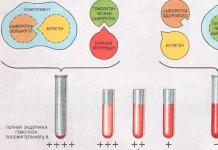
An electrical network is a system that includes inputs, wires, current consumers, as well as switching equipment. Installation of circuit breakers provides protection for the network as a whole and individual consumers in emergency situations when the current parameters go beyond normal values (short circuit, voltage surges, change in current direction, etc.). In addition, they allow, if necessary, infrequent switching of consumers remotely or in manual mode (6-30 on / off cycles per day).
Care of electrical equipment
Evolution and basic design of circuit breakers
The history of electrical equipment began long before the advent of the first commercial power grids. So, the principle of operation of the circuit breaker was discovered back in 1836 by the American scientist C. G. Page, but the modern design was patented only in 1924 by the Swiss company Brown, Boveri & Cie. Since then, each machine has included the following elements:
- block of contacts;
- arc neutralization (extinguishing) chamber;
- release of the following types: thermal, electromagnetic, electronic, microprocessor;
- control mechanism: manual, spring or driven;
- free release mechanism.
At present, a lot of electrical equipment is being produced, which is illustrated by characteristics of circuit breakers, which provide reliable switching and protection of power networks and consumers of any complexity and power in any operating conditions. The number of models of these devices from different manufacturers is incalculable.
The Skat Technology catalogs contain products from the leading companies Siemens, Andeli, Schneider, whose products rightfully occupy leading positions in the electrical engineering market. Here you can see circuit breakers in the photo, as well as familiarize yourself with their main characteristics and installation methods. If you are not a professional in electrical engineering, we recommend using the help of our specialists, which can also be obtained online.
For those who are interested in how the circuit breaker works, we will give a short explanation. Each device has settings for certain parameters of current and heating of conductors. These settings are provided by the current sensitivity of the release solenoid and a thermal relay with screw adjustment (calibration). If during the operation of the network the parameters go beyond the established limits, the circuit breaks and the consumers are de-energized.
Classification of circuit breakers
For the classification of electrical appliances, there are regulatory documents that set out the technical and operational requirements for them. Breaker classes domestic and foreign production are determined in accordance with the following documents:
- GOST 9098-78;
- GOST 14255-69;
- GOST R 50345-2010;
- GOST R 50030.2-99;
- IEC 60898-95;
- EN 60947-2;
- EN 60898.
In accordance with domestic regulatory and technical documents, the classification of automatic machines is carried out according to 12 parameters, which take into account dozens of operational characteristics of the devices. The quantitative and qualitative values of these parameters determine the purpose of the circuit breaker and the permissible conditions for its operation.
Main classification parameters of circuit breakers
The higher the level of power grid architecture, the more difficult it is to select protection and control equipment for it, since it is necessary to take into account a large number of different operation parameters. To achieve the desired result, it is necessary to carry out engineering calculations of all parameters so that the selection of a circuit breaker and other electrical devices ensures reliable and safe operation of the network. The list of the main characteristics of the machines is as follows:

- rated currents of the main circuit and releases - respectively 6.3-6300 (total 22 ratings) and 15-3200 amperes (total 12 ratings);
- design - air or ASV (800-6300 A), molded case or MCCB (10-2500 A), modular or MSV (0.5-125 A) automatic machines;
- the number of poles of the main circuit - from one to four;
- the presence or absence of current restrictions;
- types of releases: zero, minimum, independent, maximum;
- the presence or absence of contacts for connecting secondary circuits;
- input/output connection method: front, rear, combined, universal;
- mounting method: fixed, withdrawable (on a DIN rail), on connectors;
- cutoff type: normal, selective, instantaneous;
- type of drive: manual, spring, with propulsion (electromagnet, pneumatics, etc.);
- normal or protected execution.
The listed characteristics have their own designation or quantitative expression. For example, the tripping curve of a circuit breaker is a graphic representation of the tripping of a release. It indicates at what value of the rated current "In" the device trips. According to this parameter, foreign-made products are divided into 6 groups (types):

- A - 2-3 In;
- B - 3-5 In;
- C - 5-10 In;
- D - 10-20 In;
- Z - 2-4 In;
- K - 8-14 In.
The operation class of domestic-made circuit breakers is designated by the letters B, C and D, since our industry does not produce products of other types. In turn, according to the speed of the cut-off, the automata are divided into normal (0.02-1 sec.) And high-speed or instantaneous (less than 0.005 seconds). Selectivity of circuit breakers means the possibility of setting different cut-off times with a shutter speed of 0.25-0.6 seconds for slave electric devices.
Automatic machines of this type have a main and additional working circuits, which makes it possible to turn off the emergency section of the power supply network controlled by the slave device and save the current supply to the remaining consumers. The time range of the speed and selection processes also reflect circuit breakers curves. The protection devices are triggered not only by the current, but also by the heating of the wires, which is provided by a thermal relay. Simply put, the electromagnetic release responds to current consumption, and the thermal relay responds to heating of the wiring.
It is from the setting of the latter that the time-current characteristic of the circuit breaker depends. The value of the thermal load should not exceed the nominal value for wires of a certain section by more than 1.45 times. It is determined taking into account the method of laying wires and the total load. Depending on the setting, the thermal relay can operate instantly or keep the network operational for a certain time, but not more than an hour.
On the importance of timely operation of protection equipment
From the above data, it is clear how important the tripping time of the circuit breaker is. The minimum value of this indicator is necessary for powerful industrial equipment. Here, class D devices with instantaneous tripping are usually used. For domestic needs, with a margin, there are enough automata of class C of normal tripping.
The exception is worn-out networks and particularly sensitive current consumers, where class A and B devices should be used, in which the minimum tripping time of the circuit breaker in case of short circuit not only provides protection, but also prevents ignition of the wiring. By the way, the state of the latter is often of decisive importance when choosing electrical equipment. If the size of the wires does not correspond to the load on the network, the thermal response of the circuit breaker will prevent its normal operation.
Reflection of the characteristics of electrical equipment in its marking
For electrical products, it is typical to use the most important operational characteristics in the marking of products. For lighting lamps, this is the power consumption and the luminous flux. Marking of circuit breakers much more complicated, a minimum of information can be squeezed into the name of the product. This is usually the rated operating voltage. Therefore, the marking symbols are applied to the body of the machine:

