If stains or traces of moisture are visible on the walls of the room, this is a sure sign of poor waterproofing. To avoid premature destruction of the building, the appearance of mold and rot, it is imperative to equip drainage around the house.
Purpose
Drainage is a drainage system that is used to eliminate excess fluid around a house, garden, or yard. Moisture can appear near the house due to various conditions: a high level of groundwater, strong melting, or a special type of earth (clay, crushed stone, loam). Also, the drainage system is used in courtyards, where, due to the inconvenient location of the house, the water cannot leave on its own or, on the contrary, drains too quickly, leaving the ground dry and lifeless.
When to install drainage around the house:
- If liquid collects in the basement during snowmelt or heavy precipitation;
- If your area has a high level of groundwater;
- When the foundation of the house is regularly washed away with water;
- A capillary network appears on the floor or some areas of the building are prone to mold.

Drainage installation can be easily done by hand, in most cases a perimeter foundation drainage system around a private house is used. For more complex cases, it is possible to use a complex system of natural type. This is the arrangement of a number of drains, in which there are main (main) and additional ones. This technique is used on swampy soils or a very large piece of land.

How to do
There are two types of dehumidification that are used most often by craftsmen:
- Surface;
- Deep.
Surface or storm is a drain, which is protected by a special mesh. Water enters the pipeline after rain, as well as snowmelt. The system is at a certain angle to the building, which allows you to remove moisture in any quantity. Such surface drainage works well in warm regions with high average annual precipitation.
 Photo: surface drainage
Photo: surface drainage The deep system is more complex, but it is also considered much more effective than the surface one. The depth of the laying is determined by calculating the ratio of the size and depth of the foundation and the level of soil freezing. Soil type also plays a big role. To drain groundwater in this way, a separate pipeline or simply a paved trench can be used.

Without fail, wells are equipped at a certain distance from the drains, into which wastewater is collected. After that, it can be used for irrigation or simply go into the deeper layers of the earth.

The correct arrangement of drainage around the house also implies the development of a project (diagram with structural details). Using this drawing, you will be able to determine which type of system is most preferable for you, as well as draw up an approximate estimate for the work. You can use the services of specialists, or develop a scheme yourself.
Related video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DloSGrkFtYA
Step-by-step instructions on how to make proper drainage around the house:
- Calculate the communication distance from the foundation. It is very important that the drains do not touch the already laid sewage and water supply pipes. It is possible to lay wall drainage, it will run almost close to the base of the building, or more distant - at a distance of 1.5 - 2 meters from the wall;
- After you need to dig a trench. Its depth depends on the level of groundwater, the preferred type of drainage system and the level of ground freezing. You can get all the necessary data from the geological bureau of your region;
- It is necessary to dig in a place where the sewer does not pass, otherwise there is a possibility of a violation of its tightness;
- The drain must be connected to a septic tank or a drainage well. To equip it, a cylindrical hole is dug at the lowest point of the site, in which a plastic barrel or concrete rings are placed (depending on your needs). Installation is carried out simultaneously with the installation of drains, that is, the trenches must be connected to the septic tank. If everything is done correctly, then high waters themselves will drain into a prepared place;

- When the trench is ready, sand is poured onto its bottom, which will act as a filter layer. There are several options for arranging the drain itself. You can lay it with construction debris, placing large stones on the bottom and reducing their size as they approach the surface. Some craftsmen use drainage from plastic bottles, brushwood, boards for such purposes. For a country house, you can use improvised means, for example, bricks, but for a residential country cottage it is better to work with plastic pipes;
- After you need to do the insulation of the drainage around the house. If you are organizing a drainage system from improvised materials, then thermal insulation will not be needed, but when working with a plastic pipeline, it is necessary. For this, communications are covered with geotextiles. The laying technology is similar to the insulation of sewer pipes - each drain is wrapped in material and additionally reinforced with clamps;

- After the drainage site is filled up or covered with a mesh, depending on whether it is superficial or deep. With a deep arrangement, it is necessary to make the embankment a slide so that depressions and pits do not appear when the earth settles. In a large area, the ditch can be covered with a blind area. For example, a slate sheet or a brick path, then the drain will be completely invisible to prying eyes;

- Every six months, you need to inspect the septic tank, clean it of silt and dirt.
Tip from homeowners with gardens: You can put fertilizer at the bottom of the trench - then the wastewater will become a source of necessary minerals. In this case, it can later be used to water the garden and vegetable garden.
If the size of the local area allows you, then you can make a much simpler drainage system. In the lowest place of the land share, a hole is dug under the lake, it is naturally filled with water. With the right approach and organization, in the future it will be possible to make an excellent landscape design with interesting elements. For example, launch fish into an artificial reservoir or decorate it with lilies and other water-loving plants. For the fact that the ode will flow into the "pit", she will leave the house. If you solve the problem in this way, then do not forget to regularly clean the lake so that it does not flood and turn into a swamp

Price
The cost of arranging drainage around the house depends on the materials with which you will make the drainage system (for example, the price of construction waste is cheap). To work in the country, you can take the most affordable filters: wooden boards (fold them crosswise and install them with their ends on the walls of the trench), stones, fragments of bricks, slate. For the drainage system of a wooden or brick residential building, it is worth taking more complex and expensive materials - plastic pipes, old metal communications, even a pipe made of plastic bottles is suitable for low rainfall.
Be sure to take care of the insulation. If it is not possible to buy geotextiles for drainage, then cover the pipes with unnecessary rags or even humus. This will help keep the system from freezing during the cold season.
home drainage is a system whose function is to take atmospheric and underground moisture from the foundation. It's very rare to get by without it. in areas with well-permeable soil, lack of floods and low year-round groundwater levels.
In other cases, this system is necessary, since protects the foundation, basement from rain, melt water and the rise of the primer, as well as from the destructive effect of soils prone to swelling when moistened and frozen. In this way, drainage will extend the life of the building and prevents the development of mold in the basement.
For creating moisture removal systems you can use the services of specialists, as well as do all the work yourself. You just need to choose the right drainage, and there are several types of it. They differ in the complexity of arrangement, appearance and other parameters.
One of the most common classifications of drainage is based on how complex it is. According to this parameter, 3 types of drainage systems.
- open type drainage or surface is one or more ravines. The depth of each is about 0.7 m, and the width is 0.5 m. This option the easiest to set up but outwardly it is unattractive.

- Backfill view or deep looks much better. For this species, a trench is also first dug. A geofabric is laid in it, and then a draining backfill is poured in, which will accumulate and remove excess moisture. For these purposes use broken brick, crushed stone, expanded clay etc. The drainage layer is wrapped with geotextile and covered with soil. But such a system there is one significant drawback: it can only be cleaned after opening.
- The most difficult, but The most advanced system for draining water from the site is closed drainage. In the center of the backfill there is a drain, which is a perforated pipe. Water is collected in the pipeline and discharged by gravity into the drainage well.
Exactly third way water diversion in recent years has become traditional when creating a drainage system.
Classical drainage scheme around the house

Most often water drainage from the foundation is a drainage system surrounding the house, as well as revision and drainage wells. Equip such a drainage as follows:
- around the house dig trenches, the bottom of which has a slope of 5-10 mm per meter towards the lowest point of the area where the water collector will be installed;
- on the hardened bottom fall asleep rubble or other drainage material;
- above stack downhill drainage pipe;
- in places where drains form a right angle or several pipes intersect, install wells for revision;
- above drains fall asleep the same drainage material, and then sand and soil;
- at the lowest point of the site installing a drainage well which is necessary to collect water;
- backfill all wells.
This is a simplified description of the design of the near-house drainage system. In real drainage can be wall or ring, it all depends on the characteristics of the soil and the private house itself.
wall drainage

Such water protection applied in that case, if the house has a basement and a basement.
And it's worth doing until the backfill around the foundation of the house is completed. Such a measure will avoid additional financial costs for earthmoving work.
The wall system consists of revision and collector tanks, as well as drains. Latest laid around the building at a depth of at least 0.3-0.5 m from the floor level, but not deeper than the bottom edge of the foundation. The slope in this case is also important to observe.
For reliability around the foundation recommended create a waterproof half-meter a screen made of the most compacted clay, or the base of the house is covered with geotextiles.

In some cases enough to remove only atmospheric moisture application only open type wall drainage, which is a collection of trays located in a ring near the house.
From above the gutters are closed with gratings.
Trench or ring system
This type of drainage used for home protection, which is located in a sandy area and has no base. Have a trench system at a distance of 3 to 12 meters from the house foundation, it is best to remove it at least 5 m from the building in order to avoid soil shrinkage, which will lead to the destruction of the foundation of the structure. When constructing such a drainage system from the foundation of buildings, all those elements are used that are in the classical system described above.

For extra protection foundations of the house use a clay castle. Besides, the general rule is to install drains at a depth of 50 cm from the lowest point of the floor. The remaining parameters are determined on a case-by-case basis.
The device of wall drainage of the foundation around the house
Before proceeding with the installation of a near-house drainage system, it is necessary to determine its type, which depends on several parameters:
- types of soil;
- whether the building has a basement or basement;
- the origin of the water to be removed.

The wall-mounted underground version is used in the presence of a basement, high GWL and loamy and clay soils. If it is necessary to protect the foundation of the house only from precipitation, a surface system will suffice.
To protect the house located on sandy or sandy loamy soils and not having a basement, apply ring (trench) drainage.
Having decided on the type of drainage, you can begin to draw up a diagram, design a system and plan all work. This stage allows you to reduce all possible shortcomings, which are then expensive to fix.
For plan you need to determine the lowest point on the site to install a drainage well, which will be connected to the common ring of the system by a pipe.
It is better to draw a diagram on graph paper or in a special program. The drawing should show:
- the house, as well as the buildings adjacent to it;
- trees and shrubs;
- places where drains pass, depending on the type of drainage chosen;
- revision and drainage wells.
Inspection tanks are installed at the place where the pipe turns, for example, in the corners of a house, or every 30 m for a straight pipe run.
The plan should also record the depth of pipe laying. This indicator depends not only on the bottom slab of the foundation and the height of the floor, but also on the level of soil freezing. Pipes should run deeper than the zero winter ground temperature point. It is important to write down the diameter of the drains, which affects the width of the trench, and the required slope.
Design is best left to the experts. But the purchase of the necessary material and the installation of the drainage system on the basis of a competent plan can be done independently.
How to make indoor drainage around the house with your own hands
Such a device for protecting the house from water can be done independently even after the construction of the building is completed. First of all, you need to prepare working tools and all the necessary materials:
- shovels of two types (bayonet and shovel);
- spirit level for checking the slope;
- manual type rammer;
- a device for removing excess soil from the site (stretcher or wheelbarrow);
- roulette;
- geotextile;
- backfill for the moisture-collecting layer (granite crushed stone is best suited);
- sand;
- inspection and drainage wells;
- drainage pump;
- drains and fittings for their connection with each other and with wells.
Pipes must be perforated. You can purchase ready-made drains, or make them yourself from an existing orange sewer pipe. Flexible products are not recommended. The diameter of the pipeline can be 70-150 mm.
The material is preferably plastic with high strength and wall resistance to stress. Moreover, the deeper the drains go, the higher this figure should be. You can take asbestos and ceramic products.

