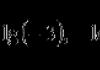1. PHILOSOPHICAL CATEGORIES (choose 3 correct answers)
A) * matter
B) *consciousness
C) power
D) integration
E) * being
F) revolution
G) demographics
H) stratum
2. FUNCTIONS OF PHILOSOPHY (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *worldview
B) technological
C) *critical
D) positivist
E) illusory-compensatory
F) *methodological
G) differential
H) class
3. ORTHODOX SCHOOLS OF INDIAN PHILOSOPHY ARE (Choose 3 correct answers)
A) Buddhism
B) *vedanta
C) charvaka
D) *vaisheshika
E) Taoism
F) *nyaya
G) Lamaism
H) Jainism
4. CONCEPTS OF ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *karma
B) yin
C) *atman
D) wu-wei
E) tao
F) xiao
G) ching
H) *brahmin
5. CONCEPTS OF ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY (choose 3 correct answers)
A) karma
B) *yang
C) atman
D) *wu-wei
E) purusha
F) *Tao
G) brahma
H) samsara
6. THE SAGES OF THE MILES SCHOOL OF PHILOSOPHY (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *Thales
B) Socrates
C) Heraclitus
D) *Anaximenes
E) Pythagoras
F) Plato
G) *Anaximander
H) Seneca
7. CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF THE RENAISSANCE (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *anthropocentrism
B) theocentrism
C) *humanism
D) creationism
E) rationalism
F) formalism
G) dogmatism
H) *pantheism
8. NATURAL PHILOSOPHERS OF THE RENAISSANCE (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *J. Bruno
B) N. Machiavelli
C) *G. Galileo
D) T. More
E) P. della Mirandola
F) F. Petrarch
G) T. Campanella
H) *N. Copernicus
9. PHILOSOPHICAL WORKS OF I. KANT (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *Critique of Pure Reason
B) Criticism of judgments
C) Criticism of humanism
D) *Critique of practical reason
E) *Critique of judgment abilities
F) Criticism of formalism
G) Criticism of criticism
H) Criticism of pantheism
10. THE MOST IMPORTANT PHILOSOPHICAL WORKS OF H. HEGEL (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *Phenomenology of spirit
B) *Science of logic
C) Capital
D) Canons of Wisdom
E) *Philosophy of law
F) The essence of Christianity
G) Scientific teaching
H) Reasoning about the method
11. REPRESENTATIVES OF NON-CLASSICAL PHILOSOPHY (choose 3 correct answers)
A) F. Engels
B) I. Kant
C) G. Hegel
D) K. Marx
E) *K. Jaspers
F) L. Feuerbach
G) *A. Schopenhauer
H) *F. Nietzsche
12. CONCEPTS OF THE PHILOSOPHY OF EXISTENTIALISM (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *existence
B) science
C) *borderline situation
D) *absurd
E) energy
F) understanding
G) text
H) falsification
13. BACKGROUND CONCEPTS OF HERMENEUTICS (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *text
B) science
C) borderline situation
D) absurd
E) * author
F) verification
G) *reader
H) falsification
14. CONCEPTS OF KANTIAN PHILOSOPHY (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *thing in itself
B) *antinomy
C) *categorical imperative
D) world mind
E) absolute idea
F) world will
G) thesis
H) synthesis
15. FORMS OF RATIONAL COGNITION ARE (choose 3 correct answers)
A) *concepts
B) sensations
C) *inference
D) memory
E) *judgments
F) perception
G) representations
H) intuition
16. THE PHILOSOPHICAL DIRECTION THAT RECOGNIZES THE EXISTENCE OF TWO INDEPENDENT PRINCIPLES OF THE UNIVERSE IS CALLED (choose one correct answer)
A) monism
B) *dualism
C) pluralism
17. THE MAIN SUBJECT OF PHILOSOPHY IS ATTITUDE (choose one correct answer)
A) *man - world
B) the world is god
C) heaven-earth
18. THE MAIN PHILOSOPHICAL QUESTION IS ABOUT ATTITUDE (choose one correct answer)
A) yin to yang
B) *thinking to being
C) idealism to humanism
D) humanism to natural philosophy
19. GNOSEOLOGY - A SECTION OF PHILOSOPHICAL KNOWLEDGE THAT CONSIDERS PROBLEMS (choose one correct answer):
A) *cognition
B) being
C) morality
D) person
20. EXPERIENCE IS THE BASE (choose one correct answer)
A) rationalism
B) sensationalism
C) *empiricism
21. THE CENTRAL CONCEPT OF R. DESCARTES’ ONTOLOGY (choose one correct answer)
A) *substance
B) monad
C) atom
22. THE MAIN CONCEPT OF LEIBNITZ ONTOLOGY (choose one correct answer)
A) substance
B) *monad
C) atom
23. T. HOBBS IS THE AUTHOR OF THE THEORY (choose one correct answer)
A) innate ideas
B) separation of branches of government
C) *social contract
24. THE POSITION THAT NOT ONLY COGNITION, BUT ALSO THE EXISTENCE OF THE WORLD IS DETERMINED BY MAN - EXPRESSES A POSITION (choose one correct answer)
A) *subjective idealism
B) agnosticism
C) objective idealism
25. DEScartes' theory of innate ideas J. LOCKE CONTRADITED THE THEORY WHERE CONSCIOUSNESS IS CONSIDERED AS (choose one correct answer)
A) *blank slate
B) seal on wax
C) soul recollection
26. THE CENTRAL CONCEPT OF I. KANT’S PHILOSOPHY (choose one correct answer)
A) *thing in itself
B) absolute idea
C) will to power
27. TENGRI IS CONSIDERED TO BE THE HABITAT (choose one correct answer)
A) *sky
B) earth
C) dungeon
28. Z. FREUD BELONGED WITH THE DISCOVERY OF THE PROBLEM (choose one correct answer)
A) consciousness
B) subconscious
C) *unconscious
29. PHILOSOPHICAL INNOVATION OF MARXISM (choose one correct answer)
A) theoretical formulation of the idea of dialectics
B) *materialistic understanding of history
C) discovery of self-organization
30. THE SUBJECT OF COGNITION IS ANY SUBJECT (choose one correct answer)
A) material world
B) spiritual world
C) *material and spiritual world
31. MAIN DIRECTIONS OF ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY (choose one correct answer)
A) *Confucianism and Taoism
B) Taoism and Buddhism
C) Buddhism and Confudianism
D) Confudianism and Hinduism
32. THE AUTHOR OF THE TEACHING ABOUT “CORRECTION OF NAMES” IS AN ANCIENT CHINESE SAGE (choose one correct answer)
A) Lao Tzu
B) Mo Tzu
C) Han Fei
D) *Kung Fu Tzu
33. THE NICKNAME “PHILOSOPHY IS THE SERVANT OF THEOLOGY” BELONGS (choose one correct answer)
A) *Middle Ages
B) Renaissance
C) New time
D) Enlightenment
34. RENAISSANCE PHILOSOPHER, CARDINAL, AUTHOR OF THE WORK “ON LEARNED IGNORANCE” (choose one correct answer)
A) G. Galileo
B) J. Bruno
C) *N. Cusanian
D) T. More
35. I. KANT’S STRICT MORAL LAW IS CALLED ______ IMPERATIVE (choose one correct answer)
A) hypothetical
B) imperative
C) *categorical
D) transcendental
36. ACCORDING TO NIETZSCHE’S TEACHINGS, THE PLACE OF THE DEAD GOD SHOULD BE TAKEN (choose one correct answer)
A) *superman
B) a representative of the Aryan race
C) new god
D) ruler
37. ZARATHUSTRA - HERO OF PHILOSOPHICAL REFLECTIONS (choose one correct answer)
A) A. Schopenhauer
B) *F. Nietzsche
C) A. Camus
D) Heidegger
38. AUTHOR OF THE WORK “TRACES OF SHAMMANITY AMONG THE KYRGYZ” (choose one correct answer)
A) Kunanbaev A.
B) Dulatov M.
C) *Valikhanov Ch.
D) Bukeikhanov A.
39. THE MYSTICAL PATH OF KNOWING GOD IN SUFISM (choose one correct answer)
A) mauriate
B) maslikhat
C) *tarikat
D) jihad
40. C. PEARCE, W. JAMES, J. DEWEY - REPRESENTATIVES OF THE DIRECTION (choose one correct answer)
A) structuralism
B) hermeneutics
C) *pragmatism
D) neopositivism
41. KNOWLEDGE CONSISTS OF TWO STEPS (choose one correct answer)
A) *sensual and rational
B) figurative and emotional
C) observable and unobservable
D) theoretical and provable
42. TWO LEVELS OF SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE (choose one correct answer)
A) sensual and rational
B) figurative and emotional
C) *empirical and theoretical
D) theoretical and everyday
43. REPRESENTATIVES MADE A GREAT CONTRIBUTION TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES (choose one correct answer)
A) *Club of Rome
B) Vienna circle
C) club of knowledge lovers
D) youth club
44. AVERROES IS A LATINIZED NAME (choose one correct answer)
A) Ibn Sina
B) Al-Ghazali
C) *Ibn Rushd
D) Al-Kindi
E) Ibn Arabi
F) Al-Farabi
45. AVICENNA - WESTERN READING OF THE NAME (choose one correct answer)
A) *Ibn Sina
B) Al-Ghazali
C) Ibn Rushd
D) Al-Kindi
E) Ibn Arabi
F) Al-Farabi
46. HISTORICALLY THE FIRST TYPE OF WORLDVIEW IS MYTHOLOGY (choose the correct answer)
A) *is
B) is not
47. PHILOSOPHY OF ANCIENT RELATES TO (choose the correct answer)
A) *classical philosophy
B) non-classical philosophy
48. N. COPERNIUS IS THE CREATOR (choose the correct answer)
A) geocentric picture of the world
B) *heliocentric picture of the world
49. IN NEOPOSITIVISM, THE COMPARISON OF ALL THE PROVISIONS OF SCIENCE WITH THE FACTS OF EXPERIENCE IS CALLED (choose the correct answer)
A) *verification
B) falsification
50. THE PRINCIPAL FALTERABILITY OF A SCIENTIFIC THEORY IN POST-POSITIVISM IS CALLED (choose the correct answer)
A) verification
B) *falsification
51. POSITION CONSIDERING TIME AND SPACE AS A SEPARATE REALITY ALONG WITH MATTER, AND THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THEM AS INTERSUBSTANTIAL EXPRESSES THE POSITION (choose the correct answer)
A) relational concept
B) *substantial concept
52. A. EINSTEIN’S THEORY OF RELATIVITY CONFIRMED CORRECT (choose the correct answer)
A) *relational theory
B) substance theory
53. CONSCIOUSNESS BY ITS NATURE (choose the correct answer)
A) financially
B) *perfect
54. IN ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY, THE EARLIEST GROUP OF VEDIC TEXTS ARE CALLED (add)______. (Rig Veda)
55. THE LAST GROUP OF VEDIC TEXTS, WHICH IS THE WORLDVIEW CORE OF HINDUISM, IS CALLED (add) ______ (Upanishads)
56. IN BUDDHISM, THE PATH LEADING TO LIBERATION FROM SUFFERING, MEANS COMPLETE EXHAUSTION OF CONSCIOUSNESS (add) _______. (Nirvana)
57. IN ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY, THE PATH WHICH MAN AND NATURE SHOULD FOLLOW IN THEIR DEVELOPMENT, THE UNIVERSAL WORLD LAW THAT ENSURES THE EXISTENCE OF THE WORLD (add) ______. (Tao)
58. THE FIRST GREEK PHILOSOPHER IS CONSIDERED (add) ______ (Thales)
59. AUTHOR OF APHORISMS: “EVERYTHING FLOWS, EVERYTHING CHANGES”, “ONE CANNOT ENTER THE SAME RIVER TWICE” (add)______ (Heraclitus)
60. THE NAME OF THE ANCIENT GREEK PHILOSOPHER WHO FIRST IDENTIFIED THE PROBLEM OF MAN IN PHILOSOPHY, THE AUTHOR OF THE STATEMENT: “KNOW YOURSELF” (add) - _______. (Socrates)
61. IN PYTHAGORUS, METEMPSYCHOSIS IS THE TEACHING ABOUT RESETTLEMENT (add) _______. (Soul)
62. ANCIENT GREEK PHILOSOPHER, CREATOR OF THE SCIENCE OF LOGIC, AUTHOR OF THE FIRST PHILOSOPHICAL SYSTEM (add)_______ (Aristotle)
63. THE HOLY BOOK OF CHRISTIANS IS CALLED (add)______. (Bible)
64. THE HOLY BOOK OF THE MUSLIMS IS CALLED (add) ______. (Koran)
65. THE DIRECTION OF MEDIEVAL PHILOSOPHY, APPROVING THAT THINGS THEMSELVES DO NOT TRULY EXIST, BUT THEIR GENERAL CONCEPTS - UNIVERSALS _______. (Realism)*
66. PERIOD IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHILOSOPHY OF THE MIDDLE AGES, THE WORK OF THE CHURCH FATHERS _______. (Patristics)*
67. SCHOOLASTICS CAME FROM THE LATIN WORD (SCNOLA), WHICH MEANS _______ IN TRANSLATION. (School)*
68. THE WORSHIP OF ONE GOD IS CALLED ______. (Monotheism)*
69. RENAISSANCE IS THE FRENCH NAME OF THE ERA ______. (Rebirth)*