- the current limit class is indicated by a number placed inside the square; the number of poles is displayed with an icon;
- the class or category of use of the circuit breakers is displayed together with the value of the rated current - for example, "C16";
- the maximum allowable value of the tripping current, at which the risk of damage to the machine is excluded, is indicated in a rectangular frame.
The listed information in the product labeling is enough for a specialist to decide how to choose / select a circuit breaker in full accordance with the parameters of the mains. However, when purchasing the device on your own, it is easy to make a mistake if you do not take into account the characteristics of the wiring and the magnitude of the loads. For example, the operating parameters of open and closed wiring, copper and aluminum wires are noticeably different.
If you are wondering how to choose / select a circuit breaker for power, it should be borne in mind that a copper wire with a cross section of 4 mm, laid in an open way, can withstand a load of 9 kW. The same wire with closed wiring will withstand 5.9 kW. It is clear that the power of the current consumer should not exceed the capabilities of the wiring.
Similarly ratings of circuit breakers must be less than the corresponding network parameters. Otherwise, there is a risk of overloading the electrical network, up to the ignition of the wiring, to which the machine simply will not react. In order to avoid this situation, preliminary calculations are necessary that will ensure a balance between current consumers, wiring, and protection and control equipment. For those who are interested in the question how to choose a circuit breaker for your home, we will give advice: choose the nominal value of the device according to the bandwidth of the wiring (the cross section and material of the wires, as well as the method of laying them).
Basic rules for connecting a circuit breaker
A competent arrangement of the architecture of power networks allows to increase their reliability by an order of magnitude. Currently, we use a lot of household appliances and equipment, including those with significant power. The old Soviet-style wiring was not designed for such loads, so consumers often face the question of how to calculate the circuit breaker current in order to ensure the safe operation of the home electrical network.

Based on its work experience, Skat Technology concluded that with a significant increase in the load on the network (for example, installing an electric stove), old wiring should not be used. The correct choice of the circuit breaker for the load current will not help either, since the wiring is not designed for it. It is best to completely reconstruct or replace the network with the distribution of current consumers into groups.
Electrical engineering is an exact applied science, therefore the production of electrical goods is carried out according to certain standards. This is clearly seen in the example of what kind of circuit breakers are, the design of which is designed for specific operating conditions. The division of consumers into groups has long been practiced in industrial networks. At the household level, this approach looks like this:
- for lighting fixtures, the rating of the machine should not exceed 10 A;
- for ordinary sockets - 16 A;
- for power sockets for electric stoves, boilers and other things, a circuit breaker is selected according to the power of consumers.
To implement this approach to the construction of networks, manufacturers offer a sufficient selection of automata with a different number of poles, differential type and other units. For domestic purposes, devices in molded cases should be used, in which all current-carrying parts are protected, which excludes accidental electric shock. In order to install a universal circuit breaker, distribution devices (cabinets, assemblies, etc.) are required.
The variety of electrical appliances is also explained by the fact that their design provides for all kinds of installation conditions. In other words, a device with identical parameters can have several versions. That's why circuit breaker connection diagram is a mandatory application for each product. It indicates the number of poles, the points of connection of phases and neutrals, the methods of preparing wires for connection, and other features of a particular model.
If a person has a minimal understanding of electrical engineering, he will not think for a long time about how to connect a single-phase circuit breaker on the switchboard of his apartment. Just look at the diagram, in which there is nothing complicated. The only warning: if you change the machine, in no case put a switch with a higher power than the previous one. First you need to make sure that the wiring is able to withstand the increased load.
Care of electrical equipment
Electrical equipment, like any other appliances, needs care. Maintenance of circuit breakers is carried out according to a certain procedure with strict frequency. Users are often unaware of this need, but it is there. Electrical engineering is subject to wear, contacts are gradually oxidized, insulation is aging, moving parts are worn out and other changes occur. Therefore, the calculation of the circuit breaker in terms of power, performed 5 years ago, may not correspond to the real state of affairs.

Probably, many of you have experienced situations when a perfectly working network starts to act up. An obvious manifestation of this is the fact that, for no apparent reason, the circuit breaker often trips. The reason may be in the device itself, but most often this happens due to wiring problems and hidden defects in the electrical circuits of household appliances and equipment.
To detect and prevent such situations, there is loading circuit breakers. It is carried out every three years using special equipment and is carried out in order to verify that the actual condition of the machine meets the requirements for the safe operation of electrical networks. The method for checking circuit breakers provides for checking the condition of the insulation, the response time of overcurrent and heating protection, the condition of the contacts, and other parameters.
Regular maintenance ensures that problems are detected early, prevent more serious consequences, and ensure the safe operation of networks for the foreseeable future. Detected malfunctions of circuit breakers are eliminated if possible, but most often in such cases a complete replacement of electrical devices is required, especially in the case of their small sizes.
Manufacturers of electrical products produce many spare parts for powerful industrial machines. For household or low-power equipment, only spare contact groups are usually produced. That's why replacement of circuit breakers- a typical action during the repair of electrical networks. Regular maintenance of electrical equipment is a completely easy procedure, including in terms of money. Its main goal is prevention.
Among the technical characteristics of the machines, the guaranteed number of on / off cycles is also indicated. According to these indicators, circuit breakers have a service life measured in decades, provided that the devices are properly installed and maintained in a timely manner. They must fully comply with the network parameters. In addition, to extend their service life, you should not use faulty electrical appliances that provoke frequent power outages.
Professional services from the company "Scat technology"
Our company specializes in works on engineering communications, including electrical networks. Our specialists are ready to give recommendations on the choice of circuit breakers and perform network design, including load calculations and their distribution, taking into account all safety standards. Experienced engineers will answer any practical questions, including how to connect a circuit breaker for different categories of current consumers, taking into account installation conditions, wiring conditions and other factors.
Our catalogs contain a wide selection of electrical products from leading manufacturers. Our range will allow you to easily carry out a complete set of works on the arrangement of electrical networks. If it bothers you cost of circuit breakers with logos of famous brands, we remind you that high-quality products cannot be frankly cheap. In addition, the service life of such electrical equipment is an order of magnitude higher than that of products of dubious origin.
Those who are wondering which circuit breakers are better should decide what meaning you put into it. For us, the determining factor is reliability and safety at adequate costs? We offer electrical products at the most fair prices, so we are convinced that our customers do not overpay. Dimensions of circuit breakers are far from always the equivalent of prices, therefore, if you want to get a normal result of arranging the power grid, use the services of Skat Technology professionals.
Circuit breakers are devices whose task is to protect the electric line from the effects of a powerful current that can cause overheating of the cable with further melting of the insulating layer and fire. An increase in current strength can be caused by too much load, which occurs when the total power of the devices exceeds the value that the cable can withstand in its cross section - in this case, the machine does not turn off immediately, but after the wire heats up to a certain level. During a short circuit, the current increases many times within a fraction of a second, and the device immediately reacts to it, instantly stopping the supply of electricity to the circuit. In this article we will tell you what types of circuit breakers are and their characteristics.
Automatic protective switches: classification and differences
In addition to residual current devices that are not used individually, there are 3 types of circuit breakers. They work with loads of different sizes and differ from each other in their design. These include:
- Modular AV. These devices are mounted in household networks in which currents of insignificant magnitude flow. They usually have 1 or 2 poles and a width that is a multiple of 1.75 cm.