Some prefabricated drainage pipes are surrounded by an additional filter material, such as coconut fibre.

Lookout and buy ready-made or they are made independently from a thick-walled plastic pipe of large diameter. They will need to buy hatches.
After acquiring everything you need, they begin to measure, allowing you to mark the place where the drains and other elements of the drainage system will pass. The site is cleared of debris and the excavation and installation work begins. Let's take a look how to properly lay the drainage pipe around the house:

The drainage system is ready.
Video on how to make a drainage system around the house with your own hands:
A few words about the plastic drainage well

In its simplest form, it can be a container for collecting water. At the point of connection with the inlet pipeline you need to install a valve that prevents the reverse flow of water. It is good if the container has a large diameter, for example, 80-100 cm.
From the drainage well, you can lay a non-perforated outlet pipeline to a ravine, filtration well or reservoir. Drainage from the collector can be done by gravity or by a drainage pump. Water from the well can be used for technical needs and irrigation.
How much does drainage cost
If you decide completely drain the site yourself, then here is the cost that you will have to pay only for the tools and all the material:
- A meter of a drainage pipe with a diameter of 11 cm can cost from 60 to 180 rubles.
- A square meter of geotextile will cost you approximately 20-40 rubles.
- Granite crushed stone fraction 20/40 mm costs from 1200 to 2000 rubles per m3.
- The average price per cubic meter of river sand is about 600-700 rubles.
In this case a running meter of drainage will cost a maximum of 2000 rubles. But that doesn't include shipping costs. Still need to add the price of wells. Ready plastic manhole minimum diameter can do in 2000- 2500 rubles apiece, and drainage - more than 10 thousand rubles. Cheaper to make them from a pipe.
If you hire specialists, then the price of the drainage system will be the sum of the cost for design services (about 10,000 rubles) and the work itself. Many firms make a project for free if you order work from them.
Specializing companies set the price for pipe laying at least 2500 rubles per meter, for the installation of a viewing well - 5-7 thousand, and a drainage one - 35-40 thousand rubles. But many of them give a guarantee on their work for 2-3 years.
But if you are confident in your abilities or have at least some experience, then you can order only a project, and the rest do it yourself. Or, in general, carry out all drainage work on our own, including drawing up a diagram.
The main thing is to decide on the type of drainage in accordance with the characteristics of the building, the climate of the region and the site. It is better to use deep drainage, and if necessary, supplement it with a storm system.
Don't skimp on pipes. and underestimate the manhole that allows the system to be cleaned. With proper organization of drainage, you can not only protect the house from moisture, but also use all atmospheric and groundwater for household needs.
Drainage around the house is an effective way to protect building elements and outbuildings from moisture. The creation of such a drainage system is especially important if the groundwater is at a depth of less than 2.5 meters. This is also necessary if the residential structure is located on a site that is prone to seasonal or weather flooding. How to make drainage around the house with your own hands - step by step instructions. The arrangement of the drainage system is not a difficult task, but for its precise organization it is necessary to follow simple rules.
With the help of special drainage pipes LightDrein, you can install the drainage system yourself. See the addresses of stores in Moscow and the Moscow region.
System description
For the effective removal of ground, rain and melt water, which not only destroy the structural elements of the building, fill the basement and cellar, but also reduce the bearing capacity of the soil, there are several ways to arrange drainage. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, the decision which type to choose and how best to make drainage around the house remains with the owner himself.
The design and location of the protection system against excessive moisture is selected taking into account the terrain, the presence of recessed rooms, the depth of groundwater, and the type of soil. By design, the following drainage systems are distinguished: filling, open and closed.
How to make drainage around the house with your own hands
Depending on what area of the land plot needs to be drained, what type and what depth of drainage will be most effective, the location of the entire system is chosen. If necessary, to exclude the effect of water on the foundation and basements, wall or ring drainage is created. The first type is appropriate in the presence of a basement or basement and is located in close proximity to the foundation walls. Trenches are dug around the perimeter, a perforated pipe is laid (below the level of the basement floor) and covered with rubble or gravel. The wall is fenced off with a layer of geotextile with one-sided conductivity. Water from the ground does not reach the walls, but enters the drainage pipe and is discharged to a safe place.
For effective drainage, you need to know how to properly drain the site. To do this, the drainage system is located around the entire perimeter. The most time-consuming, expensive, but also the most effective way is a closed system using plastic pipes. The price of such perforated pipes is affordable for any family budget. It perfectly removes excess water from the site, preventing mold from appearing, destroying garden and garden plants, destroying load-bearing building elements and not spoiling the appearance of the house.

To create such a drainage, you need to perform several operations:
- draw a diagram of the future system on paper indicating the size and distance from the edge of the site, as well as taking into account landscape design and the location of plantings;
- mark future tracks on the site itself with paint or sand;
- dig trenches along the marked routes with your own hands or with the help of small equipment (the depth and width depend on the level of groundwater and the diameter of the pipes used, vary from 70 to 150 cm in depth and from 25 to 40 cm in width);
- line the bottom and walls of the trench with geotextile (the material will significantly reduce drainage clogging and significantly increase the period of effective operation);
- apply a layer of sand (about 15 cm) to the bottom, and then a layer of crushed stone or gravel (about 20 cm);
- using the device and the gravel layer, set the desired slope level;
- with a large area of \u200b\u200bthe site, it will be necessary to create manholes at a distance of 50 meters from each other in places where pipes bend or change in slope;
- perforated pipes are laid (preferably with a filter element - fiberglass, coconut fiber, non-woven or needle-punched textiles) and interconnected using fittings;
- the most optimal diameter of the drainage pipe, which provides good water drainage, is 110 mm;
- the slope is checked again (can be easily done with a stretched rope), while it is necessary to create a uniform level, excluding sagging of the pipe;
- it is very important that the drainage system is below the freezing level of the soil;
- from above, the pipes are covered with crushed stone or gravel, the thickness of the layer should not reach the soil surface of about 15 cm;
- geotextiles are laid on a layer of crushed stone and soil is poured.
Do not be afraid of increasing the cost of creating drainage: purchasing additional geotextiles and separating all layers from each other will only increase the efficiency and service life of the entire system. Following these simple instructions will allow you to install long-term water protection with your own hands and preserve your property and health throughout the life of the house.
Backfill construction
The backfill drainage structure is a deep trench (below the upper groundwater level) filled with coarse gravel, crushed stone or other rubble material. The upper part of the trench is covered with a layer of turf, and to reduce sagging and silting of the passage space, the walls are laid with a layer of geotextile material. Such drainage is easy to create, low cost, long service life and no need for maintenance.
In addition, in its final form, it does not violate the general appearance of the site and does not introduce dissonance into landscape design. Of the minuses, one can note the low throughput of the water flow and the impossibility of cleaning the discharge channel in case of clogging.

Open type drainage device
An open option or surface drainage involves the creation of shallow trenches (about 0.5 meters) of an open type, through which rain and melt water is drained into special containers or removed from the site. To prevent sagging and destruction of the walls of the trenches, plastic or metal trays are placed in them. Lattices on top provide additional security.
How to make a closed drainage system
The most complex and time-consuming type of drainage is the closed type. When it is organized, trenches are dug, a layer of gravel or large gravel is poured onto the bottom, and then perforated pipes are laid. From above, the entire structure is again closed with crushed stone or gravel, and at the end a layer of soil is applied. To increase the efficiency of water drainage and reduce silting on perforated pipes, filter material (geotextile) is used. The material for the manufacture of perforated pipes are steel, asbestos cement, ceramics, but at present, almost all types have given way to plastic. Corrugated plastic pipes are widely used, which already have holes in finished form, are distinguished by their long length and ease of installation.
When choosing any method of removing excess moisture, be sure to take into account the slope of the drainage channels. For the system to work properly, the level of inclination towards the outlet to an artificial or natural water intake must be at least 3 ° along one branch or 1 cm per linear meter. When deciding how to properly slope the drainage, you can use the adjustment of the thickness of the gravel pad.

The cost of installation work
|
Name of works |
price, rub. |
||
|
Ring drainage device around the house |
|||
|
With a depth of up to 1 m. |
|||
|
With a depth of up to 2 m. |
|||
|
With a depth of up to 3 m. |
|||
|
Collector well |
|||
|
Wall drainage around the house |
|||
|
With a depth of up to 1 m. |
|||
|
With a depth of up to 2 m. |
|||
|
With a depth of up to 3 m. |
|||
|
Collector well |
|||
* The cost indicated on the site is not a public offer (Article 435 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) and is for informational purposes.
Pricing also depends on the volume, remoteness of the object and other factors.
Drainage around the house, waterproofing the foundation and blind area is a set of measures aimed at preventing the base of the building from getting wet and losing the bearing properties of the soil. And the device is chosen depending on the type of foundation, the type of soil, the nature of the top water and the level of groundwater.
Kinds
Drainage around the house is superficial, deep and reservoir. And to be precise, the drainage system is often a combination of these types. For example, a reservoir view will not be effective if it is not “closed” to a deep one.
Surface
This species is responsible for collecting precipitation and meltwater. It, in turn, can be of two types:
- Open. This is a system of ditches or trenches that are laid with a slope to a storm sewer or drain well. Fully open ditches are usually arranged only at the boundaries of the site. Around the house (along the perimeter of the blind area), near the platforms and paths, gutters are laid in trenches, which are covered with bars.
- Zasypnoy. This is also a system of trenches, but already covered with crushed stone (or gravel) of large and medium fractions, where a fine fraction, screenings or coarse sand are added for “splitting”.
The depth of the trenches lies in the range of 50-70 cm.
Deep
This is a closed type system, which is responsible for the drainage of sedimentary and melt water, as well as seasonal perched water. In swampy areas and in close proximity to water bodies, deep drainage around the house reduces the load on the waterproofing of the foundation from the impact of high groundwater (above 2 meters from ground level).
Types of deep drainage:
- Wall mounted. The purpose is to reduce the pressure of water on the waterproofing of the walls of the underground part of the buried foundation of a house with a basement or underground floor. It consists of drainage pipes laid along the perimeter of the base of the foundation. Passes on the border of the retaining wall of waterproofing or clay castle (provided that they exist).
- Annular. Used around a house with a shallow foundation. Drainage pipes are laid below the base of the foundation along the perimeter of the house beyond the outer boundary of the blind area.
- Solid. This type is used to drain the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe house. The scheme consists of main and auxiliary channels, in which the auxiliary ones are laid in a "herringbone" direction towards the main ones, and they, in turn, converge to the catchment wells.