70. TEACHING OF THE RENAISSANCE AGE, ACCORDING TO WHICH GOD IS IDENTIFIED WITH NATURE _______. (Pantheism)*
71. THE LOGICAL OPERATION OF TRANSITION FROM THE PARTICULAR TO THE GENERAL IS CALLED (add)______. (Induction)*
72. THE LOGICAL OPERATION OF TRANSITION FROM THE GENERAL TO THE PARTICULAR IS CALLED (add)_______. (Deduction)*
73. THE MOMENT OF THE NEW TIME, WHICH BELIEVES THAT THROUGH SCIENCE IT IS POSSIBLE TO SOLVE THE PROBLEMS OF HUMAN SOCIETY (add)______ (Rationalism))*
74. THE FIRST WISE OF THE PROTO-KAZAKHS, A SKYTHIAN, A FRIEND OF KING SOLON, WAS NAME (add) ______. (Anacharsis)*
75. THE SUPREME TOTEM SACRED TO ANIMALS OF THE PROTO-KAZAKHS WAS (add) _______. (Wolf) *
76. THREE TRUTHS OF SHAKARIM: SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE, RELIGIOUS COPENESS AND ______ (Conscience)*
77. PHILOSOPHICAL TEACHING THAT DEFENDS THE LIMITATIONS OF COGNITIVE CAPABILITIES OF THE MIND (add) _______ (Irrationalism)*
78. PHILOSOPHY OF EXISTENCE (add)_______ (Existentialism) *
79. NAME OF THE SCIENTIST WHO LAID THE FOUNDATIONS OF PSYCHOANALYSIS (add)_______ (Freud)*
80. GENERAL SCIENTIFIC THEORY OF SELF-ORGANIZATION (add)______ (Synergetics)*
81. STATE ONE WITH BEING (ALSO REAL) AND OPPOSITE TO IT (add) _______. (Nothingness*)
82. IN THE THEORY OF SELF-ORGANIZATION, RANDOM VIBRATIONS AND DEVIATIONS ARE CONSTANTLY INHERENT IN MATTER (add) _______. (Fluctuation)*
83. IN WESTERN PHILOSOPHY, A SYNONYM OF THE WORD GNOSEOLOGY (add) ______. (Epistemology)
84. CRITERION OF KNOWLEDGE IN MARXIST PHILOSOPHY (add) ______. (practice)*
85. TEACHING ABOUT COGNITION (add) ______. (Epistemology)
86. AXEOLOGY IS THE TEACHING ABOUT (add)_______. (Values)*
87. IN DIALECTICS, MEASURE IS THE UNITY OF QUANTITY AND (add)_______. (Quality)*
88. SPHERE OF MIND ACCORDING TO V.I. VERNADSKY (add)______. (Noosphere)*
89. SCIENCE OF THE FUTURE (add)______. (Futurology)*
90. PROBLEMS OF A PLANETARY CHARACTER IN MODERN SCIENCE ARE USED TO BE CALLED (add)_______. Global*
91. THE WORLD OF THE UNCONSCIOUS ACCORDING TO SIGMUND FREUD (add)_______. Correct answer(s): It
92. LIVING INSTINCT IN FREUDISM (add)_______. Correct answer(s): Eros
93. DEATH INSTINCT IN FREUDISM (add)______. Correct answer(s): Thanatos
94. ENCRYPTED UNIVERSAL IMAGES OF CARL JUNG (add)_______. Correct answer(s): Archetypes
95. MAIN WORK OF HERBERT MARCUSE (add) ______, Correct answer(s): One-dimensional man
96. THE CENTRAL CONCEPT OF PAUL RICOER’S PHILOSOPHY ______. Correct answer(s): Personality
97. JOHANN FICHETE NOT-I OPPOSED (add)______. Correct answer(s): I
98. SOCRATES METHOD (add)_______. Correct answer(s): Maieutics
99. ECONOMICS OF SOCIETY ACCORDING TO KARL MARX (add)_______. Correct answer(s): Basis
100. The criterion of truth in Marxism (add)_______. Correct answer(s): Practice
, , Test on philosophy. Shpakovskaya A.G. ZDM-2932, 2nd course.
SUBJECT OF PHILOSOPHY
From Greek the word “philosophy” is translated as:
love of truth
love of wisdom
teaching about peace
divine wisdom
For the first time he used the word “philosophy” and called himself a “philosopher”:
Aristotle
Pythagoras
Determine the time of emergence of philosophy:
mid-3rd millennium BC
VII-VI centuries. BC.
XVII-XVIII centuries.
The fundamentals of existence, problems of knowledge, the purpose of man and his position in the world are studied by:
philosophy
ontology
epistemology
Philosophy must solve specific problems facing society at a given time
Philosophy is designed to reflect the characteristics of the era, to express the spirit of the times
The thinking of philosophers is determined by the socio-economic conditions of the society in which they live
The defining feature of a religious worldview is:
belief in one creator god
denial of human freedom, belief that all actions are initially determined by God
contempt for the achievements of science, denial of their reliability
belief in supernatural, otherworldly forces that have the ability to influence the course of events in the world
The direction that denies the existence of God is called:
atheism
skepticism
agnosticism
neo-Thomism
What is characteristic of the epistemic line in philosophy?
identification of philosophy with theology
affirmation as substance of only one principle
viewing reality as constantly evolving
Ontology is:
the doctrine of the universal conditionality of phenomena
the doctrine of the essence and nature of science
the doctrine of existence, its fundamental principles
the doctrine of correct forms of thinking
Epistemology is:
the doctrine of the development and functioning of science
the doctrine of nature, the essence of knowledge
the doctrine of logical forms and laws of thinking
the doctrine of the essence of the world, its structure
Anthropology is:
the doctrine of development and universal interconnection
doctrine of man
the science of animal behavior in natural environments
philosophical doctrine about society
Axiology is:
doctrine of values
development theory
theory of justice
Ethics is:
development theory
doctrine of being
theory about the moral superiority of some people over others
the doctrine of morality and moral values
Section of philosophy in which problems of cognition are developed
Aesthetics
Ontology
Epistemology
According to Marxist philosophy, the essence of the main question of philosophy is:
relation of consciousness to matter
meaning of life
the relationship between the natural and social worlds
driving forces of social development
Idealism is characterized by the statement:
consciousness is primary, matter does not exist independently of consciousness
matter and consciousness are two principles that exist independently of each other
Dualism is characterized by the following thesis:
consciousness is primary, matter does not exist independently of consciousness
matter and consciousness are two principles that exist independently of each other
this is a strict consistent system of judgments about nature
consciousness is primary, matter does not exist
Who owns this statement: “I maintain that there are no things. We're just used to talking about things; in fact, there is only my thinking, there is only my “I” with its inherent sensations. The material world only seems to us, is it just a certain way of talking about our feelings”?
Materialist
To an objective idealist
To the dualist
To the subjective idealist
What historical type of worldview are we talking about here: “This is a holistic worldview in which various ideas are linked into a single figurative picture of the world, combining reality and fantasy, the natural and the supernatural, knowledge and faith, thought and emotions”?
Mythologies
Philosophy
Some Christian theologians argue that the whole world. The entire Universe was created by God in six days, and God himself is a disembodied intellect, an all-perfect Personality. What philosophical direction does this view of the world correspond to?
Pantheism
Subjective idealism
Objective idealism
Vulgar materialism
The representative would agree with the statement: “Thinking is the same product of brain activity as bile is a product of liver activity”:
metaphysical materialism
dialectical materialism
vulgar materialism
natural scientific materialism
Agnosticism is:
doctrine that denies the knowability of the essence of the objective world
doctrine postulating the presence of otherworldly forces
the doctrine of the development of philosophical knowledge
doctrine of values
Agnosticism is:
direction in the theory of knowledge, which believes that adequate knowledge of the world is impossible
distrust of sensory experience
philosophical position that considers all phenomena of the world in their mutual connection and development
denial of rational ways of understanding the world
They deny the possibility of knowing the world:
materialists
agnostics
dogmatists
positivists
The direction of Western European philosophy that denies the cognitive value of philosophy, the presence of its own, original subject:
philosophy of life
pragmatism
neo-Thomism
positivism
PHILOSOPHY OF THE ANCIENT EAST
The law of retribution in Indian religion and religious philosophy, which determines the nature of the new birth of reincarnation:
karma
The name of the founder of Buddhism, meaning awakened, enlightened:
Buddha
Confucius
Nagarjuna
Name of the founder of Buddhism
Badarayana
Patanjali
Mahavira
Sidhartha
The central concept of Buddhism and Jainism, meaning the highest state, the goal of human aspirations:
nirvana
"Everything Flows"
"You cannot step into the same river twice"
“The fundamental principle of the world is fire”
"The beginning of all things is water"
Anaximenes took the first principle of all things
AirFire
Number
WaterThe statement: “Number is the essence and meaning of everything that is in the world” belongs to:
Pythagoras
Protagoras
Test tasks.
1. Find correspondence between the section of philosophy and the main category:
A) ontology; 4 1) beauty;
b) epistemology; 3 2) morality;
c) ethics; 2 3) truth;
d) aesthetics; 1 4) being.
2. Establish correspondence between the philosophical category and its author:
A) moral imperative; 3 1) Democritus;
b) atom; 1 2) Aristotle;
c) ethics; 2 3) Kant;
d) being; 4 4) Parmenides.
3. Society is the subject of study of such philosophical science as:
A) cultural studies;
*b) social philosophy;
c) epistemology;
d) political science;
d) economics.
4. From Huntington's point of view, relations between civilizations in the future will lead to:
*a) conflict;
b) the world;
c) self-isolation of civilizations;
d) a single civilization;
d) classless society.
5. An individual in philosophy is understood as:
A) a synonym for the concept “person”;
*b) generic concept, i.e. expressing the common features inherent in the human race;
c) a stable system of socially significant traits, characteristics of a person as a member of society;
d) social “mask”.
6. Personality in philosophy is understood as:
A) a synonym for the concepts “individual”, “person”;
b) generic concept, i.e. expressing the common features inherent in the human race;
*c) a stable system of socially significant traits, characteristics of a person as a member of society;
d) the totality of the physical abilities of an individual;
d) social “mask”.
7. When using the concept “personality” we mean such qualities as:
a) age differences;
b) physical differences;
*c) spiritual and social qualities acquired by each person;
d) neurodynamic differences (properties of the nervous system).
8. The specificity of philosophical anthropology is that it;
a) examines human biological parameters;
b) explores the origin and development of man;
*c) tries to determine the essence of man, the humanity in man;
d) explores social determinants in human behavior;
e) tries to determine the direction of further development of humanity.