- Cast switches. They are designed to work in industrial networks, with currents up to 1 kA. Made in a cast case, which is why they got their name.
- Air electric machines. These devices are available with 3 or 4 poles and can withstand currents up to 6.3 kA. Used in electrical circuits with high power installations.
There is another type of circuit breaker - differential. We do not consider them separately, since such devices are ordinary circuit breakers, which include an RCD.
Release types
The releases are the main working components of the AB. Their task is to break the circuit when the permissible current value is exceeded, thereby stopping the supply of electricity to it. There are two main types of these devices, which differ from each other in the principle of decoupling:
- Electromagnetic.
- Thermal.
Electromagnetic type releases provide almost instantaneous operation of the circuit breaker and de-energize the circuit section when an overcurrent short circuit occurs in it.

They are a coil (solenoid) with a core that is drawn inward under the influence of a large current and causes the tripping element to operate.
The main part of the thermal release is a bimetallic plate. When a current exceeding the rated value of the protective device passes through the machine, the plate begins to heat up and, bending to the side, touches the disconnecting element, which operates and de-energizes the circuit. The time for the thermal release to operate depends on the magnitude of the overload current passing through the plate.
Some modern devices are equipped as an option with minimum (zero) releases. They perform the function of turning off the AV when the voltage drops below the limit value corresponding to the technical data of the device. There are also remote releases, with which you can not only turn off, but also turn on the AB, without even going to the switchboard.
The presence of these options significantly increases the cost of the device.
Number of poles
As already mentioned, the circuit breaker has poles - from one to four.

It’s not difficult to choose a device for a circuit according to their number, you just need to know where different types of AB are used:
- Single terminals are installed to protect lines that include sockets and lighting fixtures. They are mounted on a phase wire without capturing zero.
- The two-pole must be included in the circuit to which household appliances with a sufficiently high power are connected (boilers, washing machines, electric stoves).
- Three-terminal networks are installed in semi-industrial scale networks, to which devices such as borehole pumps or car repair equipment can be connected.
- Four-pole ABs allow you to protect electrical wiring with four cables from short circuits and overloads.
The use of machines of different poles - in the following video:
Characteristics of circuit breakers
There is another classification of machines - according to their characteristics. This indicator indicates the degree of sensitivity of the protective device to the excess of the rated current. The corresponding marking will show how quickly the device will react in the event of an increase in current. Some types of ABs work instantly, while others take time.

There is the following marking of devices according to their sensitivity:
- A. Breakers of this type are the most sensitive and respond instantly to an increase in load. They are practically not installed in household networks, protecting circuits with high-precision equipment with their help.
- B. These circuit breakers operate with a slight delay when the current increases. Usually they are included in lines with expensive household appliances (LCD TVs, computers, and others).
- C. Such devices are the most common in household networks. Their shutdown does not occur immediately after the increase in current strength, but after a while, which makes it possible to normalize it with a slight drop.
- D. The sensitivity of these devices to the increase in current is the lowest of all the listed types. They are most often installed in shields on the approach line to the building. They provide insurance for apartment machines, and if for some reason they do not work, they turn off the general network.

Features of the selection of machines
Some people think that the most reliable circuit breaker is the one that can carry the most current, which means it can provide the most circuit protection. Based on this logic, an air-type machine can be connected to any network, and all problems will be solved. However, this is not at all the case.
To protect circuits with different parameters, it is necessary to install devices with appropriate capabilities.
Mistakes in the selection of AB are fraught with unpleasant consequences. If you connect a high-power protective device to a normal household circuit, it will not de-energize the circuit, even when the current value is much higher than that which the cable can withstand. The insulating layer will heat up, then start to melt, but no shutdown will occur. The fact is that the current strength, which is destructive for the cable, will not exceed the AB rating, and the device will “think” that there was no emergency. Only when the melted insulation causes a short circuit will the machine turn off, but by that time a fire may already have started.
Here is a table that shows the ratings of machines for various electrical networks.