Plastovy
This type of drainage can be attributed to deep, but it does not pass around the house, but under it. More precisely - under the foundation slab or concrete floors on the ground.
As standard, the base of the slab itself, in the form of a pillow of sand and gravel, has good drainage properties of its own. And since the area of the bottom of the pit is larger than the area of the slab, then in order to organize the drainage of water from the foundation, it is enough to arrange annular drainage from the pipes around the perimeter.
A more complex scheme, when the bottom of the pit is made with a slope from the center to the edges or with a decrease in one direction (practiced for slopes). And the water from the drainage layer is diverted further through the pipe system to receivers or wells.
The most complicated scheme is when trenches are additionally dug along the bottom of the pit, into which crushed stone is poured. For floors on the ground, pipes are additionally laid, which are connected to wall drainage.

Device
Surface drainage differ in the way in which water channels are created.
A simpler device for filling surface drainage:
- according to the scheme, trenches are dug (at least 40 cm wide);
- tamp the bottom, forming a slope towards the water collector;
- cover the bottom with a layer of sand (up to 10 cm);
- crushed stone of medium and large fractions is poured to the surface level.

For decorative purposes, the upper visible layer can be made of pebbles and small boulders to create an imitation of a "dry stream".
The surface drainage device of the tray type (stormwater) is a little more complicated, but it is more common:
- according to the scheme, they dig trenches, taking into account the dimensions of the trays and the concrete base;
- a layer of a mixture of sand and gravel is poured onto the rammed bottom;
- a foundation is formed from lean concrete with the necessary slope;
- install gutters, fill the sinuses of the trench with concrete and ram it;
- mounted on top of the grid.
Scheme
The arrangement of deep types of drainage differs only in the level of pipe laying and layouts on the site, and the principle of construction is common for all:
- in the place allotted according to the scheme, a collector well is arranged;
- dig trenches for annular drainage, and for the general system - main and auxiliary channels;
- wall drainage pipes are laid during the construction or reconstruction of the house, when the foundation is completely open to the very heel;
- in places where the trenches turn, revision wells are arranged (if the distance from the turn to the next well is more than 20 m), and with a long straight section, revisions are arranged after 25 m;
- the bottom of the trench should not have solid protruding inclusions, and the walls should be straight for dense soils or in the form of a trapezoid with reinforced slopes for the duration of work for loose soils;
- if necessary, the bottom of the trench is “reinforced” by backfilling with sand or laying an artificial base;
- if the drainage pipe has a filter shell, then a single-layer backfill of coarse-grained sand with a high filtration coefficient is made around it;
- if the pipe does not have a geotextile sheath, then first it is backfilled with crushed stone of a fine fraction around it, then a layer of sand follows.
When laying a corrugated pipe without a sheath, the grain size should be less than the depth of the corrugation, and the crushed stone should not contain chipped particles with sharp edges.
A pipe without a sheath can be laid according to a different scheme:
- geotextiles are laid on the bottom and walls of the trench;
- fall asleep rubble;
- lay and connect pipes;
- another layer of rubble is poured on top;
- wrap the geotextile cloth so that its edges overlap, and fasten them;
- fill the trench with sand to the level of the humus layer;
- pour fertile soil or lay a hard surface of the tracks.
Deep drainage without pipes
On soils with good water permeability and low GWL, it is not advisable to arrange an expensive deep drainage system of perforated pipes around the house. Especially if the area is small. But the surface open or filling system is also not suitable - it takes up usable area. In these cases, deep drainage is arranged without pipes, or, as it is also called, soft drainage.
The simplest scheme in execution has almost the same device as deep drainage, but without pipes:
- dig a system of trenches;
- geotextiles are laid on the bottom and walls;
- fall asleep rubble;
- overlap the edges of the textile;
- sand is poured, and then soil.
Another advantage of this type is the simple nature of the work. The time for arranging the drainage is reduced, plus it is not necessary to monitor the constant and continuous slope of the pipe - it is enough if the overall level of the trench goes down towards the drainage well or beyond the boundaries of the site (to the ditches or a reservoir).

There are generally “folk” methods for arranging soft drainage without pipes, when bundles connected from long brushwood are used as a conduit. And so that they do not silt, they are covered with rubble and sand.
How to make drainage around the house with your own hands. Step-by-step instruction
If the house has already been built, and it has become obvious that the water permeability of the soil is low, and the throughput of wall or reservoir drainage is insufficient, then the easiest way to solve the problem of waterlogging the soil is to do-it-yourself ring drainage around the house:
- Draw up a layout of trenches with a depth of occurrence and slopes to a collector or drainage well.
- They dig trenches with a bottom width of more than 40 cm. The depth at the very “upper point” should be below the base by the diameter of the drainage pipe plus the thickness of the crushed stone cushion.
- The bottom of the trenches is compacted, a layer of sand is poured, then crushed stone, and a slope angle is formed towards the receiver. The slope is calculated depending on the diameter of the pipe, based on a minimum water velocity of 1 m/s. But it should lie within 0.5-3%, be constant or increase to the lowest point.
- Pipes are laid according to one of the above schemes. The connection of drainage pipes is carried out with couplings, which, unlike socket joints, do not silt. The choice of a specific type of pipe (including material and ring stiffness) depends on the depth and design pressure from above (backfill, soil, and when laying under tracks or platforms, the weight of the coating and the load on it must be taken into account).
A novelty has appeared on the market - drainage pipes with an additional filter layer made of specially shaped expanded polystyrene granules. This layer is located between the pipe and the geotextile sheath. When laying this type of backfilling with crushed stone is not required.
- Perform backfilling. The nature and order of the layers is chosen according to the type of drainage pipes.
Below is a video on the ring drainage device. The owner of the house made sure and twice used geotextiles - as a pipe shell and around the drainage backfill. Such a system will no longer silt in clay soil conditions. It also shows well how important it is to choose clean gravel.
Drainage around the house is no more difficult (but not easier) than an autonomous sewer with a septic tank and a filter well. The amount of work on laying pipes is greater, but there are no strict requirements for the tightness of the system. And make the drainage quite within the power of yourself. The only difficult moment is if the drainage well is mounted from concrete rings, then it is necessary to attract equipment.
If you ask any experienced builder, developer, landscape designer about what needs to be done, first of all, on a site that has just been acquired and not yet built up, the answer will be unambiguous: the first is drainage, if there is a need for it. And this is almost always the case. The drainage of the site is always associated with a very large amount of excavation, so it is better to do them right away so that later you do not disturb the beautiful landscape that any good owners equip in their possessions.
Of course, the easiest way is to order site drainage services to specialists who will do everything quickly and correctly, using special equipment. However, this will always come at a cost. Perhaps the owners did not plan these expenses, perhaps they will violate the entire budget planned for the construction and arrangement of the site. In the proposed article, we propose to consider the question of how to do the drainage of the site with your own hands, as this will allow you to save a lot, and in most cases it is quite possible to do these works yourself.
Why is site drainage needed?
Looking through the estimates and price lists related to the drainage of the site, some developers begin to doubt the appropriateness of these activities. And the main argument is that earlier, in principle, no one "bothered" much on this. With such an argument for refusing to drain the site, it is worth noting that the quality and comfort of human life have greatly improved. After all, no one wants to live in dampness or in a house with earthen floors. No one wants to see cracks in their house, on the blind areas and paths that appeared after the next cold season. All homeowners want to improve their yard or, to put it in a modern and fashionable way, to make landscaping. After the rain, no one wants to "knead the mud" in stagnant puddles. If so, then drainage is definitely needed. You can do without it only in very rare cases. In which cases we will describe a little later.
 Drainage? No, I haven't heard...
Drainage? No, I haven't heard...
Drainage is nothing more than the removal of excess water from the surface of the site or from the depth of the soil. Why is site drainage needed?
- First of all, in order to remove excess water or from the foundations of buildings and structures. The appearance of water in the area of \u200b\u200bthe base of the foundation can either provoke a movement of the soil - the house will “float”, which is typical for clay soils, or, in combination with freezing, frost heaving forces may appear that will create efforts to “squeeze” the house out of the ground.

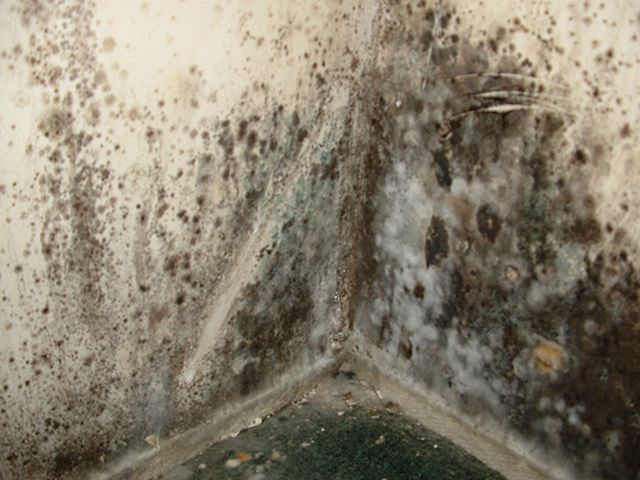
- Drainage is designed to remove water from basements and basements. No matter how effective waterproofing is, excess water will still seep through building structures. Basements without drainage can become damp and encourage the growth of mold and other fungi. In addition, precipitation in combination with the salts present in the soil very often form aggressive chemical compounds that adversely affect building materials.

- Drainage will prevent the "squeezing out" of the septic tank at a high level of groundwater. Without drainage, a wastewater treatment system will not last long.
- Drainage in conjunction with the system and around the buildings ensures that water is quickly removed, preventing it from seeping into the underground parts of the buildings.
- Drainage prevents waterlogging of the soil. In areas equipped with well-planned and made drainage, water will not stagnate.
- Waterlogged soil can cause rotting of the root parts of plants. Drainage prevents this and creates conditions for the growth of all garden, garden and ornamental plants.
- With heavy precipitation in areas that have a slope, the fertile soil layer can be washed out by water flows. Drainage directs water flows into the drainage system, thereby preventing soil erosion.
 Water erosion of fertile soil in the absence of drainage is a serious problem in agriculture
Water erosion of fertile soil in the absence of drainage is a serious problem in agriculture - If the site is surrounded by a fence built on a strip foundation, then it can "seal" the natural ways of water drainage, creating conditions for waterlogging the soil. Drainage is designed to remove excess water from the perimeter of the site.
- Drainage helps to avoid the formation of puddles on playgrounds, sidewalks and garden paths.
When Drainage Is Necessary Anyway
Consider those cases when drainage is needed in any case:
- If the site is located on a flat area, then drainage is mandatory, since when a large amount of precipitation falls or snow melts, the water will simply have nowhere to go. According to the laws of physics, water always goes under the influence of gravity to a lower place, and on a flat landscape it will intensively soak the soil in a downward direction, which can lead to waterlogging. So, from a drainage point of view, it is beneficial for the site to have a slight slope.
- If the site is located in a lowland, then its drainage is definitely needed, since water will drain from higher places to those below.
- Strongly sloping sites also require drainage, as rapidly draining water will erode the top fertile soil layers. It is better to direct these flows into drainage channels or pipes. Then the main part of the water will go through them, preventing the soil layer from washing out.
- If the site is dominated by clay and heavy loamy soils, then after precipitation or snow melt, water will often stagnate on them. Such soils prevent its penetration into the deep layers. Therefore, drainage is required.
- If the groundwater level (GWL) in the area is less than 1 meter, then drainage is indispensable.