9. The term “anthropogenesis” means:
*a) the process of historical and evolutionary formation of the physical type of a person;
d) the process of human development from birth to death.
10. The term “phylogeny” means:
*a) the process of human development from primitiveness to modernity;
b) the process of historical formation of the social essence of man;
c) the process of formation of a “superman”;
e) the process of human development from birth to death.
11. The term “ontogenesis” means:
a) the process of human development from primitiveness to modernity;
b) the process of historical formation of the social essence of man;
c) the process of formation of a “superman”;
d) the process of state formation;
*e) the process of human development from birth to death.
a) purposeful influence of the subject on the subject;
b) instinctive activity of a living being;
*c) purposeful influence of the subject on the object (where another subject may be a special case of the object);
d) the impact of the object on the subject.
13. The process of socialization means:
a) active participation of a person in public life;
b) a person’s belonging to one or another social group;
*c) the assimilation and use of sociocultural experience by a person;
d) human participation in the socialist movement.
14. The term “culture” means (choose the most correct answer):
a) culture is custom, language;
b) culture is a generally accepted way of thinking (mentality);
*c) culture is a fusion of methods of activity and the results of this activity in the form of a set of created material and spiritual values;
d) culture is, first of all, a phenomenon of art.
15. From the point of view of hedonism, the meaning of life is that:
a) life is renunciation of the world and mortification of the flesh for the atonement of sins;
b) life is the pursuit of happiness as the true purpose of man;
*c) life is pleasures, preferably as varied as possible, here and now;
d) to live means to benefit from everything;
e) life is a desire for God.
16. The subject of ethics is:
a) society;
b) person;
*c) morality;
d) the meaning of life;
d) ideal.
17. A person’s responsibility for his actions is possible only if he has:
*a) choice;
b) guilt;
c) force majeure;
d) necessity;
d) predestination.
18. Section of philosophy that studies morality and specific phenomena of social life:
a) ontology;
b) axiology;
c) aesthetics;
*d) ethics;
e) anthropology.
19. Axiology is the study of:
*
b) about beauty;
c) about good and evil;
20. The requirement of non-violence means, first of all, the renunciation of:
*a) imposing your opinion on others;
b) attacks on the life of another person;
c) encroachment on the property of another person;
d) commanding other people.
a) Heraclitus;
b) Protagoras;
c) Spinoza;
d) Plato;
*e) Aristotle.
a) Socrates;
b) Aristotle;
*c) Cicero;
d) Augustine the Blessed;
e) Thomas Aquinas.
23. Epistemology is the doctrine of:
a) about values, their origin and essence;
b) about the development of the universe;
c) about being as such;
*d) about the essence of knowledge, about the ways of comprehending the truth;
24. Cognition in modern philosophy is mainly considered as (indicate the most correct answer):
a) abilities, abilities, skills in a certain field of activity;
b) significant information in terms of activity;
c) objective reality given in the consciousness of the acting person;
*d) the practice-based process of acquiring and developing knowledge.
25. Absolutization of the role and meaning of sensory data in philosophy is associated with the direction:
a) rationalism;
b) realism;
c) skepticism;
*d) sensationalism;
d) hedonism.
26. Deduction is:
*a) a logical path from the general to the specific;
b) transmission of false knowledge as true;
c) the ascent of knowledge from particular, individual facts to generalizations of a higher order;
27. Induction is:
a) a logical path from the general to the specific;
b) presenting false knowledge as true;
*c) the ascent of knowledge from private, individual facts to generalizations of a higher order;
d) moment of intellectual insight;
d) relative, incomplete truth.
28. Method of cognition in philosophy and science, when thought moves from general provisions to particular conclusions:
a) induction;
*b) deduction;
c) analysis;
d) synthesis.
29. Empiricism is:
a) a direction in the theory of knowledge that considers thinking to be the source of knowledge;
*b) a direction in the theory of knowledge that considers sensory experience to be a source of knowledge;
c) a direction in the theory of knowledge that considers absolute consciousness to be the source of knowledge;
d) a direction in the theory of knowledge that considers intuition to be a source of knowledge;
e) a direction in the theory of knowledge that considers innate ideas to be a source of knowledge.
30. Agnosticism is:
a) doctrine in ontology that considers the problems of human existence;
*b) a doctrine in epistemology that denies the possibility of reliable knowledge of the world;
c) the doctrine of the development of the world;
d) the doctrine of universal causation;
e) the doctrine of the essence of human history.
31. In philosophy, “agnosticism” is understood as:
a) consideration of the process of cognition;
b) consideration of objects of knowledge;
*c) complete or partial denial of the fundamental possibility of knowledge;
d) doubt about the possibility of knowledge;
d) method of cognition.
32. 11. The highest level of logical understanding; theoretical, reflective, philosophically thinking consciousness, operating with broad generalizations and focused on the most complete and deep knowledge of the truth - this is:
a) reason;
*b) mind;
c) feeling;
d) experience;
d) intuition.
33. A doctrine that asserts the limited capabilities of man in understanding the world is called:
a) materialism;
*b) skepticism;
c) empiricism;
d) idealism;
d) rationalism.
34. Levels of scientific knowledge (indicate all options):
*a) empirical;
b) religious;
*c) theoretical;
d) mythological;
e) dialectical.
35. A certain stage of the cognitive process at which information about an object, received in sensations and perceptions, stored in consciousness, is reproduced later without direct influence of the object on the subject - this is:
a) sensory reflection;
b) cognitive contact with the object of knowledge;
*c) presentation;
d) explanation;
d) noumenon.
36. The main forms of living contemplation (in the theory of knowledge as reflection) do not include:
a) presentation;
b) perception;
*c) idea;
d) sensation.
37. These forms of knowledge do not relate to theoretical knowledge:
a) concept;
*b) presentation;
c) inference;
d) judgment;
*d) perception.
38. A type of knowledge woven into the fabric of a subject’s life, but not possessing evidentiary power, is called:
a) abstract;
b) theoretical;
*c) ordinary;
d) scientific;
d) divine.
39. Practice in its functions in the process of cognition is not:
a) the basis of knowledge and its driving force;
b) the purpose of knowledge;
c) criterion of truth;
*d) successful replacement of theoretical research and scientific creativity.
40. Since truth does not depend on the knowing subject, it:
a) abstract;
*b) objective;
c) subjective;
d) absolute;
d) divine.
41. A concept opposite in meaning to “truth” in epistemology:
A) propaganda;
*b) delusion;
c) judgment;
d) prejudice;
d) illusion.
42. The set of approaches, techniques, methods for solving various practical and cognitive problems is:
*a) methodology;
b) development;
c) skill;
d) mechanism;
d) process.
43. To what form of scientific knowledge does the concept of the alien origin of life on Earth belong?
*a) hypothesis;
b) theory;
c) problem;
d) paradigm;
d) model.
44. Science as a specific type of spiritual production and social institution arose in the era:
a) antiquity;
b) the Middle Ages;
c) Renaissance;
*d) New times;
d) in the twentieth century.
45. The structural components of theoretical scientific knowledge are (indicate all correct options):
*a) problem;
b) pain;
c) faith;
*d) hypothesis;
*e) theory.
46. In the theory of knowledge, mutually exclusive but equally provable concepts are called:
47. Which definition of rationality is considered the main one in philosophy?
a) calculation of adequate funds for this purpose;
b) the best adaptability to circumstances;
c) logical validity of the rules of activity;
*d) the ability of the mind to holistically embrace nature, society and its own subjectivity.
48. Empirical methods of cognition include (indicate all correct answers):
a) analysis;
*b) observation;
*c) experiment;
*d) measurement;
e) modeling.
49. Theoretical methods of cognition include (indicate all correct answers):
*a) analysis;
b) observation;
*c) idealization;
d) measurement;
*e) modeling.
50. When using this method, individual properties of the object being studied are replaced with symbols or signs:
a) induction;
b) deduction;
*c) idealization;
d) observation;
d) analysis.
51. Scientific knowledge differs from other knowledge (indicate all correct answers):
*a) accuracy;
*b) validity;
*c) great predictive ability;
d) a large degree of fantasy (not necessarily justified);
d) its exceptional aesthetic value.
52. Science has such basic functions as (indicate all correct answers):
*a) ideological;
*b) methodological;
c) aesthetic;
d) political;
*e) predictive.
53. At the earliest stages of human history, such forms of knowledge played an important role as:
a) scientific;
*b) everyday practical;
*c) gaming;
d) philosophical;
*e) mythological.
54. Consciousness is considered as a property of highly organized matter, in the philosophical direction:
a) objective idealism;
b) subjective idealism;
*c) dialectical materialism;
d) existentialism;
e) Thomism.
55. The philosophical concept of reflection refers to the phenomenon:
a) empirical knowledge;
b) logical cognition;
c) intuitive knowledge;
*d) self-awareness;
d) subconscious.
56. Consciousness arises, functions and develops in the process:
a) a person growing up;
*b) human interaction with reality;
c) getting an education;
d) scientific knowledge.
a) apeiron;
b) atom;
c) logos;
*d) soul;
d) mind.
58. For the first time, the act of self-awareness as a condition for the reliability of knowledge of the world was considered by:
a) Marx;
b) Democritus;
*c) Descartes;
d) Bacon;
d) Hobbes.
59. In what era do consciousness begin to be considered as a function of the human brain to reflect reality?
a) Antiquity;
b) Middle Ages;
c) Renaissance;
*d) Enlightenment.
60. Hegel believed that consciousness:
a) generated by matter;
b) a method of self-knowledge of matter;
*c) autonomous from matter;
d) depends on matter.
61. The first to unite consciousness and psyche:
a) Bacon;
b) Schelling;
*c) Freud;
d) Hegel;
d) Kant.
62. Reflection property:
a) is inherent only in inanimate matter;
b) is inherent only in living matter;
c) inherent only to humans;
*d) this is a global property of matter.
63. From the point of view of vulgar materialism:
a) consciousness is a property of all matter;
b) consciousness is a property of living matter;
*c) consciousness is a substrate secreted by the brain;
d) consciousness is a property of a person.
64. Human consciousness differs from the psyche of vertebrate animals:
*a) the presence of abstract thinking and speech;
b) the ability to work with real objects;
c) the presence of advanced reflection;
d) the presence of irritability.
65. Highlight the three most characteristic functions of language:
*a) constructive (a tool for expressing thoughts);
*b) reflective (cognitive tool);
c) political;
d) literary;
*e) communicative.
66. Human consciousness differs from the psyche of animals:
a) the ability to more clearly reflect the world around us;
b) the ability to influence the surrounding world;
*c) the ability to reflect, i.e. self-knowledge;
d) the ability to adequately respond to environmental influences.
67. Ontology is the doctrine of:
a) about values, their origin and essence;
b) about the development of the universe;
*c) about being as such;
d) about the spiritual culture of society and people;
d) about the essence of human history.
68. Which of the ancient philosophers was the first to formulate the concept of “being”?
a) Pythagoras;
b) Heraclitus;
*c) Parmenides;
d) Plato;
d) Socrates.
69. Which of these philosophical concepts arose first?
a) matter;
b) being;
c) substance;
*d) origin.
70. Aristotle put forward a dual concept of understanding being:
*a) passive matter and active form;
b) active matter and passive form;
c) active consciousness and passive form;
d) passive consciousness and active form.
71. Development accompanied by the appearance of a more advanced quality compared to the previous one:
a) degradation;
b) decline;
c) regression;
*d) progress;
e) integration.
72. Objective connection between individual states of types and forms of matter in the processes of its movement and development:
*a) causality;
b) determinism;
c) dualism;
d) synergy;
d) induction.
73. Determinism is a doctrine:
a) about divine predestination;
b) about the universal cognizability of the world;
*c) about the universal natural connection, the cause-and-effect conditionality of phenomena;
d) about the unknowability of the world;
e) about the creation of the world.