If the device is designed for less power than that which the line can withstand and which the connected devices have, the circuit will not be able to work normally. When the equipment is turned on, the AB will constantly knock out, and eventually, under the influence of high currents, it will fail due to “sticky” contacts.
Clearly about the types of circuit breakers in the video:
Conclusion
The circuit breaker, the characteristics and types of which we examined in this article, is a very important device that protects the electrical line from damage by powerful currents. The operation of networks that are not protected by automatic machines is prohibited by the Electrical Installation Rules. The most important thing is to choose the right type of AB that is suitable for a particular network.
yaelectric.ru
Trip unit definition
Releasers divide by two conditional groups:
- circuit breakers;
Under overcurrent
Overload current
Short circuit current (short circuit)
Therefore, as soon as R→ to 0, then I→ to infinity.
Thermal release
The thermal release is a bimetallic plate, which, when heated, bends and acts on the mechanism of free disengagement.
A bimetallic plate is made by mechanically connecting two metal strips.
two materials with different coefficients of thermal expansion are taken and interconnected by soldering, riveting or welding.
Suppose the lower material in a bimetallic plate, when heated, elongates less than the upper metal, then the bend will occur downward.
The thermal release protects against overload currents and is configured for certain operating modes.
For example, for a product of the BA 51-35 series, the overload release is calibrated at a temperature of +30ºС to:
- conditional non-trip current 1.05 In (time 1 hour for In ≤ 63A and 2 hours for In ≥ 80A);
- conditional tripping current 1.3 In for AC and 1.35 In for DC.
The designation 1.05 In - means a multiple of the rated current. For example, with a rated current In = 100A, the conventional non-trip current is 105A.
On the time-current characteristics (graphs are always available in the factory catalogs), the dependence of the response time of the thermal and electromagnetic releases on the value of the flowing overcurrent is clearly shown.
Advantages:
- no rubbing surfaces;
- have good vibration resistance;
- easily tolerate pollution;
- simplicity of design → low price.
Flaws:
- constantly consume electrical energy;
- sensitive to changes in ambient temperature;
- when heated from third-party sources, they can cause false alarms.
It consists, in principle, of the same parts as a semiconductor release: an actuating electromagnet, measuring devices and a release control unit.
The operating current and holding time are set stepwise, guaranteeing protection in case of single-phase short circuit and inrush currents.
Example: products of the BA 88-43 series with an electronic release manufactured by the IEK company.
Advantages:
- a variety of settings for the user;
- high accuracy of execution of a given program;
- health indicators and causes of operation;
- logic selectivity with upstream and downstream switches.
Minuses:
- high price;
- fragile control unit;
- exposure to electromagnetic fields.
Shunt release
With shunt trip(HP) carry out remote control specific circuit breaker. The independent release coil is energized from the control circuit, a magnetic field is created, the core moves, and it affects the free trip mechanism.
The shunt release can be designed for alternating or direct current (the manufacturer indicates the voltage range).
HP allows fluctuations in the operating voltage in the range from 0.7 to 1.2 of Un. Its mode of operation is short-lived.
After the independent release trips, you need to go to the switchboard and manually cock the circuit breaker, and then turn it on.
An alternative to HP can be an electromagnetic drive - it allows you to remotely turn off and turn on the circuit breaker.
Most common application– remote shutdown of the switching device that controls the ventilation system in the event of a fire. When a fire is detected, ventilation is turned off so that air (oxygen) is not injected into the building.
Electrodynamic forces
Electrodynamic forces act on a conductor with a current flowing through it, which is in a magnetic field with induction B.
When the rated current flows, the electrodynamic forces are insignificant, but when a short-circuit current appears, these forces can lead not only to deformation and breakage of individual parts of the switching device, but also to the destruction of the machine itself.
Special calculations are made for electrodynamic resistance, which are especially relevant when there is a tendency to reduce overall characteristics (distances between conductive parts are reduced).
A magnetic field
The magnetic field is one of the factors generating electrodynamic forces.
Magnetic fields adversely affect the operation of electrical equipment, especially measuring instruments and computers.
Thermal stress (overheating)
When any current with a force I flows through the conductor, its core heats up, which can lead to fires or damage to the insulation.
In the event of overcurrents, overheating is of current importance, if you do not block the short circuit, allowing you to reach maximum values.
Rated current
The rated current (denoted In) of the circuit breaker is understood as the current at which the device is designed for continuous operation and does not activate the protective operation. If the current indicated in the marking is exceeded, the machine, after a certain time, interrupts the supply to the network.
Small disclaimer:
- rated current of the circuit breaker - the current for which conductive elements are calculated;
- rated current of the thermal release - the current for which the release devices are adjusted (no tripping is caused by it).
In the following, by rated current we mean the rated current of the thermal release.
The rated current is one of the defining characteristics of the circuit breaker, since overcurrents are calculated relative to this value, at which the releases cause the contacts to open. For the correct choice of the circuit breaker, you need to know the rated current of the network.
The rated current of the network is calculated from the power consumption. It is certainly known which device consumes how much power. The total power is obtained and, as a first approximation, the ratio is used:
P \u003d U I, where P is the power consumption in watts, U is the mains voltage in volts, I is the mains current in amperes.
But this formula is true for a DC network, for an AC network everything is much more complicated.
Apparent power (S) is the vector sum of active power (P) and reactive power (Q):
S 2 \u003d P 2 + Q 2.
In its turn:
- active power P = I U Cosϕ;
- reactive power Q = I U Sinϕ.
Where ϕ is the angle at which the current lags or leads the voltage. Phase meters are used to measure the reactive power factor (Cosϕ).
Instantaneous trip current (protective characteristic B, C or D)
The circuit breaker is characterized by a current at which instantaneous tripping of the main contact group is caused. This occurs during a short circuit, which fixes and disables the electromagnetic release.
For modular and power circuit breakers, the instantaneous protection characteristic is specified in different ways:
- modular automata are assigned a protective characteristic: B, C, D;
- for circuit breakers, the current value is set in amperes or a multiple of the rated current.
Fast automata
Achieving a shutdown time of 0.002-0.008 s requires special measures and other principles of operation of drive electromagnets. In known designs, the following methods for obtaining speed are used:
1) according to the principle of flow displacement (speed 0.003-0.005 s). The machine is turned off not by turning off the coils of the holding electromagnet, but by displacing the flow from the core-armature section. In this case, the demagnetizing flux is created by a forced short-circuit current.
2) mechanical latches (locks) t o to 0.002 s. Switching on is also carried out by a short-term working electromagnet, and holding in the on position is carried out by a mechanical (electromechanical) latch. The latch is released by a tripping electromagnet operating in a forced mode, created by a short-circuit current.
3) systems with a shock electromagnet - an electromagnet operating with a large force creates an "impact force" that exceeds the force of the holding electromagnet and "tear off" the anchor, i.e. turns off the switch.
4) a switch with an explosive release - a trip time of 0.001 s - has not received distribution due to its complexity.
5) vacuum circuit breakers providing arc extinguishing t0=0.003-0.007s. Examples of execution of some switches are given below.
a) Switch BVP-5. Built on the principle of magnetic field displacement. It is designed to protect the power circuit of DC electric locomotives. U nom =4000 V, U max=4000 V, I nom=1850 A, own tripping time 0.003 s.
b) DC vacuum circuit breaker type VPTV-15-5/400 on the
U nom=15 kV, I nom = 400 A, I off =5 kA.
c) Automatic series VAB - 28 the most versatile I nom = 1.5-6 kA, U\u003d 825-3300 V.
HIGH VOLTAGE SWITCH
high voltage circuit breaker- a switching device designed for operational switching and emergency switching in power systems, for performing operations of switching on and off individual circuits or electrical equipment with manual or automatic control.
The high-voltage circuit breaker consists of: a contact system with an arcing device, current-carrying parts, a housing, an insulating structure and a drive mechanism (for example, an electromagnetic drive, a manual drive).
Options
In accordance with GOST R 52565-2006, switches are characterized by the following parameters:
- rated voltage Unom (mains voltage in which the circuit breaker operates);
- rated current In (current through the switched on switch, at which it can work for a long time);
- rated breaking current Iо.nom - the highest short-circuit current (effective value) that the circuit breaker is able to disconnect at a voltage equal to the highest operating voltage under given conditions of recovering voltage and a given cycle of operations;
- permissible relative content of aperiodic current in the tripping current;
- if the circuit breakers are intended for automatic reclosing (AR), then the following cycles must be provided:
Cycle 1: O-tbp-BO-180 s-BO; Cycle 2: О-180 s-VO−180 s-VO, where О is the opening operation, VO is the closing and immediate opening operation, 180 is the time interval in seconds, tbp is the minimum dead time guaranteed for circuit breakers during automatic reclosure (time from extinguishing arc until the current appears at the next turn-on) For circuit breakers with automatic reclosure it should be within 0.3-1.2 s, for circuit breakers with BAPV (high-speed) 0.3 s.
- stability with through short-circuit currents, which is characterized by thermal resistance currents It and limiting through current
- rated making current - short-circuit current, which the circuit breaker with the appropriate drive is able to turn on without welding contacts and other damages at Unom and a given cycle.
- proper tripping time - the period of time from the moment the command for shutdown is given until the moment the arcing contacts begin to diverge.
- recovery voltage parameters at rated trip current - recovery voltage rate, normalized curve, peak-to-peak ratio and recovery voltage.
Automatic breakers. Operating principle. Design and types of releases.
Trip unit definition
Releasers divide by two conditional groups:
- circuit breakers;
- releases performing auxiliary functions.
Releaser (first group), in relation to a circuit breaker, a device is called that is capable of recognizing a critical situation (the appearance of overcurrent) and preventing its development in advance (causing a divergence of the main contacts).
To the second group of releases additional devices can be distinguished (they do not complete the basic versions of the machines, but only supply custom versions):
- independent release (remote shutdown of the circuit breaker by a signal from the auxiliary circuit);
- undervoltage release (turns off the machine when the voltage drops below the permissible level);
- zero voltage release (causes tripping of contacts with a significant voltage drop).
Definitions of terms found below
Under overcurrent is understood as the current strength exceeding the rated (working) current. This definition includes short-circuit current and overload current.
Overload current- overcurrent acting in the functional network (prolonged exposure to overloads can cause damage to the circuit).
Short circuit current (short circuit)– overcurrent, which is caused by the shorting of two elements with a very low impedance between them, while in normal operation these elements are endowed with different potential (short circuit can be caused by incorrect connection or damage). For example, mechanical stress or aging of insulation causes contact between conductive wires and a short circuit.
The high value of the short circuit current is recognized from the formula:
I \u003d U / R (current strength is equal to the ratio of voltage to resistance).
Therefore, as soon as R→ to 0, then I→ to infinity.
The rated current flows through the main contacts in the circuit breaker during normal use. The free tripping mechanism of the switching device has sensitive elements (eg rotary tripping bar). The impact of the release on these elements contributes to the instantaneous automatic operation, that is, the disengagement of the contact system.
Overcurrent release (MRT)- a release that causes the opening of the main contacts with or without maintaining a certain period of time, as soon as the effective value of the current exceeds a given threshold.
MRT with inverse time delay is an overcurrent release that initiates the opening of contacts after a predetermined time has elapsed, which is inversely dependent on the current strength.
MRT of direct action is the maximum current release that initiates operation directly from the operating overcurrent.
The definitions of the overcurrent release, short circuit current and overload are taken (rephrased without loss of meaning) from the GOST R 50345 standard.
cyberpedia.su
Varieties of switches
All machines are divided according to the type of releases. They are divided into 6 types:
- thermal;
- electronic;
- electromagnetic;
- independent;
- combined;
- semiconductor.
They are very quick to recognize emergencies such as:
- the occurrence of overcurrents - an increase in the current strength in the electrical network that exceeds the rated current of the circuit breaker;
- voltage overload - short circuit in the circuit;
- voltage fluctuations.
At these moments, the opening of contacts occurs in the automatic releases, which prevents serious consequences in the form of damage to wiring, electrical equipment, which very often leads to fires.
Thermal switch
It consists of a bimetallic strip, one of the ends of which is located next to the release device of the automatic release. The plate is heated by the current passing through it, hence the name. When the current strength begins to increase, it bends and touches the trigger bar, which opens the contacts in the "machine".