- If the buildings on the site have a heavily buried foundation, then it is likely that its sole will be in the zone of seasonal groundwater rise. Therefore, it is necessary to plan drainage at the stage of foundation work.
- If a significant part of the area of the site is covered with artificial coverings made of concrete, paving stones or paving slabs, and if there are lawns equipped with an automatic irrigation system, then drainage is also needed.
From this impressive list, it becomes clear that drainage to one degree or another is necessary in most cases. But before you plan and do it, you need to study the site.
Studying the site for relief, soil type and groundwater level
Each site is individual in terms of relief, soil composition and groundwater level. Even two sites located nearby can be very different from each other, although there will still be a lot in common between them. Modern construction requirements suggest that the design of a house should begin only after geological and geodetic surveys have been carried out with the preparation of special reports that contain a lot of data, most of which are understandable only to specialists. If they are “translated” into the language of ordinary citizens who do not have education in the field of geology, hydrogeology and geodesy, then they can be listed as follows:
- Topographic survey of the area where it is supposed. The photographs must show the cadastral boundaries of the site.
- A characteristic of the relief, which should indicate what type of relief is present on the site (wavy or flat). If there are slopes, then their presence and direction are indicated, it is in their direction that water will flow. Attached is a topographic plan of the site indicating the contour lines of the relief.

- Characteristics of the soil, what kind of soil it is and at what depth it lies on the site. To do this, experts drill exploratory wells in different places of the site, from where they take samples, which are then examined in the laboratory.
- Physical and chemical properties of the soil. Its ability to be load-bearing for the planned house, as well as soil in combination with water, will affect concrete, metal and other building materials.
- The presence and depth of groundwater, their seasonal fluctuations, taking into account exploration, archival and analytical data. It is also indicated in which soils water can appear and how they will affect the planned building structures.

- The degree of heaving of soils, the possibility of landslides, subsidence, flooding and swelling.
The result of all these studies should be recommendations on the design and depth of the foundation, the degree of waterproofing, insulation, protection from aggressive chemical compounds, and drainage. It happens that on an impeccable-looking site, experts, in general, will not allow building such a house as the owners intended. For example, a house with a basement was planned, and a high GWL forces specialists to recommend not to do this, therefore, instead of the originally planned strip foundation with a basement, they will recommend a pile foundation without underground facilities. There is no reason not to trust both these studies and specialists, since they have indisputable tools in their hands - measurements, drilling, laboratory experiments, statistics and calculations.

Of course, geological and geodetic surveys are not done free of charge, and they are done at the expense of the developer and they are mandatory on a new site. This fact is often the subject of indignation of some owners, but it should be understood that this procedure will help save a lot of money during the construction and further operation of the house, as well as maintaining the site in good condition. Therefore, this seemingly unnecessary and expensive bureaucracy is necessary and very useful.
If the site is purchased with existing buildings that have been in operation for at least a few years, then you can also order geological and geodetic surveys, but you can do without them, and learn about groundwater, its seasonal rise and unpleasant impact on human life on other grounds. Of course, this will be with a certain degree of risk, but in most cases it works. What you should pay attention to?
- First of all, this is communication with the former owners of the site. It is clear that it is not always in their interests to talk in detail about problems with flooding, but, nevertheless, you can always find out if any drainage measures have been taken. This will not be hidden for anything.
- Inspection of the basement can also tell a lot about something. Regardless of whether cosmetic repairs were made there. If there is an increased level of humidity in the premises, then this will be immediately felt.

- Getting to know your neighbors and interviewing them can be much more informative than talking to the former owners of the site and the house.
- If there are wells or wells on your site and neighboring ones, then the water level in them will eloquently report on the GWL. Moreover, it is desirable to observe how the level changes in different seasons. Theoretically, the maximum water should rise in the spring after the snow has melted. In summer, if there were dry periods, the groundwater level should fall.
- Plants growing on the site can also “tell” a lot to the owner. The presence of plants such as cattail, reeds, sedge, horse sorrel, nettle, hemlock, foxglove indicate that groundwater is at a level of no more than 2.5-3 meters. If even during a drought these plants continue their rapid growth, then this once again indicates the proximity of water. If licorice or wormwood grow on the site, then this is evidence that the water is at a safe depth.

- Some sources speak of an old way of determining the level of groundwater, which was used by our ancestors before building a house. To do this, a piece of turf was removed in the area of interest and a shallow hole was dug, on the bottom of which a piece of wool was laid, an egg was placed on it, and covered with an inverted clay pot and the removed turf. After dawn and sunrise, the pot was removed and watched as the dew fell. If the egg and wool are in dew, then the water is shallow. If dew fell only on wool, then there is water, but it is at a safe depth. If both the egg and the wool are dry, then the water is very deep. It may seem that this method is akin to quackery or shamanism, but in fact it has an absolutely correct explanation, from the point of view of science.
- The growth of bright grass on the site even during a drought, as well as the appearance of fog in the evening hours, indicates the proximity of groundwater.
- The best way to independently determine the groundwater level at the site is to drill test wells. To do this, you can use a regular garden drill with extension cords. Drilling is best done during the highest rise of water, that is, in the spring after the snow melts. First of all, wells should be made at the construction site of a house or an existing building. The well should be drilled to the depth of the foundation plus 50 cm. If water begins to appear in the well immediately or after 1-2 days, this indicates that drainage measures are mandatory.
 Beginner's Geologist's Kit - Garden Drill with Extension
Beginner's Geologist's Kit - Garden Drill with Extension - If, after rain, puddles stagnate on the site, then this may indicate the proximity of groundwater, as well as the fact that the soil is clayey or heavy loamy, which prevents the water from going deep into the ground. In this case, drainage is also necessary. It will also be very useful to update the fertile soil to a lighter one, then there will be no problems with growing most garden and garden plants.
Even a very high level of groundwater in the area, although it is a big problem, is a problem that can be completely solved with the help of well-calculated and well-executed drainage. Let's give a good example - more than half of the territory of Holland lies below sea level, including the capital - the famous Amsterdam. The groundwater level in this country can be at a depth of several centimeters. Those who have been to Holland noticed that after rain there are puddles that do not soak into the ground, because they simply have nowhere to soak. Nevertheless, in this cozy country, the issue of draining the land is being solved with the help of a set of measures: dams, dams, polders, locks, canals. The Netherlands even has a special department - Watershap, which deals with flood protection. The abundance of many windmills in this country does not at all mean that they grind grain. Most mills are pumping water.

We do not call for a special purchase of a site with a high level of groundwater, on the contrary, this should be avoided by all possible means. And the example of Holland was given only so that readers could understand that there is a solution to any problem with groundwater. Moreover, in most of the territory of the former USSR, settlements and summer cottages are located in areas where the groundwater level is within acceptable limits, and you can cope with seasonal rises on your own.
Types of drainage systems
There are a great variety of drainage systems and their varieties. Moreover, in different sources, their classification systems may differ from each other. We will try to talk about the simplest, from a technical point of view, drainage systems, but at the same time effective ones that will help solve the problem of removing excess water from the site. Another argument in favor of simplicity is that the fewer elements any system has and the more time it can do without human intervention, the more reliable it will be.
Surface drainage
This type of drainage is the simplest, but, nevertheless, quite effective. It is intended mainly for the removal of water coming in the form of precipitation or snowmelt, as well as for the removal of excess water during any technological processes, for example, when washing cars or garden paths. Surface drainage is done in any case around buildings or other structures, sites, places of exit from the garage or yard. Surface drainage is of two main types:
- Point drainage designed to collect and drain water from a specific place. This type of drainage is also called local drainage. The main locations for point drainage are under roof gutters, in pits in front of doors and garage doors, and at the locations of irrigation taps. And also point drainage, in addition to its direct purpose, can complement another type of surface drainage system.
 Rain inlet - the main element of point surface drainage
Rain inlet - the main element of point surface drainage - Linear drainage needed to remove water from a larger area compared to a point. It is a collection trays and channels, mounted with a slope, equipped with various elements: sand traps (sand traps), protective grilles , performing a filtering, protective and decorative function. Trays and channels can be made from a variety of materials. First of all, it is plastic in the form of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene (PP), low-pressure polyethylene (HDPE). And also materials such as concrete or polymer concrete are widely used. Grates are most often used plastic, but in those areas where increased load is expected, stainless steel or even cast iron products can be used. Work on the organization of linear drainage requires concrete preparation of the base.

It is obvious that any good surface drainage system almost always combines elements of point and linear. And all of them are combined into a common drainage system, which may also include another subsystem, which we will consider in the next section of our article.
rain gutter prices
storm water inlet
deep drainage
In most cases, surface drainage alone cannot be dispensed with. To qualitatively solve the problem, we need a different type of drainage - deep, which is a system of special drainage pipes (drains) , laid in those places where it is required to lower the level of groundwater or divert water from the protected area. Drains are laid with a slope to the side collector, well , artificial or natural reservoir on the site or beyond. Naturally, they are laid below the level of the base of the foundation of the protected building or along the perimeter of the site at a depth of 0.8-1.5 meters to lower the groundwater level to non-critical values. Drains can also be laid in the middle of the site with a certain interval, which is calculated by experts. Typically, the interval between the pipes is 10-20 meters, and they are laid in the form of a Christmas tree, directed to the main outlet pipe-collector. It all depends on the level of groundwater and their quantity.

When laying drains in trenches, it is imperative to use all the features of the site relief. Water will always move from a higher place to a lower one, so the drains are laid in the same way. It is much more difficult if the site is absolutely flat, then the pipes are given the desired slope by giving a certain level to the bottom of the trenches. It is customary to make a slope of 2 cm per 1 meter of pipe for clay and loamy soils and 3 cm per 1 meter for sandy soils. Obviously, with sufficiently long drains, it will be difficult to maintain the desired slope on a flat area, since the level difference will already be 20 or 30 cm per 10 meters of the pipe, so the necessary measure is the organization of several drainage wells that will be able to receive the required volume of water.
It should be noted that even with a smaller slope, water, even at 1 cm per 1 meter or less, will still, obeying the laws of physics, try to go below the level, but the flow rate will be less, and this can contribute to silting and clogging of drains. And any owner who has laid sewer or drainage pipes at least once in his life knows that it is much more difficult to maintain a very small slope than a larger one. Therefore, you should not be “embarrassed” in this matter and boldly set a slope of 3, 4 and even 5 cm per meter of the drainage pipe, if the length and the planned difference in the depth of the trench allow.

Drainage wells are one of the most important components of deep drainage. They can be of three main types:
- Rotary wells – suit where the drains make a turn or there is a connection of several elements. These elements are needed for the revision and cleaning of the drainage system, which must be done periodically. They can be as small in diameter, which will only allow cleaning and washing with a jet of water under pressure, but they can also be wide, which provide human access.