74. Materialists claim that:
a) there are two independent and equal principles (principles): material and spiritual;
b) the fundamental principle of the world, nature, and existence is the spiritual principle;
*c) matter exists absolutely, it is uncreated and indestructible, infinite in the forms of its manifestation;
d) the world was created by God out of nothing.
75. Materialists claim that matter is:
a) a passive principle, transformed under the influence of consciousness;
*b) objective reality given to a person in sensations;
c) absolute One;
d) abstract concept.
76. Idealists claim that:
*a) the fundamental principle of the world, nature, and existence is the spiritual principle;
b) there are two independent and equal principles (principles): material and spiritual;
c) matter exists absolutely, it is uncreated and indestructible, infinite in the forms of its manifestation;
d) matter consists of eternal, unchanging and indivisible particles - atoms;
e) the world was created by God out of nothing.
77. Pantheism is:
*a) a doctrine that denies a personal God and brings him closer to nature, sometimes identifying them;
b) a doctrine that affirms the knowability of the world;
c) teaching about the spiritual culture of society;
d) about the essence of knowledge, about the ways of comprehending the truth;
d) about the essence of human history.
78. Hylozoism is:
a) the doctrine of nature;
*b) a doctrine that recognizes “life” as an integral property of matter;
c) the doctrine of being as such;
d) the doctrine of the world as such;
e) the doctrine of the spiritual culture of society and man.
79. What is the first principle in materialistic philosophical concepts?
a) spirit;
b) consciousness;
*c) matter;
d) logos;
d) experience.
80. What is the first principle in idealistic philosophical concepts?
*a) spirit;
b) deity;
c) matter;
d) logos;
d) experience.
81. An irreversible, unidirectional and natural change leading to the emergence of a new quality is:
a) movement;
b) deformation;
c) regression;
*d) development;
d) transformation.
82. The form of existence of matter, expressing the duration of its existence, the sequence of changes in states in the change and development of all material systems:
*a) time;
b) space;
in motion;
d) development;
e) interaction.
83. The form of existence of matter, characterizing its extension, structure, coexistence and interaction of elements in all material systems:
a) time;
*b) space;
in motion;
d) development;
e) interaction.
84. The main interpretations of space and time include:
*a) substantial;
*b) relational;
c) irrational;
d) existential;
*e) subjective-idealistic.
85. The universal form of existence of matter is:
a) immobility;
b) consciousness;
*in motion;
d) a certain set of forms;
e) limited space.
86. A significant, stable and recurring relationship is:
a) phenomenon;
*b) law;
c) condition;
d) quality;
d) karma.
87. Objective idealism recognizes the following position:
a) the world consists of material bodies, and each body is made of the smallest particles;
b) the world is an arena of war of all against all;
c) the world was created by God, and everything happens in it according to the will of above;
d) the world is the totality of experiences, ideas, aspirations and ideals of a particular person;
*e) the world of visible things is only a reflection of the real world of perfect prototypes that exist eternally and unchangeably.
88. The basic laws of dialectics are (indicate all correct options):
*a) the law of unity and struggle of opposites;
b) the law of heaven (Li);
*c) the law of mutual transition of quality and quantity;
*d) the law of negation of negation;
e) the law of moral retribution.
89. Dialectics is:
*a) the doctrine of universal connections and laws of development of nature, society, thinking;
b) a doctrine that considers the source and final goal of all changes in the nature of God;
c) a set of methods used in any area of human activity;
d) the doctrine of universal cause and effect;
e) the doctrine of divine predestination.
90. Methods of philosophical knowledge are:
a) analysis and synthesis;
b) induction and deduction;
c) description and comparison;
*d) dialectics and metaphysics.
91. The philosophical concept according to which the world has a single basis for everything that exists is called...
*a) monism
b) dualism
c) relativism
d) skepticism
92. What exists on its own and does not depend on anything else is what philosophers call...
*a) substance
b) substrate
c) attribute
d) reason
93. “Matter did not always exist, and there was a moment when it did not exist at all,” they say...
*a) creationists
b) materialists
c) spiritualists
d) naturalists
94. The subject of philosophy is not questions...
*a) private, specific nature
b) general understanding of nature
c) general understanding of a person
d) general understanding of cognition
95. From the position of _______________, consciousness is a kingdom of ideas, feelings, will, independent of material existence, capable of creating and constructing reality
*a) idealism
b) materialism
c) dualism
d) realism
96. A philosophical doctrine that asserts the equality of two principles - material and spiritual - is called...
*a) dualism
b) monism
c) agnosticism
d) deism
97. Being as an objective reality is designated by the term...
*a) matter
b) consciousness
c) substrate
d) substance
98. The doctrine of the multiplicity of substances - monads was developed ...
*a) Leibniz
b) Spinoza
c) Descartes
d) Holbach
99. Recognition of the “possibility of the impossible”, i.e. miracles, events inexplicable by natural means, constitute a necessary component of a ________ worldview
*a) religious
b) scientific
c) philosophical
d) artistic
100. A philosophical position that presupposes a multitude of initial foundations and principles of being is called...
*a) pluralism
b) dualism
c) providentialism
d) skepticism
Philosophical terms and categories.
1. Determinism– philosophical doctrine of objective, natural cause-and-effect relationships and interdependence of things, processes and phenomena of the real world.
2. Idealism– a philosophical direction that proceeds from the primacy of the spiritual in relation to the material.
3. Materialism- a philosophical direction that proceeds from the primacy of the material in relation to the spiritual.
4. Humanism– philosophical views based on the recognition of the intrinsic value of Man and his rights to absolute freedom for the purpose of development and self-expression.
5. Ontology- the doctrine of Being
6. Epistemology– the doctrine of Knowledge
7. Axiology– doctrine of values
8. Scientism– absoluteization of the role of Science in society.
9. Irrationalism- a philosophical doctrine that denies the fundamental importance of Reason
10. Nihilism– a philosophical doctrine that denies the fundamental meaning of Values
11. Sensationalism- a philosophical direction that derives all knowledge from Feelings
12. Pantheism is the idea that God exists everywhere in the world (nature).
13. Hylozoism- a philosophical direction that considers all matter to be alive and animate.
14. Rationalism- a direction in the theory of knowledge that highlights rational, abstract knowledge.
15. Empiricism- a direction in the theory of knowledge that highlights sensory knowledge.
16. Mechanism– a one-sided method of cognition based on the recognition of the Mechanical form of movement as the only objective one.
17. Subjectivism– an ideological position that denies the existence of Objective laws of nature and society.
18. Natural philosophy(philosophy of Nature) is a philosophical direction that created a new picture of the world, free from theology, based on the achievements of natural science.
19. Relativism– a methodological principle that absolutizes the relativity and conditionality of the content of knowledge.
20. Theocentrism– a picture of the world that places God at the center of the universe
21. Anthropocentrism– a picture of the world that places Man at the center of the universe
22. Conventionalism- a philosophical direction that emphasizes that scientific postulates rest on the Agreement, the agreement of scientists.
23. Hedonism– an ethical direction that considers Pleasure, pleasure as the main motive of human activity.
24. Voluntarism- a philosophical direction that recognizes Will as the fundamental principle of existence
25. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “materialism”. Idealism
26. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “idealism”. Materialism
27. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “realism”. Nominalism
28. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “nominalism”. Realism
29. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “agnosticism.” Gnosticism, epistemological optimism
30. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “induction”. Deduction
31. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “deduction”. Induction
32. Choose the opposite term to the concept of “dialectics”. Metaphysics
33. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “empiricism”. Rationalism
34. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “rationalism”. Empiricism
35. Choose the term opposite to the concept of “truth” in epistemology. Misconception
36. Choose a term opposite to the concept of “causality”. Accident
Philosophy tests with answers deepen students' knowledge
University students may be faced with studying a philosophy course, which is designed to fully understand the wisdom of ancient philosophers, their thoughts and views, and subsequently, perhaps, form their own worldview. There are a lot of materials on the course; you can study philosophy on your own, since the subject is theoretical. But teachers need to test students’ knowledge (in some cases, the student himself would like to test his knowledge). To do this, teachers use various means of testing knowledge, for example: oral examination, written examination, test, test. Tests with answers on philosophy are one of the most convenient and profitable tests of knowledge. It’s easy for the teacher to check – the test contains numbers and letters, and you can check a whole stream of students very quickly. The student will write the answers “after the fact” - the way he knows the material, that’s how he will write it. Let's look at a few examples of tests and their effectiveness in studying the subject of philosophy.
From Greek the word “philosophy” is translated as:
A) love of truth
B) love of wisdom
B) the doctrine of peace
D) divine wisdom
In this example, one can essentially test the student's basic knowledge about philosophy and the world. It is not even necessary to know Greek to answer this question - the student’s logic will be enough to successfully answer the question posed.
The basic principle of ancient philosophy was:
A) cosmocentrism
B) theocentrism
B) anthropocentrism
D) scientism
In this case, you can easily check how the student navigates time and analyzes the material covered. Theocentrism - which places God as the basis of everything - was characteristic of the Middle Ages. Anthropocentrism (man as the basis) was characteristic of the Renaissance. We can say that Socrates laid its foundation, but the anthropocentric worldview was not characteristic of the ancient era. Scientists believed in science, which is not typical for Antiquity, but typical for the 20th century.
The only answer is cosmocentrism, a belief based on space as the main system.
Plan
1. The main question of philosophy.
2. The structure of philosophy.
3. Specificity of philosophical knowledge.
4. Genesis of philosophy.
The main question of philosophy.
Philosophy arose, as we have already noted, during the formation and development of slave society almost simultaneously in Ancient China, Ancient India and Ancient Greece. Over the 2500 years of the history of philosophy, various philosophical teachings have been proposed, which ultimately reflected the level of socio-economic and political development of society and the development of specific scientific knowledge. To understand the diversity of philosophical teachings, it is necessary to identify the initial, most important problems of philosophy and ways to solve them. The worldview problem “man - world” in philosophy is posed, first of all, as a problem of the relationship between being and consciousness. From here:
This problem exists in various formulations:
- as the relationship of spirit to nature;
- thinking to being;
- relationship between soul and body;
- “I” and “Not-I”;
- whether the world was created by a spiritual principle or exists forever, etc.
The problem of the relationship between thinking and being in German philosophy, for example F. Schelling, F. Engels, was called the main question of philosophy. The main question in philosophy is traditionally considered to be the question of the relationship of thinking to being, and being to thinking (consciousness), or in other words, the question of the relationship of matter and consciousness.
The importance of this issue lies in the fact that the construction of a holistic knowledge about the world around us and man’s place in it depends on its reliable resolution, and this is the main task of philosophy.
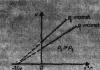
Matter and consciousness (spirit) are two inseparable and at the same time opposite characteristics of existence. In this regard, there are two sides of the main question of philosophy - ontological and epistemological.
Ontological(existential) - first side The main question is to state and solve the problem: What comes first - matter or consciousness?
The essence epistemological (cognitive) - second side main question: Do we know or do we not know the world?
Depending on the ontological and epistemological sides in philosophy, the main directions are distinguished - materialism and idealism, and empiricism and rationalism.
Let's imagine this in the form of diagram 12.
Scheme 12
By revising ontological side The main question of philosophy (what comes first: matter or consciousness?) is identified by such directions as:
Objective idealism;
Subjective idealism;
Materialism;
Vulgar materialism;
Dualism;
The ontological side of the main question of philosophy is represented by:
Materialism;
Idealism;
Dualism.
When considering the epistemological side (cognitive) side (is the world knowable), the following directions are distinguished:
Gnosticism;
Agnosticism;
Empiricism (sensualism);
Rationalism.
Materialism(in literature often referred to as the “line of Democritus”) - a direction in philosophy, whose supporters believed that in the relationship of matter and consciousness matter is primary.
According to the views of materialists:
Matter really exists;
It exists independently of consciousness;
Matter - an independent substance - does not need anything other than itself for its existence;
Matter exists and develops according to its own internal laws;
Consciousness (spirit) is the property of highly organized matter to reflect itself (matter);
Consciousness is not an independent substance existing along with matter;
Consciousness is determined by matter (being).
