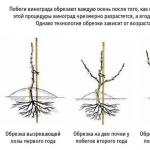
Recently, the technology of arranging plant roofs has become very popular. A green roof is a multi-level roofing "pie" on which you can grow unpretentious beautiful lawns or even set up a real garden. Today, do-it-yourself green roofs are being built not only on the roof of a private house in the countryside, but also on urban high-rise buildings.
Green roof features
Trees and grass growing on the roof are by no means a tribute to modern fashion. Suffice it to recall the Gardens of Babylon, which glorified ancient Babylon. In the 18th century, Icelanders lived in turf houses that they carved out of the hills. At the same time, it was found that the vegetation that lives on the roof is able to protect against cold and wind in bad weather.
Green roofs are a national tradition in Norway that has been around for centuries. They are covered with birch bark, peat and overgrown with grass and moss. Green roofs have firmly settled on the roofs of Toronto, Zurich, San Francisco, London, and Madrid.

Vegetable eco-roofs are very popular, and there are several good reasons for this. Let's find out what's the matter:
- Durability. A green plant roof with gas will last longer than a regular roof. After all, soil and plants in the best way protect it from negative environmental factors, as well as from weather conditions. If you properly care for such a roof, the life of the roof will exceed 20 years.
- Delay of rain runoff. This is especially true when there are heavy rains, because the sewer system often cannot cope with a large amount of water. Lawns and other vegetation located on the roof are able to absorb some of the precipitation - about 27%. This is an effective way to help prevent flooding. In addition, pollution of nearby rivers and reservoirs is reduced.
- High levels of sound insulation. Having arranged a roof garden, you will notice that the noise background has significantly decreased in the residential area. And this is especially important for residents whose houses are located in areas where it is very noisy.
- Great thermal insulation. In a house under a plant roof in the winter it is warm, and in the summer heat it is cool. Therefore, heating and air conditioning costs are reduced.
- Extra space. The territory of the exploited green roof provides additional usable area for landscape design. Here you can sow a lawn, plant a garden, and equip a pool. So you get a great place to relax.
- Improving the environment from an environmental standpoint. This is especially true for big cities. Indeed, sometimes it is difficult to find a place for a park among concrete and asphalt. Plants located on the roof are able to purify the air with high quality. They retain more than 25% of dust, harmful impurities and substances that are contained in the atmosphere. They also reduce the greenhouse effect and smog. For example, in Chicago in 2001, many green roofs were built - about 1000 square meters. m.
- Aesthetics. The house under the green roof looks unusual and original. And how much attention it draws to itself, not to convey! In America, there is even a special corporation for green roofs. She is engaged in the free installation of eco-roofs on any home. In Russia, such trends are not yet widespread.

Varieties of green roofs
There are several types of plant roofs, depending on the technology of their arrangement. Let's consider them in more detail.
Extensive green roofs
Such landscaping of roofs consists in the use of light soil (the layer should be 5-15 cm thick) and unpretentious plants that do not require constant watering. As a rule, evergreen and hardy species are chosen for planting, which form a continuous carpet on the roof, for example, sedums and other succulent specimens. The weight of the soil layer, as well as planted plants, per 1 sq. m. averages 20 kg. Therefore, there is no need to further strengthen the base.

This is a fairly simple technique for protecting the roof and creating an autonomous ecosystem. It is usually used for building a green roof on country arbors, outbuildings, garages and private houses. Creation of recreation areas is not expected. Therefore, such a solution can hardly be called a full-fledged garden.
Intensive green roofs
This option involves laying out a full-fledged garden on the roof, creating paths. It is possible to design a zone where the household will have a picnic, and install gazebos. Often on such roofs there are pools and other reservoirs. Most often they are formed on multi-storey buildings, shopping and entertainment centers. Green roofs are not uncommon for expensive hotels for a long time.

To plant trees and shrubs, a reliable foundation is built and a layer of soil is poured, which has a thickness of up to 1.5 meters. The load of the entire system with soil and plants, which is per square meter, in this case reaches 700 kg. Intensive systems require regular watering. Other care is also needed - mowing and fertilizing.
Flat and pitched eco-roofs
Roofs with a lawn or garden are divided into flat and pitched. For many centuries, plant roofs were built exclusively on flat surfaces. For example, tarred roofs in the city are such today. However, it is also possible to equip a green cover on the sloping roof of a private house located in a village. For this, special screens are used. They are intended for plants on the roof. Thus, both landscaping techniques are applied on flat roofs. On the pitched one, it will be possible to equip the lawn only using the extensive green roof technology.
Green plant roof construction
Any green roof is a so-called "layer cake". It consists of several mandatory layers. Let's consider them in more detail.
1. Foundation
The first layer of a plant roof is the load-bearing structures of the roof itself. For a flat roof - these are concrete floor slabs, for a pitched roof - a solid crate. If there is a roof covering, for example, tiles, it must first be removed. In the case of a flat slab, it is recommended to create a slight slope of the roof. It should be directed towards the drain and be about 1.5-5 degrees. To do this, use a cement-sand screed.

2. Waterproofing layer
Before you make a green roof, take care of waterproofing. Without exception, all plants need moisture and regular watering. But such exposure is extremely harmful to the materials from which the roof is made. Therefore, waterproofing is used, which separates the soil on which plants grow from the roof itself.
Make sure that the waterproofing layer is as reliable as possible. Otherwise, in the event of a leak, in order to carry out repairs, you will have a hard time. After all, removing all the layers located on top of the waterproofing is very expensive and time consuming.