The operation of the mechanism occurs even with slight excesses of the rated current and an increased operating time. If the load increase is short-term, the circuit breaker does not work, so it is convenient to install it in networks with frequent but short overloads.
Advantages of a thermal release:
- lack of contacting and rubbing surfaces;
- vibration resistance;
- budget price;
- simple construction.
The disadvantages include the fact that its work largely depends on the temperature regime. It is better to place such machines away from heat sources, otherwise there will be numerous false alarms.
Electronic switch
Its components include:
- measuring devices (current sensors);
- Control block;
- electromagnetic coil (transformer).
Each pole of the electronic automatic release has a transformer that measures the current passing through it. The electronic module that controls the trip processes this information by comparing the received result with the specified one. In the case when the received indicator is more than the programmed one, the "machine" will open.

There are three trigger zones:
- Long delay. Here, the electronic release serves as a thermal release, protecting the circuits from overloads.
- Short delay. Provides protection against minor short circuits, which usually occur at the end of the protected circuit.
- The work area "instantaneously" provides protection against high-intensity short circuits.
Pluses - a large selection of settings, the maximum accuracy of the device to a given plan, the presence of indicators. Cons - sensitivity to an electromagnetic field, high price.
Electromagnetic
This is a solenoid (a coil with a wound wire), inside of which there is a core with a spring that acts on the release mechanism. This is an instant device. During the flow through the overcurrent winding, a magnetic field is formed. It moves the core and, exceeding the force of the spring, acts on the mechanism, turning off the "automatic".

Pros - resistance to vibration and shock, simple design. Cons - forms a magnetic field, instantly works.
This is an additional device to automatic releases. With it, you can turn off both a single-phase and a three-phase machine located at a certain distance. To activate the shunt release, the coil must be energized. To return the machine to its original position, you must manually press the "return" button.
Important! The phase conductor must be connected from one phase from under the lower terminals of the switch. If it is connected incorrectly, the independent switch will fail.
Basically, independent machines are used in automation panels in highly branched power supply devices of many large facilities, where control is displayed on the operator's console.

Combination switch
It has both thermal and electromagnetic elements and protects the generator from overloads and short circuits. For the operation of the combined automatic release, the current of the thermal "automatic device" is indicated and selected: the electromagnet is designed for 7-10 times the current, which corresponds to the operation of heating networks.
Electromagnetic elements in the combination switch serve as instantaneous protection against short circuits, and thermal protection against overloads with a time delay. The combined machine turns off when any of the elements is triggered. With short-term overcurrents, none of the types of protection works.
Semiconductor switch
It consists of AC transformers, magnetic amplifiers for DC, control unit and electromagnet, which performs the functions of an independent automatic release. The control unit helps to set the selected contact release program.
Its settings include:
- regulation of the rated current in the device;
- time setting;
- operation at the moment of occurrence of a short circuit;
- protective switches against overcurrents and single-phase short circuit.