- Water intake wells - their purpose is absolutely clear from their name. In those areas where it is not possible to divert water into the depths or beyond, it becomes necessary to collect water. These wells are designed for just that. Previously, they were mainly a structure made of cast-in-place concrete, concrete rings or bricks plastered with cement mortar. Now, plastic containers of various sizes are most often used, which are protected from clogging or silting with geotextiles and sprinkling of crushed stone or gravel. Water collected in a water intake well can be pumped out of the site using special submersible drainage pumps, can be pumped out and taken out by tankers, or can be settled in a well or pool for further irrigation.

- absorption wells designed to drain water in the event that the terrain of the site does not allow moisture to be removed beyond its limits, but the underlying soil layers have good absorbency. These soils include sandy and sandy loam. Such wells are made of large diameters (about 1.5 meters) and depths (at least 2 meters). The well is filled with filter material in the form of sand, sand-gravel mixture, crushed stone, gravel, broken brick or slag. To prevent the ingress of eroded fertile soil or various blockages from above, the well is also covered with fertile soil. Naturally, the side walls and the bottom are protected by sprinkling. Water, falling into such a well, is filtered by its contents and goes deep into sandy or sandy loamy soils. The ability of such wells to remove water from the site may be limited, so they are arranged when the expected throughput should not exceed 1-1.5 m 3 per day.

Of the drainage systems, the main and most important is deep drainage, since it is it that provides the necessary water regime for both the site and all the buildings located on it. Any mistake in the design and installation of deep drainage can lead to very unpleasant consequences, which can lead to the death of plants, flooding of basements, destruction of house foundations, and uneven drainage of the site. That is why it is recommended not to neglect geological and geodetic studies and ordering a drainage system project from specialists. If it is possible to correct flaws in surface drainage without a strong violation of the landscape of the site, then with deep drainage everything is much more serious, the price of a mistake is too high.
Well prices
Overview of accessories for drainage systems
For self-execution of the drainage of the site and the buildings located on it, you need to find out what components will be required for this. Of the widest selection of them, we have tried to show the most used at the present time. If earlier the market was dominated by Western manufacturers, who, as monopolists, dictated high prices for their products, now a sufficient number of domestic enterprises offer their products, which are in no way inferior in quality.
Details for surface drainage
For point and linear surface drainage, the following parts can be used:
| Image | Name, manufacturer | Purpose and description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tray drainage concrete 1000*140*125 mm with a steel stamped galvanized lattice. Production - Russia. | Designed for surface water drainage. Capacity 4.18 l/s, able to withstand loads up to 1.5 tons (A15). | 880 rub. | |
| Concrete drainage tray with cast-iron grate, dimensions 1000*140*125 mm. Production - Russia. | The purpose and throughput are the same as in the previous example. Able to withstand loads up to 25 tons (C250). | 1480 rub. | |
| Concrete drainage tray with steel galvanized mesh grid, dimensions 1000*140*125 mm. Production - Russia. | The purpose and throughput are the same. Able to withstand loads up to 12.5 tons (B125). | 1610 rub. | |
| Polymer concrete drainage tray 1000*140*70 mm with plastic grating. Production - Russia. | The purpose is the same, the throughput is 1.9 l / s. Able to withstand loads up to 1.5 tons (A15). The material combines the advantages of plastic and concrete. | 820 rub. | |
| Polymer concrete drainage tray 1000*140*70 mm with cast-iron grate. Production - Russia. | throughput is the same. Able to withstand up to 25 tons of load (C250). | 1420 rub. | |
| Polymer concrete drainage tray 1000*140*70 mm with steel mesh grating. Production - Russia. | throughput is the same. Able to withstand up to 12.5 tons of load (B125). | 1550 rub. | |
| Tray plastic drainage 1000*145*60 mm with a galvanized stamped lattice. Production - Russia. | Made from frost-resistant polypropylene. Throughput 1.8 l/sec. Able to withstand loads up to 1.5 tons (A15). | 760 rub. | |
| Tray plastic drainage 1000*145*60 mm with a cast-iron grate. Production - Russia. | Throughput 1.8 l/sec. Able to withstand loads up to 25 tons (C250). | 1360 rub. | |
| Completed plastic rainwater inlet (siphon-partitions 2 pcs., Waste basket - 1 pc.). Size 300*300*300 mm. With plastic grid. Production - Russia. | Designed for point drainage of water flowing from the roof through the downpipe, and can also be used to collect water under yard, garden watering taps. Can be connected to fittings with diameters of 75, 110, 160 mm. Removable basket provides quick cleaning. Withstands loads up to 1.5 tons (A15). | For a set together with siphon partitions, a waste basket and a plastic grate - 1000 rubles. | |
| Completed plastic rainwater inlet (siphon-partitions 2 pcs., Waste basket - 1 pc.). Size 300*300*300 mm. With cast-iron grate "Snowflake". Production - Russia. | The purpose is similar to the previous one. Withstands loads up to 25 tons (C250). | For a set together with siphon partitions, a waste basket and a cast-iron grate - 1550 rubles. | |
 | Sand trap - plastic with a galvanized steel grate. Dimensions 500*116*320 mm. | Designed to collect dirt and debris in surface linear drainage systems. It is installed at the end of the line of gutters (trays) and later it joins the pipes of the storm sewer system with a diameter of 110 mm. Able to withstand loads up to 1.5 tons (A15). | For a set together with gratings 975 rubles. |
In the table, we deliberately showed Russian-made trays and storm water inlets, made of materials that differ from each other and have different configurations. It is also worth noting that the trays have different widths and depths and, accordingly, their throughput is also not the same. There are a lot of options for the materials from which they are made and sizes, there is no need to give them all, since it depends on many factors: the required throughput, the expected load on the soil, the specific scheme for implementing the drainage system. That is why it is best to entrust the calculations of the drainage system to specialists who will calculate both the required size and quantity, and select the components.
There was absolutely no need to talk about possible accessories for drainage trays, storm water inlets and sand traps in the table, since in each individual case they will be different. When buying, if there is a system project, the seller will always tell you the ones you need. They can be end caps for trays, mounts for gratings, various corner and transition elements, reinforcing profiles, and others.

A few words should be said about sand traps and storm water inlets. If the surface linear drainage around the house is implemented with storm water inlets in the corners (and this is usually done), then sand traps will not be required. Rain inlets with siphon partitions and waste baskets do an excellent job with their role. If the linear drainage does not have storm water inlets and goes into the sewer drainage pipe, then a sand trap is required. That is, any transition from drainage trays to pipes must be done either with the help of a storm inlet or a sand trap. Only this way and not otherwise! This is done so that sand and various heavy debris do not get into the pipes, as this can lead to their rapid wear, and both they and the drainage wells will become clogged over time. It is hard to disagree that it is easier to periodically remove and wash the baskets while on the surface than to go down into the wells.

Surface drainage also includes wells and pipes, but they will be discussed in the next section, since, in principle, they are the same for both types of systems.
Details for deep drainage
Deep drainage is a more complex engineering system that requires more details. In the table we present only the main ones, since all their diversity will take up a lot of space and attention of our readers. If desired, it will not be difficult to find catalogs of manufacturers of these systems, to select the necessary parts and accessories for them.
| Image | Name and manufacturer | Purpose and description | Approximate price (as of October 2016) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drainage pipe with a diameter of 63 mm made of HDPE corrugated single-walled in a geotextile filter. Producer "Sibur", Russia. | Designed to remove excess moisture from foundations and sites. Wrapped with geotextile to prevent clogging of pores with soil, sand, which prevents clogging and silting. They have a full (circular) perforation. Made from low pressure polyethylene (HDPE). Rigidity class SN-4. Depth of laying up to 4 m. | For 1 r.p. 48 rub. | |
| Drainage pipe with a diameter of 110 mm made of HDPE corrugated single-walled in a geotextile filter. Producer "Sibur", Russia. | similar to above | For 1 r.p. 60 rub. | |
| Drainage pipe with a diameter of 160 mm made of HDPE corrugated single-walled in a geotextile filter. Producer "Sibur", Russia. | similar to above | For 1 r.p. 115 rub. | |
| Drainage pipe with a diameter of 200 mm made of HDPE corrugated single-walled in a geotextile filter. Producer "Sibur", Russia. | similar to above | For 1 r.p. 190 rub. | |
| Single-wall corrugated drainage pipes made of HDPE with a coconut coir filter with diameters of 90, 110, 160, 200 mm. Country of manufacture - Russia. | Designed to remove excess moisture from foundations and sites on clay and peat soils. Coconut coir has increased reclamation and strength compared to geotextiles. They have circular perforations. Rigidity class SN-4. Depth of laying up to 4 m. | 219, 310, 744, 1074 rubles. for 1 r.m. (depending on diameter). | |
| Two-layer drainage pipes with Typar SF-27 geotextile filter. The outer layer of HDPE is corrugated, the inner layer of HDPE is smooth. Diameters 110, 160, 200 mm. Country of origin - Russia. | Are intended for removal of excess moisture from the bases and sites on all types of soils. They have a full (circular) perforation. The outer layer protects against mechanical stress, and the inner layer allows more water to be removed due to its smooth surface. The two-layer design has a stiffness class of SN-6 and allows you to lay pipes at a depth of up to 6 meters. | 160, 240, 385 rubles. for 1 r.m. (depending on diameter). | |
 | PVC pipes for sewerage are smooth with a socket with an outer diameter of 110, 125, 160, 200 mm, length 1061, 1072, 1086, 1106 mm, respectively. Country of origin - Russia. | Designed for organizing an external sewer system, as well as storm sewer or drainage systems. They have a stiffness class of SN-4, which allows them to be laid at a depth of up to 4 meters. | 180, 305, 270, 490 rubles. for pipes: 110*1061 mm, 125*1072 mm, 160*1086 mm, 200*1106 mm respectively. |
| Well shafts with a diameter of 340, 460, 695, 923 mm from HDPE. Country of origin - Russia. | Are intended for creation of drainage wells (rotary, water intake, absorption). They have a two-layer construction. Ring stiffness SN-4. The maximum length is 6 meters. | 950, 1650, 3700, 7400 rubles for wells with diameters of 340, 460, 695, 923 mm, respectively. | |
| Bottom-plug of wells with diameters of 340, 460, 695, 923 mm from HDPE. Country of origin - Russia. | Designed to create drainage wells: rotary or water intake. | 940, 1560, 4140, 7100 for wells with diameters of 340, 460, 695, 923 mm, respectively. | |
| Inserts into the well in place with diameters of 110, 160, 200 mm. Country of origin - Russia. | Designed for insertion into a well at any level of sewer or drainage pipes of appropriate diameters. | 350, 750, 2750 rubles for inserts with diameters of 110, 160, 200 mm, respectively. | |
 | Hatch polymer concrete for drainage wells with a diameter of 340 mm. Country of origin - Russia. | 500 rub. | |
| Hatch polymer concrete for drainage wells with a diameter of 460 mm. Country of origin - Russia. | It is intended for installation on drainage wells. Withstands loads up to 1.5 tons. | 850 rub. | |
| Polyester geotextile with a density of 100 g/m². Country of origin - Russia. | Used to create drainage systems. It is not subject to rotting, influence of a mold, rodents and insects. Roll length from 1 to 6 m. | 20 rub. for 1 m². |
The presented table shows that the cost of even Russian-made parts for drainage systems can hardly be called cheap. But the effect of their use will delight the owners of the site for at least 50 years. It is about this service life that the manufacturer claims. Considering that the material for manufacturing drainage parts is absolutely inert with respect to all substances found in nature, it can be assumed that the service life will be much longer than stated.
We deliberately did not indicate the previously widely used asbestos-cement or ceramic pipes in the table, since apart from the high price and difficulties in transportation and installation, they will not bring anything. This is yesterday's age.