Such philosophers as Democritus, philosophers of the Milesian school (Thales, Anaximander, Anaximenes), Epicurus, Bacon, Locke, Spinoza, Diderot, Herzen, Chernyshevsky, Marx, Engels, Lenin belonged to the materialist direction.
There is a special direction in materialism - vulgar materialism. Its representatives (Vocht, Moleschott) absolutize the role of matter, are carried away by the study of matter from the point of view of physics, mathematics, chemistry, its mechanical side, and ignore consciousness itself as an essence and the ability to respond to influence on matter. In their opinion, the human brain secretes thought, consciousness, just as the liver secretes bile, i.e., vulgar materialism does not recognize the qualitative difference between consciousness and matter.
The advantage of materialism, according to modern researchers, is its reliance on science, especially on the exact and natural sciences (physics, mathematics, chemistry), and the logical provability of many materialist positions.
The weak side of materialism is the insufficient explanation of the essence of consciousness, the presence of phenomena in the surrounding world that are inexplicable from the point of view of materialists.
Materialism as the dominant direction of philosophy was widespread in democratic Greece, Hellenistic states, England during the bourgeois revolution (XVII centuries), France (XVIII century), the USSR and socialist countries in the XX century.
Idealism(in literature often - Plato’s line) - a direction in philosophy, whose supporters in the relationship of matter and consciousness consciousness was considered primary(idea, spirit).
There are two independent trends in idealism:
Objective idealism (Plato, Leibniz, Hegel, etc.)
Subjective idealism (Berkeley, Hume).
Founder objective idealism Plato is considered.
According to the views of representatives of objective idealism:
Only the idea really exists;
The idea is primary;
The entire surrounding reality is divided into the “world of ideas” and the “world of things”;
- the “world of ideas” (eidos) initially exists in the World Mind (Divine Plan);
- “world of things” - the material world has no independent existence and is the embodiment of the “world of ideas”;
Each individual thing is the embodiment of the idea (eidos) of a given thing (for example, a deer is the embodiment of the general idea of a deer, a house is the idea of a house, a car is the idea of a car, etc.);
God the Creator plays a large role in transforming a “pure idea” into a concrete thing;
Individual ideas (“the world of ideas”) objectively exist independently of our consciousness.
Subjective idealists (Berkeley, Hume) believed that:
Everything exists only in the consciousness of the cognizing person (subject);
Ideas exist in the mind of man;
Images (ideas) of material things also exist only in the human mind through sensory sensations;
Outside the consciousness of an individual person, neither matter nor spirit (ideas) exists.
A weak feature of idealism is the lack of a reliable (logical) explanation for the presence of a mechanism for transforming “pure ideas” into a concrete thing.
Idealism as a philosophical trend dominated in Platonic Greece, the Middle Ages, and is currently widespread in the USA, Germany and other countries of Western Europe.
Both materialism and idealism are monistic philosophical teachings(recognize one primary beginning) - monism. But there are also other directions according to the recognized principles of the world.
Dualism - founded by Descartes, its essence is that:
There are two independent substances - material (possessing the property of extension) and spiritual (possessing the property of thinking)
Everything in the world is derived (is a mode) either from one or from the second of these substances (material things - from the material, ideas - from the spiritual)
Matter and consciousness (spirit) are two opposite and interconnected sides of a single being
The main question of philosophy (what comes first - matter or consciousness) does not actually exist, since matter and consciousness complement each other and always exist.
Pluralism (of substances) is the point of view of philosophers, according to which the world has many origins (for example, monads in the teachings of G. Leibniz).
Deism - direction in philosophy, whose supporters (18th-century French enlighteners Voltaire, Rousseau) recognized the existence of God, who, in their opinion, having once created the world, no longer participates in its further development and does not influence the lives and actions of people. Deists considered matter to be spiritual and did not oppose it to consciousness (spirit).
Eclecticism - a direction in philosophy whose proponents mix the principles of materialism and idealism.
Structure of philosophy
Already at the initial stage of the formation of philosophy, a specific structure of philosophical knowledge began to take shape and the main functions of philosophy were determined. Historically, the first, basic elements of philosophy were ontology, epistemology, and ethics. Ontology developed as a doctrine of being, epistemology - a doctrine of knowledge, ethics - a doctrine of morality, of human behavior.
Scheme 13

As philosophy develops, in addition to ontology, epistemology and ethics, new areas are formed in it, philosophical disciplines: logic (the science of the laws of thinking), aesthetics (the study of the laws of beauty), history of philosophy (studies the development of philosophical thought, from its inception to the present day). New subsections have appeared in ontology that study the most general patterns of existence of certain spheres of existence: nature, man, society.
These subsections are philosophy of nature, philosophy of technology, philosophical anthropology, social philosophy (the science of society, its genesis), philosophy of law, philosophy of culture, philosophy of history. In modern epistemology, such leading branches have emerged as epistemology(the doctrine of knowledge as such, its structure, patterns), scientific studies(a discipline that studies theoretical problems in the development of science).
The laws of mechanics were absolutized in relation to social philosophy by the following philosophical direction: French materialism of the 18th century
Absoluteness, relativity, specificity, objectivity are the main properties Truths
Agnosticism- a philosophical doctrine that denies the finally resolved question of the knowability of the world, the attainability of truth, limits the role of science only to the knowability of phenomena (Protagoras, Kant, J. Berkeley, Hume).
Agnosticism– this is: a direction in the theory of knowledge, which believes that adequate knowledge of the world is impossible
Agnosticism– this is: a doctrine that denies the knowability of the essence of the objective world
Agnosticism? (Greek A - negation, gnossis - knowledge) does NOT reflect the possibility of knowing the world
Axiology– philosophical doctrine of the nature of values.
Axiology– this is: the doctrine of values
Anaximenes took the first principle of all things Air
An ancient philosopher who believed that you cannot step into the same river twice: Heraclitus
Anthropoids are Great apes
Anthropology is: doctrine of man
Anthroposociogenesis is the process of becoming man and society, their separation from the natural world
Anthroposocioginesis, man, society, sources of development.
Anthropocentrism- the view that man is the center and highest goal of the universe.
Arthur Schopenhauer considered substance, the fundamental principle of the world Will to power
The atomic hypothesis of the structure of matter was first put forward by: Democritus
The basis of totalism? scholasticism.
He was declared crazy by Emperor Nicholas I for his philosophical views. P.Ya. Chaadaev
In "Vertograd the Multicolored" Simeon of Polotsk likens the world to a book
In antiquity, the merit of the discovery of the supersensible world of ideas belongs to : Plato
On the question of substance, Rene Descartes adhered to Dualism
In Indian philosophy - the total sum of committed actions and their consequences, which determines the nature of the new birth Karma
In what city was the Platonic Academy revived in the 15th century? Florence
In Marxism, the main factor in the development of society is considered Method of production of material goods
In Marxism, matter is interpreted like objective reality
In Marxist philosophy it is believed that relations of production are: Determining the relationship between people.
In modern Russia Mortality significantly exceeds birth rate
In the modern theory of knowledge, the rethinking of the knowing subject follows the path of abstraction from the personal qualities of a person
According to the pragmatics concept of truth – truth? this is what is useful, what helps to solve problems successfully.
In the personality structure, S. Freud identifies It, Super-I, I
In the philosophy of Heraclitus, the word Logos denotes the world law, the world order, to which everything that exists is subordinated. Which concept of Chinese philosophy has the same meaning: Tao
In the philosophy of I. Kant, a “thing in itself” is that which causes sensations in us, but cannot itself be known
In the philosophy of I. Kant, antinomies take place where, with the help of human reason, they try to draw conclusions about: the world of “things in themselves”
In Plato's philosophy, the idea of a "horse" differs from a real, living horse in that: the idea is primary, the real horse is secondary
In Plato's Philosophy, the idea of a horse differs from a real living horse in that: The idea is primary, the horse is secondary.
IN AND. Lenin developed the doctrine of Russia as the Weak Link in the Chain of Imperialism
An important feature of the philosophical thought and culture of the Renaissance? anthropocentrism (Greek Anthropos - man + Lat. Centrum - center of the circle)
The most important specific property of biological time is Anthropicity
The most important specific property of biological space: Homogeneity
The most important philosophical work of Immanuel Kant, “Critique of Practical Reason”
The most important feature of the philosophical thought and culture of the Renaissance is: anthropocentrism
Belief in the moral purity of the Russian peasantry is characteristic of: Slavophiles
The belief that the salvation of the West lies in the adoption of Orthodoxy is closest to the worldview: Slavophilov
Supreme god in Slavic mythology, creator of the Universe, manager of rain and thunderstorms, patron of family and home Rod
The internal content of an object in the unity of all its properties and relationships is expressed by the category of Essence
War of all against all is the state of nature: Thomas Hobbes
A. Schopenhauer considered will as the main principle of life and knowledge
The question of the role and place of Russia in the history of mankind was posed in “Philosophical Letters”: P. Chaadaev
First expressed the idea of the atomic structure of matter: Democritus
Aristotle was the first to define man as a “social animal” (zoon politikon).
Parmenides was the first to use the concept of being in philosophy.
Was he the first to formulate the laws of dialectics? Hegel.
First time you used the word philosophy? Pythagoras
Time is a set of relations expressing the coordination of states changing each other, their sequence and duration. Time is one-dimensional, irreversible, homogeneous.
Everything in the world is predetermined, man is absolutely not free,” say representatives of: fatalism
Everything in the world is predetermined” fatalism.
K. Marx identified the socio-economic class as the main element of the social structure of society
The statement that the soul before the birth of a person was in the world of ideas, therefore in the process of cognition it is able to recall them, belongs to: Plato
A statement that affirms or denies something. Refutation
The saying: “Man is the measure of all things” belongs to: Protagoras
They opposed the ownership of land by monasteries; they believed that the accumulation of wealth was contrary to monastic vows.
The highest ability of the subject, which directs the activity of the intellect. Reason
The highest form of movement of matter is Social Movement
The highest form of organization of scientific knowledge, giving a holistic idea of the patterns and essential connections of a certain area of reality. Theory
The highest, most perfect form of love, according to V.S. Solovyova, is Love between a man and a woman
Identification of the causes of hereditary connections, bringing individual phenomena under the general law is characteristic of: Explanation.
Hegel: “Phenomenology of Spirit”, “Science of Logic”, “Philosophy of History”.
Hedonistic love is a game that is not distinguished by the depth of feelings and manifests itself in the forms of flirting, coquetry, etc. (in ancient Greek culture) Ludus
The main task of Christian apologists was: To justify the advantages of Christianity over paganism
The main moral rule from the point of view of L.N. Tolstoy Do not resist evil
Marx believes that the most important thing in society is: the mode of production
Global problems are Problems on the solution of which the survival of all humanity depends
Global problems: Problems on the solution of which the survival of humanity depends. War and peace, demography, ecology.
Deep qualitative changes in the development of any phenomena of nature, society or knowledge, occurring in a relatively short period of time Revolution
Epistemology is the philosophical doctrine of knowledge. Founder J. Locke.
Epistemology is: the doctrine of nature, the essence of knowledge
Epistemology examines the boundaries and possibilities of human knowledge. The city in which, according to the Tale of Bygone Years, Grand Duke Vladimir Svyatoslavich Korsun was baptized
The Greek word "techne" originally meant art, skill
This definition: “The study of an object under controlled or artificially created conditions” refers to: experiment
The date of adoption of Orthodoxy in Rus' is considered to be 988
Movement is any change, interaction, unfolding in space and time. It is absolute and relative.
Movement in the direction from more perfect to less perfect Regression
Movement, any change is only an illusion of the sensory world, claimed the Eleatics
The double-headed eagle was first adopted as the state symbol of Russia by Ivan III in the 15th century
Deism is a religious-philosophical doctrine that recognizes God as the world mind, who designed the expedient “machine” of nature and gave it laws and movement, but rejects further intervention of God in the self-movement of nature (i.e., “divine providence,” miracles, etc. .) and does not allow any other path to the knowledge of God other than reason. It became widespread among the thinkers of the Enlightenment and played a significant role in the development of free thought in the 17th and 18th centuries.