Pluses - a large selection of regulation for different power supply schemes, ensuring selectivity to series-connected machines with fewer amperes.
Cons - high cost, fragile control components.
Installation
Many homegrown electricians find that installing an automatic machine is not difficult. This is fair, but certain rules must be followed. The circuit breaker releases, as well as plug fuses, must be connected to the network so that when the plug of the machine is turned out, its screw sleeve is without voltage. The connection of the supply conductor with one-sided power supply to the machine must be made to fixed contacts.
Installation of an electric single-phase two-pole machine in an apartment consists of several stages:
- fixing the switched off device in the electrical panel;
- connecting wires without voltage to the meter;
- connection to the machine from above the voltage wires;
- turning on the machine.
Fastening
In the electrical panel we mount a din rail. We cut off the desired size and fasten it with self-tapping screws to the electrical panel. We snap the automatic circuit breaker onto the DIN rail using a special lock, which is located on the back of the machine. Make sure the device is in shutdown mode.
Connection to the electricity meter
We take a piece of wire, the length of which corresponds to the distance from the counter to the machine. We connect one end to the electric meter, the other to the release terminals, observing the polarity. We connect the supply phase to the first contact, and the neutral supply wire to the third. The cross section of the wire is 2.5 mm.
Connecting voltage wires
From the central distribution electrical panel, the supply wires go to the apartment panel. We connect them to the terminals of the machine, which should be in the “off” position, observing the polarity. The cross section of the wire is calculated depending on the energy consumed.
energomir.biz

It is impossible to imagine a modern electrical network without the necessary means of protection, in particular, a circuit breaker. Unlike obsolete fuses, it is designed for reusable protection of the network and electrical equipment. At the same time, the circuit breaker protects against short circuit currents, excessive overloads, and some models even against unacceptable voltage drops. And in the center of this whole structure, the most significant element is the circuit breaker release. It is on him that the reliability and speed of response depend, so it is worth comparing all the currently existing varieties.
Comparison
So, among the first can be called a thermal release. Due to its design, the thermal release trips with a time delay. The greater the excess current, the faster the thermal release operates. So the response time can vary from a few seconds to an hour. That is why the sensitivity of the machine, where the thermal release is installed, is always determined by the time-current characteristic and corresponds to class B, C or D.
The following variety is among the instantaneous releases. We are talking about such a thing as an electromagnetic release. It works in a fraction of a second, which compares favorably with thermal releases. However, the electromagnetic release also has its own peculiarity - operation occurs at a significantly higher excess of the rated current. Based on this, the electromagnetic release also has a certain sensitivity and belongs to one of the classes - A, B, C or D.
Perhaps the most effective is the electronic release of the circuit breaker. Fast operating speed and high sensitivity make the electronic trip unit ideal for protection against overloads and short-circuit currents. For this reason, this instantaneous release is used for more currents.
It is the electronic release that is often mounted on both air circuit breakers and molded case circuit breakers. Air circuit breakers imply an open design (usually in a metal case) and are designed for currents up to several thousand amperes. As already mentioned, the electronic release is ideal for power networks due to the instantaneous response speed. As for the molded case circuit breakers, they are distinguished by their compact dimensions and closed design in a housing made of thermosetting plastic. It is convenient to mount them on a DIN rail, but the closed case implies increased requirements for the reliability of the release. This again is an electronic release, where there are no moving mechanical elements.
Principle of operation
Regardless of the type of release, the principle of its operation is based on opening the circuit in case of exceeding the current characteristics. Any release is an integral part of the circuit breaker, built into it or mechanically associated with it. The release of the circuit breaker, under the influence of short circuit currents or when the load is exceeded, initiates the release of the holding device in the circuit breaker housing. As a result, the electrical circuit is opened.
Design
The design largely depends on the type of release. So, the basis of the thermal release is a bimetallic plate - a metal tape of two strips with different coefficients of thermal expansion. When currents exceeding the permissible value pass through it, the bimetallic plate is deformed, thereby triggering the trip mechanism.
For an electromagnetic release, the design is a solenoid (cylindrical winding) with a movable core. The current passes through the solenoid winding, and if the current characteristics are exceeded, the core is drawn in, acting on the opening mechanism.
But the electronic release of the circuit breaker is not based on mechanical action and is a slightly different design. It consists of a controller and current sensors. The controller compares the values of the current sensors with the set characteristics, and if the set current parameters are exceeded, it gives a shutdown signal. Thus, the electronic release has more flexible settings, allowing you to adjust the parameters of the circuit breaker to the specific requirements of protecting the mains.
chint-electric.ru
Circuit breakers are not at all like the usual ones that are installed in every room to turn the light on and off (Fig. 1). Their task is somewhat different. Circuit breakers are installed in switchboards and serve to protect the circuit from power surges and non-periodic power outages in certain sections of the power grid.
Rice. one.
Automata, as they are often called, are installed at the entrance to a house or apartment and are located in special boxes, metal or plastic (Fig. 2).

Rice. 2. Distribution board with automatic machines
There are many types of circuit breakers. Some of them serve only as circuit breakers and protect the network from overload. Such are, for example, the old AE type circuit breakers in a black carbolite case (Fig. 3).

Rice. 3. AE series circuit breaker
In most old shields in the entrances of residential buildings there are just such. However, they are quite reliable and are still in operation.
Modern variations allow additional functions, such as undercurrent protection.
According to the response time to an unacceptable voltage, the automata are divided into 3 types: selective, normal and high-speed. The response time of a normal machine ranges from 0.02 to 0.1 s. In selective circuit breakers, this time is the same. High-speed circuit breakers work faster - they have this value is only 0.005 s.
All circuit breakers are enclosed in a plastic unbreakable case with a special fastening (bar or rail) on the rear plane. Installing the machine on such a mount is very easy - just insert it on the rail until it clicks. You can remove it with a screwdriver by gently pulling on the special tab on top of the circuit breaker. This greatly simplifies the task of installing the machine in a cabinet (Fig. 4).

Rice. four.
Inside the case is the "stuffing" of the machine, its main safety devices, which can be 2 (Fig. 5).