To create drainage systems, there are still a lot of components from various manufacturers. These include tray parts, which can be throughput, connecting, prefabricated and dead-end. They are designed to connect drainage pipes of various diameters to wells. They provide connections for drainage pipes at various angles.

With all the obvious advantages of tray parts with pipe sockets, their price is very high. For example, the part shown in the figure above costs 7 thousand rubles. Therefore, in most cases, inserts into the well are used, as indicated in the table. Another advantage of tie-ins is that they can be done at any level and at any angle to each other.
In addition to those parts for drainage systems that are indicated in the table, there are many others that are selected by calculation and during installation on site. These may include various cuffs and o-rings, couplings, tees and crosses, check valves for drainage and sewer pipes, eccentric transitions and necks, bends, plugs and much more. Their correct selection should be dealt with, first of all, during the design, and then make adjustments during installation.
Video: How to choose a drainage pipe
Video: Drainage wells
If readers find articles on drainage on the Internet that say that it is easy to make drainage with your own hands, then we advise you to immediately close this article without reading it. Making drainage with your own hands is not an easy task. But, the main thing is that it is possible if you do everything consistently and correctly.
Site drainage design
The drainage system is a complex engineering object that requires an appropriate attitude. Therefore, we recommend that our readers order the design of the drainage of the site from professionals who will take into account absolutely everything: the relief of the site, the existing (or planned) buildings, the composition of the soil, and the depth of the GWL, and other factors. After the design, the customer will have a set of documents in his hands, which includes:
- Site plan with its relief.
- A scheme for laying pipes for wall or ring drainage, indicating the section and type of pipes, the depth of occurrence, the required slopes, and the location of the wells.
- The drainage scheme of the site, also indicating the depth of the trenches, types of pipes, slopes, the distance between adjacent drains, the location of rotary or water intake wells.
 It will be difficult to independently make a detailed design of the drainage system without knowledge and experience. That is why you should turn to professionals
It will be difficult to independently make a detailed design of the drainage system without knowledge and experience. That is why you should turn to professionals - Scheme of surface point and linear drainage indicating the size of trays, sand traps, storm water inlets, used sewer pipes, location of water intake wells.
- Transverse dimensions of trenches for near-wall and deep drainage, indicating the depth, material and thickness of the backfill, type of geotextile used.
- Calculation of necessary components and materials.
- An explanatory note to the project describing the entire drainage system and the technology for performing work.
The project of the drainage system of the site is much lower than the architectural one, so we once again strongly advise you to contact the specialists. This minimizes the likelihood of errors during self-arrangement of drainage.
Wall drainage equipment at home
To protect the foundations of houses from the effects of groundwater, the so-called wall drainage is made, which is located around the entire house on its outer side at some distance from the base of the foundation. usually it is 0.3-0.5 m, but in any case not more than 1 meter. Wall drainage is done even at the stage of building a house, along with measures for warming and waterproofing the foundation. When is this type of drainage necessary anyway?
Prices for drainage systems
- When the house has a basement.

- When the buried parts of the foundation are at a distance of no more than 0.5 meters above the groundwater level.
- When a house is built on clay or loamy soils.
All modern house designs almost always provide wall drainage. An exception can only be those cases when the foundation is laid on sandy soils that do not freeze through more than 80 cm.
A typical wall drainage design is shown in the figure.

At some distance from the base of the foundation, approximately 30 cm below its level, a leveling layer of sand 10 cm is made, on which a geotextile membrane with a density of at least 150 g / m² is laid, on which a layer of crushed stone of a fraction of 20-40 mm with a thickness of at least 10 cm is poured. Instead of crushed stone, washed gravel may well be used. Crushed stone is better to use granite, but not limestone, since the latter tends to gradually erode with water. A drainage pipe wrapped with geotextile is laid on a crushed stone pillow. The pipes are given the desired slope - at least 2 cm per 1 linear meter of the pipe.
In the places where the pipe turns, inspection and inspection wells are necessarily made. The rules allow them to be done through one turn, but practice suggests that it is better not to save on this and put them on every turn. The slope of the pipes is done in one direction (in the figure from point K1, through points K2 and K3, to point K4). In this case, it is necessary to take into account the terrain. It is assumed that point K1 is at the highest point, and K4 at the lowest.
Drains are inserted into wells not from the very foundation, but with an indent of at least 20 cm from the bottom. Then the small debris or silt that has fallen will not linger in the pipes, but will settle in the well. In the future, when revising the system, you can wash out the silted bottom with a strong jet of water, which will carry away everything unnecessary. If the soil in the area where the wells are located has a good absorbing capacity, then the bottom is not made. In all other cases, it is better to equip the wells with a bottom.
A layer of crushed stone or washed gravel with a thickness of at least 20 cm is again poured over the drains, and then it is wrapped around with the previously laid geotextile membrane. On top of such a “wrapped” structure made of a drainage pipe and rubble, a backfill of sand is made, and on top, after it is tamped, a blind area of the building is already organized, which is also called upon, but already in the system of surface linear drainage. Even if atmospheric water enters from the outside of the foundation, then, having passed through the sand, it will fall into the drains and eventually merge into the main collector well, which can be equipped with a pump. If the relief of the site allows, then an overflow is made from the collector well without a pump, which removes water outside into a gutter, an artificial or natural reservoir, or a storm sewer system. Under no circumstances should drainage be connected to a conventional sewer system.

If groundwater begins to "support" from below, then they, first of all, impregnate the sandy preparation and crushed stone in which the drains are located. The speed of water movement along the drains is higher than in the ground, so the water is quickly removed and drained into a collector well, which is laid lower than the drains. It turns out that inside a closed circuit of drainage pipes, water simply cannot rise above the level of the drains, which means that the base of the foundation and the floor in the basement will be dry.
Such a wall drainage scheme is very often used and works very effectively. But it has a significant drawback. This is backfilling of the entire sinus between the foundation and the edge of the pit with sand. Given the considerable volume of the sinus, you will have to pay a tidy sum for this filling. But there is a beautiful way out of this situation. In order not to backfill with sand, you can use a special profiled geomembrane, which is a sheet of HDPE or PVD with various additives, which has a relief surface in the form of small truncated cones. When the underground part of the foundation is pasted over with such a membrane, it performs two main functions.
- The geomembrane itself is an excellent waterproofing agent. It does not allow moisture to penetrate to the walls of the underground foundation structure.
- The relief surface of the membrane ensures that the water that appears on it flows down freely, where it is “intercepted” by the laid drains.
The design of wall drainage using a geomembrane is shown in the following figure.

On the outer wall of the foundation, after the measures and insulation (if necessary), the geomembrane is glued or mechanically attached with the relief part (pimples) outward. A geotextile fabric with a density of 150-200 g / m² is fixed on top of it, which will prevent soil particles from clogging the relief part of the geomembrane. Further organization of drainage is usually carried out: a drain is placed on a layer of sand, covered with crushed stone and wrapped with geotextile. Only backfilling of the sinuses is not done with sand or gravel, but with ordinary soil excavated when digging a pit or clay, which is much cheaper.
Drainage of water, "supporting" the foundation from below, proceeds as in the previous case. But water that has entered the wall from the outside through moistened soil or penetrated into the gap between the foundation and the soil will follow the path of least resistance: seep through the geotextile, flow freely along the relief surface of the geomembrane, pass through rubble and fall into the drain. Foundations protected in this way will not be threatened for a minimum of 30-50 years. In the basement floors of such houses it will always be dry.
Consider the main stages of creating a wall drainage system at home.
| Image | Description of actions |
|---|---|
 | After the measures for the construction of the foundation, its primary coating, and then rolled waterproofing and insulation, have been carried out, the geomembrane is glued with the relief part outward on the outer wall of the foundation, including its sole, using a special mastic that does not corrode polystyrene foam. The upper part of the membrane should protrude beyond the level of the future backfill by at least 20 cm, and the lower part should reach the very bottom of the foundation, including the sole. |
 | The joints of most geomembranes have a special lock, which is "snapped" by overlapping one sheet over another, and then tapping with a rubber mallet. |
 | A geotextile fabric with a density of 150-200 g/m² is attached over the geomembrane. It is better to use not needle-punched, but thermally bonded geotextiles, as it is less prone to clogging. For fixing, dish-shaped dowels are used. The step of fastening the dowels is no more than 1 m horizontally and no more than 2 m vertically. The overlap of adjacent geotextile sheets on each other is at least 10-15 cm. Dish-shaped dowels should fall at the junction. |
 | In the upper part of the geomembrane and geotextile, it is recommended to use a special mounting strip, which will press both layers to the foundation structure. |
 | The bottom of the pit from the outside of the foundation is cleaned to the required level. The level can be controlled with a theodolite with a measuring bar, a laser level and a handy wooden bar with marked marks, stretched and set with a tensioned cord using a hydraulic level. You can also “beat off” a horizontal line on the wall and measure the depth with a tape measure. |
 | Washed sand is poured at the bottom with a layer of at least 10 cm, which is wetted with water and rammed mechanically or manually until there are practically no traces left when walking. |
 | In the designated places, inspection and inspection wells are installed. To do this, it is enough to use mines with a diameter of 340 or 460 mm. Having measured the desired length, they can be cut either with a conventional hacksaw for wood, or with an electric jigsaw, or with a reciprocating saw. Initially, the wells must be cut 20-30 cm more than the estimated length, and later, when designing the landscape, already fit it under it. |
 | Bottoms are installed on the wells. To do this, in single-layer wells (for example, Wavin), a rubber cuff is placed in the rib of the body, then it is lubricated with soapy water and the bottom is put on. It must go in with force. |
 | In Russian-made two-layer wells, before installing the cuff, it is necessary to cut out a strip of the inner layer with a knife, and then do the same as in the previous case. |
 | Wells are installed in their intended places. Sites for their installation are compacted and leveled. On their side surfaces, marks are made for the entrance and exit of the centers of drains (taking into account slopes of 2 cm per 1 linear meter of pipe). We remind you that the entrances and exits of drains must be at least 20 cm from the bottom. |
 | For the convenience of inserting couplings, it is better to place the wells horizontally and make holes corresponding to the coupling with a crown with a center drill. In the absence of a crown, you can make holes with a jigsaw, but this requires certain skills. |
 | After that, the edges are cleaned of burrs with a knife or brush. |
 | The outer rubber cuff of the coupling is placed inside the hole. It should equally go inside the well and stay outside (about 2 cm each). |
 | The inner surface of the rubber cuff of the coupling is lubricated with soapy water, and then the plastic part is inserted until it stops. The joints of the rubber part of the coupling to the well can be smeared with a waterproof sealant. |
 | Wells are installed in their places and aligned vertically. Geotextiles are laid out on a sand cushion. Granite crushed stone of a fraction of 5-20 mm or washed gravel with a layer of at least 10 cm is poured on it. In this case, the necessary slopes of the drainage pipes are taken into account. Crushed stone is leveled and compacted. |
 | Perforated drainage pipes of the required size are measured and cut. Pipes are inserted into couplings cut into wells after lubricating the cuff with soapy water. Their slope is checked. |
 | A layer of crushed stone or gravel of at least 20 cm is poured on top of the drains. Then the edges of the geotextile fabric are wrapped on top of each other and a 20 cm layer of sand is sprinkled on top. |
 | In the intended place, a pit is dug for the collector well of the drainage system. The level of its occurrence, of course, must be below the lowest drain in order to receive water from the wall drainage. To this pit, a trench is dug from the lower level of the inspection and inspection well for laying a sewer pipe. |
 | Shafts with diameters of 460, 695 and even 930 mm can be used as a collector well. A prefabricated well made of reinforced concrete rings can also be equipped. Inserting a sewer pipe into a receiving collector well is done in exactly the same way as drains. |
 | The sewer pipe leading from the lower wall drainage well to the collector well is laid on a 10 cm sand cushion and sprinkled with sand of at least 10 cm thickness on top. After compacting the sand, the trench is covered with soil. |
 | The system is checked for functionality. To do this, water is poured into the topmost well in terms of level. After filling the bottom, water should begin to flow through the drains into other wells and, after filling their bottoms, eventually flow into the collector well. There should be no reverse current. |
 | After checking the performance of the sinuses between the edge of the pit, they are covered with soil. It is preferable to use quarry clay for this, which will create a waterproof lock around the foundation. |
 | The wells are covered with lids to prevent clogging. Final pruning and installation of covers should be done along with landscaping. |
The collection well can be equipped with a check valve, which, even if it is overflowing, will not allow water to flow back into the drains. And also in the well can be automatic. When the GWL rises to critical values, water will collect in the well. The pump is set up so that when a certain level is exceeded in the well, it will turn on and pump water out of the site or into other containers or reservoirs. Thus, the GWL in the foundation area will always be lower than the laid drains.
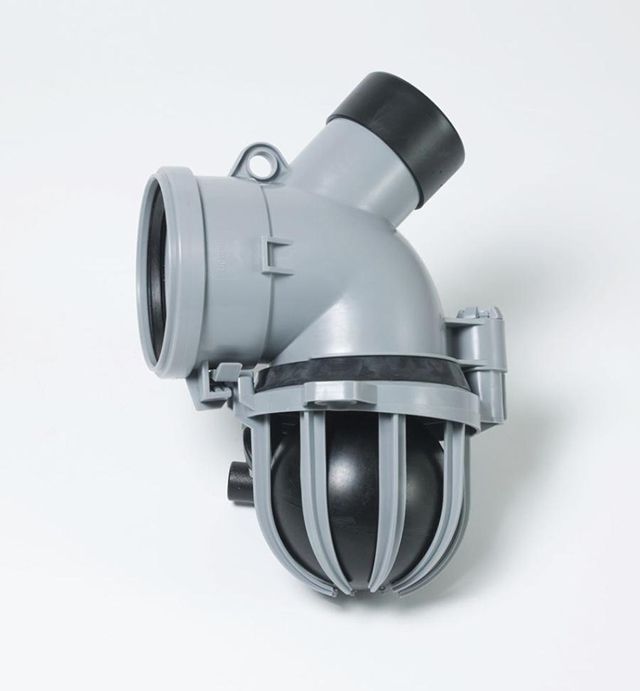