For this purpose, polyethylene film or polymer membranes are used. Liquid rubber is also great for this. Waterproofing can be placed directly on the roofing. Or pre-create a coating of marine plywood. If you use boards, then there should be no gaps between them. Usually make 2 layers of waterproofing. The lower one is fixed mechanically to the base. The top one needs to be welded on. The seams are securely soldered.
3. Thermal insulation
The heat-insulating layer, as a rule, is created from plates made of cork. Polyurethane in the form of foam or extruded polystyrene foam has also been successfully used. The plates are stacked tightly together. If the top layers do not create enough pressure, connect them using special glue.

You can not fix the plates to the base. On a pitched roof, additional insulation is not required, since this layer has already been laid from the side of the attic between the rafters. If you decide to equip a green moss roof, it will be useful to know that this plant has been used since ancient times to insulate roofs of houses.
4. Root barrier
The root protection layer is necessary to prevent damage that can be created by roots growing deep into the roof. The root barrier, as a rule, is an ordinary polymer film or foil. A film that has a metallic coating is ideal. It is laid on a layer of waterproofing.

Many manufacturers produce waterproofing materials, which contain anti-root additives. If you want to plant ground cover species on the roof, then you can not lay such a coating. This also applies to the procedure for creating a lawn, make an ordinary waterproofing, that's enough.
5. Drainage layer
Drainage material is able to retain a certain amount of water, which is needed for the life of plants. In this case, water should move freely along the roof towards the drain. In the case of a sloping roof, the water drains on its own if you provide special holes in its corners for this.
On a flat roof, care must be taken to ensure that water does not stagnate. To create lower drainage, it is recommended to lay expanded clay, which is distinguished by a large or medium fraction. Chipped pumice, perlite coconut or polyamide shows good results.
You can buy special artificial mats. Among them are "geomats" made of plastic, which are mesh-lattices of great flexibility, similar to coarse washcloths. In extreme cases, loosened clay and ordinary gravel are suitable. When arranging the drainage layer, take care to install perforated pipes to improve water flow.
6. Filtration layer
This layer is necessary to retain unnecessary precipitation. After all, they are able to clog drainage, getting from the soil with water. A good filter is geotextile, which has a high density. In addition, the geotextile helps to avoid mixing of the drainage layer with the soil, which occurs over time. It is laid flat.

7. Lathing
If you plan to green a sloping roof, then you should use a geogrid. After all, when the slopes are more than 25 degrees, the soil will slide without fixing. The geogrid looks like plastic cells. She is light enough.

When arranging a green roof with your own hands on a roof that has a slight slope, it is enough to make special partitions from wood. They will not allow the soil to slide. To create an aesthetic effect, lay out a beautiful geometric pattern with lattices. Do not forget to make sides around the perimeter for fastening the “layer cake”.
8. Fertile soil
At this stage, a layer of soil is created. In it you will plant plants. When choosing a soil mixture, the exactingness of the planted plants is taken into account. For ground cover species and grass, a layer of 5-10 cm thick is required to create a lawn. The height of the soil for planting shrubs and trees should be up to 1 m. Soils for use on the roof should be light in weight, be warm, absorbent and porous. Well, if they are resistant to compaction. The usual mixture from the garden is not suitable for this business.

You are advised to use a light soil mixture that consists of neutral peat with special ingredients such as fine expanded clay, perlite. Also add sand, clay and shale. Optionally - chopped bark and wood chips. Don't forget about fertilizers. The top layer can be mixed with grass seeds, which is intended for growing lawns.
9. Plants on the roof
After laying all the layers for the green roof of a wooden house, you can start planting plants.
- When choosing representatives of the flora, keep in mind that conditions will be created here that are close to desert ones. It is the sun and the wind. Therefore, choose the most unpretentious species.
- Among trees, give preference to dwarf species. They should have a small root system.
- The roof planted with frost-resistant grass, as well as ground cover plants according to the technology of extensive gardening, looks favorably - sedum, stonecrop, young, creeping phlox.
- Choose moss, various meadow flowers, some bulbs, bluebells for planting on the roof. Also look out for cloves, oregano, and lavender.