F. Bacon’s division of experiences into “fruitful” and “luminous” corresponds to the division of knowledge into: Empirical and theoretical
Dialectics is a system of universal principles and regulations that guide the cognitive and practical activities of people. The idea of mutually exclusive and simultaneously presupposing opposites.
Dialectics is the Doctrine of development and universal interrelations
Dialectics differs from metaphysics by understanding development
Dialectical source of self-movement and development of nature, society and knowledge Contradiction
Dialectical materialism - the teaching of Marxism
Old Russian thought is characterized by: Revaluation of external material existence
Dualism is characterized by the thesis: matter and consciousness are two principles that exist independently of each other
Idealism is characterized by the statement: consciousness is primary, matter does not exist independently of consciousness
For which of the following thinkers was not the central problem of the meaning of life? I. Lakatos
Renaissance philosophy is characterized by nostalgia for ancient culture
Reliable knowledge about the world is impossible, says Skepticism
Another concept of the Renaissance? Renaissance.
The dualism of spirit and matter, God and nature is characteristic of the philosophy of N.A. Berdyaev
Dualistic philosophy is characteristic of R. Descartes
Spiritual leader of Westerners A.I. Herzen
Spiritual leader of non-possessors Nil Sorsky
There is no single history of humanity, there is only the history of local civilizations according to the civilizational approach
If a theory does not reveal an empirical consequence in a prediction in practice, then they talk about: Falsification of knowledge.
The law of retribution in Indian religion and religious philosophy, which determines the nature of the new birth of reincarnation: karma
The law of dialectics answering the question about the source of development? the law of unity and struggle of opposites.
The law of dialectics, revealing the most general mechanism of development Unity and struggle of opposites
The law of dialectics, answering the question about the source of development: The law of unity and struggle of opposites.
The law of dialectics, revealing the sources of self-propulsion and development of the world? the law of unity and struggle of opposites.
The law of dialectics characterizing the direction, form and result: the transition of quantitative changes into qualitative ones
The laws of dialectics were first formulated by G.V.F. Hegel
Sigmund Freud identified three levels in the structure of the mental apparatus. Among the authorities listed below, indicate the extra one, i.e. one that Freud did not single out. Fore-We
The famous Russian icon painter is: Theophanes the Greek
Knowledge according to Socrates is identical to: virtues
Knowledge corresponding to reality, adequately reflecting reality Truth
The golden rule of morality: “What you do not wish for yourself, do not do to others” was first formulated by: Confucius
I. Kant believes that space and time: are innate, pre-experimental forms of sensibility
Idealism is a direction of philosophy that resolves the main issue of philosophy in favor of the primacy of spirit, consciousness, and subjectivity.
The ideological leader of the Slavophiles is: Khomyakov.
The ideological leader of the Slavophiles was A.S. Khomyakov
The ideologeme “Moscow is the Third Rome” was first substantiated by Filofei
Ideology is a theoretical expression of the interests of a particular group of people
Ideology relates to the Social Sphere
The idea of the rule of law includes the provision of Separation of Powers
The name of the founder of Buddhism is Sidhartha
Name of the founder of Buddhism, meaning awakened, enlightened: Buddha
Individualism – placing one’s own interests above the interests of society.
Individual consciousness is a reflection of the individual existence of a specific person
The initiator of the correction of church books, which was the reason for the schism, was: Patriarch Nikon
Interest is a specific, conscious need
Interest in painting is a concretization of an aesthetic need
Intuition? This is the ability to comprehend the truth without direct recourse to logical arguments.
Irrationalism - belittles the role of reason.
Irrationalistic trend in the philosophy of the 20th century Existentialism
The art of interpreting sacred texts, developed in the Middle Ages Exegesis
Study of an object in controlled or artificially created conditions Experiment
The source of knowledge is the soul’s recollection of the world of ideas, believed: Plato
The original, simplest form of sensory knowledge Sensation
Peace does not belong to the attributes of matter
The most important features of Russian philosophy cannot be attributed to the pre-systematic, pre-logical character
The most important functions of culture cannot be classified as the destructive function.
The most important functions of scientific theory include Systematizing
Are they global problems? war and peace, environmental, demographic.
Ancient Indian philosophical texts include the Upanishads
Ancient Chinese philosophical texts include the Tao Te Ching
The “Tale of Law and Grace” belongs to the genre of social utopia in ancient Russian literature.
Ideal phenomena include Conscience
What type of love does this description refer to: “This is a tender and soft feeling, selfless love-self-giving, embodied in the love of a mother for her child or in Christian love for her neighbor”? Agape
One of the central ideas of Freemasonry includes: Improvement of man through personal and collective self-knowledge
The main ideas of the “Philosophical Letters” cannot include following the Christian commandments as the only path to salvation, to the Kingdom of Heaven
The main methods of studying the unconscious in psychoanalysis do not include Belief Analysis
Representatives of the “philosophy of life” include F. Nietzsche
The characteristic features of Russian philosophy include: Empiricism
The idea of equality of all people cannot be considered among the most important ideas of French philosophy of the Enlightenment.
What do you think, the hypothetical dispute of which philosophers was depicted by A.S. Pushkin in the poem “Movement”? Zeno and Heraclitus
Who do you think the following statement belongs to: “The idea of romantic love, according to which only one person in the world can be the object of true love and that the main task is to find this particular person, is wrong. It is also not true that love for him, even if you are lucky enough to meet such a person, will result in a rejection of love for others. Love, which can be experienced in relation to only one person, this very fact shows that this is not love, but a symbiotic relationship.” E. Fromm
Who do you think the following lines might belong to: “Any attempt to once again raise the spirits of the people in the concentration camp assumed that we would be able to direct them to some goal in the future. The one who could no longer believe in the future, in his own future, was lost. Along with the future, he also lost his spiritual core, broke internally and degraded both physically and mentally... However, the courage to live or, accordingly, fatigue from life turned out to depend each time solely on whether a person had faith in the meaning of life, his life. The motto of all psychotherapeutic work in a concentration camp could be the words of Nietzsche: “He who has a Why to live can endure almost any How”? V. Frankl
How is philosophy translated? love of wisdom.
Which of the following features is not characteristic of medieval philosophical thought? Scientism
Which of the following pairs of adjectives is not used in the philosophical analysis of nature? pristine and man-made
Which of the following problems is not a global problem? The problem of combating international terrorism
Which concept of time does not allow the possibility of creating a “time machine”? Dynamic
What meaning did G. Hegel put into the statement that “philosophy is an epoch captured by thought”? The thinking of philosophers is determined by the socio-economic conditions of the society in which they live
Kant wrote a work: "moral duty"
Kievan Rus took the “cultural baton” from: Byzantium
Chinese philosopher, founder of Taoism Lao Tzu
A class capable of reorganizing society, according to K. Marx Proletariat
Key principle of dialectics? principle of contradiction.
The key point of the dialectical concept is the principle of Contradiction
Coherence is Self-Consistency of Knowledge
The Code of Feudal Lifestyle, which prescribed how to build a family and run a household, created in Rus' in the 16th century “Domostroy”
Collectivism is the establishment of the interests of society above one’s own.
Who owns the following statements: “There is meaning for everyone and for everyone there is its own special meaning”, “Meaning cannot be created artificially, it can only be found”, “Our conscience guides us in the search for meaning”? V. Frankl
Who owns the following pessimistic lines: “Alone in the world, we gave nothing to the world, took nothing from the world, we did not contribute in any way to the forward movement of the human mind, and we distorted everything that we got from this movement. Since the very first moments of our social existence, nothing suitable for the common good of people has come from us, not a single useful thought has sprouted in the barren soil of our homeland, not a single great truth has been brought forward from our midst”? P.Ya. Chaadaev
Who owns this statement: “I maintain that there are no things. We're just used to talking about things; in fact, there is only my thinking, there is only my “I” with its inherent sensations. The material world only seems to us, is it just a certain way of talking about our feelings”? To the subjective idealist
Concept… characteristic of V. Solovyov: All-Unity
The criterion of truth in Marxist philosophy Practice
Who first used the term “philosophy”? Pythagoras.
Which of the ancient philosophers taught that everything develops, that the first cause of the world and its fundamental principle is fire, that you cannot enter the same river twice? Heraclitus
Which of the named scientists-philosophers first established that solar activity affects people’s well-being? Chizhevsky
Which of the following thinkers is not a representative of German classical philosophy? F. Nietzsche
Personality is Since the concept of “personality” is inseparable from the concept of “society” - every person is a potential personality
Personality is: one is not born as a person, one becomes a person
Logical deduction of particular consequences from the general position Deduction
Marx "Capital"
Freemasonry was brought to Russia from: England
Materialism is a direction of philosophy that solves the main question of philosophy in favor of primary matter, nature, and objective being. The term "materialism" has been used since the 17th century. mainly in the sense of physical concepts of matter, and from the beginning. 18th century in a philosophical sense to contrast materialism with idealism. Historical forms of materialism: ancient materialism (Democritus, Epicurus), Renaissance materialism (B. Telesio, G. Bruno), metaphysical (mechanistic) materialism of the 17th-18th centuries. (G. Galileo, F. Bacon, T. Hobbes, P. Gassendi, J. Locke, B. Spinoza; French materialism of the 18th century - J. La Mettrie, C. Helvetius, P. Holbach, D. Diderot), anthropological materialism (L. Feuerbach), dialectical materialism (K. Marx, F. Engels, V. I. Lenin).
Matter is the primary source of being, says Materialism
Metaphysics is the View according to which the world or a separate part of it is viewed as unchanging, qualitatively constant
The approximate calculation method is most widely used in the humanities
Method not used in scientific and technical knowledge Hermeneutic
The Milesian school is a symbol for the first ancient Greek natural philosophers and natural scientists who lived in the 6th century. BC e. in the city of Miletus (Thales, Anaximander, Anaximenes).
Worldview is: a set of views, assessments, emotions that characterize a person’s attitude to the world and to himself
A worldview form of social consciousness that rationally substantiates the ultimate foundations of existence, including society and law: philosophy
The worldview function of philosophy is that: philosophy helps a person understand himself, his place in the world
The ideological principle according to which the world was created by God out of nothing is called: Creationism
Mental or real decomposition of an object into its component elements Analysis
The thinker whose name is usually associated with the discovery of the unconscious in the human psyche? Freud.
The thinker who believes that man is driven by sexual instincts: Freud
A thinker who believed that man is driven primarily by sexual instincts Z. Freud
A thinker who lived his entire life in Konigsberg and taught at the Kant University there
The thinker whose name is usually associated with the discovery of the sphere of the unconscious in the human psyche S. Freud
The idea “never accept as true something that I do not clearly know to be true” belongs to: R. Descartes
The thought whose name is associated with the discovery of the unconscious: Freud
A thought that identifies and generalizes objects based on an indication of their essential and necessary properties Concept
The thought: “Man is the measure of all things” belongs to Protagoras
The name of the period of creative ministry of the “Church Fathers” (III-VIII centuries), who laid the foundations of Christian philosophy and theology; in their works, in opposition-dialogue with Greco-Roman philosophy, the formation of a system of Christian dogmatics takes place: patristics
Name the philosopher who is considered the founder of ancient dialectics, Heraclitus
The ideology of the Union of Right Forces party is closest to the views of the “Westerners.”
The most ancient human ancestor (according to modern science) Australopithecus
The most common fundamental concepts Categories
The most complex form of reflection is Consciousness
The direction of Western European philosophy that denies the cognitive value of philosophy, the presence of its own, original subject: positivism
Direction of modern Western philosophy Pragmatism
The direction of modern Western philosophy Thomism
The direction of modern Western philosophy? pragmatism.