It happens that one collector well is used for the wall drainage system and the surface one. Experts do not recommend doing this, since during intense snowmelt or heavy rains, a very large amount of water will be collected in a short time, which will only interfere with inspecting the GWL in the foundation area. Water from precipitation and melted snow is best collected in separate containers and used for irrigation. In case of overflow of storm wells, water from them can be pumped in the same way to another place with a drainage pump.

Video: Wall drainage at home
Ring drainage equipment at home
Annular drainage, unlike wall drainage, is located not close to the foundation structure, but at some distance from it: from 2 to 10 meters or more. In what cases is ring drainage arranged?
- If the house has already been built and any intervention in the foundation structure is undesirable.
- If the house does not have a basement.
- If the house or group of buildings is built on sandy or sandy loamy soils that have good water permeability.
- If other types of drainage cannot cope with the seasonal rise of groundwater.
Regardless of the fact that ring drainage is much simpler in practical implementation, it should be treated more seriously than wall drainage. Why?
- A very important characteristic is the depth of the drains. In any case, the laying depth must be greater than the depth of the base of the foundation or the level of the basement floor.
- The distance from the foundation to the drain is also an important characteristic. The more sandy the soil, the greater the distance should be. And vice versa - the more clay soils, the closer the drains can be located to the foundation.
- When calculating the ring foundation, the level of groundwater, its seasonal fluctuations and the direction of their inflow are also taken into account.
Based on the foregoing, we can safely say that it is better to entrust the calculation of the annular drainage to specialists. It would seem that the closer the drain is to the house and the deeper it is laid, the better it will be for the protected structure. It turns out not! Any drainage changes the hydrogeological situation in the foundation area, which is far from always good. The task of drainage is not to completely drain the site, but to lower the GWL to such values that will not interfere with human and plant life. Drainage is a kind of contract with the forces of Mother Nature, and not an attempt to "rewrite" existing laws.
One of the options for the device of the annular drainage system is shown in the figure.

It can be seen that a trench has been dug around the house outside the blind area to such a depth that the upper part of the drainage pipe lies 30-50 cm below the lowest point of the foundation. The trench is lined with geotextiles and the pipe itself is also in a shell from it. The minimum underlying layer of crushed stone should be at least 10 cm. The minimum slope of drains with a diameter of 110-200 mm is 2 cm per 1 linear meter of pipe. The figure shows that the entire trench is covered with rubble. This is quite acceptable and does not contradict anything but common sense, in terms of excessive spending.
The diagram shows that the inspection and control wells are installed through one turn, which is quite acceptable if the drainage pipe is laid in one piece, without any fittings. But still it is better to do them at every turn. This will greatly facilitate the maintenance of the drainage system over time.
An annular drainage system can perfectly "get along" with a system of surface point and linear drainage. In one trench, drains can be laid at the lower level, and sewer pipes leading from trays and storm water inlets to the well for collecting rain and melt water can be laid next to them or on top in a layer of sand. If the path of both one and the other leads to one collector catchment well, then this is generally wonderful, the number of earthworks is reduced significantly. Although, we recall that we recommended collecting these waters separately. They can be collected together in only one case - if all water from precipitation and extracted from the soil is removed (naturally or forcibly) from the site into a collective storm sewer system, gutter or reservoir.

When organizing ring drainage, a trench is first dug to the estimated depth. The width of the trench in the area of its bottom should be at least 40 cm; a certain slope is immediately given to the bottom of the trench, the control of which is most convenient to carry out with a theodolite, and in its absence, a horizontally stretched cord and a measuring rod from improvised means will help.
Washed sand is poured at the bottom with a layer of at least 10 cm, which is carefully rammed. It is obvious that it is impossible to do this in a narrow trench in a mechanized way, therefore, a manual rammer is used.
Installation of wells, tie-in couplings, adding crushed granite or gravel, laying and connecting drains is done in exactly the same way as when organizing wall drainage, so there is no point in repeating. The difference is that with ring drainage, it is better to fill the trench after crushed stone and geotextiles not with soil, but with sand. Only the upper fertile layer of soil is poured, about 10-15 cm. Then, already with the landscape equipment of the site, the places for laying drains are taken into account and trees or shrubs with a powerful root system are not planted in these places.
Video: Drainage around the house
Surface point and line drainage equipment
As in all cases, a surface drainage system can only be successfully installed if there is a project or at least a self-made plan. On this plan, it is necessary to take into account everything - from water intake points to a tank where rain and melt water will merge. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the slopes of pipelines and trays, the direction of movement along the trays.

The surface drainage system can be installed with an existing blind area, paths made of paving slabs or paving stones. It is possible that one of their parts will have to be intervened, but this still does not require complete dismantling. Consider an example of the installation of a surface drainage system using the example of polymer concrete trays and sand traps (sand traps) and sewer pipes.
To carry out the work you will need a very simple set of tools:

- Shovels shovel and bayonet;
- Building bubble level from 60 cm long;
- Bench hammer;
- Rubber hammer for laying tiles or paving stones;
- Construction marking cord and a set of stakes made of wood or pieces of reinforcement;
- Trowel and spatulas;
- Roulette;
- Construction knife;
- Chisel;
- Angle grinder (grinder) with discs of at least 230 mm for stone and metal;
- Container for preparation of solutions.
We present the further process in the form of a table.
| Image | Process description |
|---|---|
 | Given the plan or design of surface drainage, it is necessary to determine the points of water discharge, that is, those places where water collected from the surface will go into the sewer pipeline leading to the drainage well. The laying depth of this pipeline should be made below the depth of soil freezing, which is 60-80 cm for most populated climatic zones in Russia. It is in our interests to minimize the number of discharge points, but to ensure the required drainage capacity. |
 | Discharge of water into the pipeline must be done either through sand traps or through storm water inlets to ensure the filtering of debris and sand. First of all, it is necessary to provide for their connection using standard shaped elements of external sewerage to the pipeline and try on these elements at the installation site. |
 | It is better to foresee the connection of storm water inlets located under downpipes in advance, even at the stage of arranging wall drainage, so that when snow melts during the thaw and off-season, water flowing from the roofs immediately falls into the underground pipeline and would not freeze in trays, on blind areas and paths. |
 | If it is not possible to install sand traps, then the sewer pipeline can be connected directly to the trays. For this, polymer concrete trays have special technological holes that allow you to connect a vertical pipeline. |
 | Some manufacturers have special baskets fixed in the vertical water outlet, which protect the drainage system from clogging. |
 | Most plastic trays, in addition to a vertical connection, can also have a side connection. But this should be done only when there is confidence in the purity of the water being drained, since it is much more difficult to clean drainage wells and catchment tanks than baskets. |
 | To install surface drainage elements, you first need to select the soil to the required depth and width. To do this, with an already existing lawn, the turf is cut to the required width, which is defined as the width of the installed element plus 20 cm - 10 cm on each side. It may be necessary to dismantle the curbs and extreme rows of paving slabs or paving stones. |
 | In depth for the installation of drainage elements, it is necessary to choose the soil by the depth of the element plus 20 cm. Of these, 10 cm for sand or crushed stone preparation, and 10 cm for a concrete base. The soil is removed, the base is cleaned and rammed, and further filling is made of crushed stone of a fraction of 5-20 mm. Then pegs are driven in and a cord is pulled, which will determine the level of the installed trays. |
 | Surface drainage elements are tried on at the installation site. In this case, one should take into account the direction of the water flow, which is usually indicated on the side surface of the trays. |
 | Holes are made in the drainage elements for connecting sewer pipes. In plastic trays, this is done with a knife, and in polymer concrete trays with a chisel and a hammer. |
 | When fitting parts, it may be necessary to cut off part of the tray. Plastic are easily cut with a hacksaw, and polymer concrete with a grinder. Galvanized metal gratings are cut with scissors for metal, and cast-iron gratings are cut with a grinder. |
 | On the last trays, end caps are installed using a special adhesive-sealant. |
 | To install surface drainage elements, it is best to use ready-made dry mixes of sand concrete M-300, which are in the assortment of many manufacturers. In a suitable container, a solution is prepared, which should be dense in consistency. Installation is best done from discharge points - sand traps. Concrete is laid out on the prepared base. |
 | Then it is leveled with a trowel and a sand trap is installed on this pillow. |
 | Then it is exposed along the previously stretched cord. If necessary, the tray is seated in place with a rubber mallet. |
 | The correctness of the installation is checked by the cord and by the level. |
 | Trays and sand traps are set so that when the grate is installed, its plane is 3-5 mm below the surface level. Then the water will flow freely into the trays, the gratings will not be damaged by the wheels of the car. |
 | The sand trap installed according to the level is immediately fixed on the sides with a concrete mixture. The so-called concrete heel is formed. |
 | Similarly, drainage trays are installed on a concrete base. |
 | They also align with both cord and level. |
 | After installation, the joints are covered with a special sealant, which is always offered when buying trays. |
 | Experienced installers can apply sealant before installing the trays, applying it to the ends even before installation. |
 | When installing plastic trays in concrete, they can be deformed. Therefore, it is better to install them with installed gratings, which, in order to avoid contamination, are best wrapped with plastic wrap. |
 | If the surface is flat and has no slopes, then it will be problematic to provide the required slope of the trays. The way out of this situation is to install a cascade of trays of the same width, but different depths. |
 | After installing all the elements of surface drainage, a concrete heel is formed, and then paving stones or paving slabs are installed in place if they were dismantled. The surface of the paving stones should be 3-5 mm higher than the grate of the drainage tray. |
 | Between the paving stones and the trays, it is imperative to make a deformation seam. Instead of the recommended rubber cords, you can use a double-folded strip of roofing material and sealant. |
 | After the concrete has set, after 2-3 days, backfilling of the excavated soil can be done. |
 | After compacting the soil, the previously removed layer of turf is laid out on top. It must be laid 5-7 cm higher than the rest of the lawn surface, as over time it will compact and settle. |
 | After flushing the entire surface drainage system and checking its performance, the trays, storm water inlets and sand traps are closed with gratings. It is possible to expose elements to vertical loading only in 7-10 days. |
When operating a surface drainage system, it is imperative to periodically clean the storm water inlets and sand traps. If necessary, you can remove the protective grids and rinse the trays themselves with a strong jet of water. Water collected after rains or snowmelt is the most suitable for further use for watering the garden, vegetable garden or lawns. The groundwater collected by a deep drainage system may have a different chemical composition and may not always be used for the same purposes. Therefore, we once again remind and advise our readers to collect groundwater and atmospheric water separately.
Video: Installation of a drainage system
Site deep drainage equipment
We have already described in which cases deep drainage of the site is needed and found out that it is almost always needed in order to forever forget about the problems of stagnant puddles, permanent dirt or the death of various plants that cannot tolerate waterlogged soils. The complexity of deep drainage equipment is that if the site has already been landscaped, trees and shrubs have been planted, there is a well-groomed lawn, then this order will have to be violated at least partially. Therefore, we recommend to immediately organize a deep drainage system on the acquired new construction sites. As in all other cases, the project of such a drainage system must be ordered from specialists. Independent incorrect calculation and execution of the drainage system can lead to the fact that waterlogged places on the site will be adjacent to dry ones.
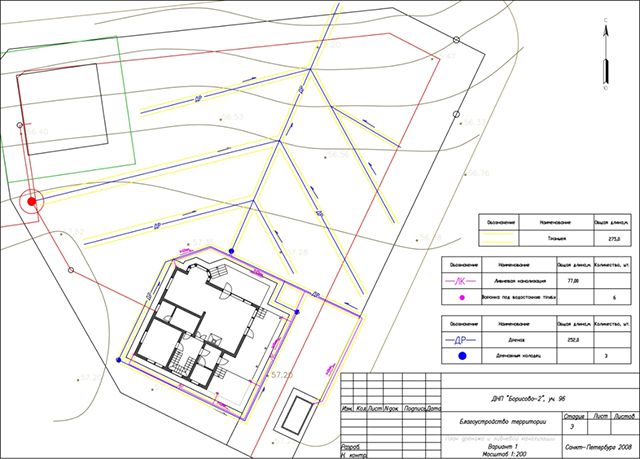
In areas with a pronounced relief, the drainage system can become a beautiful part of the landscape. To do this, an open channel or a network of channels is organized, through which water can freely leave the site. Rainwater from the roof can also be directed into these channels. But readers will certainly agree with the authors that the presence of a large number of channels will bring more inconvenience than benefits from their contemplation. That is why closed-type deep drainage is most often equipped. Opponents of deep drainage may argue that such systems can lead to excessive drainage of fertile soil, which will negatively affect plants. However, any fertile soils have a very good and useful property - they retain exactly as much water in their thickness as necessary, and plants growing on soils take exactly as much water from it as is necessary for their root system.

The main guiding document for the organization of the drainage system is a graphic plan of the drainage system, which indicates everything: the location of the collector and storage wells, the cross section of the drainage pipes and their depth, the cross section of the drainage trench and other useful information. An example of a drainage system plan is shown in the figure.
Consider the main stages of creating a deep drainage site.
| Image | Process description |
|---|---|
 | First of all, the site is marked, in which the position of the main elements of the drainage system is transferred from the plan to the terrain. Drainage pipe routes are marked with a stretched cord, which can immediately be pulled either horizontally or with a slope, which should be in each of the sections. |
 | A pit is dug under the storage drainage well of the required depth. The bottom of the pit is compacted and 10 cm of sand is poured and compacted on it. The body of the well is tried on in place. |
 | In the direction from the well towards the beginning of the main collector pipe, a trench is dug, the bottom of which is immediately given the desired slope specified in the project, but not less than 2 cm per 1 linear meter of the pipe. The width of the trench in the bottom area is 40 m. The depth depends on the specific project. |
 | From the collector trench, trenches are dug for drains, which will be connected to the collector pipe. The bottom of the trenches is immediately given the desired slope. The width of the trenches in the bottom area is 40 cm. The depth is according to the project. On clay and loamy soils, the average depth of drains is 0.6-0.8 meters, and on sandy soils - 0.8-1.2 meters. |
 | The locations of rotary and collector inspection manholes are being prepared. |
 | After checking the depth and the required slopes, 10 cm of sand is poured onto the bottom of all trenches, which is then wetted and compacted manually. |
 | Geotextile is lined at the bottom of the trenches so that it also goes onto the side walls. Depending on the depth of the trench and the width of the geotextile fabric, it is fixed either on the walls of the trench or on top. |
 | The wells are installed and tried on in their places, the places where the couplings are inserted are marked. Then the wells are removed and the necessary couplings are cut into them to connect the drains, the bottoms are mounted. |
 | Wells are installed in their places, leveled. A layer of crushed granite or washed gravel with a fraction of 20-40 mm, 10 cm thick is poured into the trenches. The crushed stone layer is compacted, the necessary slopes are created. |
 | The necessary sections of drainage pipes are cut off, which are completed with plugs (if necessary). In most cases, drain-beams are made from pipes with a diameter of 110 mm, and collectors - 160 mm. Pipes are laid in trenches and connected to well couplings and fittings. Their depth and slopes are checked. |
 | A 20 cm layer of crushed stone or washed gravel is poured over the drains. After tamping, the crushed stone layer is covered with geotextiles previously attached to the walls of the trenches or from above. |
 | The drainage system is checked for operability. To do this, in various places where drains are laid, a large amount of water is poured into the trenches. Its absorption into the crushed stone layer and flow through rotary, collector wells and getting into the main catchment well are controlled. |
 | A layer of sand is poured over the geotextile, at least 20 cm thick. The sand is compacted, and on top of it, the trenches are covered with fertile soil - 15-20 cm. |
 | Covers are put on the wells. |
Even if the deep drainage of the site was done without a project, it is still necessary to draw up, on which to indicate the location of the drains and the depth of their occurrence. This will help in the future when carrying out any excavation work to leave the system intact. If the relief allows, then the catchment wells may not be arranged, and the water collected by drains is immediately sent to sewers, reservoirs or a collective storm sewer system. Any of these steps must be coordinated with the neighbors and the administration of the villages. But the well is still desirable, if only to control the GWL and its seasonal fluctuations.
The collector well for collecting groundwater can be made overflow. When the water level in such wells becomes higher than the overflow pipe, part of the water flows through the sewer pipe into another storage well. Such a system allows you to get clean water in the storage well, since all the dirt, silt and debris settles in the collector overflow well.
When well-known thinkers, called great ones, whose statements are constantly quoted and cited as examples, put their thoughts on paper, they probably did not even suspect that they were writing about deep drainage. Here are some examples:
- The collective image of the thinker, which is known to most people, as Kozma Prutkov said: "Look at the root!". Great phrase talking about deep drainage! If the owner wishes to grow garden trees on his site, then he simply must know where the groundwater lies, since their excess in the root system area has a bad effect on most plants.
- The very famous thinker and “generator of wisdom” Oscar Wilde also said, without knowing it, about deep drainage: “The greatest vice in a person is superficiality. Everything that happens in our life has its own deep meaning.
- Stanisław Jerzy Lec said the following about depth: “A swamp sometimes gives the impression of depth.” As well as possible, this phrase fits the drainage, since without it the site may well turn into a swamp.
You can cite many more quotes from great people and connect them with drainage, but we will not distract the readers of our portal from the main idea. For the safety of houses and the comfort of their inhabitants, the creation of ideal conditions for the growth of the necessary plants, the arrangement of a cozy landscape, drainage is definitely needed.
Conclusion
It should be noted that residents of most regions of Russia are unspeakably lucky if the issue of drainage is raised. An abundance of water, especially fresh water, is much better than its lack. Residents of arid and desert regions, after reading such an article, would sigh and say: “We would have your problems!” Therefore, we simply must consider ourselves lucky that we live in a country that does not lack fresh water.
As we have already noted, you can always “negotiate” with water using the drainage system. Modern market abundance offers just a gigantic range of various components, allowing you to create a system of any complexity. But in this matter one must be very selective and careful, since the excessive complexity of any system reduces its reliability. Therefore, we again and again recommend ordering a drainage project from specialists. And the independent implementation of the drainage of the site is quite within the power of any good owner, and we hope that our article will help in some way.

















