mounted on it are flush with the rear plate. Each plate can be individually raised and lowered with a screw.

Rice. 1. Device for balancing knife shafts
A guide ruler is fixed on the table, which can be moved along the width of the table. The jointer is powered directly by the electric motor through a V-belt transmission.
When jointing, the material to be processed is placed on the front plate of the table, if possible at a right angle to the knife shaft, and, pressing tightly to the plate with the left hand near the knives, with the right hand farther from them, they push it onto the knives, which plan the lower surface of the part.

Rice. 2. Planer SF6-2:
a - general view: 1 - electric motor, 2 - rear plate of the desktop, 3 - guide ruler, 4 - handle of the front plate height indicator, 5 - knife shaft, 6 - fan guard, 7 - front plate of the desktop, 8 - starting device , 9 - bed; b - jointing scheme: 1 - rear plate, 2 - front plate, 3 - chip thickness
When the front end of the part passes behind the knives, the part is taken with the left hand to the surface of the back plate, and with the right hand to the surface of the front plate. The pressure should be as uniform as possible, and the feed should be smooth and even.
First, the wide side of the part (face) is sharpened, and then the narrow side (edge). When planing the second adjacent side, the part should be pressed against the table and against the guide ruler.
To avoid excessive scuffing of the fibers, it is necessary to cut along the layer. When planing parts from pine wood, it is recommended to wipe the desktop with a rag moistened with kerosene, since the resin released from the wood sticks to the table and makes it difficult to move the parts.
With a very careful installation of knives on the knife shaft, it is still not possible to arrange their cutting edges exactly along the same circle, and a difference of 0.5-0.1 mm is obtained in the cutting radii. Because of this, waves appear on the treated surface. To reduce this difference, a device for planing and straightening knives is used at the installation site. The device is produced together with a folding machine and separately attached. After planing and straightening the knives, the difference between the cutting radii decreases to 0.03-0.02 mm and the planed surface is smoother.
The sharpening part of the tool is brought into contact with the blade of one knife on the knife shaft and fixed in this position. Then turn on the device and move it along the guide ^ along the entire length of the knife, aligning the blade and straightening it. Having finished editing one knife, turn the knife shaft, bring the second knife under the grinding part of the device and repeat jointing and editing. In this way, the blades of all knives fixed on the cutter shaft are processed.
To feed the material, it is necessary to use special pads-pushers that ensure the safety of work and prevent fingers from touching the knives.
The planing width on the SF6-2 machine is 600 mm, the thickness of the removed layer is 6 mm, the cutting diameter is 125 mm, the number of knives on the shaft, the number of revolutions of the knife shaft per minute is 5000, the power of the knife shaft electric motor is 4.5 kW. Machine weight 860 kg.
Jointing machine SF4-4 is designed for planing and leveling the surface along the plane and for milling into the corner of boards and bars. The machine has a round two-knife shaft with wedge-mounted knives. The spindle for vertical milling consists of front and rear guide rulers and a spindle block with a double-knife head. The front ruler is movable, it is moved in accordance with the specified milling depth; the rear line is fixed motionless. The spindle is driven by an individual electric motor via V-belts. The machine is equipped with automatic feeder UPA-3, which automatically feeds the workpieces.
The planing width on the machine is 400 mm, the thickness of the layer to be removed is 6 mm, the diameter of the knife shaft is 125 mm, the cutting diameter is 128 mm, the number of knives on the shaft, the power of the electric motor of the knife shaft is 2.8 kW, the number of revolutions of the knife shaft per minute is 5000, the weight of the machine is 620 kg .
jointing machine SF4-4 makes it possible to perform jointing and milling, i.e., on one machine to combine several operations that require two different machines. It creates savings in production space, equipment productivity increases. Labor productivity is doubled by speeding up supply and reducing the number of workers.

Rice. 3. Planer SF4-4
To prevent accidents, a protective shield or safety curtain is installed above the knife shaft, which are moved aside during operation by the workpiece itself, and after the workpiece passes, under the action of a spring, the entire knife shaft is closed again.
To mechanize the supply of the workpiece, you can use attached roller automatic feeders, in which the rollers are driven by an electric motor through a gearbox. The body of the auto-feeder, with the help of levers and a rack, can be installed so that the rollers will press the workpiece to be processed against the table or against the guide ruler.
Existing fences for woodworking machines are mostly bulky and do not differ in versatility. The Kurgan woodworking machine plant produces the UPA-3 automatic feeder, which can be used as a universal fence on circular saws, planers and milling machines.
Using the UPA automatic feeder, the rack with the fixture is installed either on the machine table, or on a platform fixed next to the machine, as well as on a separate foundation to the right or left of the machine.

Rice. 4. Protective fences for planer:
a-shield of Erokhin; b - fan fence; 1 - spring shield, 2 - curtain; c - automatic feeder with top clamp: 1 - stand, 2 - automatic feeder, 3 - front table
The body of the automatic feeder with the help of hinges and a rack can be installed so that the rollers will press the workpiece during its processing to the table or to the guide ruler.
On the jointer, the UPA-3 automatic feeder is installed so that the first pair of rollers is located above the front part of the table, the second and third pairs are located above the back. According to the width of the machine, the feed rollers are installed in the middle of the planed material.