Thus, roof gardening is a fashionable trend that allows you to radically change the appearance of buildings and add useful space to your garden. In addition, if you follow the technology correctly, you can protect your home from bad weather and excessive noise.
This idea originated in Northern Europe and Russia. The inhabitants of Scandinavia have long warmed their homes with natural materials, pieces of moss. In Russia, thatched roofs were covered with turf to avoid fires.
The rebirth of a forgotten design solution is associated with the name of the German architect Karl Rabitz. He revived the concept of "green roof" by presenting at the World Exhibition in Paris a house with green spaces instead of a traditional roof in the 19th century.
The simplest solution to the issue of roof gardening is container gardening. With this system, the plants are placed in boxes or containers.
"Green roof" is a way to emphasize the sense of style of the owner of the house. It will give your estate a unique original look.
"Green roof" are divided into two types - intensive and extensive. Intensive method, more complex and requires special care. But on such a roof you can make not only a green lawn, but also relax on it.
The extensive view is unpretentious and can be located on roofs with a slope of up to 45 degrees. Access to such roofs is limited.
Studies conducted by scientists from the Scandinavian countries (and especially Norway) have convincingly proved that grass roofs can significantly reduce the level of air pollution, enrich it with oxygen and moisture. The most important thing is that the grass carpet of the roof creates a special energy in the home, where a person, tired of the modern hectic life, can again feel in harmony with nature.
However, greening the roof is beneficial not only from an environmental point of view, but also from an economic point of view. In particular, a grass-covered roof contributes to the conservation of heat and energy resources, can significantly reduce temperature fluctuations in a dwelling, and improves the sound insulation of a building.
The "green" roof owes its high thermal properties, first of all, to the air gap formed between the stems of plants.
Unlike modern roofs, which heat up to 80°C on hot days (which causes air movement and, as a result, pollution of it with dust particles), a grass roof only heats up to 25°C, and due to convection, almost no heat is lost. . In addition, due to the “breathing” of plant roots, the temperature of the grass cover, even in frosts, is always above zero. The heat radiated from the walls of buildings is also partially absorbed by the grassy roofing carpet and accumulated by the soil layer and the moisture contained in the plants.
Thanks to these properties, houses with a green roof have an excellent microclimate. In the summer, a pleasant coolness reigns in such a dwelling. In fact, the grass carpet of the roof is a kind of natural air conditioning system.
Finally, the green roof is a great self-cleaning natural air filter. After all, the grass perfectly captures dust particles, and the rain washes them away again.
Roof gardening is a new direction in landscape design in our country. But every year the "green roof" finds its fans and pleases more and more admirers with its appearance.
How to make such a grass roof
The construction of a grass roof is similar in most cases. This is a supporting truss structure and a crate made of unedged boards, on top of which turf was laid.
Instead of the waterproofing that is widely used today from rolled bitumen or other materials, a layer of birch bark was laid on the crate, on top of which turf was laid in two layers or the soil mixture was poured for sowing it with grass seeds.
However, before touching on the technology of laying bark and turf, it should be noted that the own weight of a green roof is about 250 kg/m2. This means that the shear load (especially on roofs with steeper slopes) can move the entire grass cover down. To avoid this, fences were an indispensable constructive element of green roofs. Their function was traditionally performed by sod-protecting beams or boards laid along overhangs - the so-called sod holders.
At the same time, when creating a grass carpet, the construction of the roof had to ensure unhindered runoff of rainwater from the roof slopes. To do this, it was necessary not only to choose the right shape of the sod holders, but also to properly attach them to the crate.
Strips of birch bark were laid overlapping each other. In the overhang zone they were laid in 5…8 layers. At the same time, the strips released from under the fencing beam and put on it were laid with the outer side up. This was done in order to ensure effective water drainage and protect the sod holder and the end parts of the batten boards from moisture. In addition, the bark, laid with the outside up, is an important decorative element of a green roof.
To increase the life of the roof, the rest of the bark was laid with the outer side down, since the inner side of it provides more effective protection of the batten from the mixture of sigumic acids contained in the soil.
To protect the turf laid on the sides of the pediment from wind and water erosion, natural stones were laid on the edges of the pediment. Later, gabled wind elements, which were used as logs, began to be used for this. They were laid so that the ends protruded above the ridge. Connected logs crosswise. And since the logs had the same thickness as the turf holders, together they formed a kind of wooden frame for the entire roof.
In another version, a windboard was used to protect the turf from erosion. They fastened it with wooden pins, and covered it with birch bark from moisture. Sometimes, instead of bark, a horizontally laid covering board was used.
One of the important elements of traditional grass roofs is a wooden gutter, which was made from boards connected to each other on screws at right angles or hollowed out from a tree trunk.
The weak point of grass roofs is openings (in particular, for chimneys). To avoid the flow of water along the walls of the pipe into the house, stone slabs protruding beyond the pipe were immured into its masonry.
At the same time, sheets of birch bark were placed under these slabs, diverting the flow of water to the roof. Stone slabs on the side of the slopes were arranged in steps, which contributed to a more efficient removal of rain or melt water from the pipe walls.
As a fencing element, a log is used here, supported by a thrust hook fixed under the crate. In this case, the hook, cut into the log of the upper crown, is fixed under the crate, and the round timber itself lies completely on the birch bark. So that water does not accumulate on the roof, slots are made in the sod holder for its drain.
Round timber, in turn, is also lined with birch bark. Despite the presence of such moisture protection, the sod holder still needed to be periodically replaced with a new one.
For example, when attaching a thrust hook over a crate, a space is formed between the birch bark and the sod holder, which ensures effective water drainage. And when fastening the enclosing element with the help of a dowel, special slots were provided in the sod holder for water drainage.
The solution is also interesting, when the fencing beam is attached to the side, with an indent of 5 cm from the edge of the overhang, which also ensures a quick runoff of water.
In all these cases, the sod holders are protected by birch bark. The overhang zone itself is covered with bark in several layers.
You can also apply the option of fastening the fencing beam using a powerful dowel, cut into the end part of the rafter. This method of fastening was used for roofs with hanging rafters protruding from the overhang by about 12 cm.
Often, in order to save wood, instead of logs or beams for fencing grass cover, boards 3 ... 4 cm thick and 12 ... 16 cm wide were used, depending on the thickness of the green roof
To ensure water runoff, holes or cuts 3 × 3 cm in size were made on the lower edge of the board every 20 cm. On the side of contact with the turf, they were expanded, giving the shape of a funnel. Sometimes boards were installed without drain holes. In this case, they were fastened so that they protruded 2 ... 3 cm beyond the overhangs. For this, as a rule, persistent steel corners were used, which were screwed to the crate with screws.