Rice. 5. Internal
We are talking about electromagnetic and thermal releases - peculiar mechanisms for automatically breaking the circuit. A bimetallic plate, when heated by an unacceptably high current passing through it, straightens and opens the contacts - this is a thermal release. In terms of response time, it is the slowest.
The electromagnetic release operates according to the "dead hand" rule. The coil, located in the center of the machine, is continuously maintained in place by a stable voltage. As soon as he jumps out of the nominal limits, the coil literally jumps out of its place, breaking the circuit. This way of breaking the chain is the fastest.
All circuit breakers have contacts for connecting incoming and outgoing wires (Fig. 6).

Rice. 6. Wires are connected to the contacts of the circuit breaker using screw terminals
Automata are distinguished by the degree of sensitivity to tripping. In the standard most common models, circuit breakers with a threshold value approximately equal to 140% of the nominal are most often used. With an increase in voltage by one and a half times, an electromagnetic (fast) release is triggered. With a slight excess of the rated voltage, the thermal release operates. The shutdown process can take hours, which is highly dependent on the ambient temperature. However, the machine will react to voltage changes in any case.
Circuit breakers are distinguished by the number of poles. What does it mean? In one machine there can be several electrical lines independent of each other, which are interconnected by a common shutdown mechanism (Fig. 7 and 8). Automatic machines are one-, two-, three- and four-pole (this applies to domestic use).

Rice. 7. in a plastic box in the off state

Rice. 8. : all lines are triggered at the same time when disconnected, they are connected together with one lever jumper
The circuit breaker has differences in other indicators. They differ in the threshold current strength that they pass through themselves. In order for the machine to work and turn off the power supply in an emergency, it must be set to a certain sensitivity threshold. This setting is made by the manufacturer, so the machine immediately writes the numerical value of this threshold. For domestic needs, machines with indicators of 6.3, 10, 16, 25, 32, 40, 63, 100 and 160 A are used (Fig. 9). There are machines with values of both 1000 and 2600 A, but they are not used in everyday life. These figures mean the total power of all consumers of electric current that will be connected to the circuit "guarded" by the machine.
Machine sensitivity it is necessary to calculate not only the total power of the proposed energy consumers, but also the wiring and electrical installation products - sockets and switches.
Table 1 shows the typology of automata.
Table 1. Types of machines
| Type of | Purpose |
| A | For opening circuits with a large length of electrical wiring and protecting semiconductor devices |
| B | For lighting networks of general purpose |
| C | For lighting circuits and electrical installations with moderate starting currents (motors and transformers) |
| D | For circuits with active-inductive loads, as well as protection of electric motors with high starting currents |
| K | For inductive loads |
| Z | For electronic devices |
Table 2. Two-core copper cable laid in a conduit
| Section, mm2 | Cable current/1.45, A | Automatic, A | Excess current, % | |
| 1,5 | 19 | 13,1 | 13 | - |
| 2,5 | 27 | 18,62 | 16 | - |
| 4 | 38 | 26,2 | 25 | - |
| 6 | 50 | 34,48 | 32 | - |
| 10 | 70 | 48,27 | 40(50) | 3,5 |
| 16 | 90 | 62,06 | 50(63) | 1,5 |
Table 3. Two-core copper wire laid in a box
| Section, mm2 | Maximum continuous cable current, A | Cable current/1.45, A | Automatic, A | Excess current, % |
| 1 | 15 | 10,34 | 10 | - |
| 1,5 | 18 | 12,41 | 10(13) | 4,7 |
| 2 | 23 | 15,86 | 13(16) | 0,87 |
| 2,5 | 25 | 17,24 | 16 | - |
| 4 | 32 | 22,06 | 20 | - |
| 6 | 40 | 27,58 | 25 | - |
| 10 | 48 | 33,1 | 32 | - |
| 16 | 55 | 37,93 | 32(40) | 5,4 |
The maximum continuous current of the cable is assumed for core temperature +65 and air +25 °C. The number of simultaneously laid conductors is up to 4. A number of automatic machines: 0.5 A, 1 A, 2 A, 3 A, 4 A, 6 A, 10 A, 13 A, 16 A, 20 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 50 A and 63 A. Data in Table. 3 are also suitable for a three-core cable. In this case, the third core must be a protective earth or neutral wire.

Rice. 9. A row of 16 A single-pole automata. Let's say for a separate section in an apartment, for example, a kitchen, we have one 6.3 A automaton (it happens, too - electricians were joking). According to the well-known formula Watt \u003d Volt x Ampere, we calculate how many devices (and which ones) can be powered from our network. It turns out that this value is equal to 1386 W, since the default voltage is 220 V. This means that even a powerful kettle cannot be turned on in such a kitchen, not to mention a refrigerator or electric stove - the machine will work instantly and will not allow unacceptable, in its opinion, current to pass through controlled territory. In this case, it is urgent to change the circuit breaker to 25 or even 32 A.
Circuit breakers are devices whose task is to protect the electric line from the effects of a powerful current that can cause overheating of the cable with further melting of the insulating layer and fire. An increase in current strength can be caused by too much load, which occurs when the total power of the devices exceeds the value that the cable can withstand in its cross section - in this case, the machine does not turn off immediately, but after the wire heats up to a certain level. During a short circuit, the current increases many times within a fraction of a second, and the device immediately reacts to it, instantly stopping the supply of electricity to the circuit. In this article we will tell you what types of circuit breakers are and their characteristics.
Automatic protective switches: classification and differences
In addition to residual current devices that are not used individually, there are 3 types of circuit breakers. They work with loads of different sizes and differ from each other in their design. These include:
- Modular AV. These devices are mounted in household networks in which currents of insignificant magnitude flow. They usually have 1 or 2 poles and a width that is a multiple of 1.75 cm.

- Cast switches. They are designed to work in industrial networks, with currents up to 1 kA. Made in a cast case, which is why they got their name.
- Air electric machines. These devices are available with 3 or 4 poles and can withstand currents up to 6.3 kA. Used in electrical circuits with high power installations.
There is another type of circuit breaker - differential. We do not consider them separately, since such devices are ordinary circuit breakers, which include an RCD.
Release types
The releases are the main working components of the AB. Their task is to break the circuit when the permissible current value is exceeded, thereby stopping the supply of electricity to it. There are two main types of these devices, which differ from each other in the principle of decoupling:
- Electromagnetic.
- Thermal.
Electromagnetic type releases provide almost instantaneous operation of the circuit breaker and de-energize the circuit section when an overcurrent short circuit occurs in it.