Rice. 5. Universal fence - automatic feeder UPA-3 (view from the side of the processed material)
The distance between the rollers and the machine table is set less than the thickness of the feed material. The material is fed manually up to the second pair of rollers, and then by an automatic feeder.
The double-sided planer S2F-4 with mechanical feed and edge jointing head is shown in fig. 6. The machine is used for simultaneous planing and planing of the lower layer and the right edge of one workpiece (corner planing). The machine consists of a cast-iron bed, on which two plates are located on eccentric supports - front and rear, between them there is a knife shaft with a diameter of 125 and a length of 410 mm, which has a fan guard. The knife shaft rotates on ball bearings and is driven by a 4.5 kW electric motor through a V-belt drive. There is a guide line on the plates. The front plate serves as a guide for the workpieces before planing, and the rear plate is designed to move the workpieces during planing. The size of the removed layer of wood is regulated by raising or lowering the front table using the handle, which has a height indicator. The rear plate is adjusted with a screw or nut. The planing width of the machine is 400 mm. The thickness of the workpiece being processed is 15-100 mm, the thickness of the layer being removed is 6 mm, the number of knives on the shaft is 2-4, the number of revolutions per minute of the knife shaft is 6000, the weight of the machine is 800 kg. On the machine, in addition to the horizontal knife shaft, a vertical knife head is mounted, through which the edge of the workpiece is planed. The vertical cutterhead is mounted on a edge jointing spindle mounted on a special support. The autofeeder and edger head have individual electric motors. Therefore, the drive of the spindle of the vertical cutter head is carried out from one electric motor with a power of 1.7 kW through a V-belt transmission. The blanks and lumber are fed to the horizontal cutterhead by an automatic feeder, which is driven by another electric motor through a gearbox. The automatic feeder is located on the side of the machine on a vertical bar and, depending on the thickness of the workpieces being processed, can move in vertical and transverse directions. Button control.

Rice. 6. Double-sided jointer S2F-4 with automatic feeder and edge jointer head:
1 - control buttons, 2 - knife shaft fan guard, 3 - rear table, 4 - automatic feeder, 5 - edge jointing spindle, 6 - rear table height adjustment screw, 7 - guide ruler, 8 - handle of the eccentric mechanism for front table height adjustment , 9 - front table
Jointers with mechanical feed of parts are more productive than the machines with manual feed discussed above.
The device for mechanized feeding of parts has rollers covered with rubber or a conveyor chain. The rollers are driven by an electric motor through a gearbox. The conveyor chain has spring pins. Endless chains of fingers, moving towards the knife, capture the workpiece and advance it over the knife shaft of the machine. Depending on the thickness of the workpieces, the conveyor chain can be set at different heights. The chain is driven by a built-in individual electric motor with a power of 0.6 kW.
The jointer SF6A-2 with conveyor feed is more powerful, it is used for processing one or more workpieces up to 600 mm wide. The four-knife shaft of the machine is driven by an electric motor through a belt drive. For quick braking of the knife shaft, an electromagnetic brake is used, acting on the end surface of the disk mounted on the end of the shaft. Along the circumference of the disk there are holes for a stopper that fixes the position of the shaft when sharpening knives. The material is fed by a double-chain conveyor equipped with cross bars with springy claws. Due to the large number of claws, the pressure of each of them on the workpiece is insignificant and therefore the workpiece does not deform when moving along the table. Chains with straps are stretched over two pairs of sprockets - one drive and the other tension. For sharpening and jointing of knives directly on the machine there are removable devices.

Rice. 7. Jointing machine and device for mechanical feeding of parts:
a - general view of the machine; b - scheme of the conveyor mechanism on the planer: 1 - knife shaft, 2 - workpiece, 3 - rear plate, 4 - pressure fingers, 5 - conveyor chain, 6 front plate

Rice. 8. Kinematic diagram of a planer with conveyor feed:
1 - rear table height adjustment mechanism, 2 - rear table, 3 - conveyor drive mechanism, 4 - conveyor, 5 - front table, 6 - front table height adjustment mechanism, 7 - conveyor height adjustment mechanism for workpiece thickness, 8 - knife shaft
The layout of the workplace at the jointer is shown in fig. 9. The parts processed on the machine should be located near the machine so that the worker does not have to make unnecessary transitions and movements.
On the working table, at the slot of the knife shaft, sharp steel plates should be installed, fixed flush with the surface of the table. The distance between the edges of the overlays and the surface that the knife blades describe is not more than 3 mm.
The knife shaft must have a quick-acting device for fixing the knives.

Rice. 9. Scheme of the workplace at the jointer:
1 - machine operator's place, 2 - blanks, 3 - planed parts
Workpieces shorter than 400 mm, narrower than 50 mm or thinner than 30 mm when manually fed, must be planed only using special blocks - pushers. Planing thin and short parts in batches can only be done with the use of a cleat. Shaped, curvilinear planing is prohibited.
Once both halves of the table have been set to the desired height, the lifting mechanism must be securely fixed in that position. The plane of the back table must be tangent to the cylindrical surface described by the blades of the knives.
The non-working part of the knife shaft must be covered with a guard that automatically moves with the guide bar. Fastening the guide line with clamps is prohibited.
On planing machines with mechanical feed, the simultaneous planing of two or more parts of different thicknesses is allowed only if each of them is firmly pressed.