The construction of an earthen (grass, green) roof is not at all more difficult, and in some ways easier, than any other type of roof. The most important thing in the construction of a grass roof is that the truss system provides the necessary margin of safety for the supporting structures of the roof, since the weight of the earthen roof is quite large. For wooden houses made of carriage and logs (and even houses made of timber), the large weight of an earthen roof is rather a plus - it accelerates the shrinkage of a wooden house and ensures good closing of the crowns of a building, whether it be a cottage, a bathhouse, a summer house or another structure. For heavy roofs (turf, tiled, slate, etc.), a slab roof structure is usually used, where powerful slabs and a horse transfer the load to chopped gables. The bearing capacity of the truss structure, according to building codes, must withstand a load of about 300 kg / m2.
The grass roof consists of the following components:
1. Grass (vegetation)
2. Turf (earth, peat)
3. Geogrid (if necessary)
4. Waterproofing (if necessary)
5. Insulation 150-200 mm
6. Insulation 100 mm
7. Waterproofing
8. Sod board 50*200(250) mm
9. Drainage (rubble, gravel)
10. Drainage pipe (with an organized drain)
11. Fasteners (galvanized metal profile)
12. Lathing (flooring) board 45-50 mm
14. Gutter 30*250 mm auxiliary
15. Support bar 50*100(75) mm
16. The outer wall of the house
It is advisable to use a geogrid with a sufficiently large roof slope (over 25 °), the upper waterproofing of the insulation (4) is also used only in the case of using a heater with a high degree of moisture absorption, commonly used PPS boards do not require this. Whereas the most stringent requirements must be imposed on the quality of waterproofing (7). It is desirable to cover drainage (crushed stone) with geotextile.
In the old days, peat was used as a heater, waterproofing was made of birch bark, and an ordinary log was used as a turf board.
When erecting roofs with hanging rafters in the southern and western regions of Norway, the length of the rafters was taken equal to 3/5 of the width of the house, which corresponds to the slope of the roof slopes of 33 °.
When constructing a roof with layered rafters, the slope of the slopes was determined by the ratio of the height of the roof in the ridge to the width of the house. For example, with a slope of 22 °, this parameter is 1/5.
Such a green roof garden has numerous advantages, among which it is worth noting such as:
Green roofing helps to create a unique and original design of the house.
1. A significant improvement in the environment in the area around the house. Plants on the roof perfectly purify the air, make it fresher and more pleasant. In addition, the presence of such a small garden can perfectly supply its owner with only the freshest and most environmentally friendly products.
2. Having a roof garden allows you to control the level of humidity. Slow evaporation of moisture from the soil surface makes it possible to establish a normal microclimate around. In addition, in summer it becomes noticeably cooler and more pleasant, and in winter the soil layer allows you to effectively insulate the entire structure, which greatly reduces heating costs.
3. The vegetative layer on the roof protects the building and residents from electromagnetic radiation, ultraviolet rays, and mechanical damage. Such a roof often simply does not need an additional layer of insulation, since this function is performed by the soil substrate.
4. The dust content of the site is reduced, since green spaces trap dust particles, the effect itself only increases when watering.
5. Living in the house becomes more comfortable, especially on the upper floors. Plants generally have a beneficial effect, relieve stress.
6. Increases the aesthetics of the building, which means an increase in its value. Today, such roofs are more and more relevant and prestigious, many architects immediately, when designing, lay the possibility of having their own small but very useful garden on the roof.
In addition, it is necessary to note such advantages as the possibility of implementing any landscape design in which a house with a green roof will fit perfectly. The roof is covered with bright and unusual flowers, you can plant low shrubs and miniature trees, or just lay a solid green carpet.
Repair of such a roof is not required as often as a conventional one, which is due to the excellent protection provided by the earth layer and the root system of plantings. Such a “load” allows you to control temperature and humidity, ultraviolet and negative weather conditions can no longer have a destructive effect on the roof structure.
Disadvantages of a green roof
But, like any design, the green roof has disadvantages that need to be mentioned separately. When building and arranging such a garden, it is necessary to take into account the many structural difficulties that will have to be faced. This is not only a lot of weight from such a layer, but also the need to protect the structure from moisture, the influence of the soil, the root system, which has fantastic abilities to grow into any material and destroy it.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the factor that not everyone can feel at ease at a height, especially on open terraces. For some who are intolerant of heights, building a rooftop garden is almost useless, as it needs to be looked after, and for this you still need to climb up.
When constructing a roof of this type, additional costs may arise, often taking on substantial dimensions. This is not only the creation of a special structure, but also the delivery and lifting of materials upstairs, planting plants, and constant care for them. If necessary, the soil should be changed, fed with fertilizers. On the roof itself, it is recommended to provide some kind of handrails so that there is no accident when leaving.
Greening technology
Roof gardening can be done on roofs of various types, although flat roofs are considered the most convenient. Its design consists of the following layers:
1. Bases, that is, floor slabs.
2. Root protection film, which will prevent the root system of plants from damaging the roof structure. Such a film will not allow the roots to grow into the floor material, it will reliably protect it from excess moisture.
3. Next comes a special geotextile material and a plant mat. This allows you to regulate the moisture level, provide the necessary nutrition to the plants, and prevent the root system from freezing in winter when the surface is cooled.
4. Above is a layer of earthen mixture, into which the plants themselves are planted.
There is an option with strengthening a special mesh on the base, into the cells of which the substrate is poured, after which you can start planting plants, there is also a method of using a polymer base, which is soldered to the base.
There are many options for installing a green roof today, but when laying any of them, it is necessary to comply with such conditions as:
protection of the roof structure from excess moisture and germination of the root system;
accounting for a significant load from the weight of the earthen substrate and the plantations themselves;
· the need to care for the green roof, that is, there must be a hatch to exit to the surface.
Roof greening methods
Today, greening the roof can be done in two ways, which are radically different. If you wish, you can choose the most optimal method for a particular house, but we will describe the characteristics and features of each of them.
Extensive Method
The extensive method is now considered one of the simplest, many prefer it, since after the installation the roof is practically maintenance-free. Such landscaping can be used on flat roofs, on sloping ones, taking into account the presence of a slope of up to forty-five degrees. In this case, access to the roof surface is not supposed, that is, green spaces do not need constant care.
This method is not only the arrangement of an earthen carpet with planted plants, often a ready-made grass carpet is simply spread, perennial, unpretentious plants are planted. When installing, a layer of gravel is required, which will act as a drainage system. The soil layer is selected not very thick, it is possible to plant only grass, low flowers.
intensive method
This is one of the most difficult gardening methods. Not just a beautiful green lawn is being set up, but a whole system with flower beds, paths, and recreation areas. Ideal intensive landscaping is suitable for high-rise administrative buildings, for large private cottages with flat roofs and terraces on their surface. With the correct calculation of all loads, you can even put small ponds, rock gardens, arrange the most beautiful multi-tiered flower beds.