The direction of modern philosophy that is materialist Marxism
The direction of philosophy in which man is viewed as a self-determining, self-creating being Existentialism
The movement that denies the existence of God is called atheism
A movement that considers sensory experience to be the only source of our knowledge about the world. Sensualism
Directed, qualitative change Development
Naturalistic approach to society: In it, society is viewed as the highest creation of nature, as a natural continuation of cosmic laws.
Scientific hypothesis refers to Conceptual means of cognition
Scientific assumption, assumption that needs additional justification Hypothesis
Does not belong to the most important dimensions of spirituality Pluralism
Does not apply to the main types of social production: Production of resources
Does not belong to the types of means of cognition Technical
The law of the intertwining of causes and effects is not a law of dialectics
Is not a problem studied by the philosophy of history The problem of the structure (structure) of society
Not a characteristic feature of German classical philosophy Denial of transcendental, divine existence
Impossible to falsify? existence of God.
A negative attitude towards earthly life, viewing it as a continuous series of sufferings is characteristic of Buddhism
Some Christian theologians argue that the whole world. The entire Universe was created by God in six days, and God himself is a disembodied intellect, an all-perfect Personality. What philosophical direction does this view of the world correspond to? Objective idealism
An inherent essential property of a thing, phenomenon, object is called an Attribute
Consistency refers to the next scientific criterion: Logical
descend from the abstract to the concrete, rely on experience and move from the individual to the general
Noosphere is the Sphere of the Mind
Carrier of deliberate, purposeful activity Subject
What historical type of worldview are we talking about here: “This is a holistic worldview in which various ideas are linked into a single figurative picture of the world, combining reality and fantasy, the natural and the supernatural, knowledge and faith, thought and emotions”? Mythologies
Socio-economic philosophy: Marx
Social consciousness is a reflection of social existence
A socio-economic formation is a Society with its inherent economic basis and a political and legal superstructure rising above it
Social progress is the progressive movement of society from simple forms to more complex ones
Objective-idealist philosophy was founded by: Plato
Restriction or suppression of sensual desires, voluntary enduring of physical pain, loneliness: asceticism
One of the founders of the philosophy of technology P. Engelmeyer
One of the first supporters of the idea of Pan-Slavism (unification of all Slavs) Yuri Krizhanich
One of the main ideas of the philosophy of unity is the inadmissibility of any forms of violence in public and state life.
One of the authorities that Sigmund Freud identified in the personality structure of the id
One of the main works of S.N. Bulgakov "Non-evening light"
One of the basic rules of “cosmic ethics” by K.E. Kill Tsiolkovsky the Suffering
One of the cross-cutting ideas of Russian philosophy is the idea of apokatastasis, the essence of which is the Salvation of all people without exception: both righteous and sinners
In Freud's psychoanalysis it refers to: the sphere of the unconscious
Ontology is a philosophical doctrine of being. The founder of the doctrine of ontology, Francis Bacon.
Ontology is: the doctrine of being, its fundamental principles
Determine the time of emergence of philosophy: VII-VI centuries. BC.
Defining relationships between people in Marxist philosophy Production
The defining feature of a religious worldview is: belief in supernatural, otherworldly forces that have the ability to influence the course of events in the world
Liberation from church influence Secularization
The basis of being, existing in itself independently of anything else, Substance
The founder of Russian book printing is: I. Fedorov
Founder of idealism? Plato.
Founder of logic? Aristotle.
Founder of materialism: Democritus.
Founder of sociology as a positive science O. Comte
The main idea of the philosophy of the French Enlightenment The priority of reason as the highest authority in solving the problems of human society
The main problem solved by the philosophers of the Milesian school: the problem of the beginning
The basic concept of epistemology V.I. Vernadsky Empirical generalization
The main statement of rationalism is that Reason plays a priority role in human cognitive activity
The main statement of empiricism: All human knowledge is based on experience.
The main idea of Westernism is that Russia should develop along the European path
The main object of study of the Renaissance: Man.
The main object of study, the measure of things and relationships in the Renaissance: man
The basic principle of ancient philosophy? cosmocentrism.
The main work of K. Marx: “Capital”
The main forms of idealism are objective and subjective. The first asserts the existence of a spiritual principle outside and independently of human consciousness, the second either denies the existence of any reality outside the consciousness of the subject, or considers it as something completely determined by his activity. The largest representatives of objective idealism: in ancient philosophy - Plato, Plotinus, Proclus; in modern times - G. W. Leibniz, F. W. Schelling, G. W. F. Hegel.
The main method of scientific knowledge, according to F. Bacon, should be Induction
The main principle of ancient philosophy was: cosmocentrism
The founder of space ecology and heliobiology A.L. Chizhevsky
Nikolai Fedorov is considered the founder of Russian cosmism
The foundations of being, problems of knowledge, the purpose of man and his position in the world are studied: philosophy
Features of rationalism of the 17th century. Caused by Mathematics
The domestic thinker who first created a comprehensive philosophical system based on Christian humanism V.S. Soloviev
Reflection is (choose the most complete and accurate definition) the property of matter to capture the characteristics of objects affecting it
Denies the existence of God? atheist.
Deny the possibility of knowing the world: agnostics
Sensations, perceptions, concepts, thinking are part of the structure: consciousness
The fundamental principle of the world according to Hegel is? absolute idea.
According to I. Kant, in order for knowledge to be reliable, it must: be universal and necessary
According to G.S. Skovoroda, all reality falls into three worlds, of which society is not one
According to I. Kant, moral duty is of fundamental importance for the formation of man as a moral being
According to L. Shestov, a person can achieve the impossible only through Faith in God
According to contemporaries, “he created in us a love for science and a desire to read” N.I. Novikov
According to Kant's philosophy, “the thing in itself”? it is something that causes sensation but cannot itself be known.
According to the functional purpose and research objectives, knowledge is divided into fundamental and applied
Falsified hypotheses about: The existence of life on Mars
The “Legend of the Grand Inquisitor” by F.M. can be considered a true hymn to freedom. Dostoevsky
The cognitive attitude consists of three main aspects (elements). Indicate which of the indicated sides is the odd one here? The purpose of knowledge
Statement: “Number is the essence and meaning of everything that is in the world”, belongs to: Pythagoras
The propositions about the infinity of the Universe in time and space, about the identity of God and nature were substantiated by: J. Bruno
The provisions about the absolute freedom of man, his abandonment and loneliness, about the borderline situation that can reveal the true essence of man, were substantiated in the philosophy of Existentialism
The concept of “Logos” in the philosophical teachings of Heraclitus means: Universal law, the action of which everything in the world is subject to
The concept of ancient Chinese philosophy denoting the feminine, dark and passive principle: Yin
The concept of ancient Chinese philosophy, denoting the masculine, bright and active principle: Yang
The concept of socio-economic formation belongs to Marxism
A follower of Pythagoras, the first to draw the system of the world and place the Central Fire at the center of the universe Philolaus
They posed the problem of being in antiquity: the Eliates
Gradual changes in society and nature Evolution
Act in such a way that the maximum of your will can at the same time become the principle of universal legislation”: Kant
Pragmatism is a Western philosophy.
The subject of theoretical philosophy according to I. Kant should be the study of: the laws of reason and its boundaries.
Intentional, purposeful perception of an object, phenomenon in order to study its properties, characteristics of its course and behavior. Observation
The representative of materialism is L. Feuerbach
The representative of Slavophilism was I.S. Kireyevsky
The representative of subjective idealism is: J. Berkeley
Representatives of which philosophical school posed the problem of being, contrasted the world of feelings with the world of reason and argued that movement, any change is only an illusion of the sensory illusory world: Eleanian
Representatives of German philosophy: Kant, Hegel, Feuerbach.
Representative of the philosophy of life? Nietzsche
Representative of German classical philosophy: L. Feuerbach
Representative of Russian Marxism G.V. Plekhanov
Representative of medieval Western European philosophy: F. Aquinas
Representative of medieval philosophy? Thomas Aquinas.
Representative of the philosophy of the French Enlightenment J.-J. Rousseau
Representative of Renaissance philosophy: G. Bruno
Representatives of “Russian cosmism” are: K. Tsiolkovsky, V. Vernadsky
The idea of a “noble husband” as an ideal personality was developed by: Confucius
The pre-philosophy of Kievan Rus is characterized by: mysticism
When Moscow University opened, its three faculties did not include: physics
The principle according to which God determines the entire course of history and the destiny of each person Providentialism
The priority of the interests of society over the interests of the individual is characteristic of Collectivism
The priority of individuals over the social whole is affirmed by Individualism
The reason, the primary source of evil in the world according to N.A. Berdyaev State power
The cause of inequality in human society is J.-J. Rousseau believed Property
Rousseau believed that the cause of inequality in human society was: Property.
The problem of proving the existence of God was one of the central ones for Thomas Aquinas
The problem of the meaning of life was central to the philosophy of V. Frankl
Problems of war and peace, demographic and environmental in the modern world are called... problems. Global
Producing a general conclusion based on generalization of particular premises Induction
Works of early Christian literature not included in the biblical canon, i.e. Apologies recognized by the official church as “false”
Simple indivisible substance according to Leibniz Monad
Space is a set of relations expressing the coordination of existing objects, their location relative to each other and their relative size. Space is three-dimensional, homogeneous, isotropic.
The opposition of the individual to society is characteristic of: individualism
Archpriest Avvakum was the spiritual leader of the schismatics
The procedure for mentally dividing a whole into parts Analysis
The process of moving from general premises to conclusions about particular cases Deduction
The manifestation of cause-and-effect relationships that bring individual phenomena under a general law is characteristic of? explanation.
The work “On Man, His Mortality and Immortality,” which is one of the first philosophical and anthropological works in the history of Russian thought, was written by A.N. Radishchev
A work about a person, his mortality and death: Radishchev.
Works about man, his death and immortality." Author? Radishchev.
The equality of the material and spiritual principles of existence is proclaimed by Dualism
Section of philosophy in which problems of cognition are developed. Epistemology
Kant divided reality into the “world of things in themselves” and the “world of phenomena.”
The method developed by Freud is called: Psychoanalysis.
Growing interdependence of different regions of the world Globalization
Reality, which forms the basis of the world, according to Hegel: The Absolute Idea
Revolution is a profound qualitative change in the development of any phenomena of nature, society or knowledge (for example, a social revolution, as well as a geological, industrial, scientific, technical, cultural revolution, a revolution in physics, in philosophy, etc.).
Regression is a type of development characterized by a transition from higher to lower, processes of degradation, lowering the level of organization, loss of the ability to perform certain functions; also includes moments of stagnation, a return to obsolete forms and structures. The opposite of progress.
Reflection is: a person’s reflection on himself
The founder of positivism, Auguste Comte
The Russian Academy of Sciences was founded in 1724
Growing interdependence of different regions of the world: Globalization.
The Russian thinker... in his work “Self-Knowledge” stated that he laid the foundation of philosophy not on being, but on freedom. ON THE. Berdyaev
Russian thinker, who in his work “Names” argued that there is a deep connection between a name and its bearer P.A. Florensky
Russian philosopher, who wrote in the book “Self-Knowledge”: “The originality of my philosophical type lies primarily in the fact that I based philosophy not on being, but on freedom.” Nikolai Berdyaev
Russian Socrates" was nicknamed G.S. frying pan
From Greek the word “philosophy” is translated as: love of wisdom
A representative of Vulgar materialism would agree with the statement “thinking is the same product of brain activity as bile is a product of activity.”
The most famous icon of Andrei Rublev: “Trinity”
The secular world position of the Renaissance, opposed to scholasticism and the spiritual dominance of the church? humanism.
The originality of my philosophical type lies, first of all, in the fact that I based my philosophy not on being, but on freedom: N. Berdyaev.
Sensualism is a direction in the theory of knowledge, according to which sensations and perceptions are the basis and main form of reliable knowledge. Opposes rationalism.
Sergius of Radonezh was a contemporary of the Battle of Kulikovo
Synthesis of philosophical and scientific teachings, united by the idea of the relationship between man and nature, humanity and the Universe Cosmism
Systematizer of scholasticism - Thomas Aquinas.