They are a coil (solenoid) with a core that is drawn inward under the influence of a large current and causes the tripping element to operate.
The main part of the thermal release is a bimetallic plate. When a current exceeding the rated value of the protective device passes through the machine, the plate begins to heat up and, bending to the side, touches the disconnecting element, which operates and de-energizes the circuit. The time for the thermal release to operate depends on the magnitude of the overload current passing through the plate.
Some modern devices are equipped as an option with minimum (zero) releases. They perform the function of turning off the AV when the voltage drops below the limit value corresponding to the technical data of the device. There are also remote releases, with which you can not only turn off, but also turn on the AB, without even going to the switchboard.
The presence of these options significantly increases the cost of the device.
Number of poles
As already mentioned, the circuit breaker has poles - from one to four.

It’s not difficult to choose a device for a circuit according to their number, you just need to know where different types of AB are used:
- Single terminals are installed to protect lines that include sockets and lighting fixtures. They are mounted on a phase wire without capturing zero.
- The two-pole must be included in the circuit to which household appliances with a sufficiently high power are connected (boilers, washing machines, electric stoves).
- Three-terminal networks are installed in semi-industrial scale networks, to which devices such as borehole pumps or car repair equipment can be connected.
- Four-pole ABs allow you to protect electrical wiring with four cables from short circuits and overloads.
The use of machines of different poles - in the following video:
Characteristics of circuit breakers
There is another classification of machines - according to their characteristics. This indicator indicates the degree of sensitivity of the protective device to the excess of the rated current. The corresponding marking will show how quickly the device will react in the event of an increase in current. Some types of ABs work instantly, while others take time.

There is the following marking of devices according to their sensitivity:
- A. Breakers of this type are the most sensitive and respond instantly to an increase in load. They are practically not installed in household networks, protecting circuits with high-precision equipment with their help.
- B. These circuit breakers operate with a slight delay when the current increases. Usually they are included in lines with expensive household appliances (LCD TVs, computers, and others).
- C. Such devices are the most common in household networks. Their shutdown does not occur immediately after the increase in current strength, but after a while, which makes it possible to normalize it with a slight drop.
- D. The sensitivity of these devices to the increase in current is the lowest of all the listed types. They are most often installed in shields on the approach line to the building. They provide insurance for apartment machines, and if for some reason they do not work, they turn off the general network.

Features of the selection of machines
Some people think that the most reliable circuit breaker is the one that can carry the most current, which means it can provide the most circuit protection. Based on this logic, an air-type machine can be connected to any network, and all problems will be solved. However, this is not at all the case.
To protect circuits with different parameters, it is necessary to install devices with appropriate capabilities.
Mistakes in the selection of AB are fraught with unpleasant consequences. If you connect a high-power protective device to a normal household circuit, it will not de-energize the circuit, even when the current value is much higher than that which the cable can withstand. The insulating layer will heat up, then start to melt, but no shutdown will occur. The fact is that the current strength, which is destructive for the cable, will not exceed the AB rating, and the device will “think” that there was no emergency. Only when the melted insulation causes a short circuit will the machine turn off, but by that time a fire may already have started.
Here is a table that shows the ratings of machines for various electrical networks.

If the device is designed for less power than that which the line can withstand and which the connected devices have, the circuit will not be able to work normally. When the equipment is turned on, the AB will constantly knock out, and eventually, under the influence of high currents, it will fail due to “sticky” contacts.
Clearly about the types of circuit breakers in the video:
Conclusion
The circuit breaker, the characteristics and types of which we examined in this article, is a very important device that protects the electrical line from damage by powerful currents. The operation of networks that are not protected by automatic machines is prohibited by the Electrical Installation Rules. The most important thing is to choose the right type of AB that is suitable for a particular network.
Circuit breakers are devices that provide wiring protection under short circuit conditions, when a load is connected with indicators exceeding the set values. They should be chosen with special care. It is important to consider the types of circuit breakers, their parameters.
Automatic machines of different types
Characteristics of machines
When choosing a circuit breaker, it makes sense to focus on the characteristics of the device. This is an indicator by which you can determine the sensitivity of the device to a possible excess of current values. Different types of circuit breakers have their own marking - it is easy to understand from it how quickly the equipment will respond to excess current values to the network. Some switches respond instantly, while others are activated over a period of time.
- A - marking, which is affixed to the most sensitive models of equipment. Automatic machines of this type immediately register the fact of overload and quickly respond to it. They are used to protect equipment characterized by high accuracy, but in everyday life they are almost impossible to meet.
- B - characteristic, which have switches that operate with an insignificant delay. In everyday life, switches with the appropriate characteristics are used together with computers, modern LCD TVs and other expensive household appliances.
- C - a characteristic of automata, which are most widely used in everyday life. The equipment begins to function with a slight delay, which is enough for a delayed response to registered network congestion. The network is turned off by the device only if it has a fault that really matters
- D - characteristic of switches that have a minimum sensitivity to exceeding current indicators. Basically, such devices are used as part of the supply of electricity to the building. They are installed in shields, almost all networks are under their control. Such devices are selected as a fallback option, since they are activated only if the machine does not turn on in time.

All parameters of circuit breakers are written on the front
Important! Experts believe that the ideal performance of circuit breakers should vary within certain limits. Maximum - 4.5 kA. Only in this case, the contacts will be under reliable protection, and current discharges will be discharged in any conditions, even if the established indicators are exceeded.
Types of machines
The classification of circuit breakers is based on their types and features. As for the types, we can distinguish the following:
- Rated breaking capacity - this is the resistance of the contacts of the switch to the effects of currents with high rates, as well as to the conditions in which the circuit is deformed. Under such conditions, the risk of burning increases, which is neutralized by the appearance of an arc and an increase in temperature. The higher the quality and durability of the equipment material, the higher are its corresponding abilities. Such switches are more expensive, but their characteristics fully justify the price. Switches have a long service life, do not require regular replacement
- Rating calibration - we are talking about the parameters in which the equipment operates in normal mode. They are installed at the stage of equipment production, and are not regulated already in the process of its use. This characteristic allows you to understand how strong overloads the device can withstand, the period of time of its operation in such conditions
- Setpoint - usually this indicator is displayed as a marking on the equipment case. We are talking about the maximum current values in non-standard conditions, which, even with frequent shutdowns, will not have any effect on the functioning of the device. The setting is expressed in current units, marked with Latin letters, digital values. The numbers, in this case, display the face value. Latin letters can be seen in the marking of only those machines that are made in accordance with DIN standards