The device of a green corner of nature on the roof
So how can you make such an unusual home garden with your own hands? What features should be taken into account so that the roof retains its integrity, and the garden pleases with its beautiful appearance?
Making a green roof with your own hands is actually quite a simple and exciting activity, although a specialist should be involved here. The scheme of the roofing pie in this case will be as follows:
Wooden or concrete floor base;
A layer of waterproofing film that will protect the structure from water. The film is laid only with an overlap, it should not have gaps and defects;
· film for protection against destruction of the root system, the so-called barrier. This is necessary so that the roots do not grow through the protective system and destroy the roof;
thermal insulation layer (not always used, it is necessary to first determine the type of construction);
Special materials for green roofs can be used as drainage, but it is also possible to simply add a layer of gravel, expanded clay and sand;
Installing a filter
· soil substrate;
ornamental plants.
Roofs on which green areas are specially arranged have existed for a long time. In Scandinavia and the Baltic states, a sod roof on private houses is found everywhere. And in cities with dense buildings and very expensive land - Tokyo, New York, real parks with footpaths, benches and fruit trees are broken on the roofs of skyscrapers. Of course, setting up such a park on the roof of your own house is not a cheap pleasure and is not yet in high demand in our country. But the device of a green roof on their own house is quite within the power of anyone who wants to do it. The classic version of the Scandinavian green roof does not involve movement on it. It can be a gable, single-pitched and even a hip roof.
But since the turf must lie well on it, the angle of its slope should not exceed 28 degrees. In this embodiment, the lawn will not “move out” from the roof, and the water will not stagnate. For individual houses, two variants of green roofs are used: Norwegian and German. European houses under "green" roofs can be seen in the video. Norwegian method of roof installation Green roofs of Norway Roofing "pie" in Norwegian roofs is laid as follows: insulation is placed between the rafters, waterproofing and a special layer of material spread over the rafters, which prevents grass roots from growing through it. Then a mesh and a drainage layer are laid, for which expanded clay, broken brick, etc. can be used. The mesh is needed so that the drainage layer does not slip off the roof slopes. A layer of sod is laid on the drainage with the roots up, and the second layer is laid with the roots down. There is a Norwegian sod roof, when the mesh is supposed to be stretched after laying the first layer of sod, but then an additional crate must be installed for the drainage layer, otherwise it will simply crumble from the pitched roof.
In addition, there is an option to use special geomats instead of a layer of turf with roots up. They are made of polymer fibers, which have a multidirectional structure. The “clawed” surface of the geomat keeps the drainage layer and turf from shedding. German method of roof installation Green roofs in Germany It is widely used in inverted roofs with slight slopes. But it is also suitable for pitched roofs. waterproofing is laid on a continuous crate; a layer of insulation is placed on it, which is not afraid of constant exposure to water; then geotextiles are laid, it limits the germination of plant roots; followed by a drainage layer and turf. Plants for green pitched roofs should be chosen that do not require any regular maintenance and do not grow more than 15 cm. Otherwise, they will need to be mowed somehow, and this is an almost impossible task for pitched roofs. In addition, regardless of which option you choose - Norwegian or German, a turf roof weighs a lot. Its weight is from 45 to 60 kg per 1 sq. m roof. Therefore, for the construction of such a roof, a reinforced truss structure and a continuous crate will be required. Roof made of slag It is possible to use the old method of arranging a sleg roof for a green roof.
The main load-bearing elements in it are slegs or side girders, made of 2/3 of the logs, which are based on chopped or stone pediments. For additional support, if the house is longer than 5.5 m, vertical posts can be mounted under the girders, which rest on the internal load-bearing partitions of the house. There may be three or more runs. A continuous crate is mounted on them, and, further, a roofing "pie" is laid.
Green roof variations
Green grass roof is classified into intensive and extensive. For the latter option, only grass cover is used, sown on a thin layer of soil, and for taller plants, cassettes and containers are used. Drought-resistant plants are suitable for this type of roof, which should be watered sparingly. Care consists in weeding, cutting, the surface can not be fertilized if mixtures with gravel, peat, organic matter, sand and expanded clay were used for planting in the required proportions (depending on the type of planting material).
The thickness of the peat should be 5-15 cm, this must be taken into account when planning. This type of roof landscaping is inexpensive, easy to maintain, great for any type of building. It is ideal to use it for the southern regions with a dry climate.
Green roofs of the intensive type are beautiful and presentable, but they require a large layer of soil, which allows growing not only shrubs, but also low trees.
The device requires a powerful system and a complex "pie", of particular importance is hydroprotection and a barrier to the root system, which can be longer than average. Most often, this roof improvement option is used for large flat roofs with a large landing area.
When installing, it is necessary to take into account the weight of the substrate and plantings, i.e. the crate and truss system must be powerful, additionally reinforced. The total depth of laying the soil is up to 60 cm, not every truss system can withstand such conditions. The loads are preliminarily calculated, it is best to involve specialists in this, since it will not be possible to make the calculations correctly on your own. In addition to the usual loads (wind, snow), it must be taken into account that during rains the soil gains moisture and becomes heavy. This is the most important moment, without which it is impossible to start the installation of the roof. The substrate is selected fertile, rich in organic matter. Watering is required frequent, so you must first take care of waterproofing.
Do-it-yourself green roof device
Green grass roofs can be easily made by hand. It is only necessary to choose the type of roof, contact a specialist for help with calculations, and decide on the necessary elements. There are many options for creating a base. It can be an ordinary wooden crate or solid slabs, but we must remember that a grass roof needs waterproofing, which will prevent moisture from penetrating inside, protecting the under-roof space from adverse atmospheric phenomena.
The "pie" of the roof will include the following elements:
top layer - plants of the selected type (today you can buy special seed, not only grass, but also low shrubs with a root system that does not penetrate deep);
arrangement of a suitable layer of soil (attention should be paid to the composition of the substrate for planting);
filter;
drainage layer (special spongy material);
thermal insulation;
a special barrier that prevents the germination of the root system of plants;
waterproofing - special durable films that prevent moisture from penetrating inside the roof structure;
The base of the roof is a crate in the form of processed OSB boards or moisture-resistant plywood.
When planning a green roof, it is important to immediately foresee the need for regular watering, otherwise the plants will turn yellow and begin to dry. It is required to periodically fertilize so that the plants do not lose their decorative effect. You should immediately provide for the presence of cassettes for planting plants, arranging a drain for excess moisture. As waterproofing, you can use films made of liquid rubber, polymer membranes, polyethylene. Such films are spread over the surface of the crate, after which they are fastened with an overlap (if the material is rolled out in stripes).