The words “beauty will save the world” belong to F.M. Dostoevsky
A Word on Law and Grace" written by Hilarion
The meaning of Dostoevsky's parable about the “tear of a child” from the novel “The Brothers Karamazov” is that world harmony is not worth even one human life
Conciliarity in the philosophy of the Slavophiles: Free unity of people in Christ.
The totality of natural conditions for the existence of man and society Nature
A set of unique traits that distinguish a given individual from all others. Individuality
The totality of social feelings, emotions, moods Social psychology
The body of religious doctrines and teachings about the essence and action of God: theology
A set of religious doctrines about the essence of God's action? theology. The set of essential necessary properties of a thing constitutes it: Quality
According to ... approach, there is no single history of humanity, there is only the history of local cultures. Civilization
According to Aristotle, the human soul does not include the Mineral Soul
According to G. Hegel, the true engine of history is the World Spirit
According to modern science, Homo sapiens appeared on earth 100-150 thousand years ago
According to Carl Rogers, the self-concept consists of four main elements. Which of the following is not one of them? I am a mirror
According to L. Shestov, the main enemies of man in the “struggle for the impossible” are Reason and morality
According to Marxism, the main factor of anthropogenesis is Labor
According to Marxist philosophy, the essence of the main question of philosophy is: the driving forces of the development of society
According to N.F. Fedorov, the highest moral duty of earthlings, the central task of all people is to Eliminate suffering on earth
According to modern science, Australopithecines did not have articulate speech.
According to the sociology of Marxism, the main driving force for the development of society is: Class struggle
According to T. Kuhn, “a scientific achievement recognized by all, which over a period of time provides the scientific community with a model for posing problems and solving them” Paradigm
According to Francis Bacon, any knowledge must: be based on experience and move from the individual to the general
According to Spengler, civilization is the final stage in the development of culture
According to... “everything in the world is predetermined, man is absolutely not free” Fatalism
Combining the elements of the object being studied into a single whole, selected in the analysis. Synthesis
Solovyov: “The meaning of love”, “beauty in nature”, “justification of goodness”.
According to Z. Freud, a dream is: symbolic
Savior, deliverer from troubles, God's anointed Messiah
Companion of Peter the Great, Archbishop of Novgorod, author of the “Spiritual Regulations” Feofan Prokopovich
The mode of existence of matter: Movement
The ability of living organisms to navigate the external world and manage their activities Consciousness
The ability to comprehend the truth by directly observing it without resorting to logical arguments Intuition
A supporter of deistic materialism in Russian philosophy was M.V. Lomonosov
The country where Vladimir Solovyov for the third time met with the vision of Sophia as an image of eternal femininity and the wisdom of God Egypt
Stages of knowledge? sensual and rational.
Newton defended the substantial concept of space and time
Subjective idealism is most clearly expressed in the teachings of J. Berkeley, D. Hume, and the early J. G. Fichte (18th century). In everyday usage, “idealist” (from the word “ideal”) often means an unselfish person striving for lofty goals.
The essence of Socrates' "ethical rationalism": virtue is the result of knowing what is good, while lack of virtue is the result of ignorance
The essence of the Big Bang cosmogonic hypothesis is the assumption that the Universe arose as a result of the explosion of a microscopic particle
The essence of Socrates' ethical rationalism? “Virtue is the result of knowing what good is, while lack of virtue is the result of ignorance.
An essential, necessary, repeating, stable connection between phenomena is called the Law
The existence of many initial foundations and principles of being is affirmed by Pluralism
There are... socio-economic formations Five
There are five main types of social communities. Please note which of the six types of communities listed below is incorrectly named here? State
The essence of deism is to reduce the role of God to the creation of matter and the first impulse
The essence of naturalism, as an approach to explaining social life, is what? social life depends on natural factors.
The essence of the problem of biological and social in man is the question of? about the interaction and correlation of gene and upbringing.
The essence of the relational concept of space and time is that Space and time depend on material processes
The essence of Epicurus' ethical teaching is that: One should enjoy life.
Scholasticism is a type of religious philosophy characterized by a combination of theological and dogmatic premises with rationalistic methodology and interest in formal logical problems.
Scholasticism is: a type of philosophizing characterized by speculativeness and the primacy of logical and epistemological problems
Such features as speculativeness, interest in formal-logical problems, subordination to theology are inherent in: scholasticism
Thesis belonging to the thinker Thales “The beginning of all things is water”
Thesis belonging to the thinker Thales: “Know yourself”
Thales' thesis: "Know thyself."
T. Hobbes adhered to the theory of “social contract”
The theory of scientific knowledge is called: Epistymology.
Hegel's theory of development, which is based on the unity and struggle of opposites, is called: dialectics
Theory of self-organization of complex systems Synergetics
Theocentrism is a worldview position based on the idea of supremacy: God
The term “conciliarity” in Slavophil philosophy means the free unity of people in Christ
The term "existentialism" comes from the French word, which translated into Russian means Existence
Type of worldview according to which man is the center and highest goal of the universe: anthropocentrism
A type of worldview characteristic of the Renaissance, which is based on the opposition of the individual to society: individualism
Marx's work? "Capital".
Statement based on the combination of many related facts Empirical generalization
Statement corresponding to the metaphysical understanding of matter Matter is eternal, uncreated and indestructible
The statement: “It’s not what happens to us that matters, but how we feel about it” corresponds to the worldview of the Stoics
The statement: “Act in such a way that the maxim of your will can at the same time become the principle of universal legislation” belongs to I. Kant
The statement: “I think, therefore I exist” was expressed by R. Descartes
The doctrine of the salvation of the soul Soteriology
A doctrine that developed during the Renaissance, and asserts the identity of God and nature, that “nature is God in things” Pantheism
A factor that, according to social Darwinism, is the main driving force in the development of society. The struggle for existence
Fatalism is the idea of the inevitable predetermination of events in the world; belief in impersonal fate (ancient stoicism), in unchangeable divine predestination (especially characteristic of Islam), etc.
The phenomenon to which this definition refers: “The totality of material and spiritual values, as well as methods of their creation, transmission from one generation to another” culture
Phenomenology of spirit", "science of logic", "philosophy of history". Author? Hegel.
Philosopher who considered logic the main tool of knowledge: Aristotle
Philosopher who took the so-called “monads” as the basis of existence G. Leibniz
The philosopher who lived in a barrel considered himself a “citizen of the world” and called for poverty and ignorance Diogenes of Sinope
Philosopher who understood social progress as the development and change of socio-economic formations K. Marx
Philosopher who considered logic the main tool of knowledge: Aristotle
Philosopher who believed that the child’s consciousness is like a blank slate tabula rasa J. Locke.
The philosopher who believed that a child's mind is like a blank slate? J. Locke.
Philosopher, student of Plato: Aristotle
The philosophy of G. Hegel is characterized by: panlogism
Philosophy in the Middle Ages occupied a subordinate position in relation to: theology
Philosophy from Greek: Love of wisdom.
A philosophical principle that states that all phenomena are connected to each other by causal connections and determine each other. The principle of unity and struggle of opposites
A philosophical movement that denies that reason is the basis of cognition and behavior? irrationalism.62
Philosophical direction that absolutized the laws of mechanics in relation to social philosophy French materialism of the 18th century
A philosophical movement that denies or limits the role of reason in cognition, highlighting will, contemplation, feeling, and intuition. Irrationalism
A philosophical movement that recognizes reason as the basis of human cognition and behavior. Rationalism
A philosophical movement that recognizes reason as the basis of cognition and behavior? rationalism.
A philosophical movement that asserts that the mind only floats on the surface of things, while the essence of the world is revealed to us through intuition, experience, and understanding. Philosophy of life
Philosophical doctrine of the development of being and knowledge, based on the resolution of contradictions Dialectics
Philosophical doctrine founded by Lev Nikolaevich Tolstoy Ethics of non-violence
The form of existence of matter, expressing its extension, structure, coexistence and interaction of elements in all material systems Space
The form of being that is the focus of existentialism Individual human existence
A form of thinking that reflects the presence of a connection between an object and its attribute, between objects, as well as the fact of the existence of an object. Judgment
Form of rational knowledge: Concept
Form of empirical knowledge Fact
V.I. adhered to the formational approach to the analysis of social development. Lenin
The formational approach to the problem of the historical development of society asserts that: World history is united, each society consistently passes through a number of stages in its development, the same for all societies
French philosopher who believed in the omnipotence of education and argued that people from birth have equal abilities Helvetius
French philosopher, also the creator of algebra and analytical geometry R. Descartes
French philosopher, supporter of sensationalism Condillac
A characteristic feature of medieval philosophers: Theocentrism.
A characteristic feature of medieval philosophy? theocentrism (Greek Theos - God + Lat. Centrum - center of the circle)
A characteristic feature of Renaissance philosophy is: anthropocentrism
Chronological framework of German classical philosophy of the 18th – 19th centuries.
Chronological framework for the development of ancient philosophy: VI century. BC – VI century AD
The central idea of I.V.’s philosophy Kireevsky The integrity of spiritual life
The central problem in the philosophy of the French Enlightenment of Man
The central philosophical problem of D. Hume Cognition
The central concept of Buddhism and Jainism, meaning the highest state, the goal of human aspiration: nirvana
The central concept of A. Bergson’s philosophical teaching is the vital impulse (élan vital). Its knowledge is possible with the help of: intuition
France was the center of the European Enlightenment in the mid-18th century.
Man is the measure of all things": Protagoras
Man is born to be free, and yet everywhere he is in chains,” asserted J.-J. Rousseau
In Plato's philosophy, how does the idea of a “horse” differ from an actual, living, real horse?
Please indicate the wrong answer. The idea is richer in content than a live horse
How does dialectics differ from metaphysics? understanding of development.
What did Heraclitus represent as the fundamental principle of the world? fire.
Which of the following is not an attribute of matter? Stability
Which of the following is not one of the basic features of scientific knowledge? irrefutability
Which of the following is not a form of social consciousness? Theology
What does the concept of “dharma” mean in traditional Indian philosophy: An eternal moral law that prescribes from above for everyone a certain way of life
What do the concepts of Brahman in Vedanta and apeiron in the philosophy of Anaximander mean: The substance of all things
What does the original thesis of Descartes' philosophy, which in Latin sounds like “cogito ergo sum”, mean? if I think, therefore I exist
What is produced within the spiritual sphere of society? Give the most complete and accurate answer. Information and spiritual meanings
What is individualism? the individual opposes himself to society.
What is collectivism? public over personal.
What is a worldview? Worldview is a set of the most general views on the world and a person’s place in it.
What is characteristic of the epistemic line in philosophy? identification of philosophy with theology
Sensory cognition differs from rational cognition in that the former is based on sensations, the latter on the arguments of reason.
Six Days" is a book that sets out: Christian ontology and cosmogony
Evolution is the irreversible historical development of living nature.
Heuristic refers to the Probabilistic criteria of scientificity
Existentialism – philosophy of existence, existence (human existence); the main modes (manifestations) of human existence - care, fear, determination, conscience; a person perceives existence as the root of his being in borderline situations (struggle, suffering, death). By comprehending himself as existence, a person gains freedom, which is the choice of himself, his essence, which imposes on him responsibility for everything that happens in the world
The existentialist view of man corresponds to the statement that Man is doomed to be free and bear absolute responsibility for his actions
The era of restoration of the ideals of antiquity in Europe: Renaissance
The era of restoration of the ideals of antiquity in Europe: Renaissance (Renaissance).
Eschatology is the Doctrine of the ultimate destinies of the world and man
Eschatology? the doctrine of the ultimate destinies of the world and man.
Ethics is the science of morality. The term was first used by Aristotle to designate a special field of study.
Ethics is: the study of morality and moral values
The ethical meaning of the problems of euthanasia lies in? does the patient have the right to leave and live so as not to experience suffering.
The ethical meaning of the problem of euthanasia lies in the question: Does a person have the right to commit suicide?
This is a psychological formation that is social in nature, relatively stable and occurs throughout life, representing a system of socially significant human traits.” Personality
I think therefore I am: Descartes