A root barrier is also necessary so that the plants do not damage the waterproofing and the truss structure. It must be done so as not to change it annually. Today you can buy special materials for green roofs, which are very easy to attach to the surface, do not allow roots to penetrate into the base.
Due to the drainage device, all excess moisture is removed, water is retained for the necessary time to feed the plant. It is most convenient to organize landings in special cassettes. For a sloping roof, it is necessary to arrange special drainage systems with drains perpendicular to the ridge. On a flat roof, it is required to provide for a slight slope, to ensure the removal of moisture into the general storm drain. It is allowed to install a hidden gutter system, which not only preserves the stylish look of the facade, but also ensures the correct, quick drain of excess moisture. The cost of such a hidden system is higher, but its effectiveness is many times better.
In addition to the drain, a layer of expanded clay of large and medium fractions should be arranged, evenly distributing it over the surface (for flat blood). For sloping roofs, you can purchase special geomats that quickly roll out along the slopes. In appearance, they slightly resemble washcloths, but their drainage properties correspond to the required ones.
Any grass roof should have a filtration layer that prevents clogging of the drainage from various small inclusions. It is usually recommended to use geotextiles for this purpose, which prevent mixing of two different layers: drainage and substrate.
The green roof includes several layers, each of which performs a specific function:
- plant layer. The choice of green spaces depends on the thickness of the soil layer, the location of the roof, the climate and the personal wishes of the customer. The most popular is not picky vegetation: lawn grass, moss, wild flowers, alpine plants. In cold regions, frost-resistant plantings are planted on the roof.
- soil layer. Instead of ordinary earth, a substrate is used, which has a lower specific gravity. This reduces the load on the ceiling, which is especially important for intensive roofs. Two types of mixtures are popular. The first includes expanded clay, perlite, brick chips and compost. The composition of the second includes tree bark, expanded clay, perlite, foliage, compost, coconut fiber. In economy options, a simplified soil of perlite, expanded clay and compost is used. For ease of maintenance, the soil can be placed in plastic boxes placed on pallets.
- filter layer. It protects the drainage from clogging with soil particles and is made of geotextiles. Thermally bonded material is used, which does not silt up during the entire period of operation. To protect the roofing cake from destruction by plant roots, a root protective film is used. It is made from non-woven polypropylene material.
- Drainage. Four types of drainage systems are used, made on the basis of geomats, perforated polystyrene sheets, geomats or a perforated layer, supplemented with drainage pipes. For drainage, perforated pipes made of polyethylene or polystyrene, made under pressure, are used. As an alternative, perforated asbestos pipes are used or, in a budget option, a layer of expanded clay.
- Waterproofing. This layer prevents moisture from penetrating the floor slab and external walls. It is a PVC membrane or bitumen-based waterproofing membrane equipped with anti-root protection. Alternatively, liquid rubber or polymer film is used.
Important: when installing a flat roof, waterproofing is laid with a slope of 3-5% to ensure water runoff.
- thermal insulation. Perlite sand or foam glass is used as an insulating material. They are not toxic to the microflora contained in the soil, and ornamental plants, do not deteriorate their properties when exposed to moisture. Mineral wool or extruded polystyrene foam boards can be used for thermal insulation.
The main difference between the design of an intensive roof and an extensive one is the location of the thermal insulation. To protect against mechanical damage during the operation of the roof, it is laid on top of the waterproofing coating.
Surely at least once, but you have heard about this miracle of Scandinavian gardeners - the “green” roof. It covers many houses of our northern neighbors. Beauty: instead of tiles or slates - a real carpet of flowers and herbs ... But Scandinavia, with its cool summers and warm winters, is one thing, and Russia is quite another. Here you gape for a week, and sorry, goodbye, beloved garden! Will the "green" roof survive in domestic conditions? Are alternative solutions possible? Let's try to understand our article.
Why is it necessary? Or why not
There are several obvious advantages of a “green” roof at once: they are beautiful, practical and perfectly enrich the air with oxygen. Such roofs absorb rainwater well. A layer of soil up to 10 cm thick absorbs three-quarters of rainfall. This reduces the load on the drainage system and storm sewers.
Scandinavian roofing is an excellent sound insulator. Neither the sound of rain, nor the clatter of birds that tire you in houses with metal tiles will disturb you. Another advantage is passive energy saving. Green spaces prevent the heating of the roof in summer and retain heat in winter. Accordingly, the rooms themselves will have a more balanced climate all year round.
Oddly enough, but Scandinavian roofs also have financial benefits. Greenery protects the roofing from ultraviolet radiation, bad weather and mechanical damage (for example, as a result of hail), and therefore the roof will last much longer. If you want to sell a “green” house, then for sure its price will be higher than the cost of an ordinary building.
Now - about the shortcomings.
The most important, of course, has to do with money. The arrangement of the Scandinavian roof will require serious investments. Especially when it comes to intensive gardening. In addition, not all roofs can be made “green” (unless they can be painted! :)). Some of the houses already built may not be able to withstand the additional load.
Another important issue is the protection of the roof from leakage. Even if you lay down a waterproof membrane, the roots of plants (especially trees and shrubs) can tear it. If during installation you did something wrong, leaks will begin. And repairs will be expensive and difficult. We'll have to dismantle the entire roofing "pie". Finally, such roofs are simply difficult to assemble. Surely, you will spend a lot of time trying to find or grow the most resilient plants.
What is more profitable?
A typical Scandinavian roof is with slopes and a layer of soil of about 20 cm. This is enough to grow not only grass, but even trees and shrubs on it. This type of landscaping is called intensive.
A rooftop garden is a spectacular, but also expensive option. But sod roofs with extensive landscaping require almost no maintenance. Low unpretentious plants are planted on a thin layer of soil or compost. Enough 5-7 cm.
“Green” roofs are made not only flat, but also tilted. The pitched design has advantages over the flat one. For example, thanks to it, excess moisture itself flows down. Therefore, sometimes waterproofing and drainage systems, without which a flat roof with vegetation cannot do, are not installed on slopes at all.
What to plant?
The most inexpensive and suitable landscaping option for the Russian climate is steppe grasses: dandelion, plantain, knotweed, wormwood, cuff. They can be allowed to grow without mowing. This will add a special “Russian” charm to the roof. You can also try bent grass. This grass does not need to be mowed, but it does not like to dry out.
A more “cultural” option is stonecrop, young, sedum. They are quite decorative: there are many types with different shades, from yellow and green to reddish. These plants practically do not need watering, rain is enough for them. They also do not require fertilizer. The disadvantage is that these herbs grow for a long time.
In the nursery, one such plant costs 25-40 rubles. To save money, many summer residents grow them below, and then transplant them to the roof. Florists note that it is better to grow sedums not from seeds, but from cuttings: cut branches and immediately plant them in the ground.
An even simpler option is moss. It is known that it can grow even on rocks. This hardy plant is perhaps the most suitable option for those regions where winter lasts nine months.

Installation cost
The price per square meter of a Norwegian roof depends on many factors, including the type of greenery on the roof. Protection (hydro, steam, thermal insulation), drainage and filtering layer will cost about 10 euros per sq.m. The substrate costs about 11 euros, plants - 10 euros. On average, extensive landscaping per 1 sq. m will cost from 30 European "money", for intensive gardening you will pay from 50 euros per sq.m.
Domestic experience
Not only summer residents have been interested in the installation of Scandinavian roofs in Russia for more than a decade. Back in 2000, standard solutions for greening flat roofs were developed. The Moscow Committee for Architecture, with the support of the Moscow Government, even issued recommendations for the design and improvement of such coatings for residential and public buildings. But already there it was stipulated that roof gardens can be arranged only on a limited number of objects. That is, in other words, this pleasure is not for mere mortals.
And yet, many summer residents dared to implement a bold idea. Others, after a grueling struggle for the life (and happiness!) of plants, gave up. But someone did a really good job...
So, one summer resident near Moscow built a real “Hobbit house” on his site. When calculating the loads, I studied different options for the frame structure. In his choice, he was guided by two criteria: low cost and ease of installation. As a result, the owner settled on a round metal frame sheathed with waterproof plywood.
Not bad, right?


The story of a resident of St. Petersburg is known (as you know, this city differs from Moscow in an even harsher climate). Once Alla Sokol was carried away by the overseas project “Feed Yourself”: she watched a program where they talked about growing ornamental plants and vegetables on the roof. Back in the 1990s, as a pioneer of urban gardening, she volunteered to green up apartment buildings. I started, as usual, from my own roof. I just planted greens. And then ... For many years of landscaping, I have not tried anything. Well, except that she didn’t grow potatoes!

In 2002, the hobby has already grown into a whole project "City Mini-Farm", which was financed by the charitable "Gagarin Fund". Gardeners themselves prepared biosoil from peat, made biohumus. They proved that it is possible to grow vegetables on the roof, and seedlings for sale, and flower seedlings ...

In the course of their work, Alla Sokol's associates made another important discovery. The sections of the roof that were under the “green” coverlet were better preserved than those that were “bare”. There were no cracks on them: the film on which the lawn was located protected the roof from drying out ...
By the way, you can read more about Alla Sokol and her experiments.
Have we still not convinced you that a green roof is worthy of your attention? Then there is another example. A very original house was built for himself by the Russian architect Igor Firsov. The building is located on the shores of the Gulf of Finland, 140 km from St. Petersburg.

The handmade log cabin was made of rounded logs. The architect laid the rafter system like a fan. As a result, an unusual construction was obtained, which the author calls the “canonical hyperboloid”. Small house of 60 sq. m harmoniously blended into the landscape, which is called the "northern": with ship pines, gray boulders and crystal clear air. The cottage seemed to have grown up in the midst of this wild splendor ...
"Green" roof only enhances the impression. For its device, the architect used a special flooring made of logs. It was laid on top of a wooden truss system. Then there was such a “pie”: three-layer waterproofing, insulation 10 cm thick, expanded clay, geotextile material, soil and grass. To prevent the soil from sliding down, stones were laid along the perimeter of the roof. The edges of the grass roof are lowered - this allows excess moisture to drain.

By the way, to collect rainwater, Igor Firsov came up with an equally beautiful structure - he walled up a plastic barrel with a tap into stones. The sloping roof, moreover, makes it easy to climb it if the need arises. And to make it easier to do, on one side of the house there is another ingenious design in the form of a stone staircase. And how beautiful it must be that rainwater flows from the roof along this cascade!
Alternative Solutions
What about those who do not want to mess with a complicated structure, but still want to make their roof “green”? There are several simpler solutions.
- The easiest thing is to arrange plants in pots with a soil substrate on a flat roof. In the summer you can enjoy a mini-garden, for the winter it is removed into the house.
- Grass can be grown on the roof in temporary pallets. In November you remove the cassettes, in the spring you put them out again ...
- On a flat roof, you can equip greenhouses. They will become a kind of winter gardens. By the way, according to research, roofs with greenhouses protect the house well from overheating - they take away excess heat.

Finally, another interesting option, which has already been partially mentioned, is moss. Surely, many summer residents have noticed how this velvet plant eventually settles on tiled roofs. And not one has already tried various ways to deal with the green scourge. But why not look at the problem differently? ..
Agree - the moss on the roof makes the house more romantic and colorful. But how do you grow moss if you don't wait for nature to take its course? There are many ways. We will talk about the most unusual - drawing with moss.
For three handfuls of moss, you will need 2 tsp. hydrogel (sold in flower shops, it absorbs well, but also gives off water), water, kefir. Mix all the ingredients in a blender and pour into a bucket. Then apply to the surface (roofs, walls, fences, etc.) with a brush or spray gun. All! All you have to do is water once a week.
Summer residents note that moss grows especially well on the north side of the house. After all, it was not in vain that in childhood we were taught to look north in the forest along the moss-covered side of the trees! So that this plant does not dry out in summer, it is better to plant tall trees on the south side of the buildings. Keep in mind that as moss grows, it regularly blocks drains. This can be avoided by using wider drains (up to 125 mm).

Hassle with the arrangement of sod roofs still not scared you? Then in the next issue we will tell you about green roof installation technologies, how to calculate roof loads, and much more…